2) Stream Morphology
1/16
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
what is a watershed?
land area that is drained by all the tributary systems above a chosen point in main channel
what is discharge
volume of water passing through a channel per unit time (rate)
Q=V*A
m³/s = (m/s)(m²)
what is strahler classification system? information
order increases when two streams of same order join
high number of low-order streams occur in a watershed
lower order streams are shorter than higher order streams
More length of a watershed is low-order streams
what are types of permanence of flow?
perennial, intermittent, ephemeral
what is perennial vs intermittent vs ephemeral flow?
perennial: flowing all the time
intermittent: flowing sometimes and receiving water from groundwater
ephemeral: flowing rarely, not receiving water from groundwater
what is info on ephemeral flow?
Ex: in spring from increased snowmelt
some animals may have aquatic larvae and stream is only there when they are reproducing but it doesn’t matter to them because it’s there when they need it
what is info on surrounding vegetation? example?
orgs rely on inputs from surrounding terrestrial vegetation
water drains through plants around it
concentration of ions
cattle nearby a river will cause erosion from trampling, and bring in coliforms from feces
explain pool-riffle structure?
riffle: forms when water moves fast over boulder, gravel, or some structure
pool: when water slows down, finer sediments collect
run: intermediate between riffle and pool, smooth surface
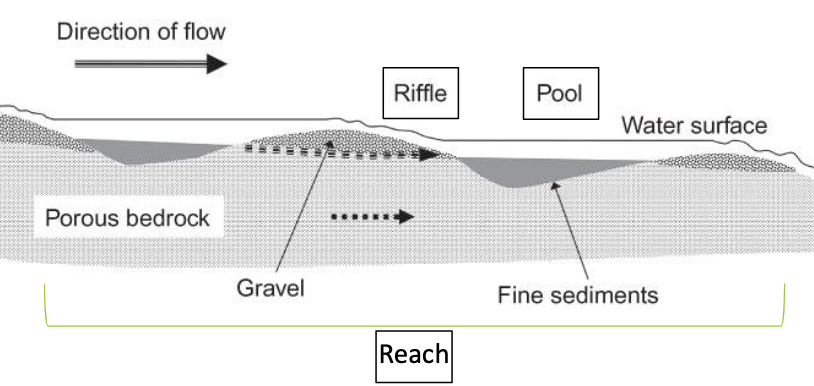
explain streams meander
thalweg is fastest velocity, outside edge
sediments accumulate on other side
a straight river has ____ of energy, can become ___ and possibilty for ___, hence, meanders help ____
no dissipation
extremely fast
flooding
dissipate energy
what are morphometric parameters for streams?
channel width/bankfull width
wetted width
channel slope
bank height
max depth
drainage basin length (straight line distance), land slope, and area
explain considerations of bankful width, what is it?
Change in vegetation: from bare ground with no trees to vegetated ground with trees, from no moss to moss covered ground, or from bare ground to grass covered ground
If there are no trees it means a river was there recently
topographic break from vertical to flat floodplain or steep to gentle slope
Change in texture of deposited sediment
Highest elevation below which no fine woody debris (needles, leaves, cones, or seeds) occur
what might impact presence of braided streams
hardness/stability of rocks
loose sediments will turn into braided rivers much easier
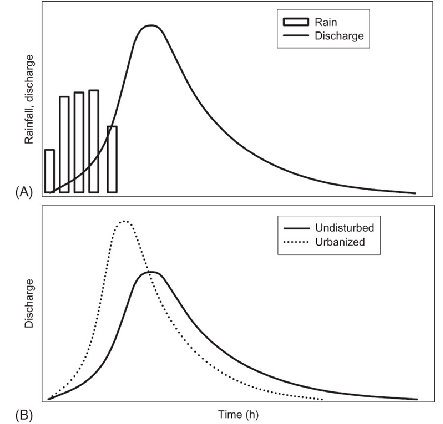
Explain graph A
hypothetical hydrograph of a storm event with precip and runoff in a natural area
rainfall happens earlier than discharge because it takes time for the rain to make it to the river after it falls, has to travel through ecosystem, dirt, plant
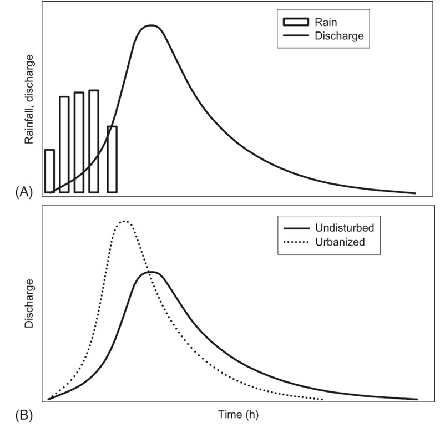
Explain graph B
Comparison of watershed response in urbanized vs non-urbanized
poor drainage from paved areas, water flows right through and enters the river quicker than undisturbed, causing earlier water peak
Plant in undisturbed will use some water, causing the lower peak
Some water doesn’t even make it to river from plant absorption
Define wetland
land saturated with water long enough to promote wetland or aquatic processes as indicated by poorly drained soils, hydrophytic vegetation, and various kinds of biological acitivity that are adapted to a wet environment
details on wetland loss
loss driven by agriculture
peatland under pressure as a source of fuel and peat moss for gardening