biol 1100 exam 2
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapters 3, 4, 6, 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
(CH2O)n
general formula for carbohydrates
1:2:1
ratio of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen in carbohydrates
monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose; number of carbons range from 3-7
aldehyde group
H-C=O at the top
ketone group
C=O in the middle
C6H12O6
chemical formula for glucose
in aqueous solutions
monosaccharides form rings
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis. (lactose, maltose, sucrose
glycosidic bond
covalent bond between two monosaccharides
alpha bond
Type of chemical bond that can be broken by human intestinal enzymes in digestion, faces down
beta bond
a type of chemical bond that cannot be easily digested by enzymes found in the human intestine, faces up
polysaccharides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
branched polysaccharides
multiple types of glycosidic bonds (amylopectin and glycogen)
unbranched polysaccharides
only one type of glycosidic bond (amylose and cellulose)
glycogen
storage form of glucose in animals
cellulose
carbohydrate component of plant cell walls.
metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
carbohydrate metabolism
changes glucose to glycogen, breaks glycogen down into glucose
C6H12O6+602 -> 6CO2+6H20
catabolic reaction
any chemical reaction that breaks down complex molecules into simpler molecules
anabolic reaction
any chemical reaction that combines simple molecules to build more-complex molecules
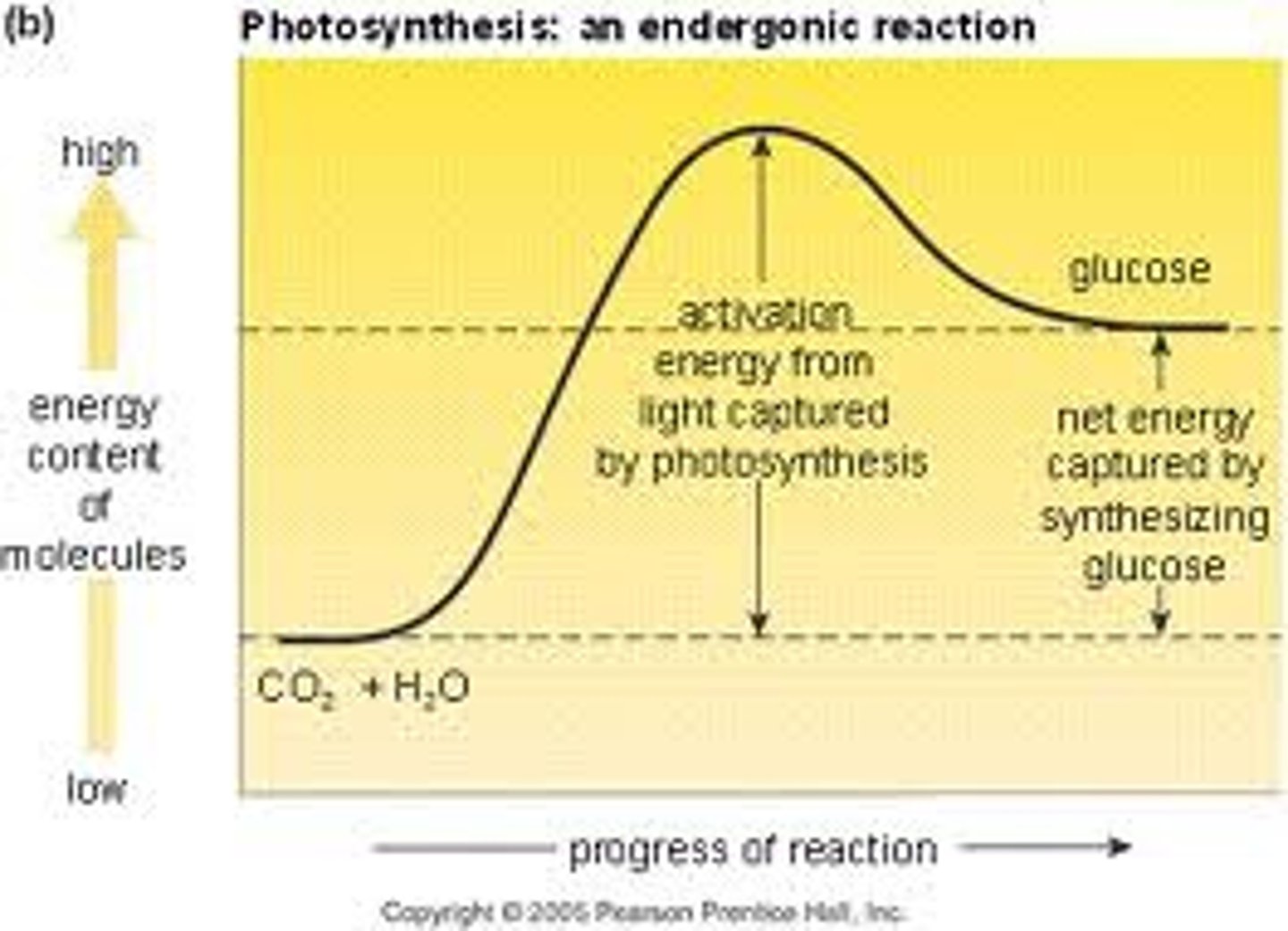
endergonic reaction
A non-spontaneous chemical reaction in which free energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
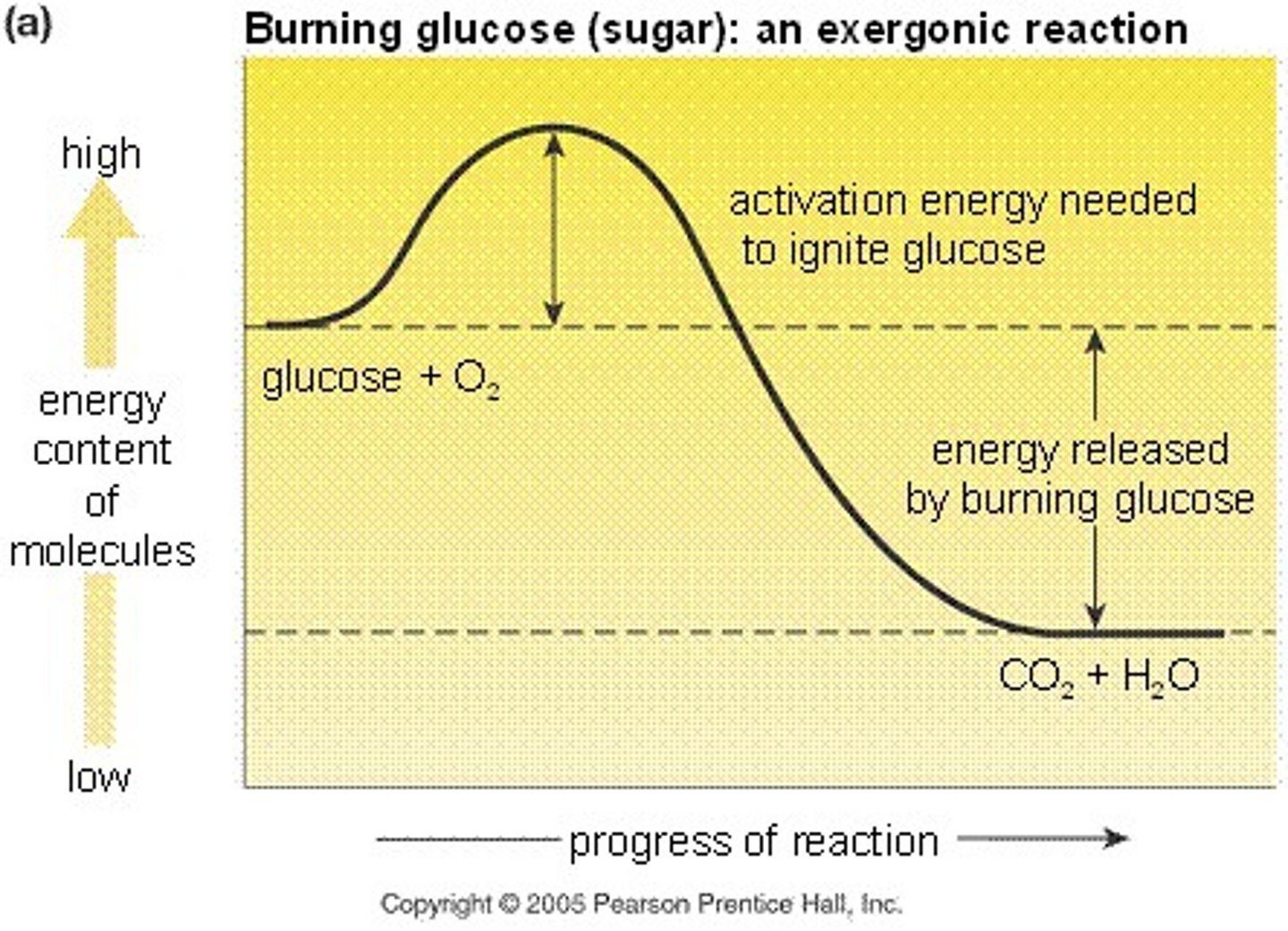
exergonic reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
Gibbs free energy
energy available to do work
metabolic pathway
Begins with a specific molecule, which is then altered in a series of defined steps, resulting in a certain product.
anabolic pathway
A metabolic pathway that consumes energy to synthesize a complex molecule from simpler compounds.
catabolic pathway
A metabolic pathway that releases energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler compounds.
kinetic energy
energy of motion
potential energy
stored energy
chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds
free energy
energy available to do work (delta G)
𝛥G=𝛥H−T𝛥S
enthalpy
total energy of a system (delta H)
entropy
measure of disorder (delta S)
activation energy
Energy needed to get a reaction started (Ea)
transition state
a high-energy intermediate state of the reactants during a chemical reaction that must be achieved for the reaction to proceed
heat energy
the energy transferred from one system to another that is not work
spontaneous reaction
process that occurs without the input of free energy
non-spontaneous reaction
process that occurs with the input of free energy
first law of thermodynamics
Energy can be transferred and transformed, but it cannot be created or destroyed.
second law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
3 carbons
triose
4 carbons
tetrose
5 carbons
pentose
6 carbons
hexose
7 carbons
heptose
8 carbons
octose
dehydration synthesis
two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
types of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose
Function of monosaccharides
short term energy, basic energy
Sources of Monosaccharides
honey and fruits
types of disaccharides
sucrose, lactose, maltose
Function of disaccharides
sugars that we use for energy; ex: lactose and sucrose
types of polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, cellulose
Function of polysaccharides
energy storage and structure
cytoskeleton
A network of protein fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
microfilaments
Long, thin fibers that function in the movement and support of the cell
intermediate filaments
twice as thick as microfilaments; no role in cell movement, only structural function
microtubules
help the cell resist compression, pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell
intercellular junctions
The connections between one cell and the other
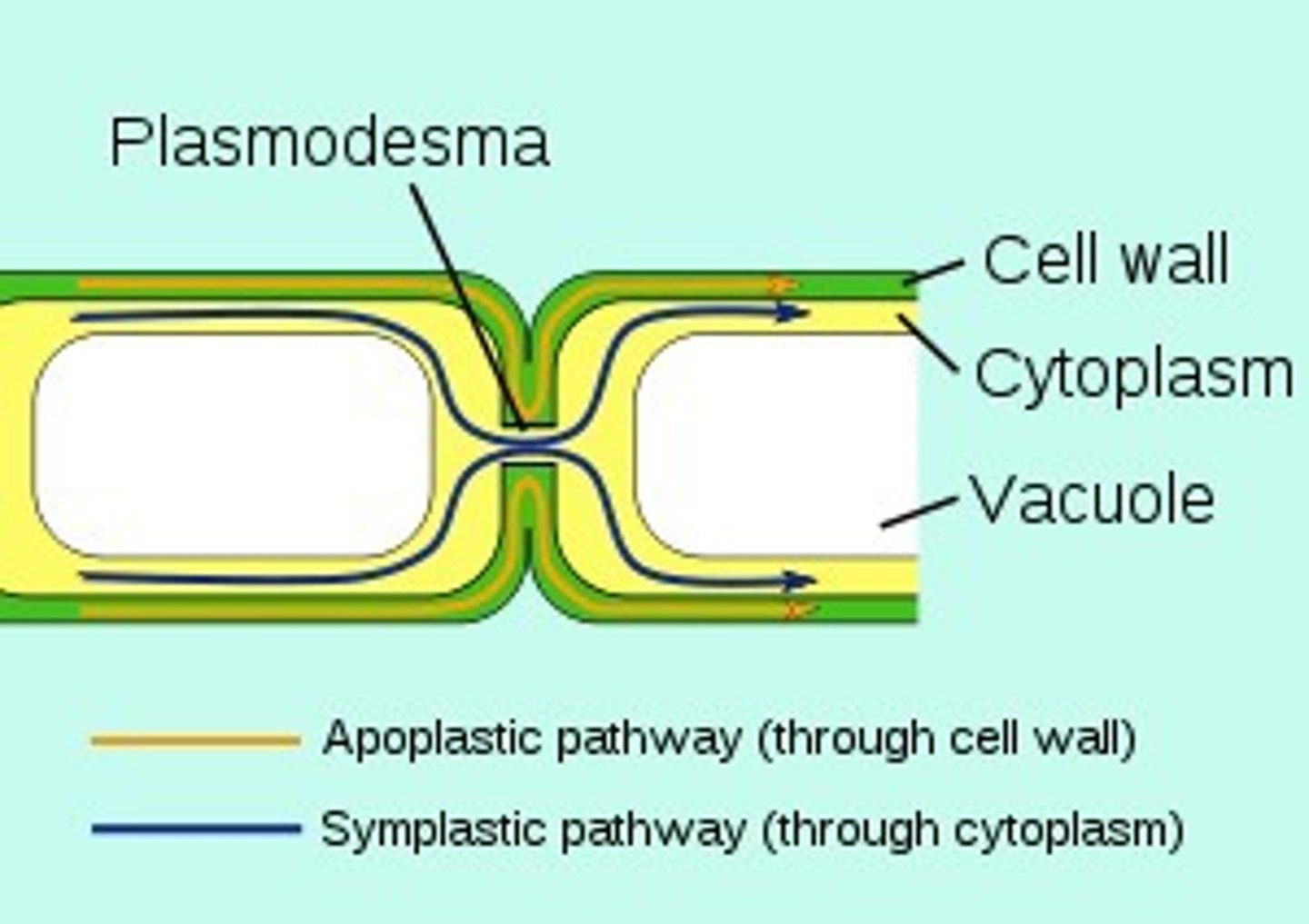
plasmodesmata
An open channel in the cell wall of plants through which strands of cytosol connect from adjacent cells
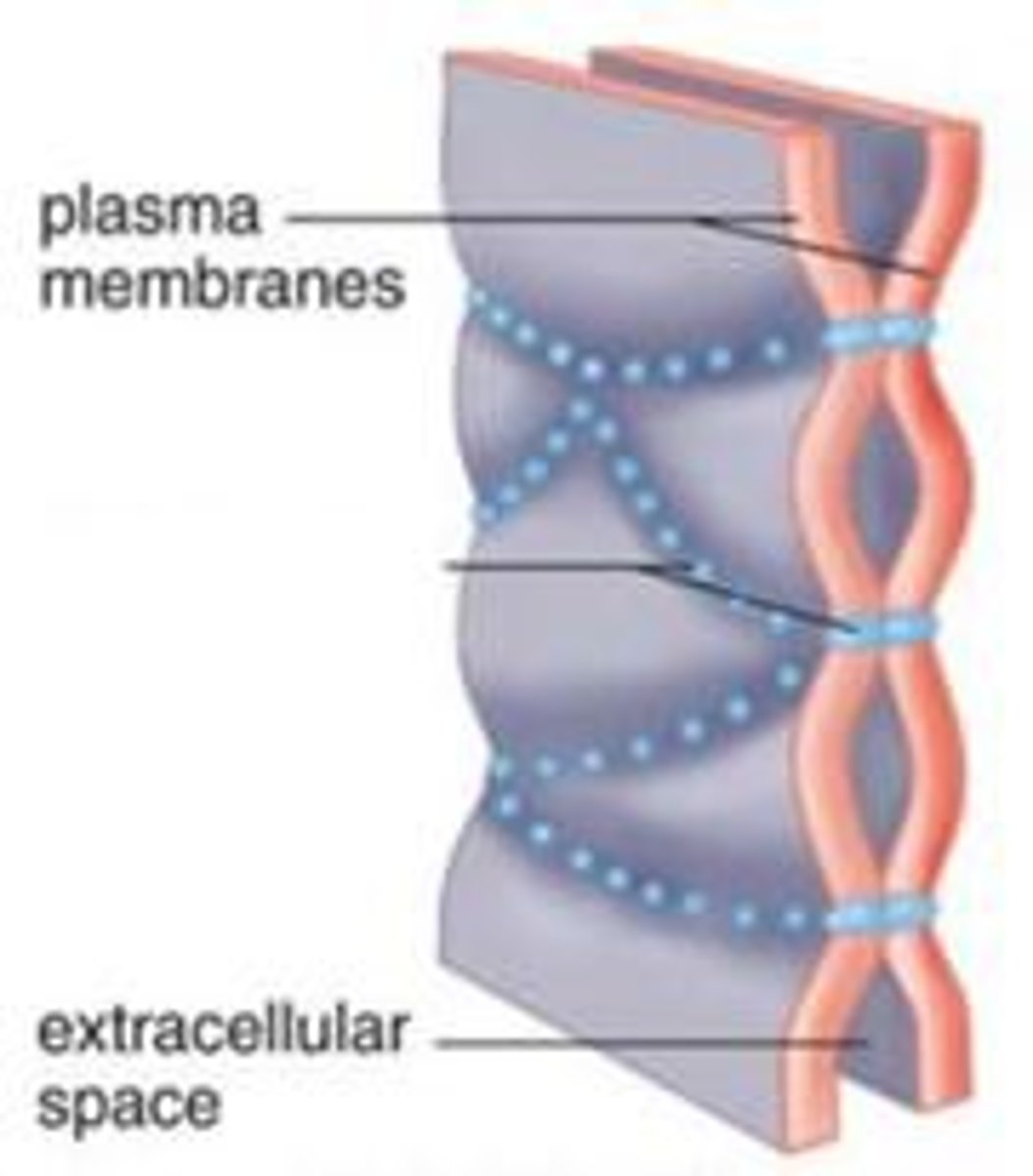
tight junctions
watertight seal between two animal cells; prevent leakage of extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells
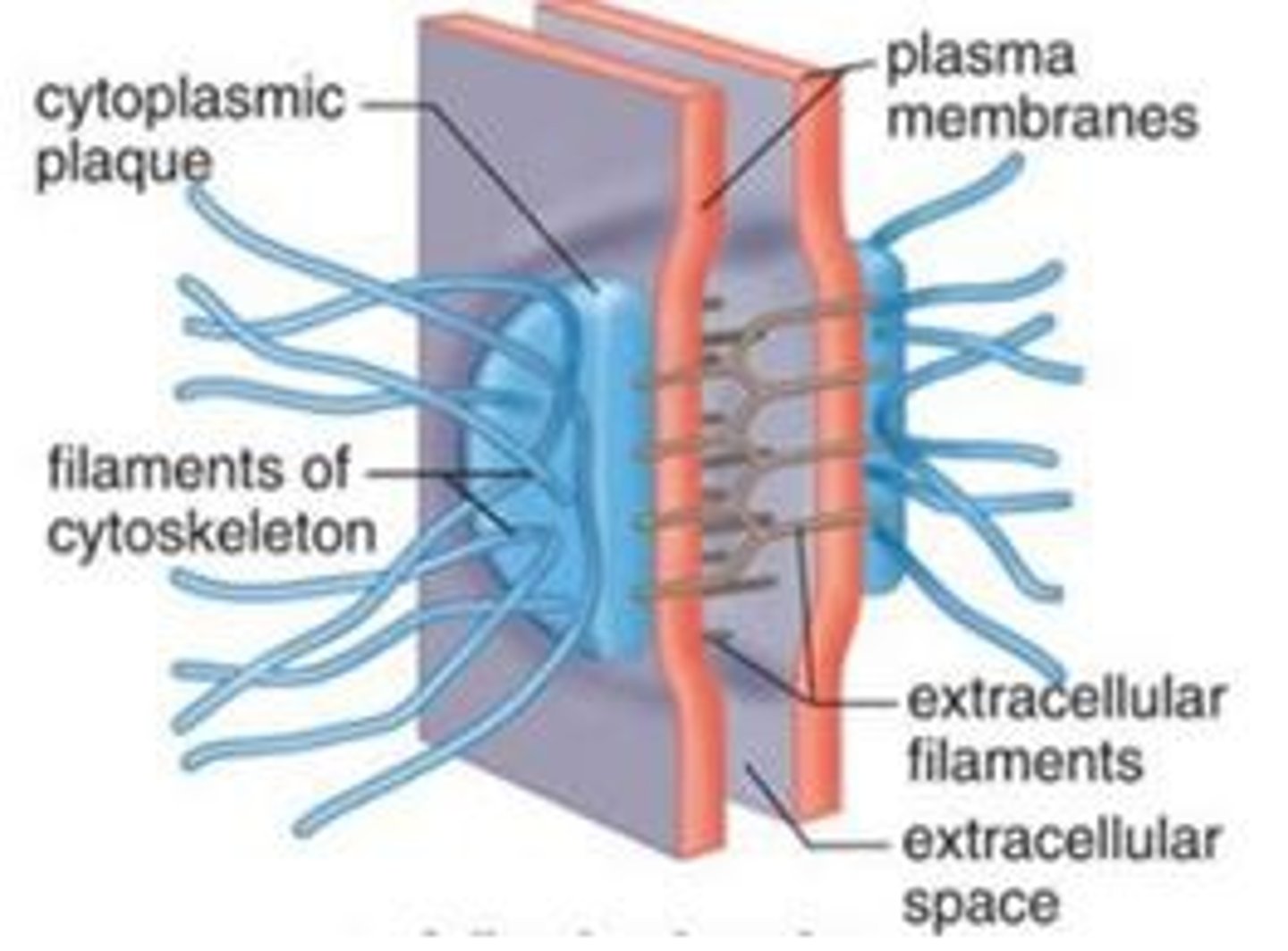
desmosomes
Anchoring junctions that prevent cells from being pulled apart
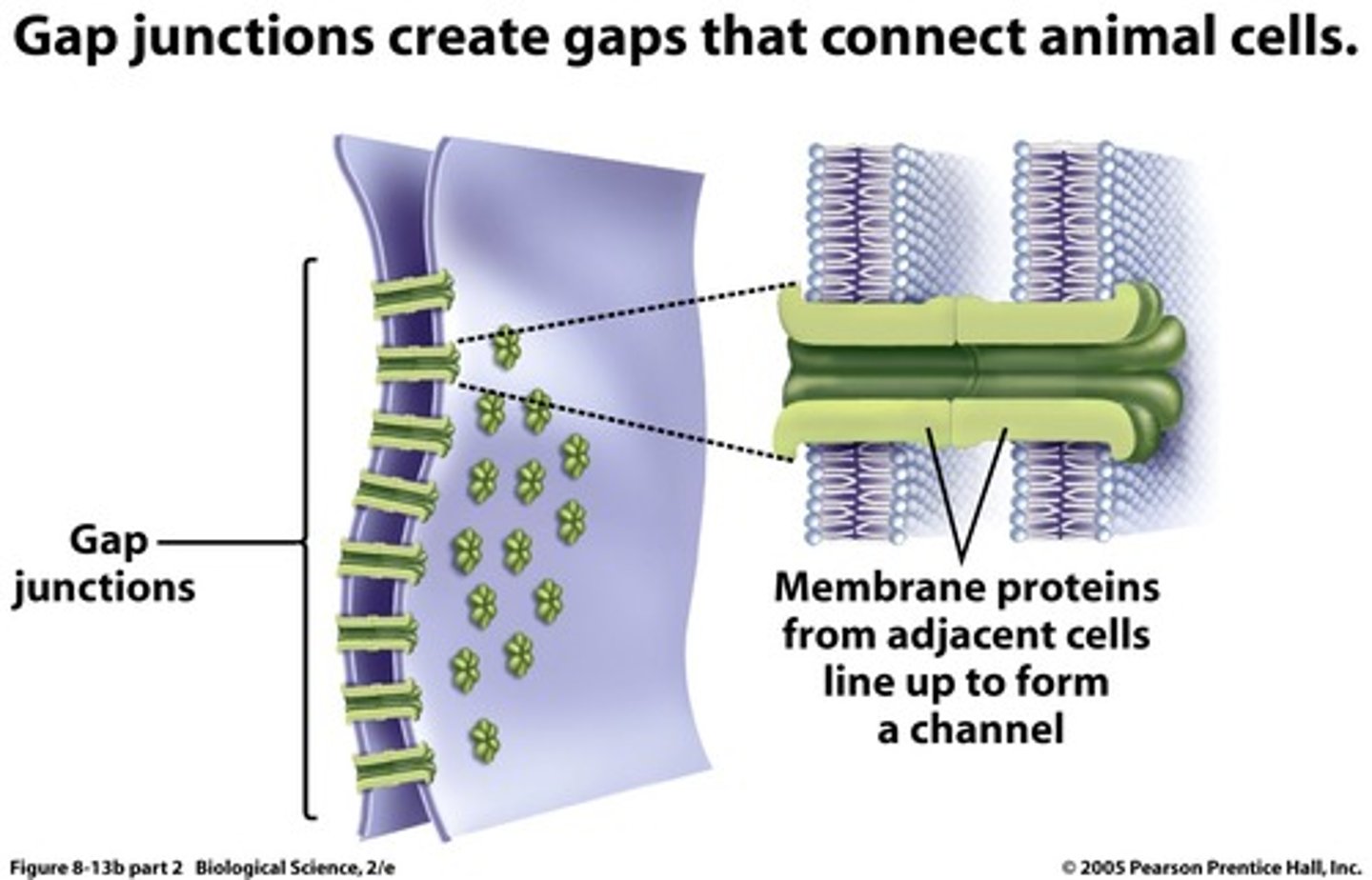
gap junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells
extracellular matrix
The chemical substances located between connective tissue cells
ATP hydrolysis
ATP is converted to ADP & phosphate energized myosin heads (removal of phosphate) need energy (exergonic)
ATP synthase
Large protein that uses energy from H+ ions to bind ADP and a phosphate group together to produce ATP
ATP synthesis
occurs in the mitochondria
ATP coupling
- anabolic reactions require energy (couple with ATP hydrolysis)
- catabolic reactions release energy (couple with ATP synthesis)
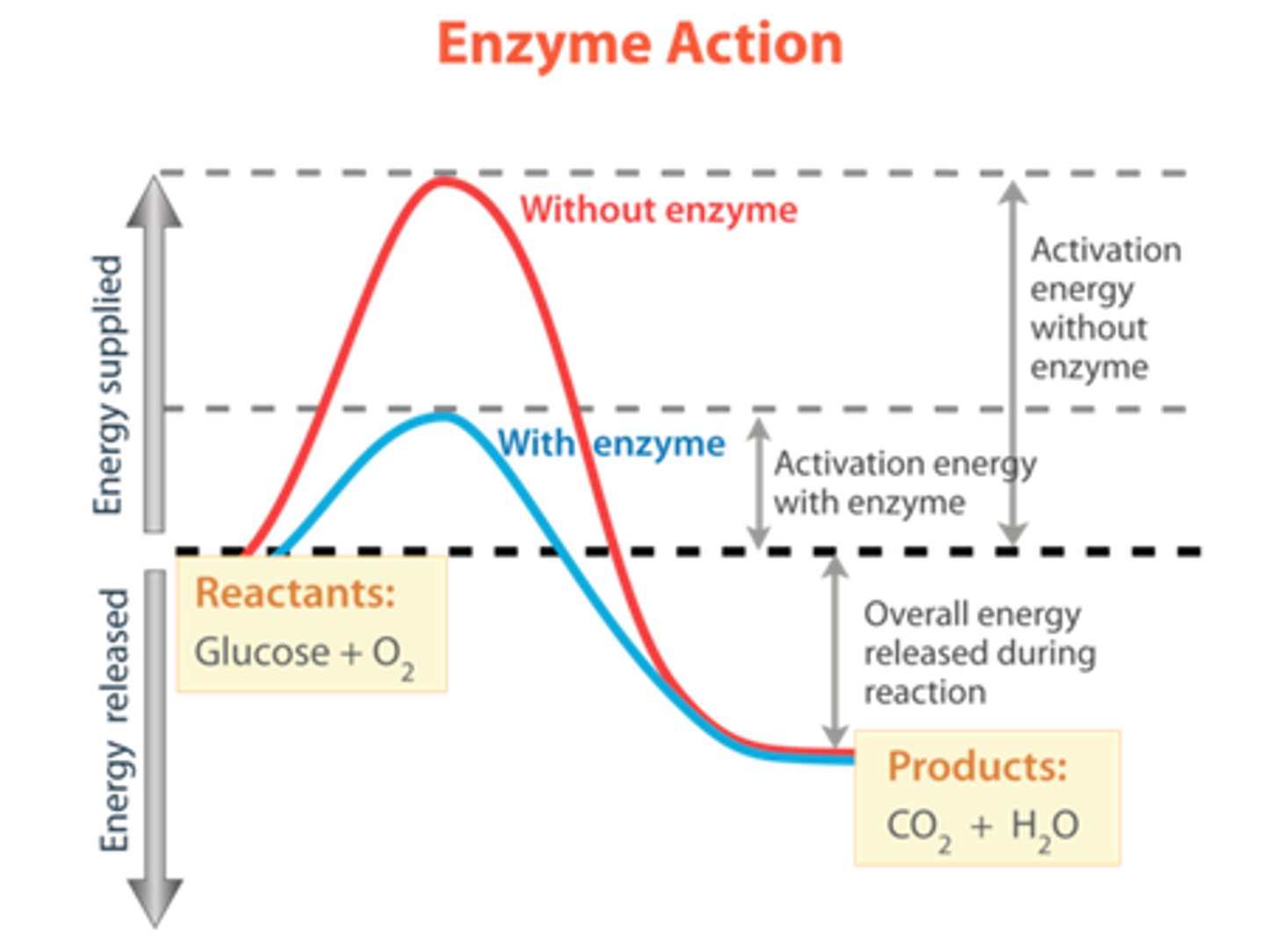
enzyme mediated reactions
with these type of reactions the rate of product formation is greatly influenced by the concentrations of the reactants
enzyme active site
Site of the enzyme surface where substrate molecules binds
Enzyme substrate
The reactant that an enzyme acts on
substrate specificity
ability of an enzyme to discriminate between very similar molecules
induced fit
The change in shape of the active site of an enzyme so that it binds more snugly to the substrate, induced by entry of the substrate. (lock and key model)
competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
noncompetitive inhibition
inhibitor binds elsewhere on the enzyme; alters active site so that the substrate cannot bind
allosteric inhibition
inhibition by a binding event at a site different from the active site, which induces a conformational change and reduces the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate
equilibrium
a state in which opposing forces or influences are balanced.
enzyme-substrate complex
A temporary complex formed when an enzyme binds to its substrate molecule(s).
redox reaction
transfer of one or more electrons from one reactant to another; also called oxidation-reduction reaction.
reducing agent
The electron donor in a redox reaction.
oxidizing agent
The electron acceptor in a redox reaction.
oxidation
The loss of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction.
reduction
The gain of electrons from a substance involved in a redox reaction.
electron carrier
a compound that can accept a pair of high-energy electrons and transfer them, along with most of their energy, to another molecule (NAD+)
cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen
cellular respiration equation
C6H12O6+6O2---> 6CO2+6H2O+ATP
cytoplasm and mitochondria
where cellular respiration takes place
glycolysis
releasing the energy of glucose, in which a molecule of glucose is broken into two molecules of pyruvic acid
pyruvate oxidation
occurs on the way to the mitochondrial matrix. Pyruvate is oxidized into 1 CO2, 1 NADH, 1 acetyl-COA (2 carbons attached to coenzyme A)
Krebs cycle
energy stored in pyruvate is transferred to NADH and FADH2, and some ATP is produced
oxidative phosphorylation
results in the formation of ATP from the flow of electrons across the inner membrane to bind with oxygen.
electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP.