lab med final lecture 17
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
- Helpful to document and quantify the degree of tissue hypoxia
- Shock
- Trauma with internal bleeding
- Post-cardiac arrest
- Respiratory Failure
- Monitoring response to fluids
- Unexplained AMS
- Concern for mesenteric ischemia
when would you do a lactic acid test
Lactate
fairly sensitive indicator of tissue hypoxia
anaerobic metabolism produces lactate
what happens if Oxygen to tissue diminished
- general
- localized
Hypoxia may be _______ (shock, hypotension) or _______ (mesenteric or extremity ischemia)
- Medications (ex: metformin)
- Decreased hepatic clearance (cirrhosis)
- Glycogen Storage Disease
What do you have to Beware of Type (B) Lactic Acidosis
not
Type b lactic acidosis you see Elevated lactate that is _____ caused by hypoxia
- Seen in small bowel bacterial overgrowth, short bowel syndrome, or intestinal bypass
- Malabsorbed carbohydrates are fermented by colonic bacteria -> produce d-lactic acid
what do you have to Beware of D-Lactic Acidosis
Creatinine Kinase
Enzyme found predominantly in the heart muscle, skeletal muscle, and brain
- CK-MB
- CK-BB
- CK-MM
- total CK
what are the test for Ck
CK-MB
specific to myocardial cells (though some exists in skeletal muscle)
CK-BB
brain or lung for CK
CK-MM
specific to skeletal muscle for CK
Total CK
does not differentiate source for CK
Support diagnosis of myocardial muscle injury, neurological or skeletal muscle disease
what are indications to get a CK test
C.The patient needs cardiac cath lab without diuresis
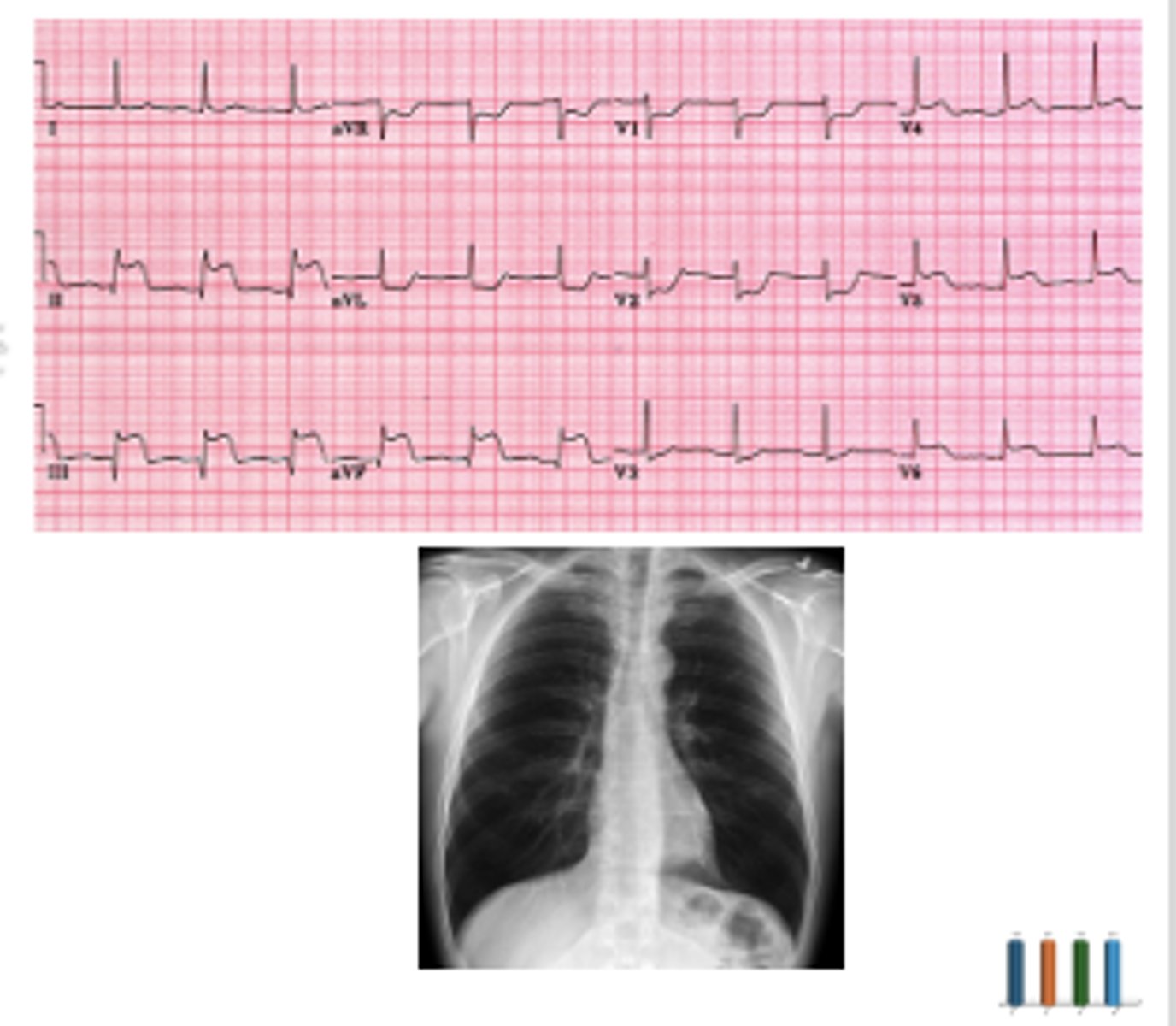
A 73-year-old male with a past medical history of hyperlipidemia and tobacco use disorder presents to the emergency department with chest pain. His symptoms began 4 hours ago when he was returning up his driveway from getting the mail. He reports the pain feels like "crushing" in his chest and radiates into his jaw. You note that the patient is diaphoretic but otherwise exam is normal. High-sensitivity troponin 60 ng/L (normal <10 ng/L). BNP is 300 pg/mL (normal <100 pg/mL). ECG and chest xray as below. Which of the following is true?
A.The patient needs diuresis to offload excess volume from his heart
B.The patient needs cardiac cath lab AND diuresis
C.The patient needs cardiac cath lab without diuresis
D.The patient can be safely discharged home
C.The patient should receive a GI cocktail
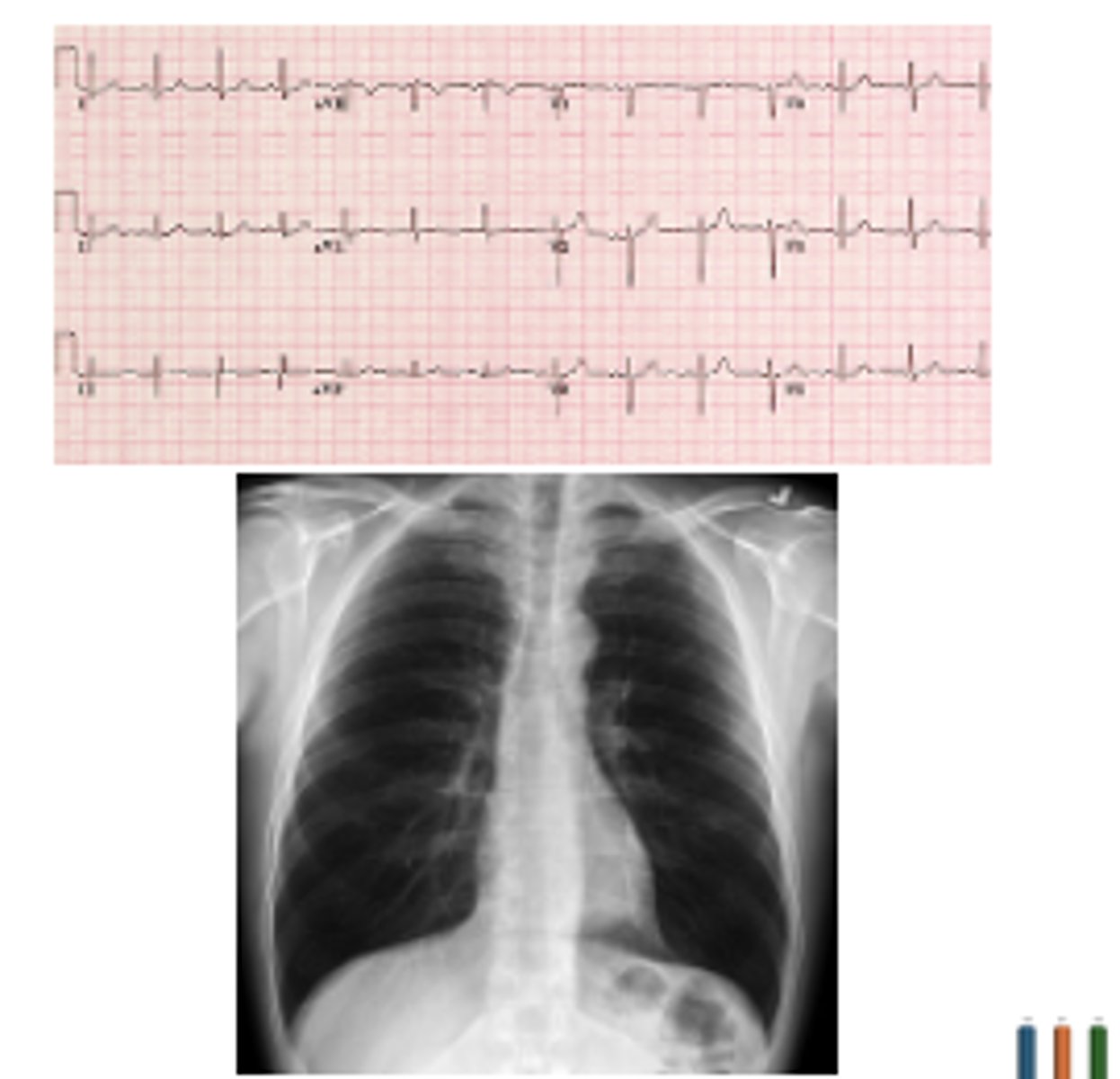
A 93-year-old female with a past medical history of congestive heart failure (CHF) and GERD presents to the emergency department with chest pain. She states her symptoms began yesterday after a large meal. She describes the pain as a burning in her chest. She also notes some regurgitation and excessive belching. Physical exam reveals mild epigastric tenderness but is otherwise unremarkable. She denies shortness of breath, diaphoresis, or exertional chest pain. Vitals= Temp 37C, BP 120/80, HR 78, O2 95% on RA. ECG and chest xray are as below. High sensitivity troponin is normal. BNP is 117 pg/mL (Normal <100 pg/mL). Which of the following is true?
A.The patient should receive diuresis to offload excess volume and relieve stress on her heart
B.The patient should be admitted for an acute MI
C.The patient should receive a GI cocktail
D.The patient is suffering from increased preload on her heart
D.BNP levels will be increased due to increased preload
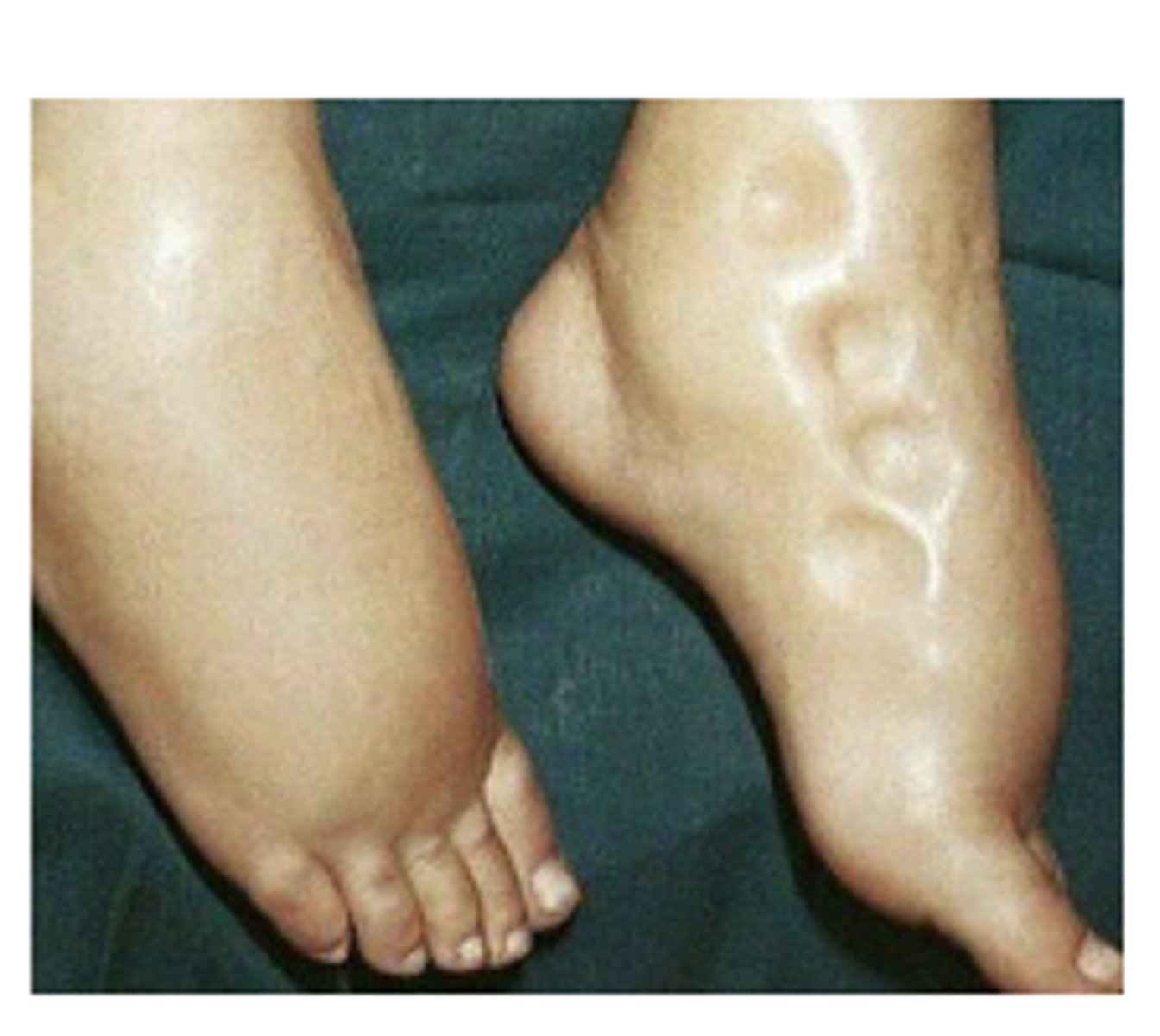
A 73-year-old male with a past medical history of congestive heart failure (CHF) presents to the emergency department with shortness of breath. His symptoms began sometime last week and have been gradually worsening. He reports that he "stopped taking his water pill a while ago" because it was making him "pee too much". On physical exam you note crackles in bilateral lung bases as well as +3 pitting edema in bilateral lower extremities. Vitals= Temp 36.5C, BP 100/70, HR 100, O2 87% on RA. Which of the following is true?
A.BNP levels will be decreased to promote R ventricular stretch
B.BNP levels will be increased due to increased afterload
C.BNP levels will be decreased due to increased third spacing of fluid
D.BNP levels will be increased due to increased preload
C.The patient is having an MI and interventional cardiology should be consulted STAT
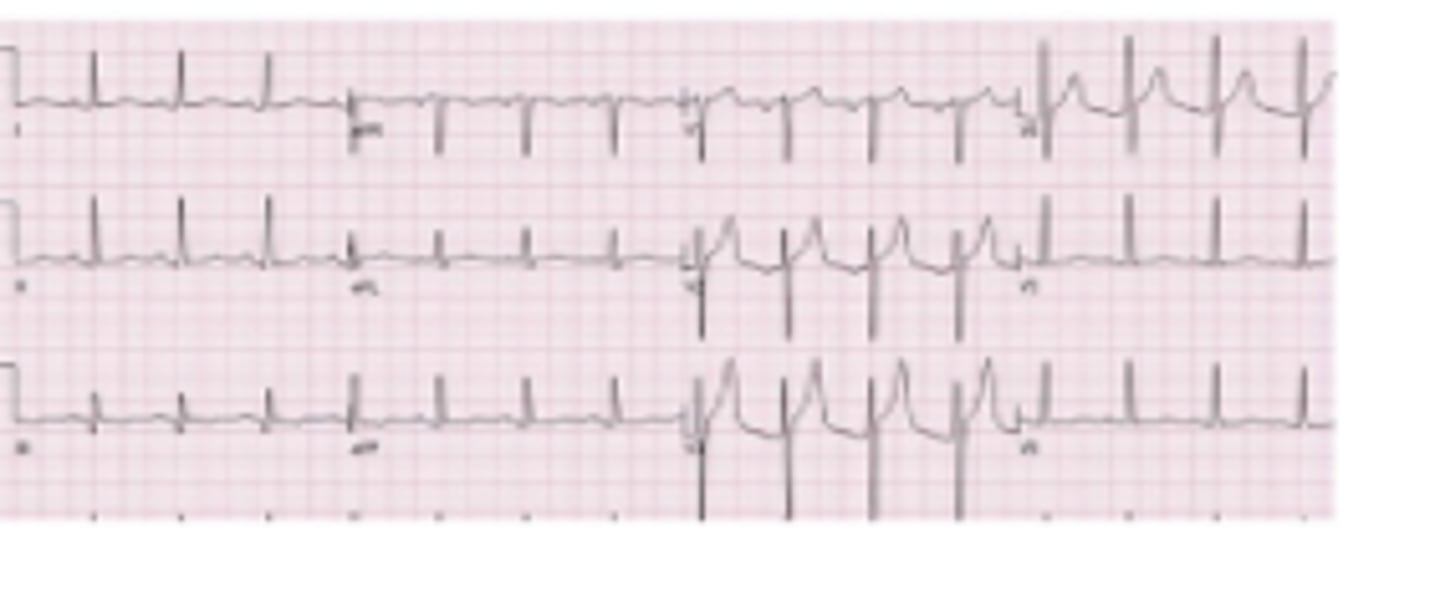
A 62-year-old male with a past medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type II diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency room with crushing substernal chest pain, shortness of breath, and diaphoresis. His symptoms began roughly 1 hour ago. ECG is as below. You are concerned for myocardial infarction and order a high sensitivity troponin. It is normal. Which of the following is true?
A.The patient is not having an MI and should be evaluated for other causes of chest pain
B.The patient is not having an MI and is safe for discharge home
C.The patient is having an MI and interventional cardiology should be consulted STAT
D.The patient may be having an MI; troponin levels should be repeated in 3 hours to check for elevations
skeletal muscle
CK-MM released by __________ when inflamed, injured, or ischemic
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Crush Injury
- Myopathies
- Vigorous exercise
- Repeat IM injections
- Surgery
- Chronic alcoholism
- Compartment syndrome
- Ischemic limb
what are some specific things that will cause the release of CK-MM
true
T/F Normal values of CK-MM vary depending on person's muscle mass
3-6
CK-MB levels rise _____ hours after infarction
12-24 hours
CK- MB peak ____ after a MI
12-48 hours
CK-MB return to normal ________ after infarction
CK-MB
what quantifies the degree of infarction
Cardiac troponin I and T
most sensitive and specific biomarkers of myocardial injury
Cardiac Biomarkers
what is a Preferred serologic tests for evaluation/suspicion of acute MI and are highly sensitive
Cardiac troponin ( hs-cTn)
Preferred Biomarker for Acute Chest Pain
- Enzyme found in almost every cell in the body; helps convert lactate -> pyruvate during anaerobic metabolism
- Cells damaged or destroyed -> LDH release into bloodstream
- LDH is nonspecific- elevated in many different diseases
what os lactate dehydrogenase
- Hemolysis (found with elevated indirect bilirubin, anemia, low haptoglobin)
- Myocardial Infarction (historically, no longer)
- Ischemic Hepatitis
- Muscle Injury/Rhabdomyolysis
- Prognosis in cancer
what is the utility to LDH
- Combined with other labs
- Interpreted in the right clinical context
- Used for trending and prognostic marker in cancer
LDH is non-specific but because clinically valuable when:
b-type Natriuretic peptide
what is Brain Natriuretic peptide also called
BNP
Hormone produced primarily by ventricles of the heart in response to ventricular stretch
- Promotes natriuresis (sodium excretion)
- Causes vasodilation
- Suppresses RAAS
what is the response to BNP
identify and stratify patients with congestive heart failure
what is the primary utility for BNP
- Myocardial Infarction
- Hypertension
- Valvular Heart Disease
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Chronic Kidney Disease
what can BNP also be elevated in
- BNP levels generally higher in women than men
- BNP levels higher in older patients
- Nesiritide (CHF med) increases BNP for several days
what are interfering factors to BNP
CHF diagnosis
the BNP cutoff of 100 pg/mL = 83.4% accuracy for _____________
more severe CHF
Higher BNP =
- Cardiac-specificity
- Highly sensitive (even subclinical MI can elevate troponin); better able to detect smaller infarction
- Long half-life (help detect patients who do not present immediately)
- Ease of use and accessibility
cardiac biomarkers like troponin I and B are