APUSH Gilded Age, Industrialization, and U.S. Expansion Key Concepts
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What encouraged the rise of industrial capitalism in the United States?
Technological advances, large-scale production methods, and the opening of new markets.
How did migrations during industrialization affect the United States?
They transformed both urban and rural areas, causing dramatic social and cultural change.
What new cultural movements emerged during the Gilded Age?
New cultural and intellectual movements, public reform efforts, and political debates over economic and social policies.
What was the impact of technological innovation on the economy between 1870 and 1890?
National economy boomed due to rapid expansion of factory production, mining, and railroad construction.
What role did the government play in the rise of industrial capitalism?
The government passed high tariffs, granted land and political favors to railroad companies, and used military force against indigenous populations.
What economic structures emerged due to lack of regulation during the Gilded Age?
Corporations formed pools and trusts, leading to consolidations, mergers, and monopolies.
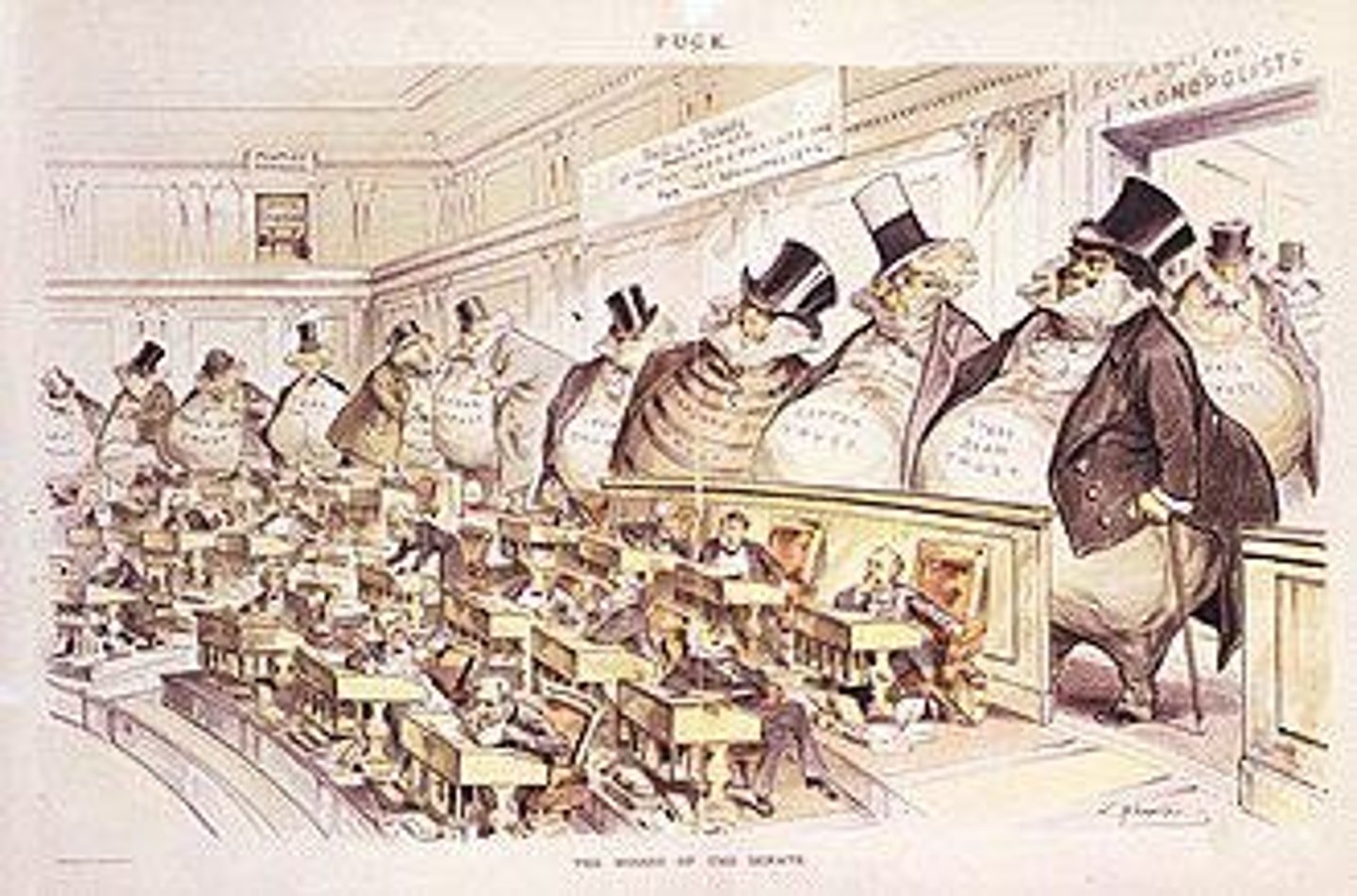

What percentage of the world's industrial output did the U.S. produce by 1913?
One-third of the world's industrial output.
How many Americans moved from farms to cities between 1870 and 1920?
11 million Americans.
What ideology justified wealth inequality during the Gilded Age?
Social Darwinism, which misapplied Darwin's theory of evolution to economic conditions.
What was the primary labor organization during the Gilded Age?
The Knights of Labor, which organized both skilled and unskilled laborers.
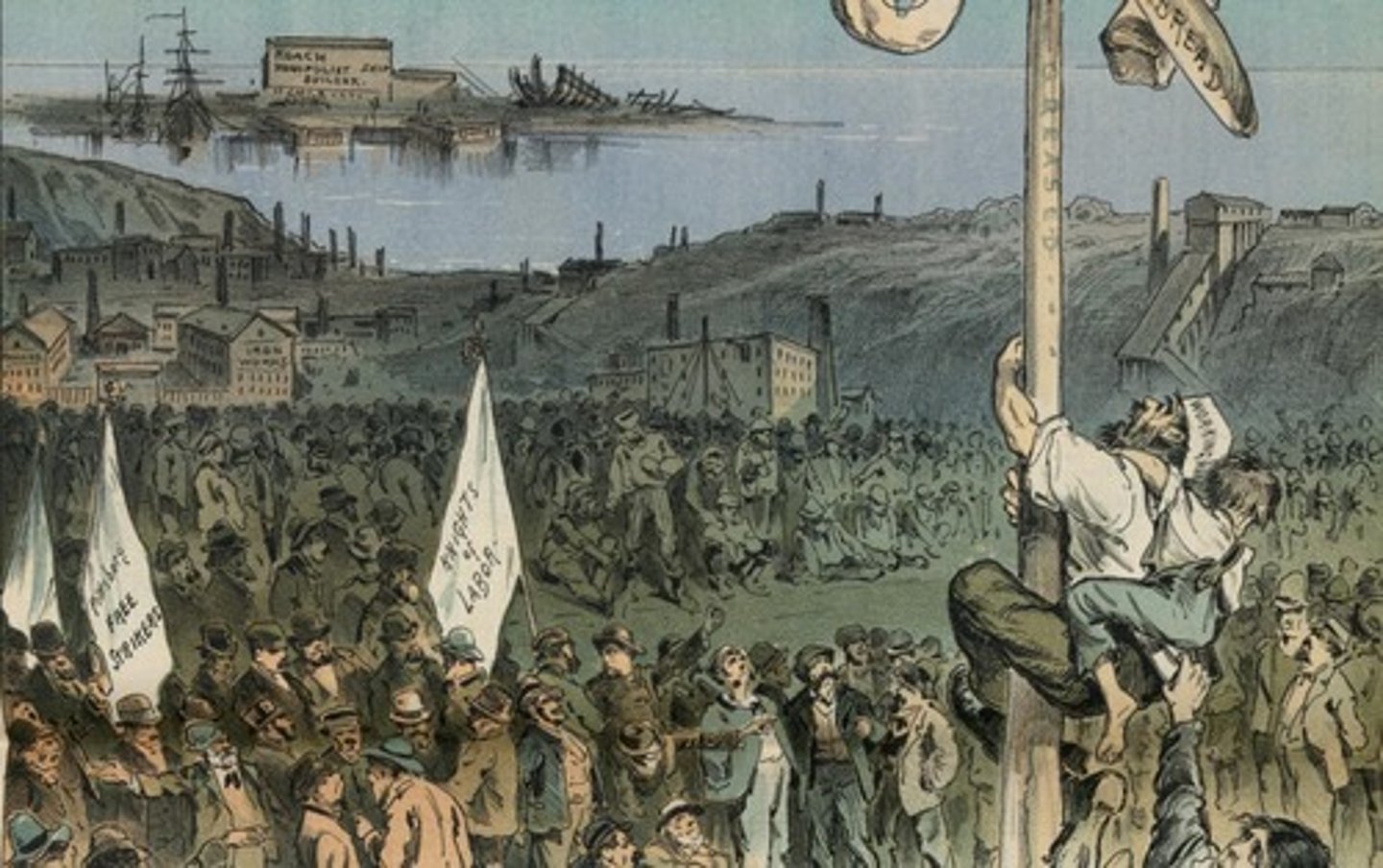

What was a significant consequence of workplace accidents between 1880 and 1900?
Over 35,000 workers died annually due to unsafe working conditions.
What was the public perception of labor unions during the Gilded Age?
Unions faced political pushback and were seen as dangerous and un-American.
Who were some prominent figures of capitalism during the Gilded Age?
John D. Rockefeller, Andrew Carnegie, Andrew Mellon, JP Morgan, and Cornelius Vanderbilt.
What was the effect of technological advancements like the telephone and electricity?
They improved living standards, communication, and political participation.
What was the common justification for the wealth held by the richest 1%?
The belief that the wealthy were 'more fit' and 'more deserving' based on Social Darwinism.
What was the Haymarket Affair?
A labor protest that turned violent, leading to a backlash against labor movements.
What was the impact of industrialization on the American workforce?
Two-thirds of Americans worked for wages, leading to increased economic insecurity.
What was the significance of the Gilded Age in American history?
It marked a period of rapid economic growth, technological innovation, and significant social changes.
What was the role of railroads in the economic expansion of the U.S.?
Railroads facilitated the movement of goods and people, contributing to the growth of commercial markets.
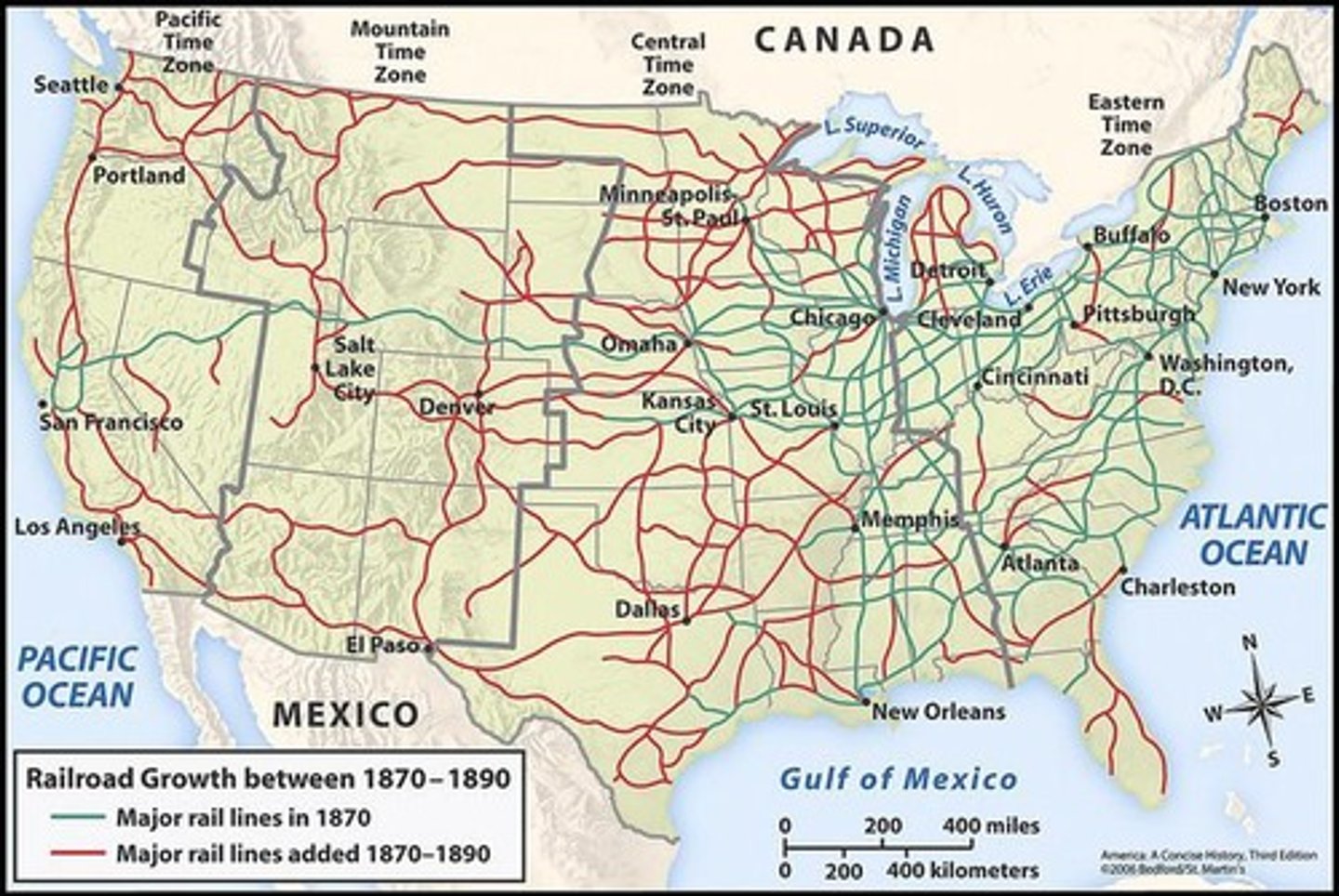
What were the consequences of the lack of government regulation in the Gilded Age?
It led to unsafe working conditions, monopolies, and significant wealth inequality.
What was the relationship between industrialization and immigration during this period?
25 million immigrants entered the country, many seeking jobs in industrial cities.
What did the term 'Gilded Age' imply about American society?
It suggested a superficial glitter of wealth masking deep social problems and inequalities.
What legislation initiated mass movement westward in the United States?
The Homestead Act of 1862
What was the population increase in the U.S. from 1860 to 1900?
From 300,000 in 1860 to 5 million in 1900
What type of agriculture emerged due to westward expansion?
Commercial agriculture from small family farms
What cultural symbol did the West represent for many Americans?
Rugged individualism
What major conflict involved violent clashes between settlers and Indigenous populations?
The Battle of the Little Bighorn and the Wounded Knee massacre
What act aimed to assimilate Native Americans into American society?
The Dawes Act
What was the role of the Bureau of Indian Affairs?
To manage relations with Native American tribes
What characterized the political landscape during the Gilded Age?
Unregulated capitalism leading to political corruption
What were the names of the political scandals involving bribery during the Gilded Age?
Tweed Ring, Credit Mobilier Scandal, Whiskey Ring
What reform legislation was passed in 1883 to address corruption?
The Civil Service Act
What was the purpose of the Interstate Commerce Commission (ICC)?
To regulate railroad rates and practices
What was the significance of the Sherman Antitrust Act?
To combat monopolies and promote competition
What was the Populist Party's main goal?
To represent the interests of farmers and laborers
What key idea did the Populist Party advocate for regarding senators?
Direct election of senators
What was the impact of the Redeemers in the South post-Reconstruction?
They undid Reconstruction efforts and imposed Jim Crow laws
What discriminatory practices emerged during the Jim Crow era?
Poll taxes, literacy tests, and segregation
What was the Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882?
A law that prohibited Chinese laborers from immigrating to the U.S.
What event sparked the Spanish-American War?
The explosion of the U.S.S. Maine in 1898
What territories did the U.S. acquire as a result of the Spanish-American War?
The Philippines, Puerto Rico, and Guam
What was the duration of the fighting in the Philippines after the Spanish-American War?
Four years of further fighting
What was the outcome of the Spanish-American War for U.S. foreign policy?
It marked the beginning of American dominance in the Caribbean and Pacific Islands