TERMS Unit 3: Finance and accounts Chapter 16: Final accounts
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
final accounts
the end of year financial accounts produced by a business
creditors
suppliers to a business who have not yet been paid
window dressing
presenting the accounts of a business in the best possible, or most flattering, way which could potentially mislead users of accounts
profits and loss accounts
records the revenue, costs and profit (or loss) of a business over a given period of time
gross profit
equal to sales revenue minus cost of sales
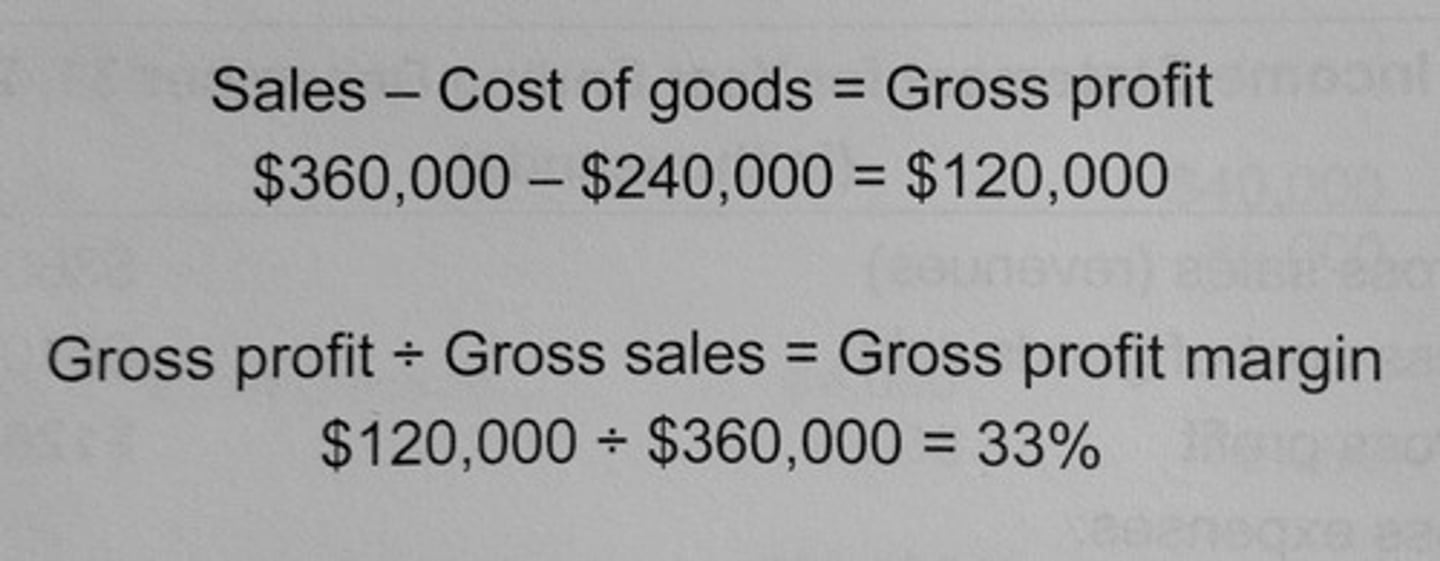
profit before interest and taxation
gross profit minus overhead expenses
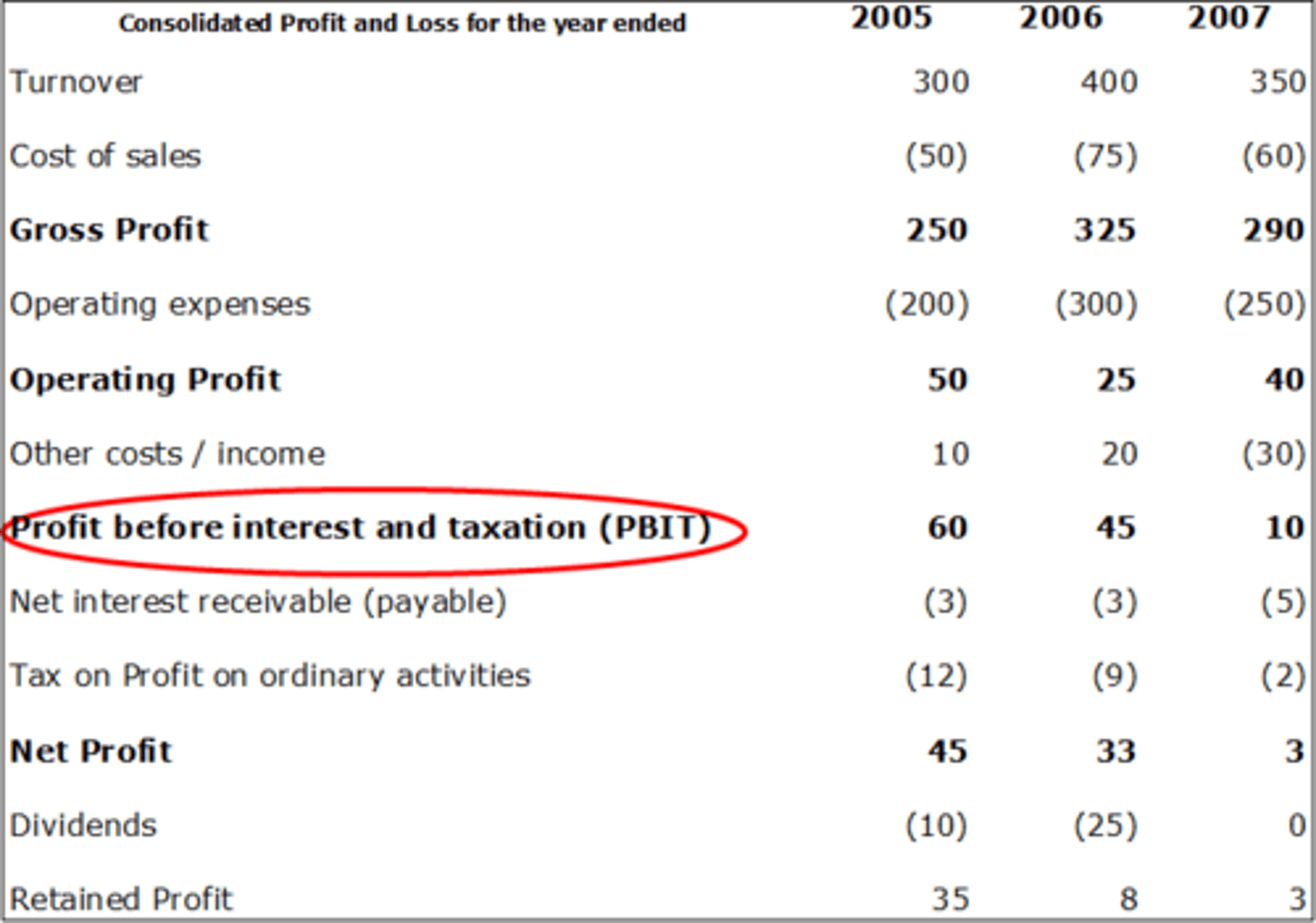
profit after tax
profit made after corporation tax has been deduced
dividends
the share of the profits paid to shareholders as a return for investing in the company
retained profit
the profit left after all deductions, including dividends, have been made; this is 'ploughed back' into the company as a source of finance

cost of sales (or cost of goods sold) COS or COGS
this is the direct cost of purchasing the goods that were sold during the financial year

balance sheet (statement of financial position)
an accounting statement that records the values of a business's assets, liabilities and shareholders' equity at one point in time
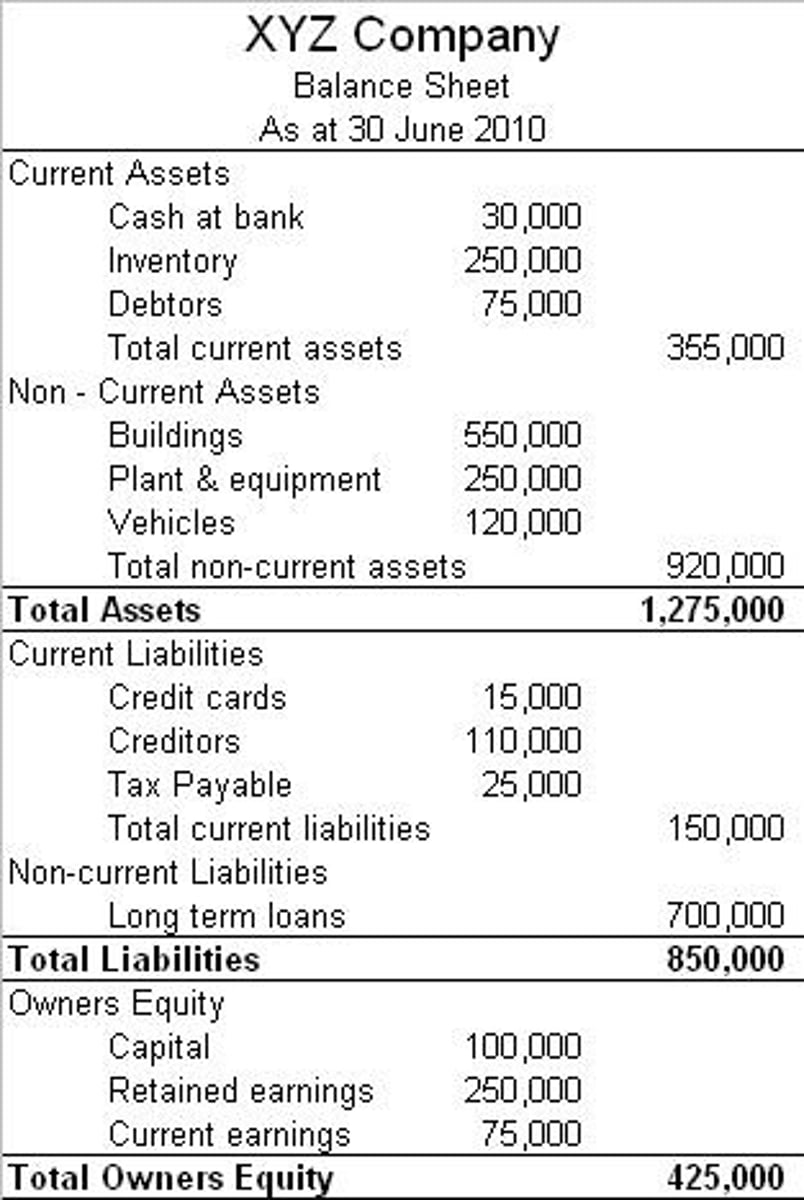
shareholders' equity
total value of capital invested in the business by shareholders either in the form of share capital or retained profit; shareholders' funds
shareholders' equity
total value of assets - total value of liabilities
current liabilities
debts of the business that will usually have to be paid within one year; e.g. creditors, bank overdraft, unpaid dividends and unpaid tax
share capital
the total value of capital raised from shareholders by the issue of shares
debtors
customers who have brought products on credit and will pay cash at an agreed date in the future
current assets
the value of all assets that could reasonably be expected to be converted into cash within a year; e.g. inventories (stock), accounts playable and cash/bank balance
intangible assets
an identifiable non-money asset without physical substance
goodwill
arises when a business is valued at or sold for more than the balance sheet value of its assets
intellectual property
an intangible asset that has been developed from human ideas and knowledge

market value
the estimated total value of a company if it were taken over

straight-line depreciation
a constant amount of depreciation is substracted from the value of the asset each year
units of production method
depreciating an asset on the basis of its usage
net book value
the current balance sheet value of a non-current asset = original cost - accumulated depreciation
annual depreciation charge =
(historic cost of asset - residual value) / useful life of asset (year)
depreciation per unit =
(cost of asset - residual value) / total units of production