immuno- L3: complement system and inflammation
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
adaptive
is inflammation in relation to innate or adaptive immunity?
an influx of WBCs and fluid to fight infection and aid tissue repair
what happens during acute inflammation?
chronic inflammation, which leads to tissue damage and loss of tissue function
what happens if the inducer of inflammation is not removed?
if the inducer of inflammation is not removed
why does chronic inflammation occur?
neutrophils
when bacteria enters, what is the first cell to arrive?
dendritic cells and macrophages
after the influx of neutrophils to the site of invasion, what cells arrive next?
neutrophils
which are arrive quicker to the site of invasion- macrophages or neutrophils?
macrophages
which are more efficient at producing immune responses- macrophages or neutrophils?
cytokines, chemokines, lipid mediators
what are the inflammatory regulators?
phagocytizing the invadors
when macrophages are activated innately, they respond by...
phagocytizing the invadors and then displaying the MHC II and producing enzymes
when macrophages are activated by an adaptive immune response, they respond by...
both
if innate, they just phagocytize the invador and are done
if adaptive, they phagocytize the invador and then act as APCs
are macrophages activated innately or adaptively?
TNF
IL-1
IL-6
macrophages and dendritic cells secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines, especially what types?
signal endothelial cells to make them leaky to fluid (so plasma with antibodies and complement can be secreted) and sticky for leukocytes
what do TNF and IL-1 do?
produce inflammation symptoms- heat, swelling, pain, redness
act on neutrophils to enhance their ability to kill microbes
what are the effects of TNF?
TNF
what is the main cytokine for producing symptoms of inflammation?
macrophages, dendritic cells
what cell secretes the cytokine TNF?
activate lymphocytes for adaptive immunity
send signals to the brain and liver
what are the main effects of IL-1?
IL-1
which is the main cytokine for activating lymphocytes?
mediates septic shock
promotes adaptive immune response
has C reactive protein
what are the main effects of IL-6?
CRP- C reactive protein
what is the protein thats levels are measured to indicate systemic inflammation?
IL-6
which cytokine has CRP- C reactive protein?
IL-6
which cytokine produces a systemic response?
the secretion of cytokines (TNF, IL-1) by macrophages and dendritic cells
what triggers neutrophils to begin their response?
short
are neutrophils short or long lived?
they often damage host tissue as a by-product of their response
what is a problem that neutrophils cause?
chemotaxis- chemical signals
how do neutrophils find the site of infection?
the type of chemokines
the type of cell that responds to an invasion depends on what?
Kupffer cells (macrophages of the liver)
in dogs, bacterial clearance is mostly done by....
pulmonary macrophages
in cats, bacterial clearance is mostly done by....
loss of appetite
fever
depression
neutrophilia
what are the symptoms of systematic inflammation?
CRP and opsonin
what are the main proteins that play a role in the acute phase of systemic inflammation?
systemic inflammatory response syndrome
what is SIRS?
in response to massive tissue injury
when does SIRS occur?
an exaggerated defense response- the release of large amounts of cytokines and oxidants
what does SIRS cause?
fever
rigors
myalgia
headache
nausea
acidosis
low blood pressure
organ damage
MODS- multiple organ disfunction syndrome
death
what are the symptoms of SIRS?
E. coli, salmonella
what are the most common bacteria that cause SIRS?
SIRS- systemic inflammatory response syndrome
what disease may occur in response to massive tissue injury?
because of SIRS (systemic inflammatory response syndrome)-
the bacteria somehow triggered the body to induce a very exaggerated immune response, which is too much for the body. it leads to MODS- multiple organ disfunction syndrome, which causes death
why is an immune response causing death?
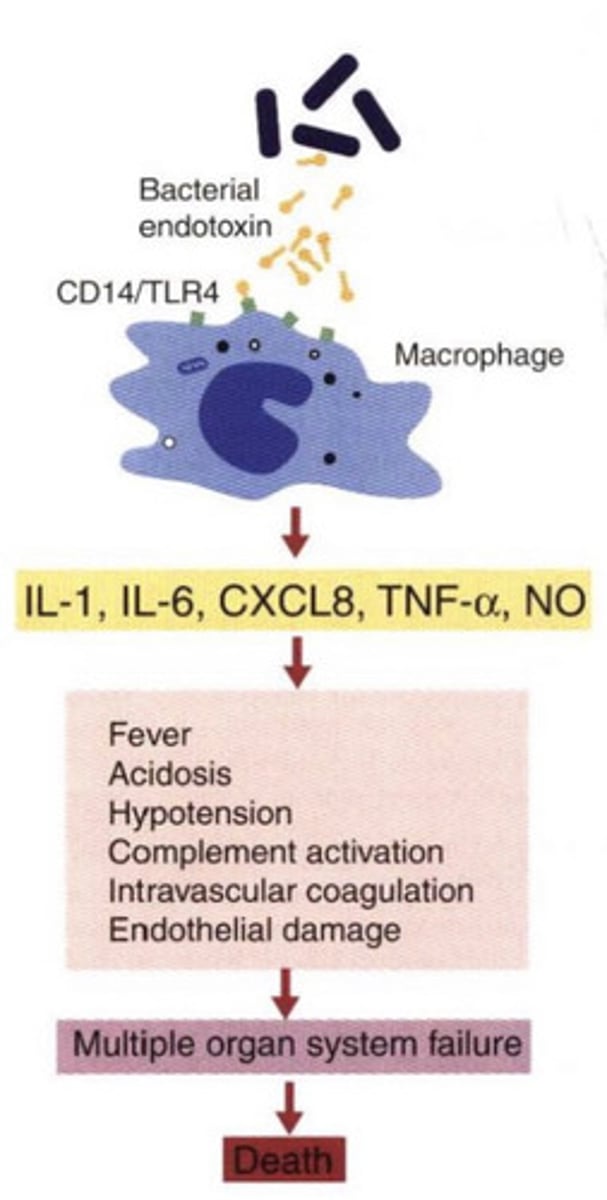
SIRS-
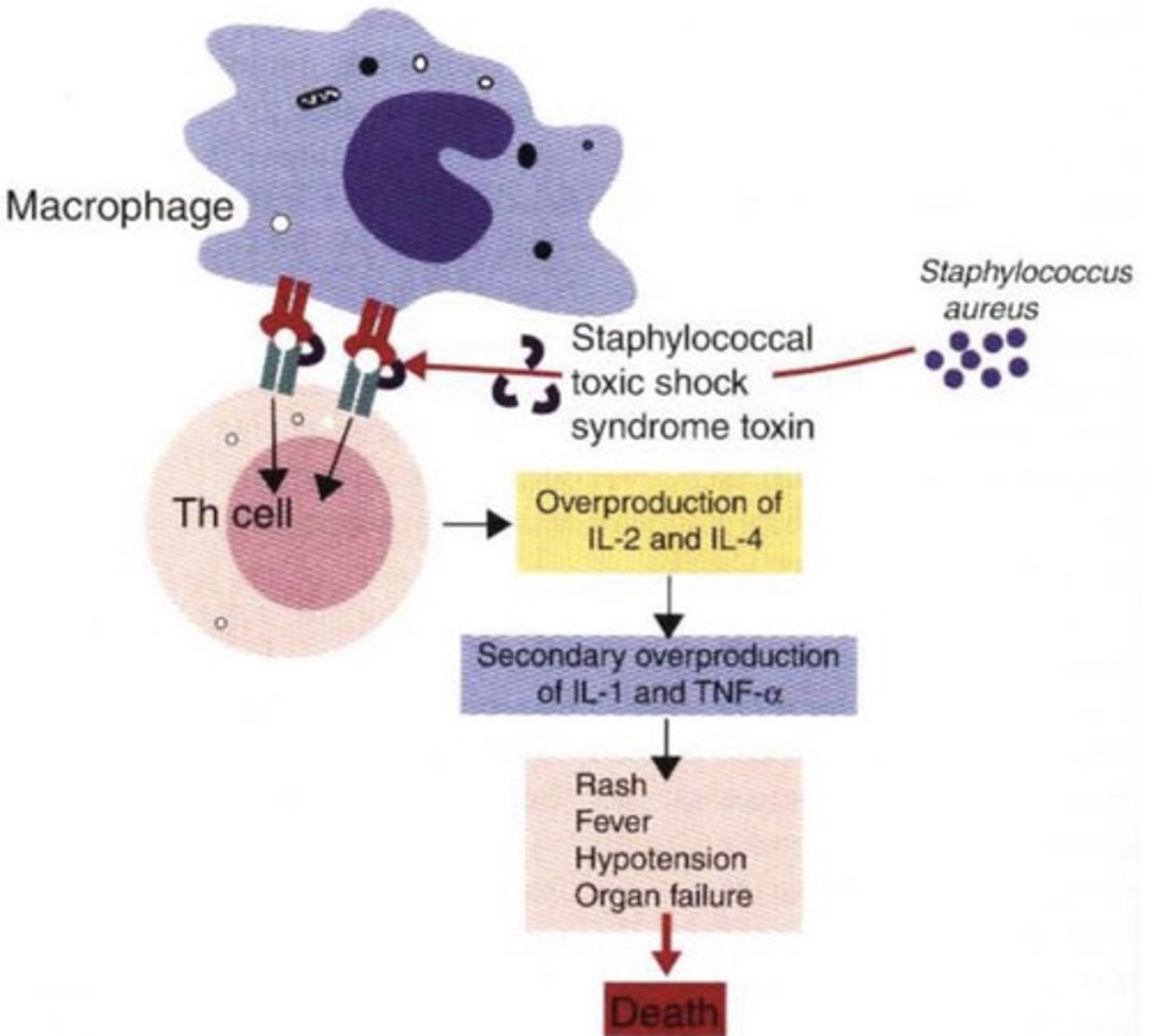
the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus has ensotoxins (staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome toxin) which interfere with the macrophage-T helper cell communication, causing the overproduction of cytokines, and therefore and extreme immune response that results in death
what problem does this represent?
foreign material is not completely destroyed
chronic inflammation occurs if...
-macrophages, fibroblasts, and lymphocytes accumulate
-giant cells are formed to try to ingest the particles
-fibrosis- cells deposit collagen in infected tissues
-granuloma (a cluster of WBCs and other tissue) forms
if foreign material is not completely destroyed, chronic inflammation occurs. what exactly happens?
chronic inflammation-
accumulation of WBCs to attempt to ingest the invador, and fibrosis occurs
what causes a granuloma to form?
C3
what is the most important component of the complement system?
usually the adaptive immune system- the immune complexes bind to CIq
OR the innate immune system- C3b binds to the the microorganism surface
what activates the complement system?
yes, it can distinguish self from nonself
does the complement system have self-recognition?
25-30
how many proteins are involved in the complement system?
a cascade of proteolytic reactions on microbial surfaces- coats the microbe with fragments that are recognized by macrophages
the activation of the complement system activates.....
no, only microbial invadors
does the complement system also act on infected host cells?
defends against pyogenic bacterial infections
bridges/connects innate and adaptive immune systems
assists in disposing immune complexes
what are the roles of the complement system?
the coating of bacteria with a protein (usually C3b in the complement system) so that it can be recognized by a phagocyte
what is opsonization?
opsonizes microbes
what does C3b do (part of the complement system)?
causes inflammation by causing mast cell degranulation
what does C3a do (part of the complement system)?
C3a
what part of the complement system causes mast cell degranulation?
opsonization- C3b
inflammation (by degranulating mast cells)- C3a
cytolysis- C5-C9
what are the 3 functions of the complement system?
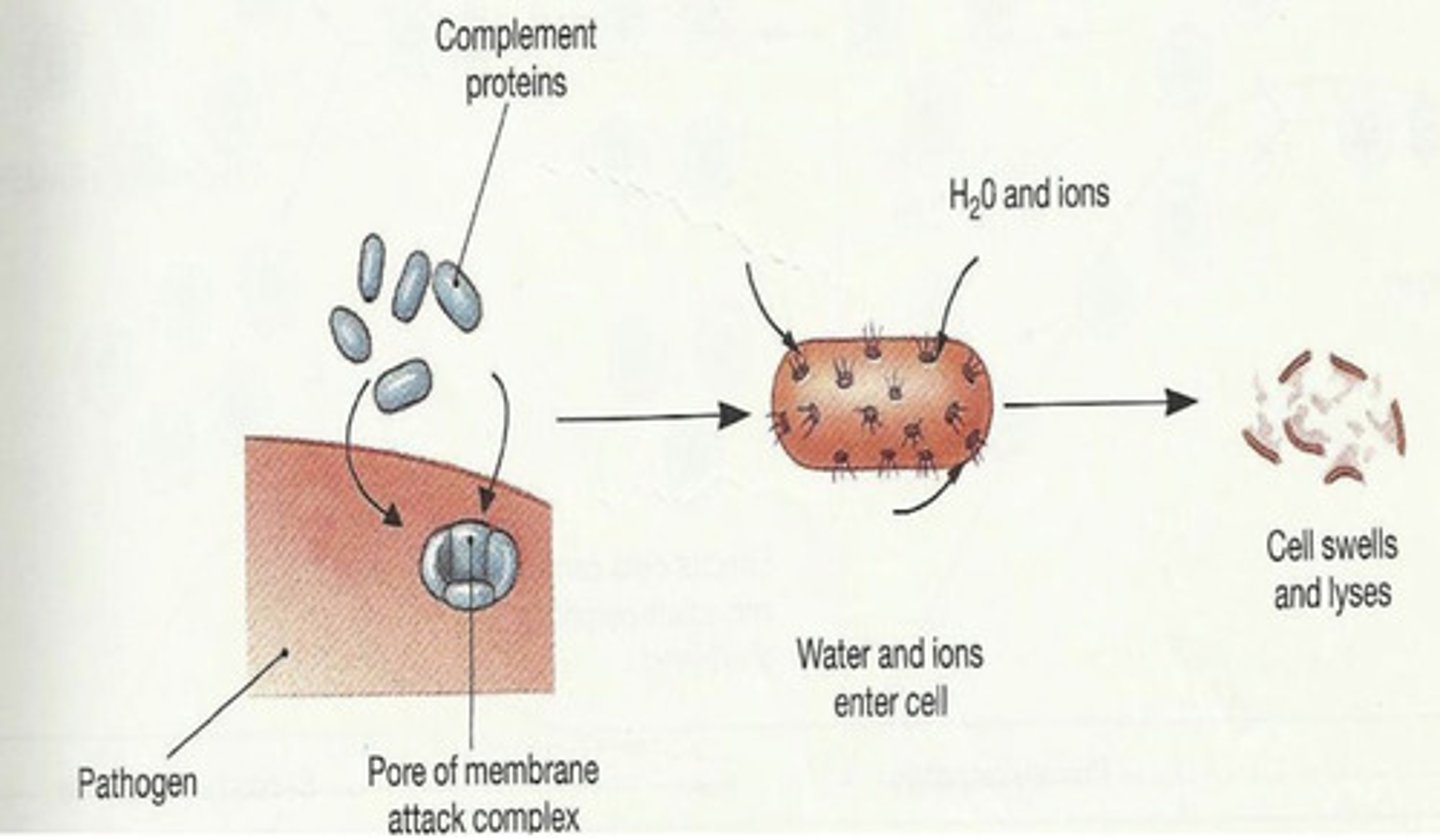
cytolysis- they form a membrane attack complex- a pore in the target cell that causes the breakdown of the cell
what do C5-C9 do in the complement system?
complement system
what system does this represent?
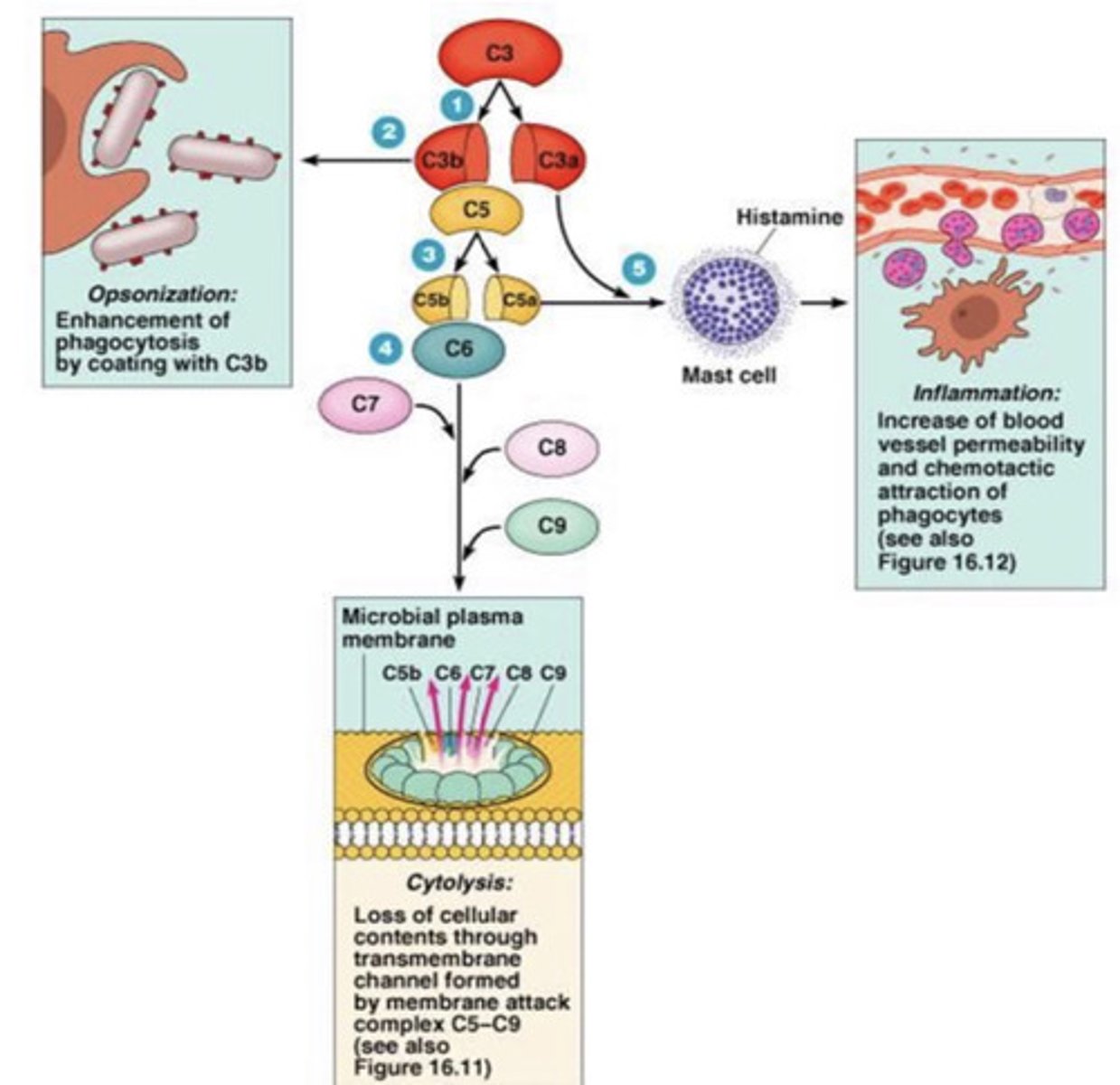
C5-C9
which are the complement proteins here?
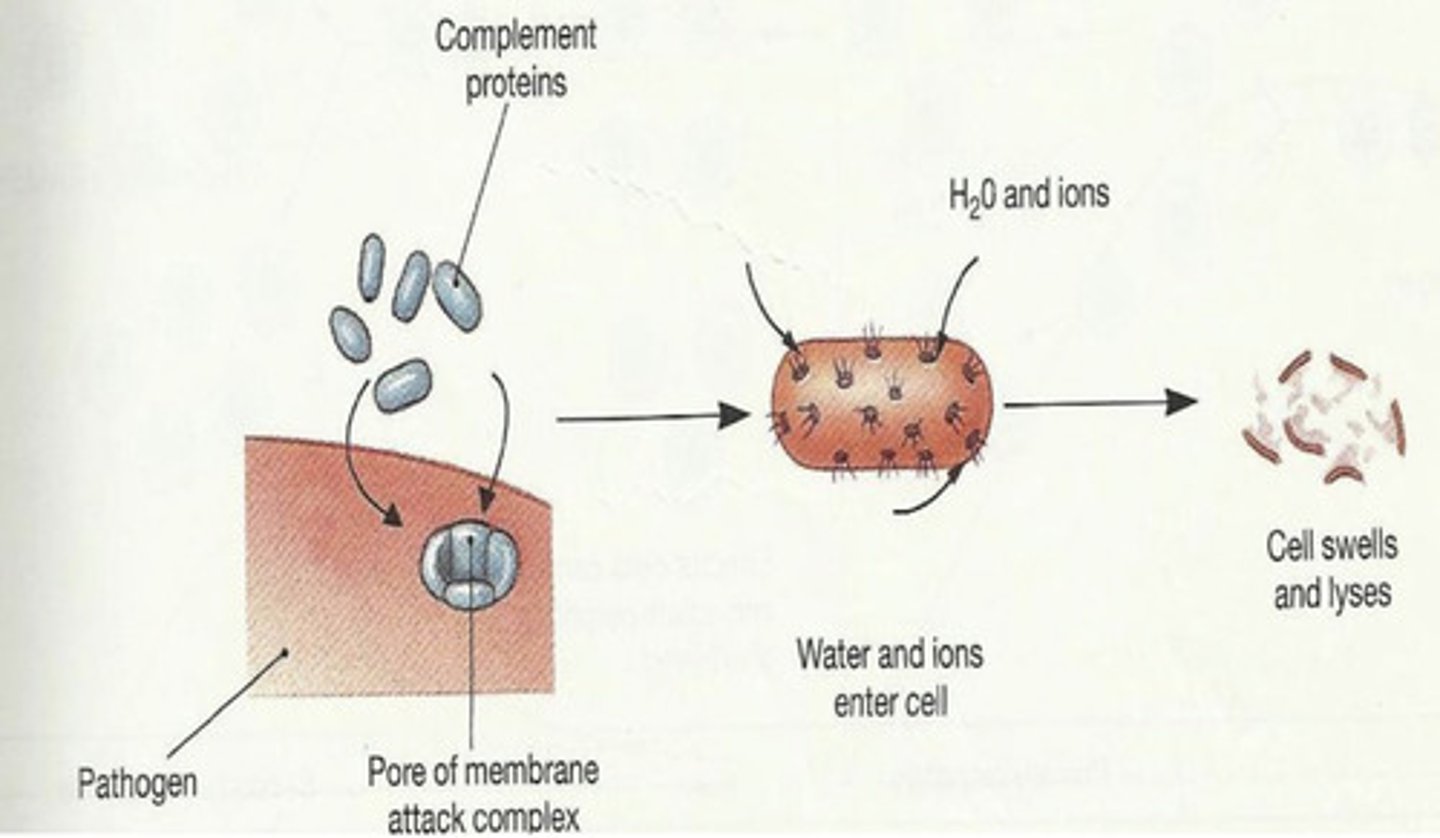
cytolysis
what is this action called?
local arteriolar vasodilation and increased local capillary permeability, which leads to increased blood delivery to the tissue and accumulation of fluid, which increases plasma proteins and phagocytes in the area for a defense response
what is the purpose of mast cells releasing histamine?
-activation of coagulation and complement system
-increased regulation of acid metabolism
-release of proinflammatory factors (C3a, C5a)
-activation of macrophages, which release proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1, IL-6, TNF)
what exactly occurs during innate immunity?
-accumulation of mononuclear cells
-antigen processing and presentation
-immune recognition
-activities of T cells and B cells
what exactly occurs during adaptive immunity?
reparation:
-elimination of insult
-decreased immune functions
-immune memory
-activation of fibroblasts
-repair of blood vessels and skin integrity
-elimination of inflammatory cells
-scar formation
after the adaptive immune response is successful, what must occur?
fever
what is the most common symptom of systemic immunity?