Freshwater Ecology Lab exam
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
how can plankton be used as bioindicators of ecosystem health?
Because they’re sensitive to various pollutants and nutrient inputs, changes in their populations manifest prior to changes in larger organisms
what are some results of undesirable plankton?
Releasing toxins, produce unpleasant tastes and odours that are difficult to remove
Phytoplankton
plants like algae
zooplankton
animals like copepods
features used to describe and differentiate plankton
size
colour
shape
motile
unicellular/colonial/filamentous
cell wall types
food storage materials
what is the function of a gas vacuole in phytoplankton
allow them to control their position in the water, can sink lower for more nutrients and then go higher for light
cyanobacteria: example and traits
example: microcystis of the order Chroococcales
unicellular
thin cell wall
growth at high temperatures
capable of massive blooms
produce toxins apon cell death/lysis
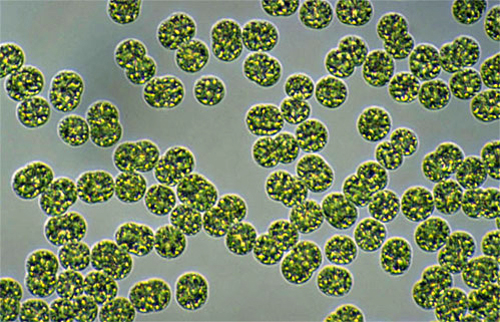
what is this
microcystis
chlorophyta example and traits
volvox
can be unicellular, filamentous, or colonial
can be motile or non motile
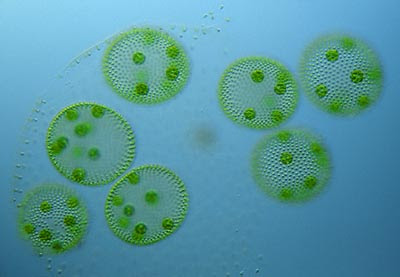
what is this
volvox
what class do diatoms belong to
class bacillariophyta
diatom traits
thick silica cell walls
non-flagellated
unicellular
low temp and low light tolerant
bloom in spring
disadvantage of diatoms
only remain in suspension when conditions are turbulent because they’re so heavy
two orders of diatoms and how to determine
centrales and pennales
centrales are discoid or cylindrical
pennales are elongate with bilateral symmetry
euglenophyta example and traits
euglena
unicellular and motile with flagella
spindle shaped and have several chlorplasts per cell
euglena are facultative heterotrophs
environments abundant with decaying matter such as shallow lakes and ponds
Rotifera
unsegmented and pseudocoelomates
ciliated apical region known as the corona
muscular pharynx known as the mastax
cilia are used for filter feeding and locomotion
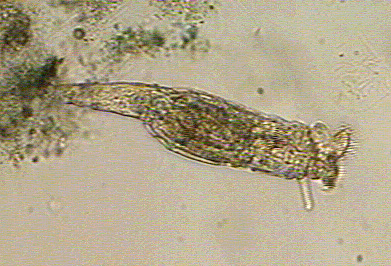
what is this
rotifera
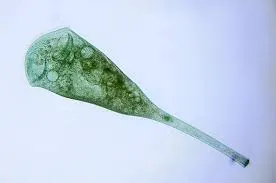
what is this
stentor
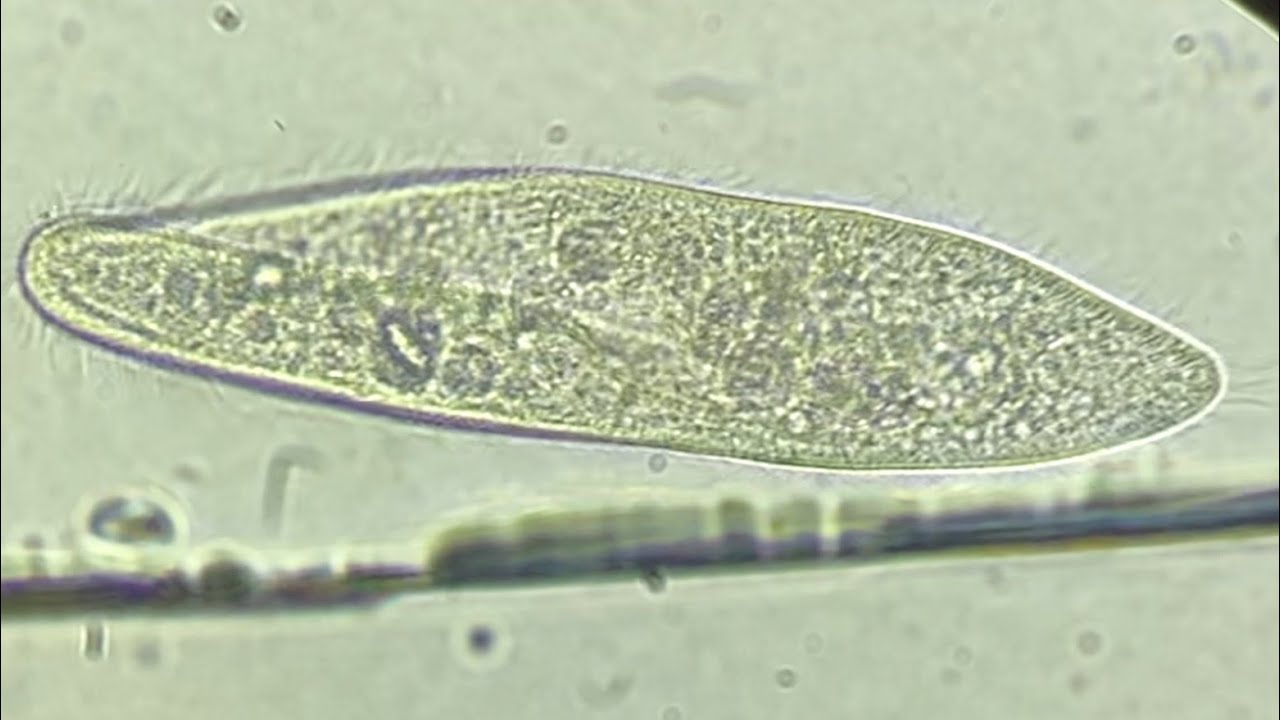
what is this
paramecium
how does chlorophyll a make photosynthesis possible?
by passing its energized electrons onto molecules that manufacture sugars
how can chlorophyll pigments be quantified?
using spectrophotometric, fluorometric, or high pressure liquid chromatographic methods
the ratio of chlorophyll a to phaeophytin is an indicator of what?
the ratio serves as an indicator of the physiological condition of the phytoplankton. 1.7 is completely healthy and anything lower especially 1 indicates an unhealthy culture/degradation
what does chlorophyll a measure and why is it reliable?
used as an indicator of phytoplankton biomass, as it is the main pigment involved in photosynthesis and found in all PS organisms directly correlating to the amount of biomass of these organisms in the water
what is a bioassay
an experiment that uses living organisms or systems to determine the activity/diversity of the substance
What is LC50?
50% lethal concentration, this is the concentration that kills 50% of the organisms over a specified period of time
What is the NOEL
no observable effect level, where there was no observable effect on the organisms
What is an IC50
The inhibitory concentration, the concentration where 50% inhibition was noted
what are normal vs abnormal swimming behaviours of daphnia
normal would be characterized as a hop and sink movement using their second antennae for propulsion
abnormal would be deviation from this pattern, staying sunk in the water column or not swimming to the rhythmic jerk of the hop and sink movement
what is a spectrophotometer used for
measures the intensity of light of different wavelengths in the visible spectrum
why do you need to set the blank for the spectrophotometer?
everything absorbs a bit of light, so if you want to determine the absorbance of the sample you don’t want to include the absorbance of the liquid that the sample is in
what is a standard curve and what’s on each axis
plotting results for samples of known concentrations. Concentration on the x axis and absorbance on the y axis
what is the life cycle and morphology of lamprey?
eel like body with mouth full of rows of sharp teeth in a circle.
larval filter feeders in streams for several years, parasitic juvenile phase in lakes/oceans, migrate back to rivers/streams to spawn and then die
what methods were used to bring lamprey under control
lampricide treatments of TFM to kill larvae in streams. Sterile male release technique.

What is this and what’s it used for
Van Dorn sampler. Used for obtaining samples at discrete depths
what is Lugol’s solution
what samples should be placed in immediately after sampling to preserve microscocpic aquatic organisms

What is this and what is it used for
Ekman dredge. Used for quantitative macrobenthos samples by takinga scoop of known area from the bottom sediments
what gear should be used to measure phytoplankton and zooplankton
tow nets and plankton nets, or the schindler-patalas sampler
what should be used for macrophytes
rakes
what should be used for benthos
ekman dredge