Chapter 16 - Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
1
New cards
Electrophilic aromatic substitution

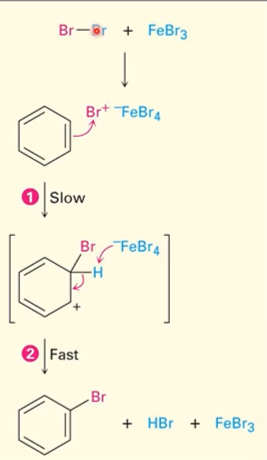
2
New cards
Electrophilic substitution example
The goal is to stabilize everything
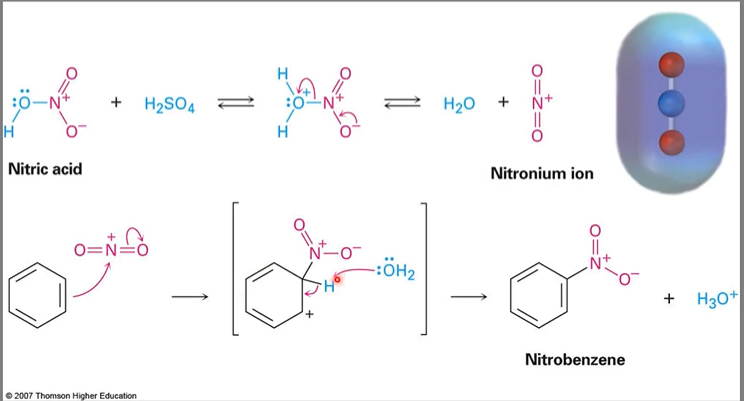
3
New cards
Aromatic nitration
usually forms water as a by product
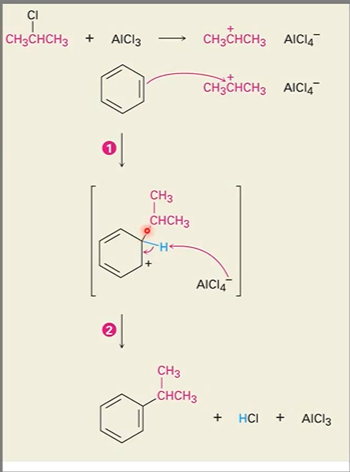
4
New cards
Alkylation reaction
Called Friedl-Crafts alkylation reaction
Carbocation is created when reacting with AlCl3
Now the carbocation can react with a ring.
Extra H can be used to stabilize AlCl3
Because a carbocation is formed, carbocation rearrangement can happen, particularly when a primary alkyl halide is used. (Hydride and methanide shifts)
5
New cards
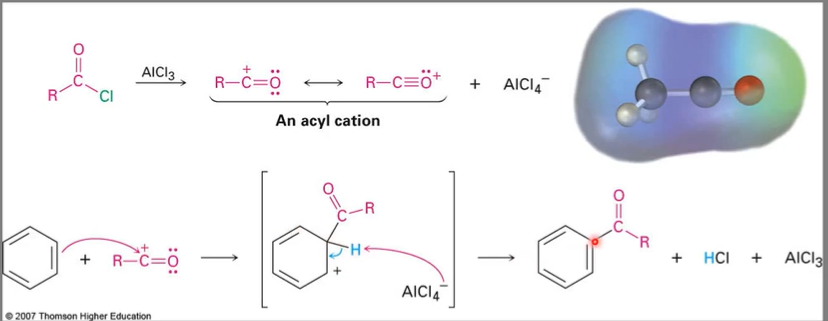
Acylation reaction
Because of the resonance stabilized acyl cation, no carbocation rearrangement occurs during acylation.