IT ELECTIVE 1 - BOND ENERGY ALGORITHM
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Bond Energy Algorithm (BEA)
is a common method used in vertical fragmentation of distributed databases.
Vertical fragmentation
involves splitting a table into smaller, more manageable sub-tables based on columns (attributes) rather than rows (tuples)
STEP 1 OF BEA
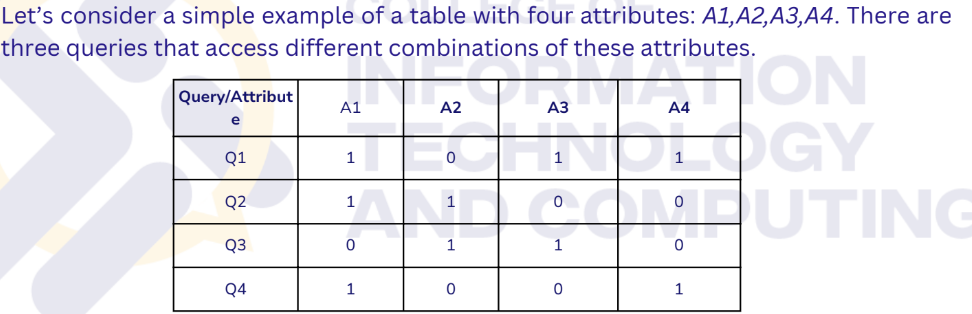
Create an Attribute Usage Matrix:
Construct a matrix where rows represent queries and columns represent attributes (columns) of the table.
The matrix indicates how each query accesses different attributes (e.g., a 1 represents that a query uses a particular attribute, and 0 means it doesn’t).
STEP 2 OF BEA
Calculate Affinity Values:
Compute the affinity value between every pair of attributes. The affinity value measures how closely related two attributes are based on their frequency of being accessed together.
Affinity value between two attributes Ai and Aj is given by the sum of products of their usage by each query:
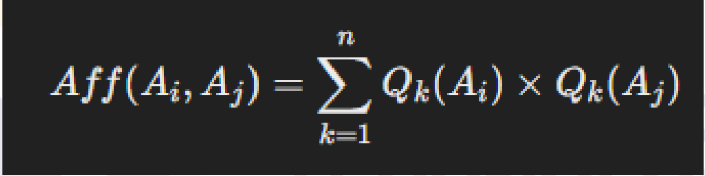
STEP 3 OF BEA
Rearrange Attributes:
The attributes are rearranged to maximize the bond energy (affinity) between neighboring attributes. The goal is to place attributes with higher affinity values next to each other.
STEP 4 OF BEA
Generate Fragments:
Group neighboring columns that have high affinity into fragments. These fragments represent the sub-tables for vertical fragmentation.
Step 1
What step of BEA is this?
Step 2
What step of BEA is this?
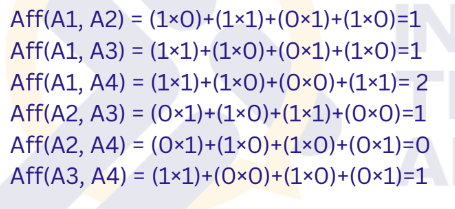
Step 3
What step of BEA is this?

Step 4
What step of BEA is this?
