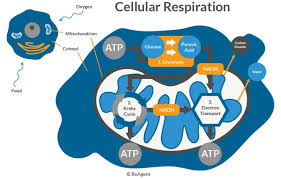
Cellular Respiration: Pathways and Processes: Section 1: Foundational Concepts & Overview
1/36
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
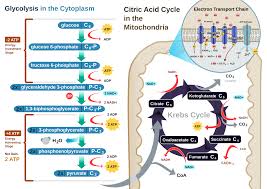
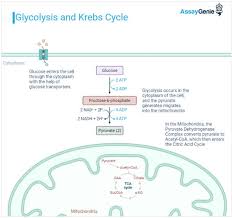
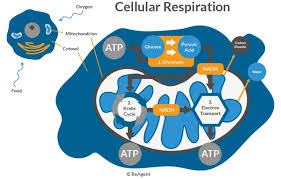
Cellular Respiration
Food converts to energy through glucose oxidation and ATP for celluar function.
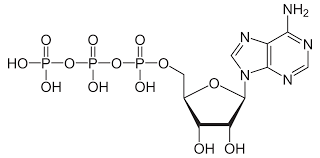
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate is the energy currency of the cell, produced during respiration, providing 7.3 kcal/mol.
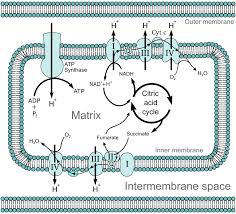
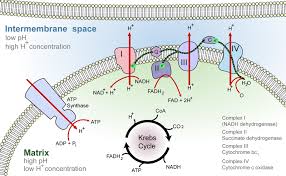
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Electron transport chain produces ATP via chemiosmosis and oxygen.
Catabolic Pathways
Metabolic routes that release energy by breaking down molecules.
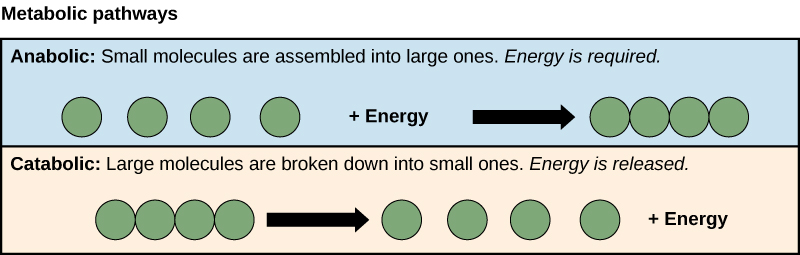
Electron Transfer
Movement of electrons during catabolic pathways, releases energy.
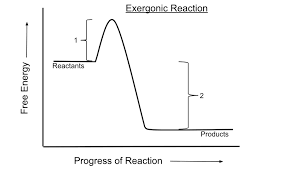
Exergonic Reaction
Glucose catabolism releases energy, −53 kcal/mol change.
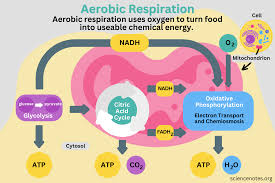
Aerobic Respiration
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor in organic breakdown.
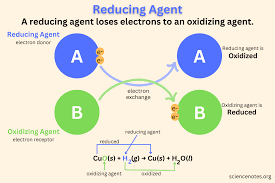
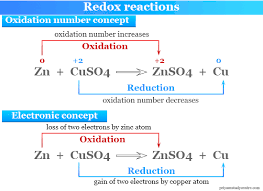
Reduction
Gain of electrons by a substance.
Reducing Agent
Substance that donates electrons in a redox reaction.
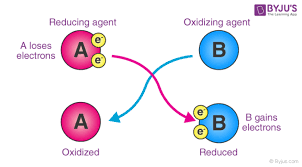
Oxidizing Agent
Electron-accepting substance in redox reaction.
Potential Energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds of organic molecules.
Heat Dissipation
Energy lost as heat during metabolic processes.
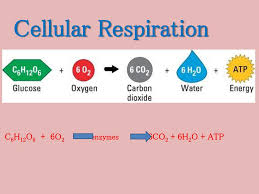
Overall Reaction of Respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy.
DG of Glucose Catabolism
ΔG = −686 kcal per mole of glucose.
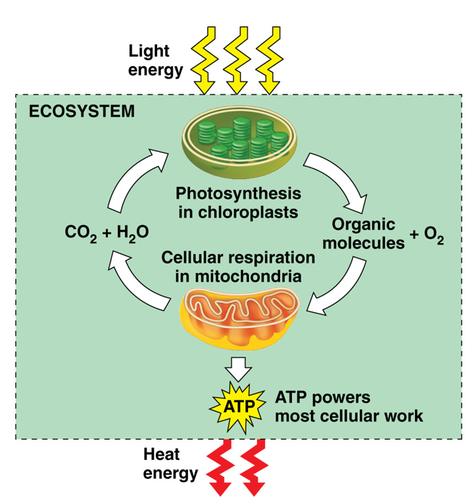
Chemical Elements Recycling
Essential elements are reused in ecosystems.
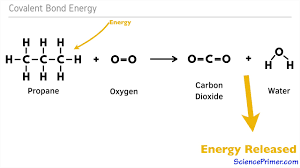
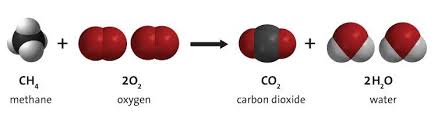
Combustion of Methane
Reaction of methane with oxygen producing water and CO2.
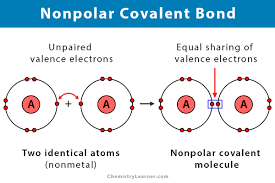
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
Bonds where electrons are shared equally between atoms.
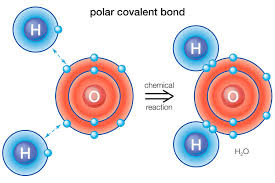
Polar Covalent Bonds
Bonds with unequal sharing of electrons, creating partial charges.
Electronegativity
Tendency of an atom to attract electrons.
Oxidation of Methane
Methane loses electrons during its reaction with oxygen.
Reduction of Oxygen
Oxygen gains electrons when forming water from methane.
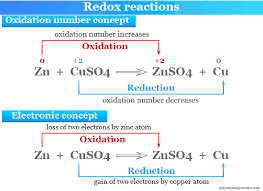
Redox Reaction
Chemical reaction involving transfer of electrons.
Hilltop Electrons
High-energy electrons in organic fuel molecules.
Chemical Energy Release
Energy liberated when electrons move closer to oxygen.
Molecular Stability
Resistance of molecules to react without energy input.
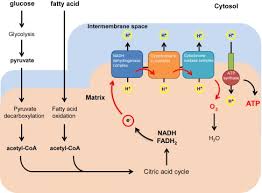
Energy Yield from Glucose
686 kcal released per mole of glucose burned.
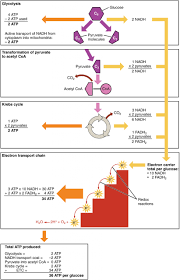
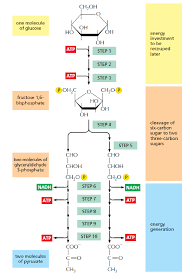
Stepwise Electron Transfer
Gradual oxidation of glucose through multiple reactions.
Proton Release
H+ ions released during the reduction of NAD+.
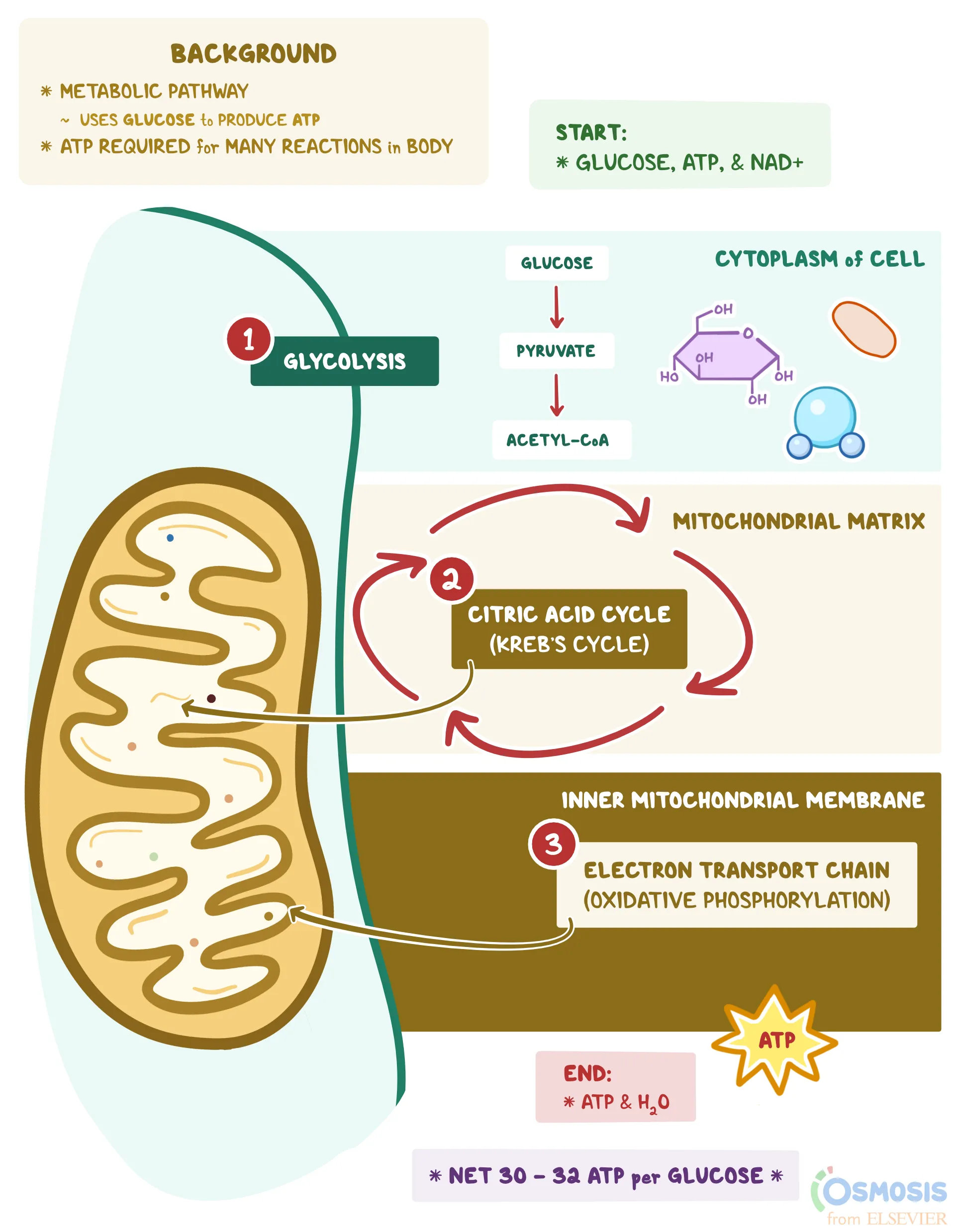
Mitochondria
Site of cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells.
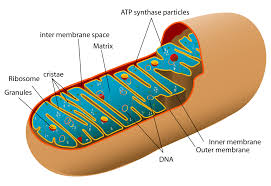
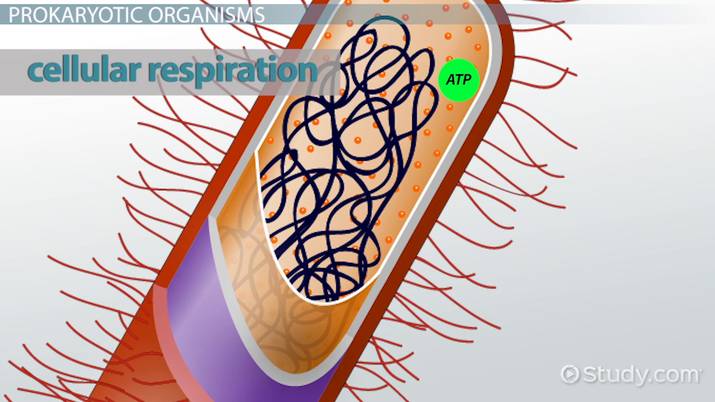
Prokaryotes
Organisms where respiration occurs in plasma membrane.
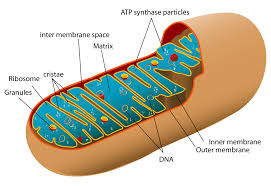
Mitochondrion
Organelle where aerobic respiration occurs.
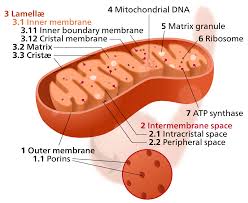
Mitochondrial membrane
Site of ATP synthesis and electron transport.
Energy yield
Total ATP from glucose is 38 ATP.
Kcal/mol
Unit measuring energy released from glucose oxidation.
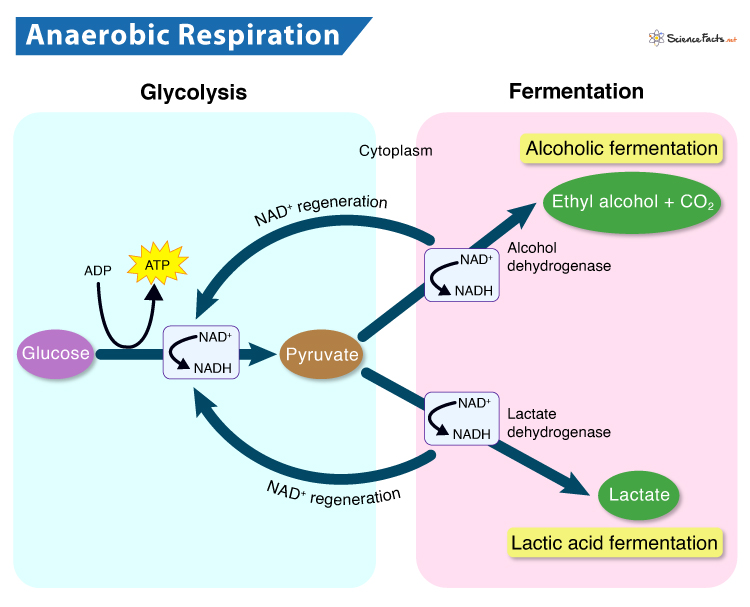
Anaerobic Respiration
Uses non-oxygen molecules as final electron acceptors.
Fats
Lipids that can be metabolized for ATP production.
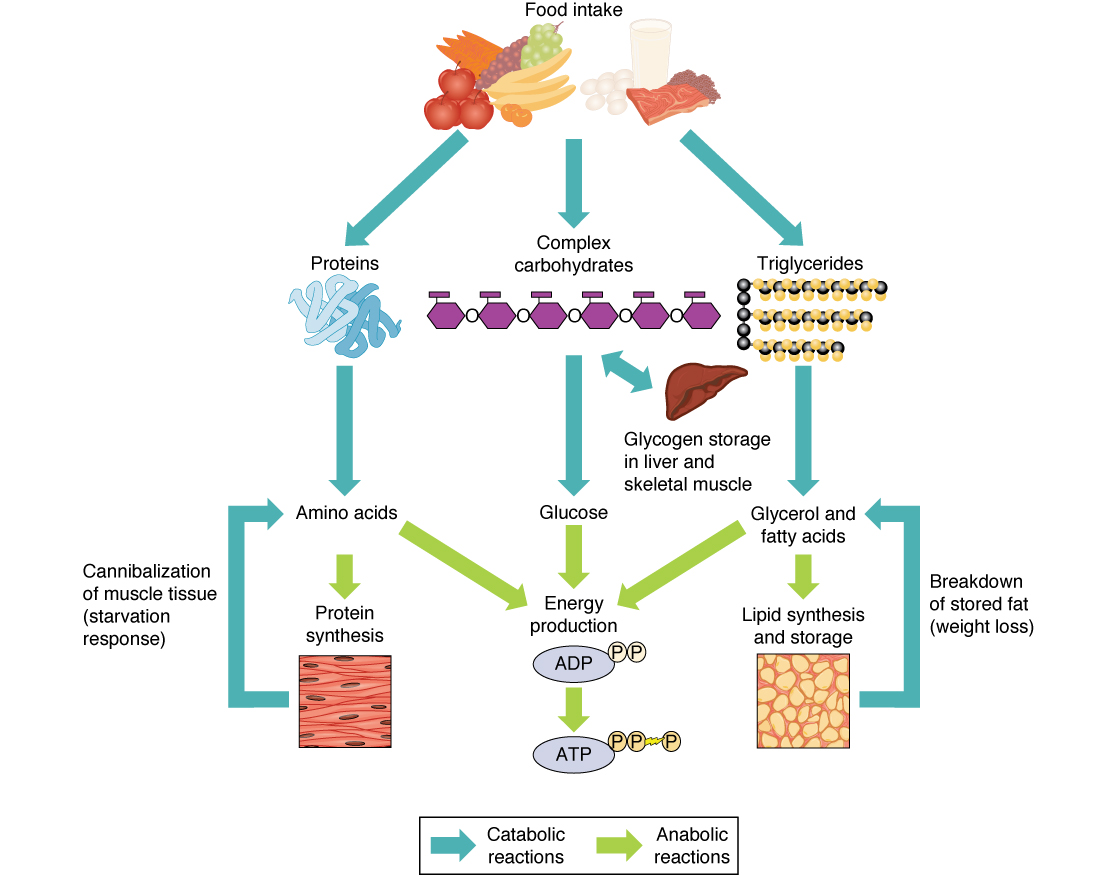
Disaccharides
Sugars like sucrose