C11 Organic Chemistry
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is organic chemistry?
the study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions and preparation of carbon-containing compounds
What is a functional group?
an atom or group of atoms that determine the chemical properties of a homologous series
What is a homologous series?
a family of similar compounds with similar chemical properties due to the presence of the same functional group
What are the general characteristics of a homologous series?
-having the same general formula
-displaying a trend in physical properties
What is a saturated compound?
has molecules in which all carbon–carbon bonds are single bonds
What is a unsaturated compound?
has molecules in which one or more carbon–carbon bonds are not single bonds
What is the displayed formula?
shows all the atoms of each element and all the bonds in the molecule
Draw the displayed formula of methane (CH4) +state what type it is
alkane
Draw the displayed formula of ethane (C2H6) +state what type it is
alkane
Draw the displayed formula of ethene (C2H4) +state what type it is
alkene
Draw the displayed formula of ethanol (C2H50H) +state what type it is
alcohol
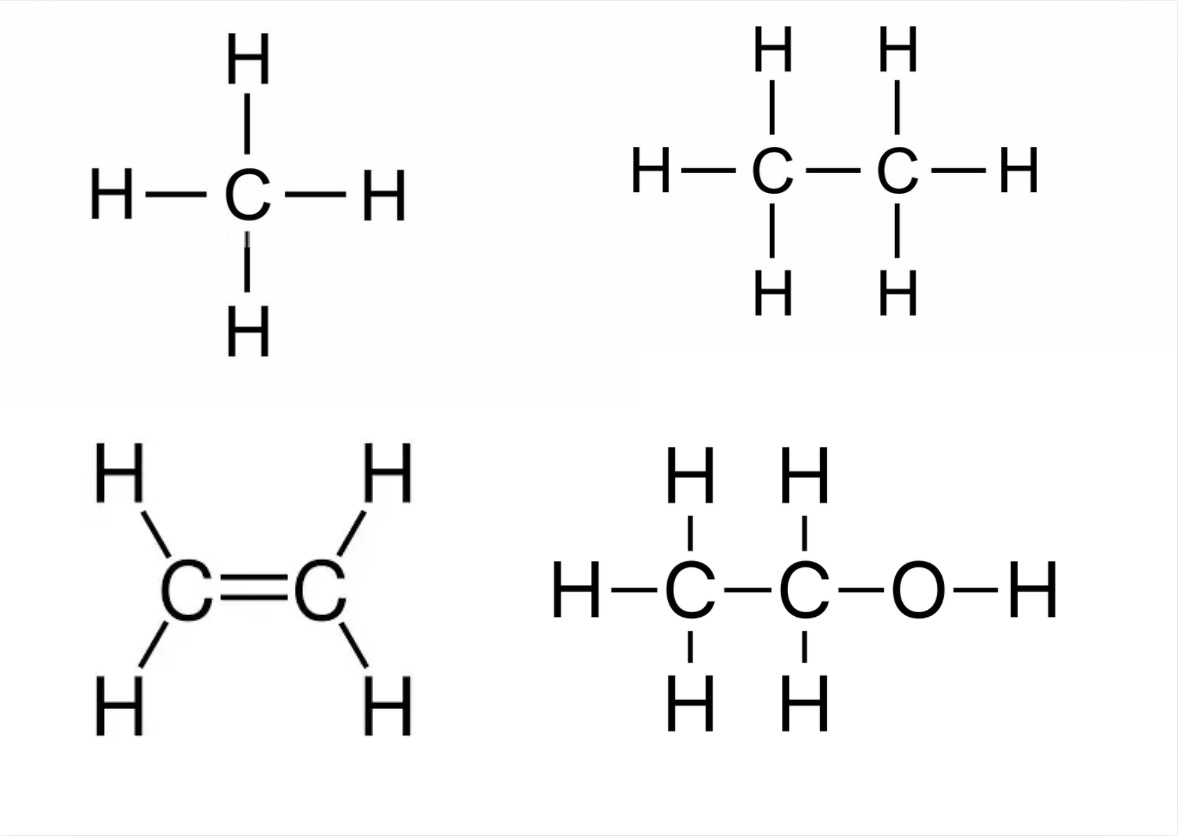
Name these compounds for the displayed formula
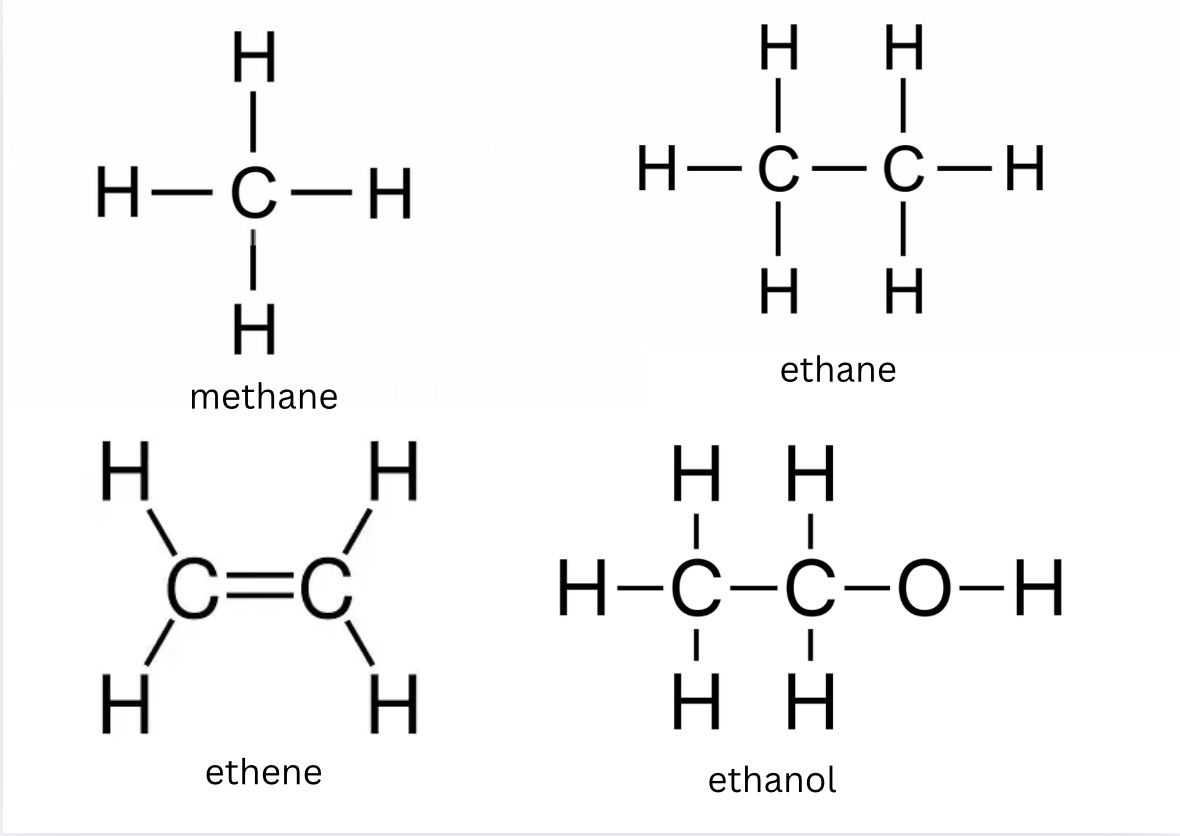
What is the compound present when chemical name ends with -ane?
alkane
What is the compound present when chemical name ends with -ene?
alkene
What is the compound present when chemical name ends with -ol?
alcohol
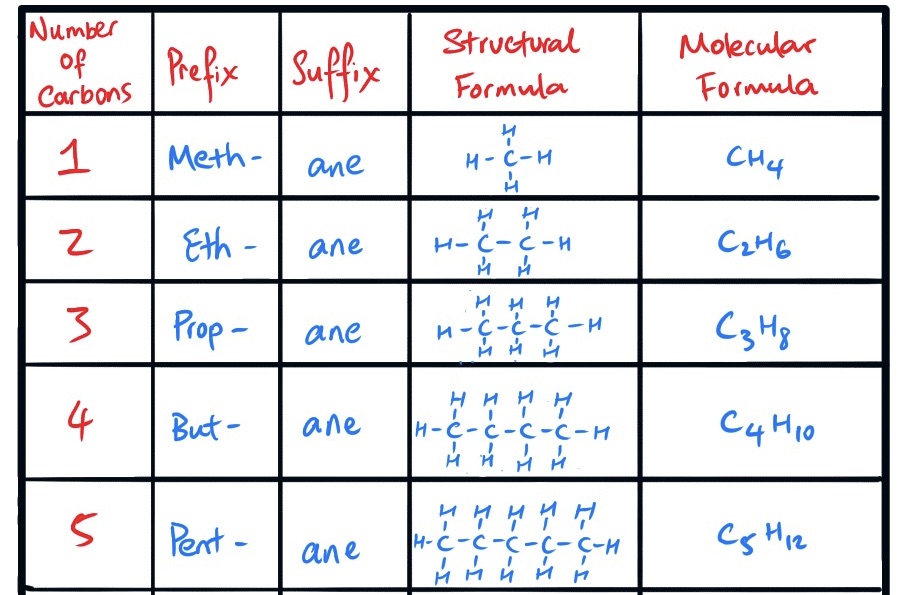
General formula for alkanes
CnH2n+2
General formula for alkenes
CnH2n
General formula for alcohol
CnH2n+1OH
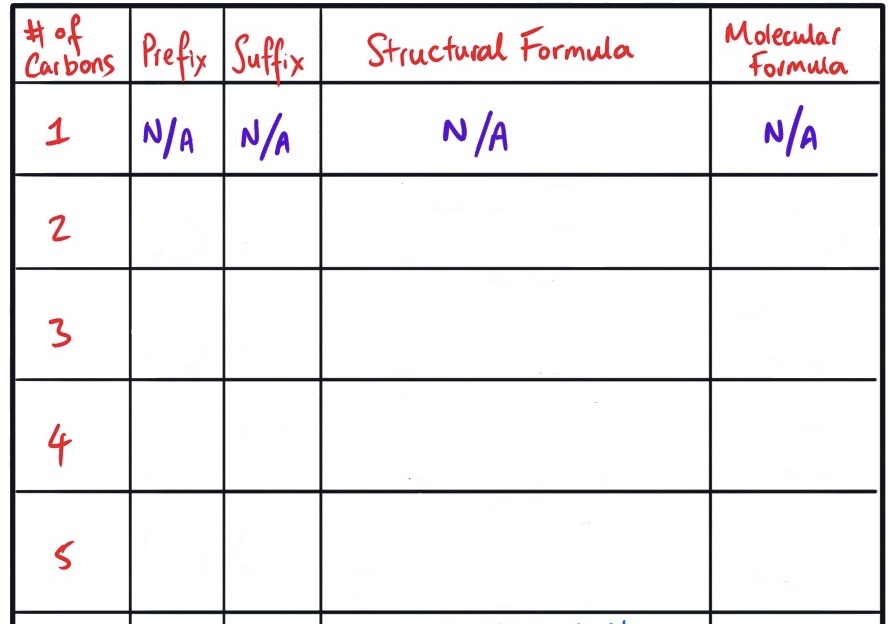
Fill in this table for naming alkanes
What are the 4 rules to remember when drawing the displayed formula for alkane?
-there are only single carbon-carbon bonds
-carbon atoms must have 4 bonds
-hydrogen atoms must have 1 bond
-if there are side groups, attach to the correct carbon as numbered in the name
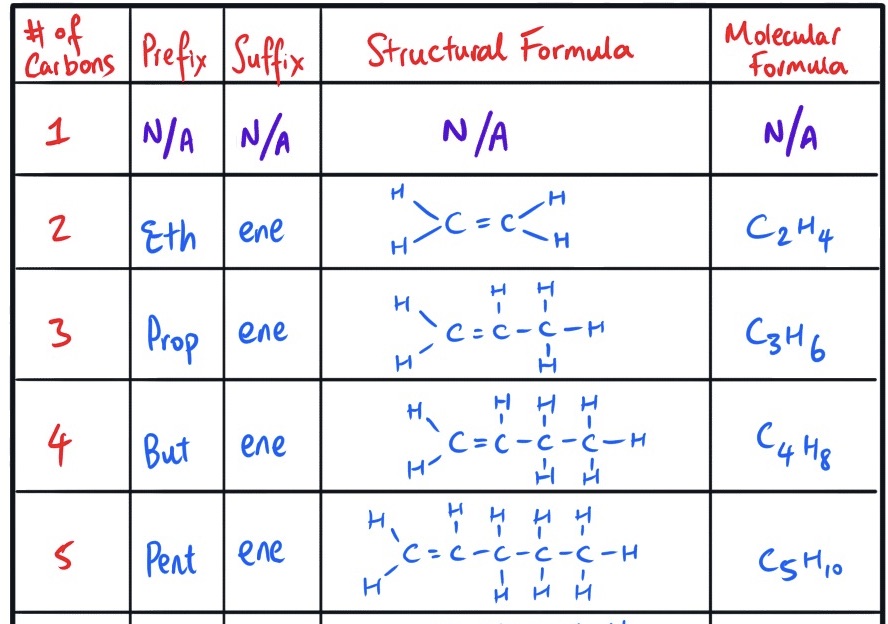
Fill in this table for naming alkenes
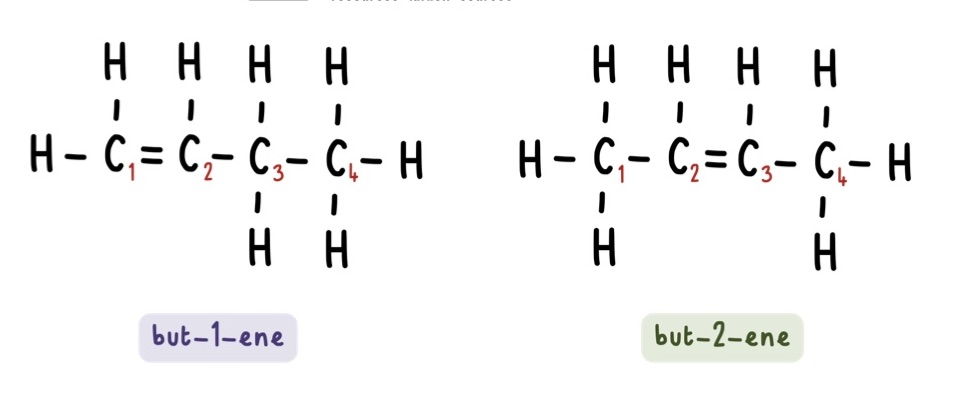
What is the difference between but-1-ene and but-2-ene?
but-1-ene has the double carbon bond between carbon 1 and carbon 2 while
but-2-ene has the double carbon bond between carbon 2 and carbon 3
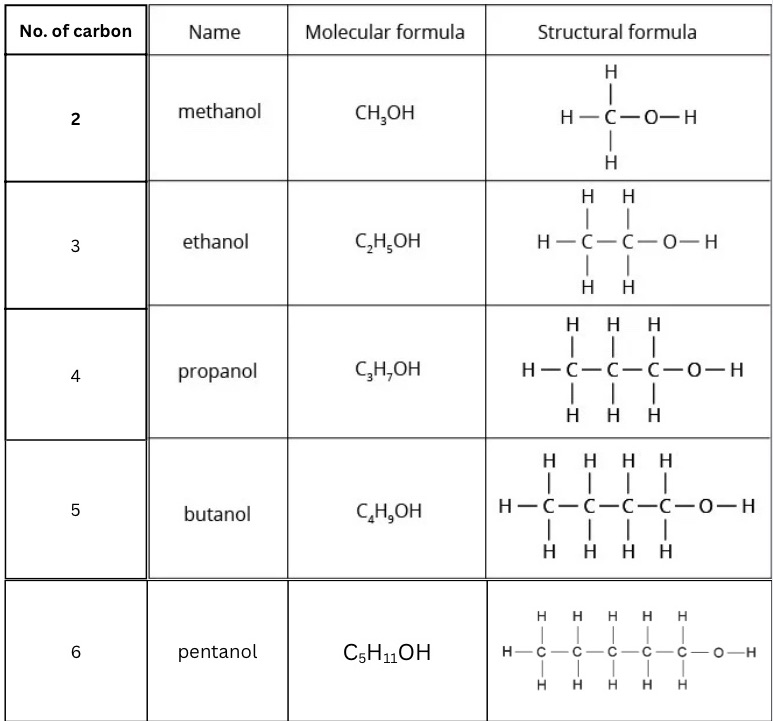
Fill in this table for naming alcohols
Name the 3 main fossil fuels
coal, natural gas and petroleum
What is the main constituent of natural gas?
methane
What are hydrocarbons?
compounds that contain hydrogen and carbon only
What is petroleum?
a mixture of hydrocarbons
How is petroleum separated into useful fractions?
by fractional distillation which is where compounds are separated into its constituent substances based on their differences
Describe the process of petroleum seperation from fractional distillation
-petroleum is heated in a furnace until its vaporised and is added to a fractionating column that has divisions at different levels to collect the various constituents/fractions
-fractions will separate into its constituent levels based on their different properties: different boiling points, chain length, volatility and viscosity
Describe how the properties of fractions obtained from petroleum change from the bottom to the top of the fractionating column from decreasing chain length
-fractions with shorter carbon chains, such as propane, will be tapped from the top of the fractionating column.
-fractions with longer chain lengths will collect at the bottom of the fractionating column.
Describe how the properties of fractions obtained from petroleum change from the bottom to the top of the fractionating column from higher volatility
-fractions with higher volatility will separate off at the top of the fractionating
column
-fractions with lower volatility will collect at the bottom of the fractionating column
Describe how the properties of fractions obtained from petroleum change from the bottom to the top of the fractionating column from lower boiling points
-fractions with lower boiling points condense at higher levels (top of the
column)
-fractions with higher boiling points condense at lower levels (bottom of the
column)
Describe how the properties of fractions obtained from petroleum change from the bottom to the top of the fractionating column from lower viscosity
viscosity refers to how thick and sticky and substance is
-hydrocarbons with lower viscosity, such as refinery gases, will separate off at the top of the column
-hydrocarbons with higher viscosity, such as bitumen will collect at the bottom of the fractionating column
Name all the types of fractions collected and what is each used in [8]
Refinery gas fraction- Gas used in heating and cooking
Gasoline/petrol fraction- Fuel used in cars
Naphtha fraction- Used as a chemical feedstock
Kerosene /paraffin fraction- Used for jet fuel
Diesel oil/ gas oil fraction- Fuel used in diesel engines
Fuel oil fraction- Fuel used in ships and home heating systems
Lubricating oil fraction- Used for lubricants, waxes and polishes
Bitumen fraction- Used for making roads
What are alkanes?
saturated hydrocarbons, meaning they only consist of single bonds and have only hydrogen and carbon atoms
What is the bond in alkanes like?
all bonds are single covalent bonds
What are the properties of alkanes?
generally unreactive unless in combustion/burning
What are alkenes?
unsaturated hydrocarbons, meaning they consist of at least one double bond and have only hydrogen and carbon atoms
What is the bond in alkenes like?
has at least one double carbon–carbon covalent bond
How does the manufacture of alkenes and hydrogen happen?
manufactured by cracking long chain of larger alkanes molecules using a high temperature and a catalyst
-long chain hydrocarbons are heated until vaporised. The vapours are either passed over a hot catalyst to break the long chains or are mixed with steam at very high temperatures so that thermal decomposition occurs.
-cracking of long chain alkanes produces alkenes, shorter chain alkanes andhydrogen
What is the reason for the cracking of larger alkane molecules?
-Produces alkenes which can be used as chemical feedstock
-Helps to meet supply and demand of fractions
How to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons?
to test for the presence of a double bond (whether a molecule is
unsaturated), add aqueous bromine
-there will be a colour change from orange to colourless
-in saturated compounds, aqueous bromine will remain orange
Describe the properties of alkenes in terms of addition reactions with bromine
alkenes will react with aqueous bromine and decolourise it from orange to colourless.
-this is because the double bond is more reactive than a single covalent bond and will react with bromine to form a dibromoalkane.
E.g. reaction between ethene and bromine.
Ethene + Bromine → 1,2-dibromoethane
C2H4 + Br2 → C2H4Br2
Describe the properties of alkenes in terms of addition reactions with hydrogen in the presence of a nickel catalyst
alkenes will react with hydrogen in an addition reaction to produce an alkane, by replacing the double carbon-carbon bonds with single covalent bonds.
E.g. reaction between propene and hydrogen, in the presence of a nickel catalyst.
Propene + Hydrogen → Propane
C3H6 + H2 → C3H8
Describe the properties of alkenes in terms of addition reactions with
alkenes will react with steam in an addition reaction to produce an alcohol, replacing the double carbon-carbon bond with a hydroxyl group (-OH) and a hydrogen atom
E.g. reaction between ethene and steam, in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Ethene + Steam → Ethanol
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
How does combustion in ethanol work?
ethanol can be burnt in air or oxygen (complete combustion) to produce carbon dioxide and water?
What is balanced chemical equation for the complete combustion of ethanol?
C2H4OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Why do we combust ethanol?
ethanol releases a lot of energy when burnt
What is the use of ethanol?
a solvent and a fuel
What are polymers?
large molecules built up from many smaller molecules called monomers