Understanding Economic Cycles and Investment Strategies
1/213
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
214 Terms
What does Joel Greenblatt suggest about prices and values?
Prices tend to fluctuate more than values, which creates opportunities.
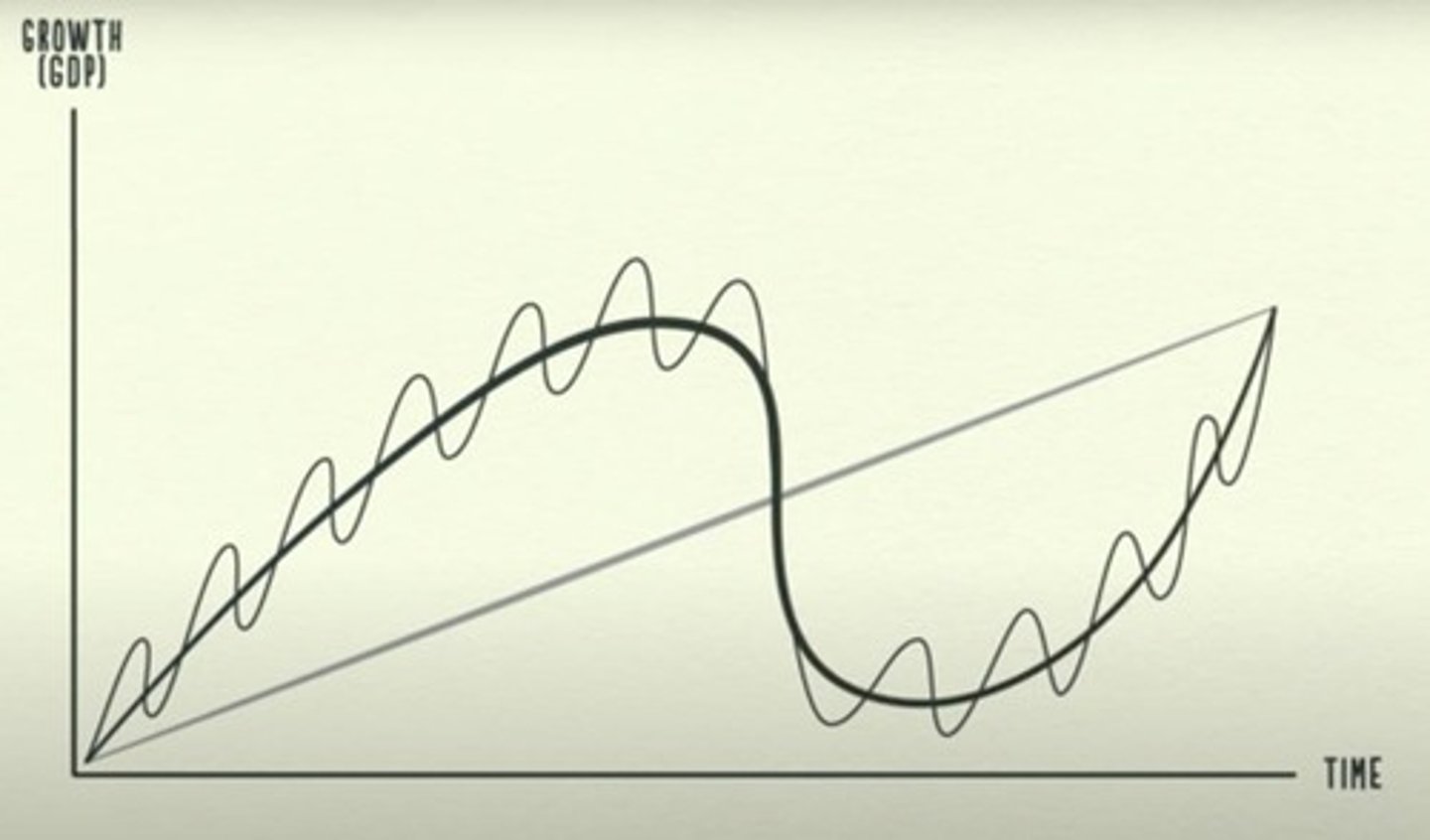

How does Ray Dalio describe the economy?
The economy works as a simple machine, where bubbles, panics, and credit move price, while fundamentals move value.
What historical trend is noted regarding nations and financial markets?
Nations like the Netherlands, UK, and US developed large financial markets and owned the world's reserve currency, allowing for tremendous borrowing and growth.
What are some signs of economic peaks and valleys according to Howard Marks?
They are mathematical metrics that indicate what to look for in market cycles.
How do individual stocks relate to economic cycles?
Individual stocks are impacted by economic cycles, as illustrated by the price movements of CISCO stock during the internet bubble.
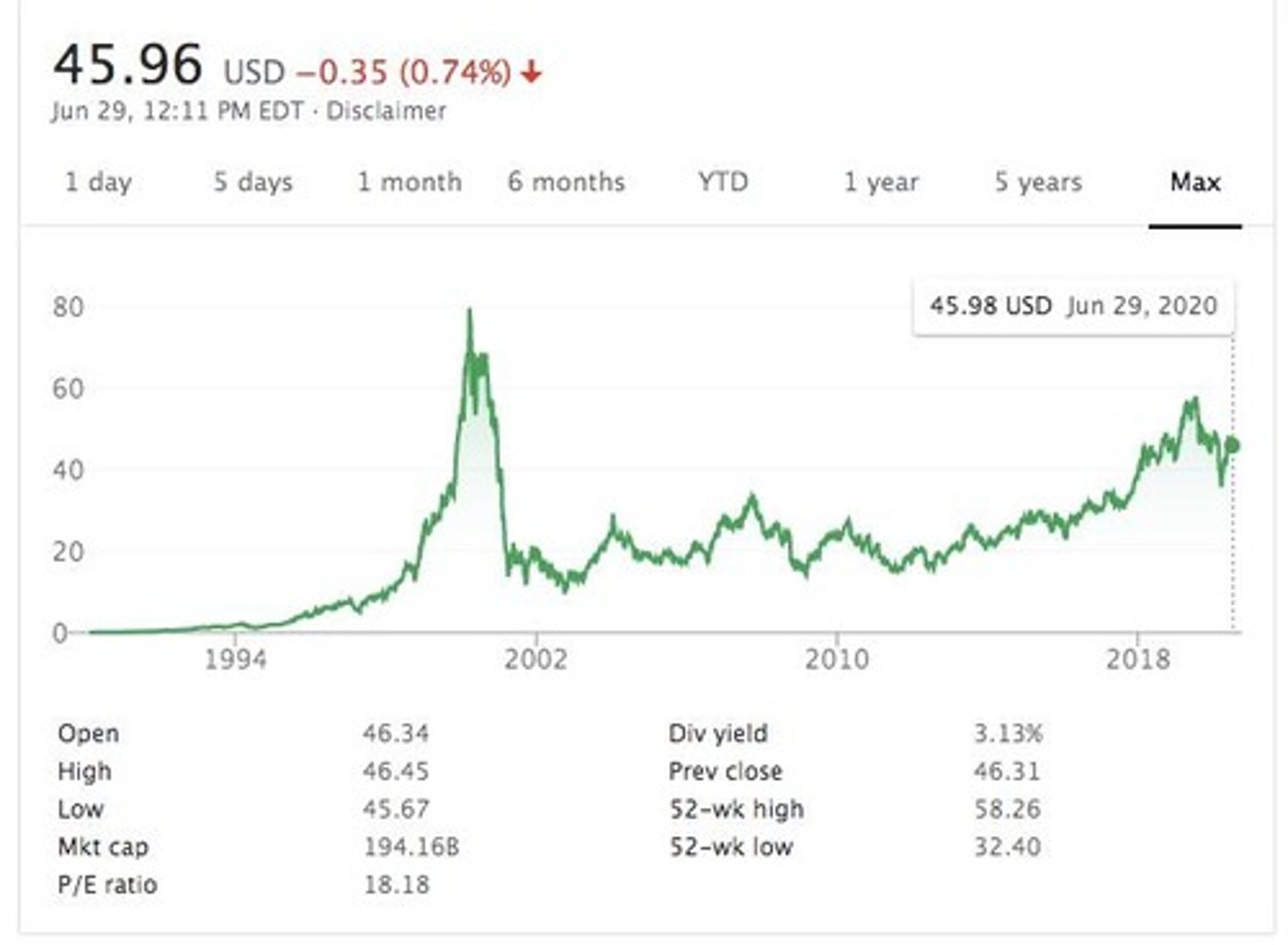
What emotions drive economic cycles?
Greed, euphoria, optimism drive prices up, while fear, panic, and pessimism drive prices down.

What did Daniel Kahneman contribute to the understanding of market cycles?
He highlighted the importance of emotions in market cycles and won a Nobel Prize in Economics for his work in Behavioral Finance.
What is a key takeaway from Kahneman's book 'Thinking Fast and Slow'?
Recognizing your own cognitive errors is difficult, and the book provides insights to help with this.
What behavior does Kahneman suggest for saving money?
He suggests automating savings, such as putting money from each paycheck into a retirement account.
What is the definition of debt?
Debt is money borrowed by one person from another, to be paid back at a later date, usually with interest.
What is credit in relation to debt?
Credit is the extension of buying power, which creates a debt obligation.
How do changes in debt and credit volumes affect economic cycles?
Changes in debt and credit volumes drive the economic cycle, as credit provides buying power in exchange for a promise to pay it back.
What happens to prices when interest rates decline?
When interest rates decline, money becomes easier to borrow, which tends to drive prices up.
What is the relationship between emotions and market behavior?
Emotions can lead to irrational market behavior, as seen in bubbles and busts.
What is the significance of the phrase 'this time it's different' in market cycles?
It reflects the common belief during market extremes that current conditions will not follow historical patterns.
What role do fundamentals play in economic cycles?
Fundamentals, such as innovations and productivity growth, move value in the economy.
What is the impact of credit on economic activity?
Credit allows individuals, companies, and countries to raise money through loans, influencing economic activity.
How does the concept of 'opt-out' relate to behavioral finance?
Kahneman suggests that making certain behaviors, like saving money, should be 'opt-out' rather than 'opt-in' to encourage participation.
What is a key characteristic of economic bubbles?
Economic bubbles are often driven by excessive optimism and can lead to significant market corrections.
What is the importance of understanding cognitive errors in investing?
Understanding cognitive errors can help investors avoid pitfalls associated with emotional decision-making.
What is the relationship between credit and buying power?
Credit provides buying power, allowing consumers to make purchases they might not afford upfront.
What does credit create in an economy?
Credit creates both spending power and debt.
What are the consequences of too much credit?
Too much credit can lead to financial issues if there is an inability to pay it back.
What happens if there is too little credit in society?
Too little credit can result in missed productive opportunities (i.e., NPV > 0).
How does growing credit/debt affect the economic cycle?
Growing credit/debt is beneficial for the economic cycle as long as it leads to productive endeavors that generate sufficient income to pay off the debt.
Give examples of productive uses of credit.
Loans for college, buying rental property, or a bank loan to start a company.
What is Rule 1 regarding debt and credit?
Do not let debt grow faster than credit, or you risk bankruptcy.
What is Rule 2 regarding income and productivity?
Do not let income rise faster than productivity, or you risk becoming uncompetitive.
What is Rule 3 for maintaining economic health?
Continuously raise your productivity.
Why do debt crises occur in cycles?
Expansion and contractions in credit drive economic cycles, which occur for logical reasons.
How does personal borrowing relate to economic cycles?
The pattern of borrowing and spending resembles a cycle where spending exceeds income and later requires spending less to pay back debt.
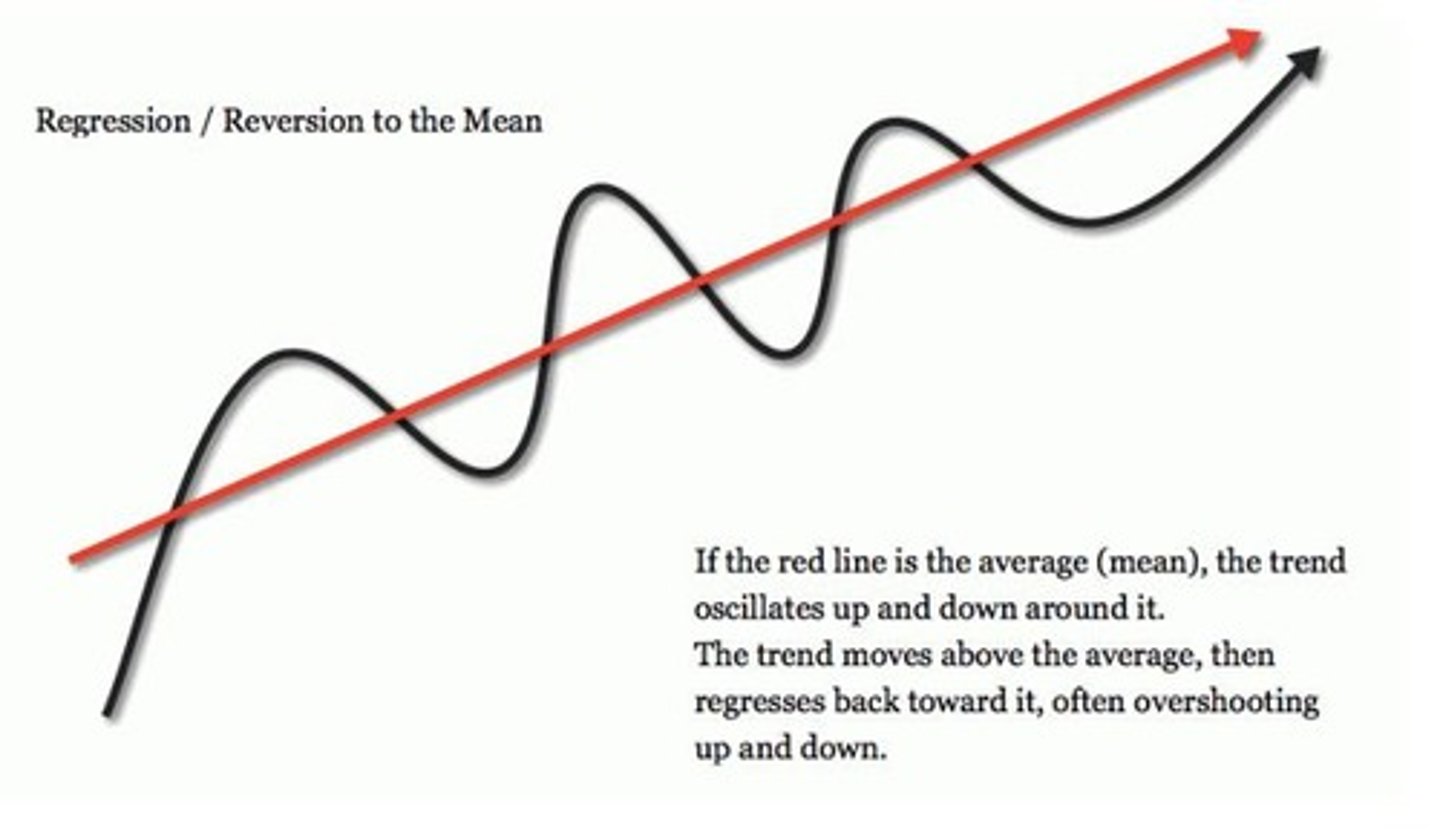
What is the concept of Reversion to the Mean (RTM)?
RTM is the idea that prices straying far from the long-term norm will eventually return to their normal state.
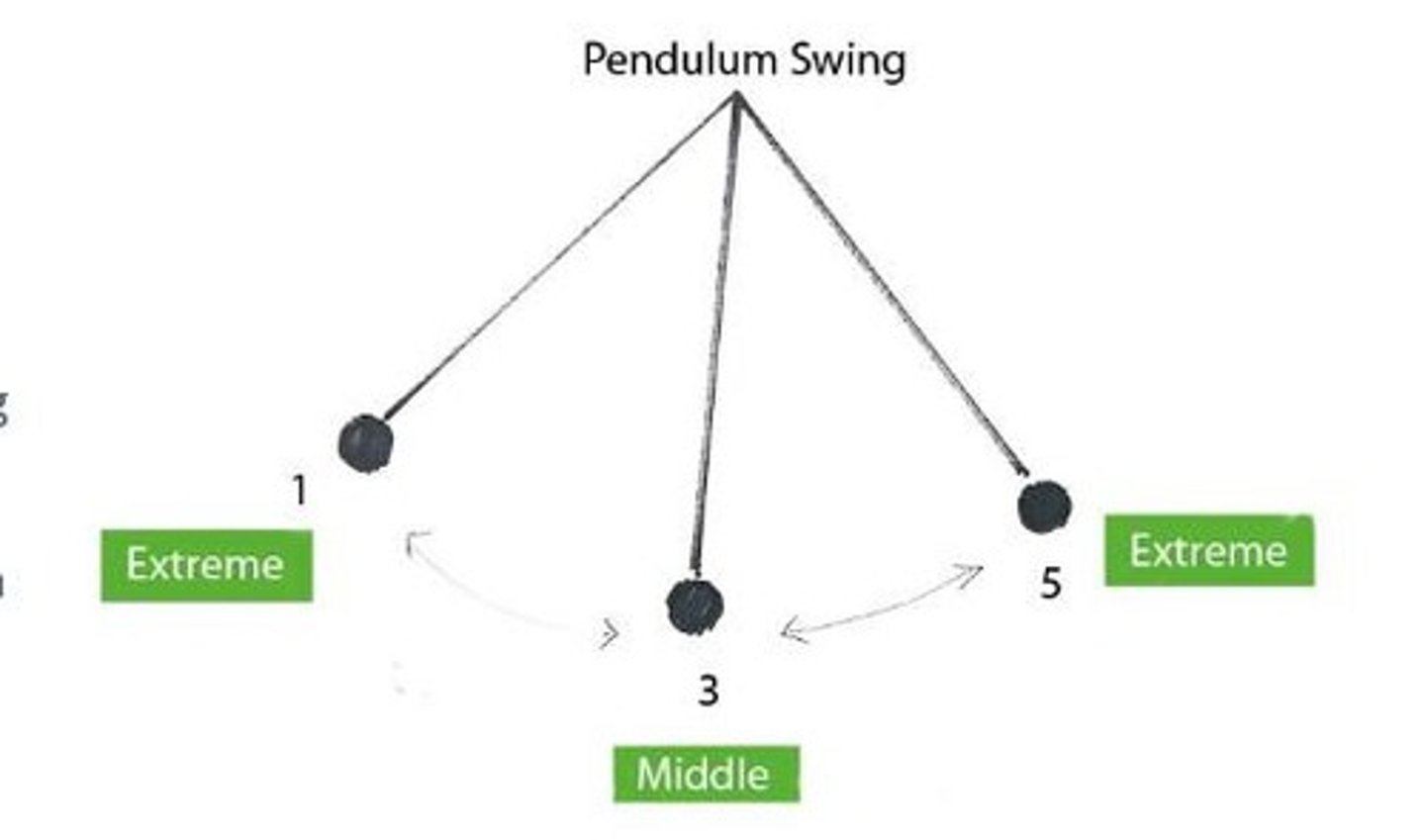
How does the pendulum analogy relate to RTM?
The pendulum swings between extremes (crash and bubble), indicating that the best buying opportunities often occur during crashes.
What does RTM suggest about past performance of funds?
Generally, yesterday's winners may become tomorrow's losers, as performance does not persist.
What is the role of the Federal Reserve (the Fed) in the economy?
The Fed conducts US monetary policy by influencing money and credit in pursuit of full employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates.
How does the Fed influence credit availability?
If interest rates (r) go down, credit is 'easy'; if r goes up, credit is 'tight'.
What are Howard Marks' '7 Worst Words' regarding economic conditions?
'Too much money chasing too few deals' indicates a negative climate for returns and safety.
What investment strategy does Howard Marks suggest during economic downturns?
Investors should favor strategies that limit losses in declines rather than ensuring full participation in gains.
What is the significance of productivity growth in the long run?
Productivity growth matters most for economic health over the long run.
What does 'NPV > 0' signify in terms of credit use?
It signifies that the investment or endeavor is expected to generate more income than its cost, making it a productive use of credit.
What is the relationship between borrowing and future spending?
Borrowing now means spending more than you make, leading to a future where you must spend less to repay the debt.
What is the importance of managing short-term interest rates?
Managing short-term interest rates influences the overall availability and cost of credit in the economy.
What is the long-term impact of economic cycles on individuals and nations?
Economic cycles affect both individuals and nations, requiring adherence to rules regarding debt, income, and productivity.
What economic conditions did the U.S. experience by 2018 according to Howard Marks?
Roughly ten years of artificially low interest rates, quantitative easing, and other forms of stimulus.
What can excessive economic stimulus lead to in investment markets?
Overpriced investments and a peak in the economic cycle.
How do investment professionals often misinterpret market conditions during a long bull run?
They associate the market's run-up with their skill, not realizing it's part of a larger cycle.
What does Mark Twain's quote 'History does not repeat itself, but it does rhyme' imply about economic cycles?
Each economic cycle has unique characteristics but shares similarities with past cycles.
What is often referred to as The Greater Fool Theory?
Buying assets at inflated prices with the hope of selling them to someone else at an even higher price.
How do bubbles function according to Robert Schiller?
Bubbles act like positive feedback loops, where euphoria builds as credit standards loosen.
What happens to a bubble when the supply of 'greater fools' runs out?
The bubble pops.
What is the ultimate determinant of a stock's value?
The present value of its future cash flows.
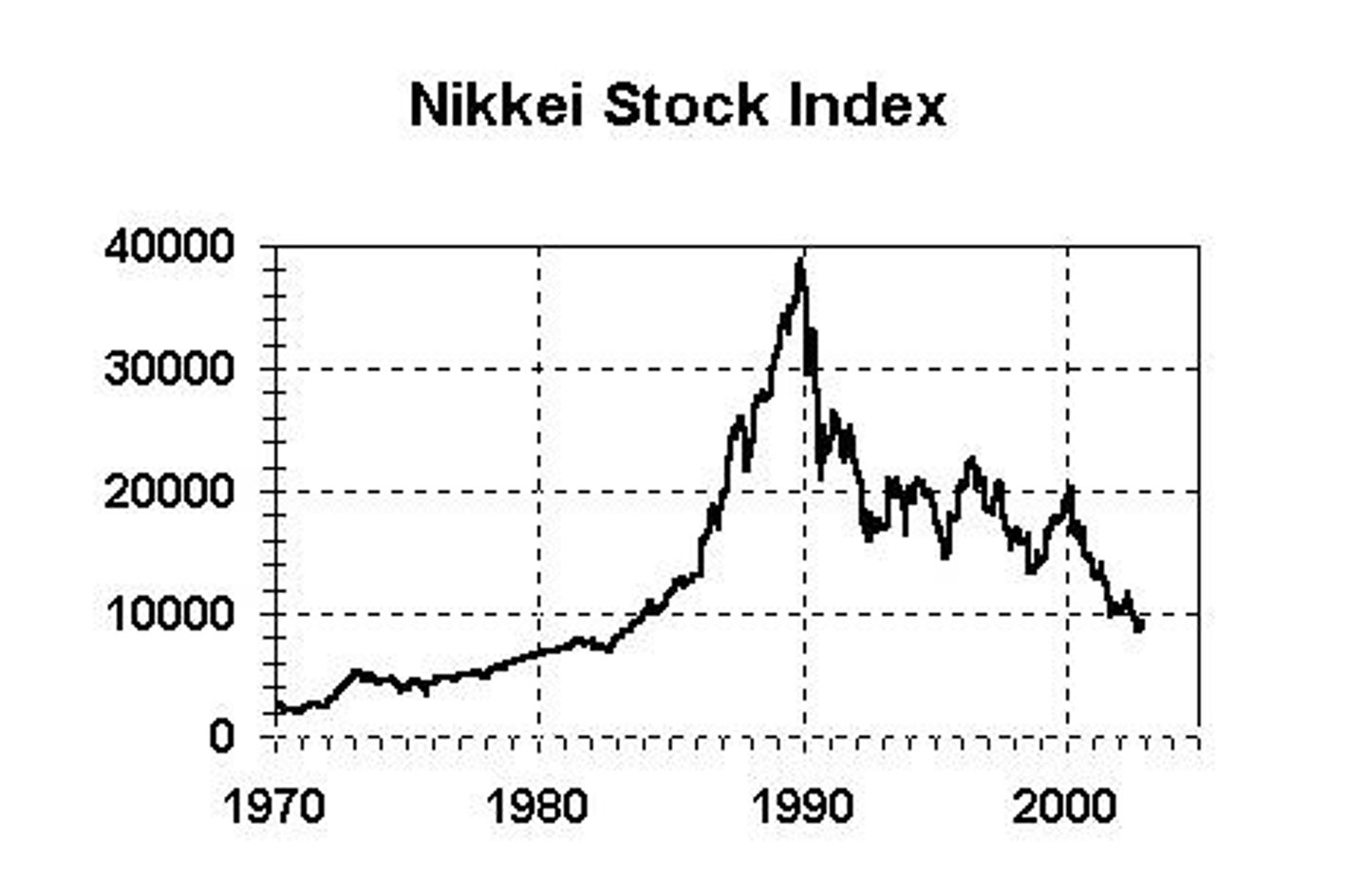
What was notable about the value of the Imperial Palace in Japan at its peak in 1990?
It was appraised to be enough to buy the entire state of California.
What was the market worth of Japan's stock market compared to the US stock market in the 1980s?
150% more than the US stock market.
What was the stock rating ratio during the 1990s Internet Bubble?
Nearly 100:1 'buy' ratings compared to 'sell' ratings.
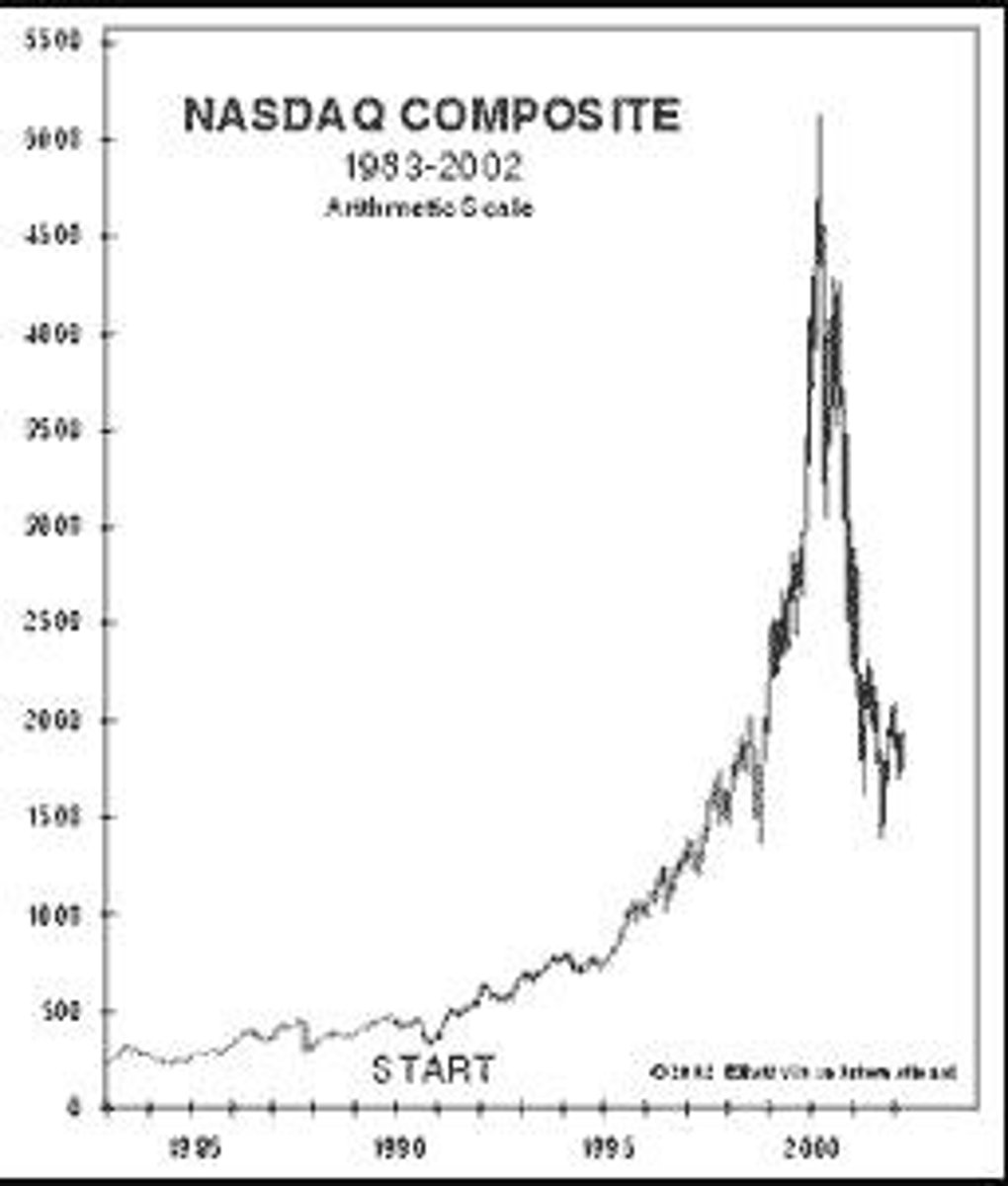
What did Goldman Sachs claim about internet stocks in 2000?
That burning through cash and lacking earnings was 'not a long-term risk'.
What is one of the largest examples of stock market wealth creation and destruction?
The late 1990s / early 2000s Internet Bubble.
What was a notable marketing strategy used by Pets.com?
They spent a significant amount of investor money on a Super Bowl ad featuring a sock puppet.
What is Pets.com recognized as in the context of the dot-com era?
One of the greatest dot-com disasters in history.
What was the percentage gain of the Munder Net Net fund in 1999?
164% gain in 1999.
What was the percentage loss of the Munder Net Net fund from its 2000 peak to the 2002 low?
~90% loss.
What happened to nearly all internet stocks after the 1990s bubble burst?
They dropped massively.
What was the high and low stock price of Amazon (AMZN) during the 2000-2002 period?
2000 high: $4.75; 2001-2 low: $0.36.
What was the percentage change in Amazon's stock price from its 2000 high to its 2001-2 low?
-92.4%.
What is the price of Amazon (AMZN) as of June 24, 2025, compared to its low?
$208.47, up 58,000% from the low.
What are some examples of market bubbles mentioned in the notes?
1999 Internet bubble, 2008 Housing bubble, 2020 Bull Run.
What advice does Warren Buffett give regarding market behavior?
Be fearful when others are greedy and greedy when others are fearful.
What historical event is referred to as 'Tulip mania'?
A historical event representing speculative bubbles, similar to modern market bubbles.
What does the phrase 'Eventually the Bubble Pops' imply?
Market bubbles are unsustainable and will eventually burst.
What is the criticism of daily financial news and social media regarding investment advice?
Much of it is 'info-tainment' rather than sound investment analysis.
What is the implication of using entertainment-focused traders in financial news?
They are featured for being entertaining, not for providing factual or data-driven advice.
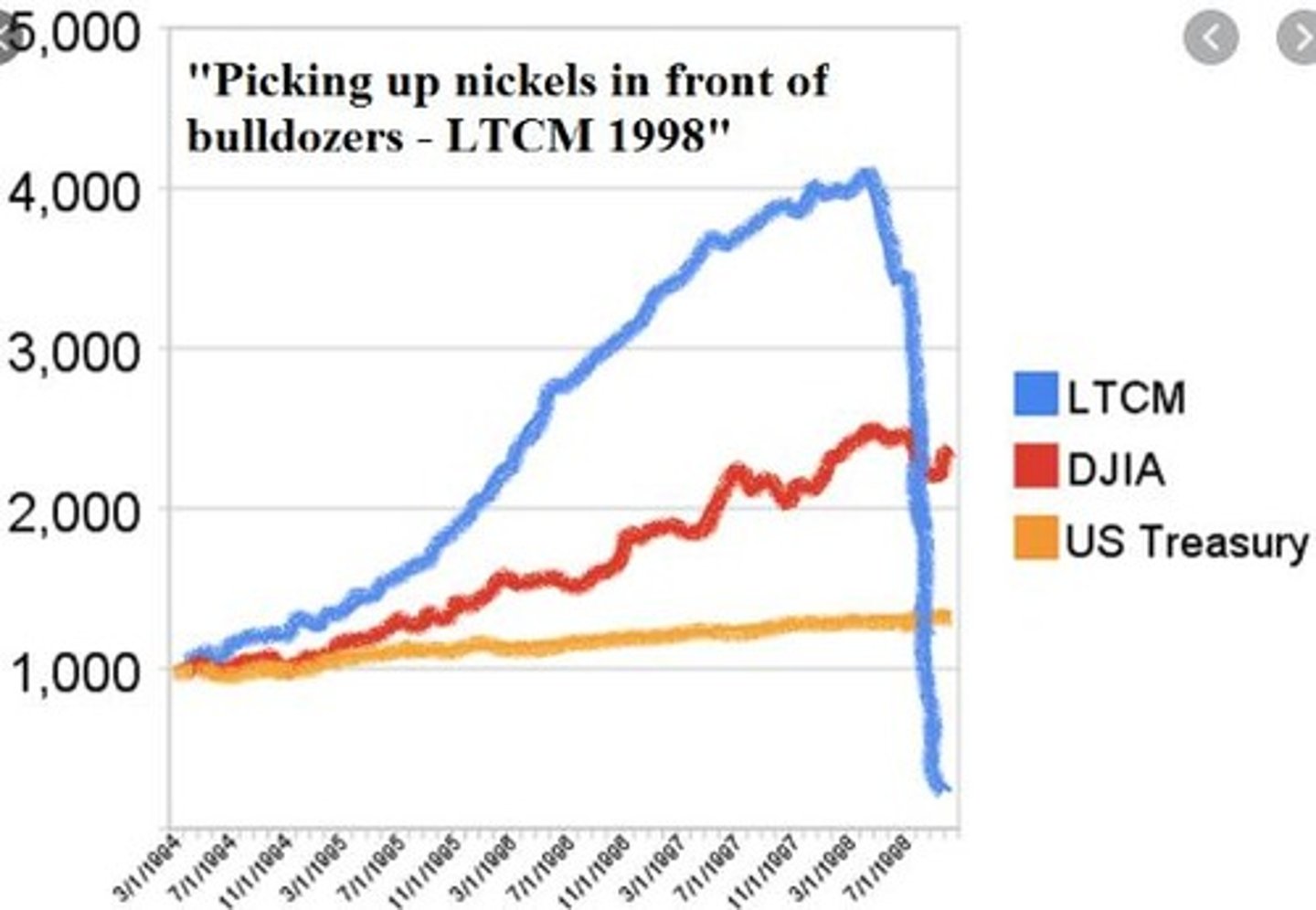
Who were the notable figures behind Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM)?
Nobel Prize Winners Scholes and Merton, led by John Merriwether.
What was the downfall of LTCM attributed to?
Overconfidence, massive leverage, and failure to account for fat tails (Black Swans).
What is the essence of long-term investing according to the notes?
Fluctuations are dominated by rational long-term growth.
What does the final question in the notes suggest about learning from history?
It implies that historical trends can provide insights for future investment strategies.
What do stock returns indicate according to historical trends?
Stock returns are very volatile, influenced by changes in risk, interest rates, and psychological factors like optimism and fear.
What is the significance of long-term growth in stock investments?
Even with poor investment timing, long-term growth will prevail, as evidenced by the longest recovery time of 5 years and 8 months for an investor since 1945.
What is expected value in the context of investment?
Expected Value is the sum of all possible future values, each multiplied by the probability of its occurrence.
How is expected value calculated using a dice example?
For a dice with six sides, the expected value is 1/6*(1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6) = 3.5.
What is the expected value of a $1 bet on a roulette wheel with a probability of winning 1/38?
The expected value is (1/38)(+$35.00) + (37/38)(-$1.00) = -$0.05.
Why is understanding expected value important for investors?
Knowing the probability of future events helps estimate potential profit from repeated investments.
What does the Gaussian Distribution represent in investment modeling?
It provides a framework to think through future stock price returns, though it should be approached with skepticism.
What does the phrase 'All models are wrong. Some are useful.' imply?
It suggests that while models can be flawed, they can still provide valuable insights.
What is the relationship between risk and distribution width in Gaussian distributions?
Risk is related to the width of the distribution; wider distributions indicate higher risk.
What is a 'fat tail' in the context of stock returns?
A fat tail refers to a distribution where extreme outcomes are more likely than predicted by a normal distribution.
What does the S&P 500 histogram of returns illustrate?
It shows the actual distribution of stock returns over the past 150 years, which may deviate from Gaussian assumptions.
What is compounding in investment terms?
Compounding is the process where an investment earns interest on both the initial principal and the accumulated interest from previous periods.
How does compounding benefit an investment over time?
Each year, the investment earns interest on the initial amount plus the interest earned in previous years, leading to exponential growth.
What historical lesson do stocks provide compared to other investments?
Stocks tend to outperform other investments over the long run.
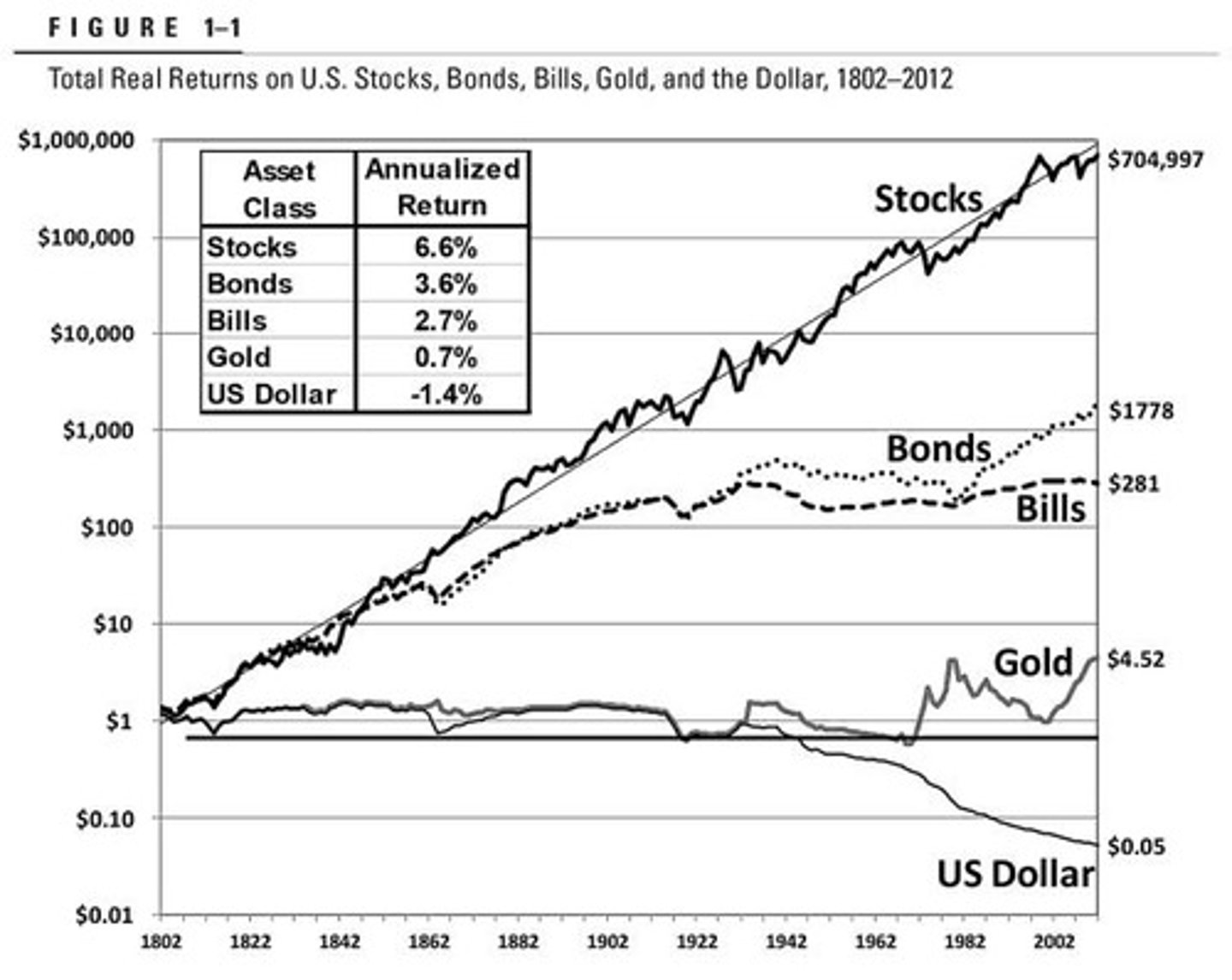
What are some alternative investments mentioned that may be discussed during office hours?
Bonds, Real Estate, Bitcoin, and commodities.
What is the main takeaway from the volatility of stock returns?
Short-term market swings are insignificant compared to the overall upward trend in stock returns.

What is the longest recovery period for an investor in the stock market since 1945?
Five years and eight months, from August 2000 to April 2006.
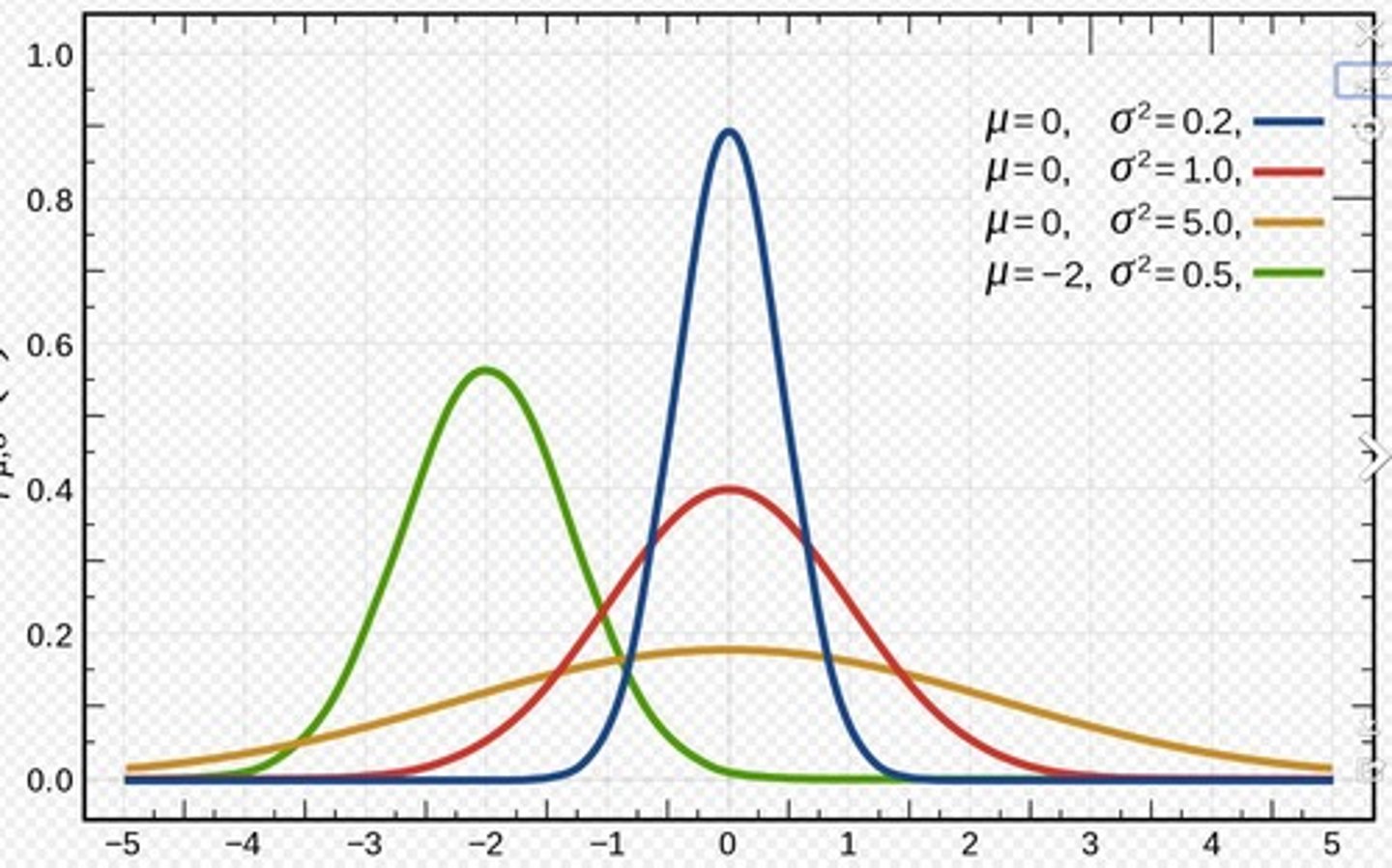
What psychological factors influence stock market volatility?
Optimism, greed, pessimism, and fear.
Why might the future not follow a Gaussian distribution?
The real world may exhibit characteristics such as fat tails, which are not captured by normal distribution models.
What does the term 'log scale' refer to in financial analysis?
A logarithmic scale is used to represent data that covers a wide range of values, allowing for easier comparison of percentage changes.
What does the phrase 'Ole tyme days' suggest in the context of stock market history?
It likely refers to a nostalgic view of historical stock market performance.
What does the reference 'Stocks for the Long Run' by Jeremy Siegel emphasize?
The importance of long-term investment strategies in the stock market.
What is compounding in finance?
Compounding is the result of reinvesting interest rather than paying it out, allowing interest to be earned on both the principal and previously accumulated interest.
How does compounding work mathematically for one year?
$1 compounded for 1 year = ($1)*(1 + r) after 1 year.
What is the formula for compounding money over N years?
$1 compounded for N years = ($1)*(1 + r)^N.
What is the result of compounding $1,000 for 3 years at a 10% annual interest rate?
$1,000 compounded for 3 years at 10% results in $1,331.