History of the Atomic Model in Chemistry
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Aristotle's theory
4 elements: Earth, Water, Air, Fire

Democritus' theory
Atoms are indivisible (atomos) and are empty space

Dalton's Model
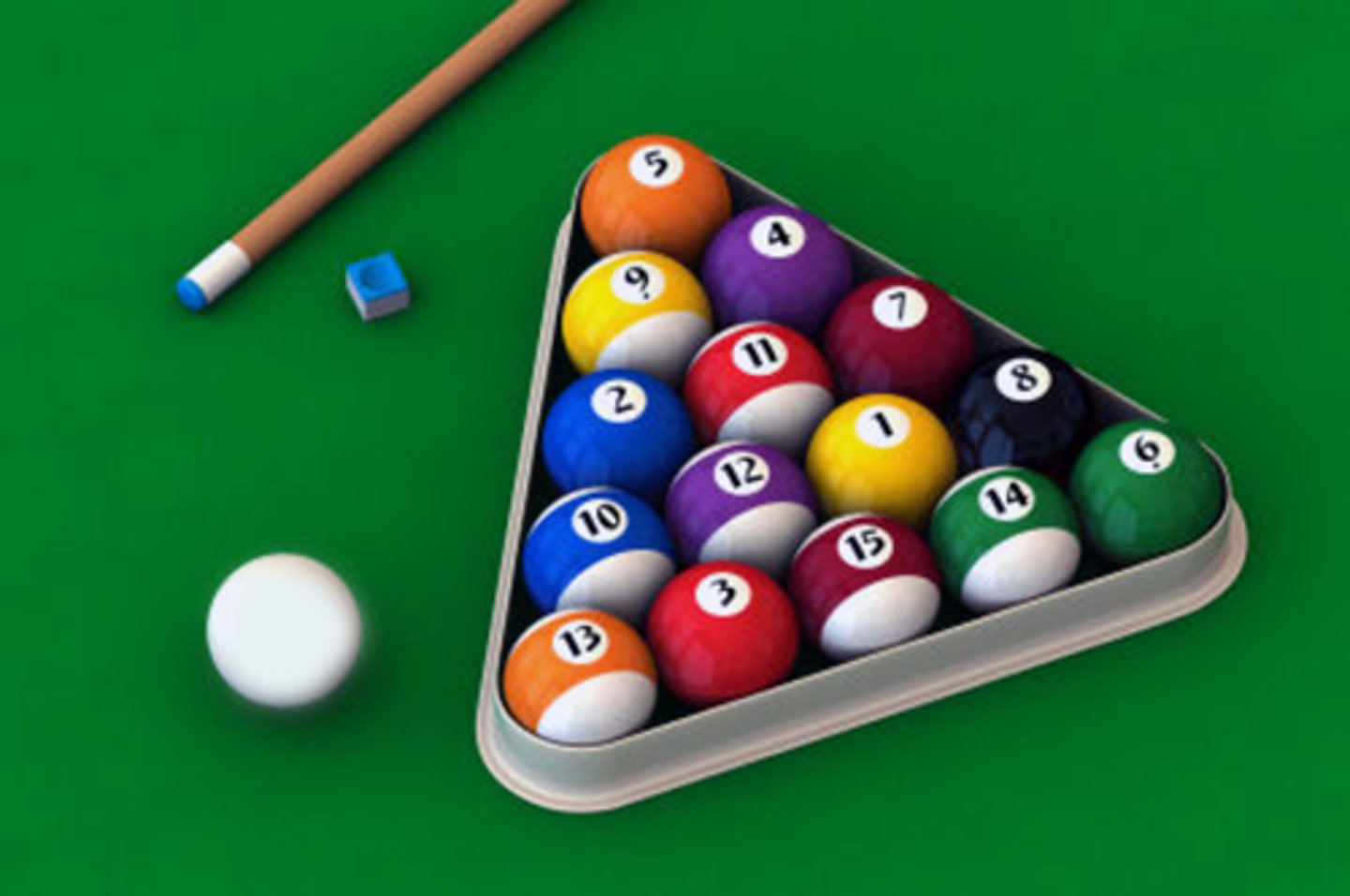
Atoms are solid spheres, much like billiard balls: "Matter is composed of indestructible, indivisible atoms"

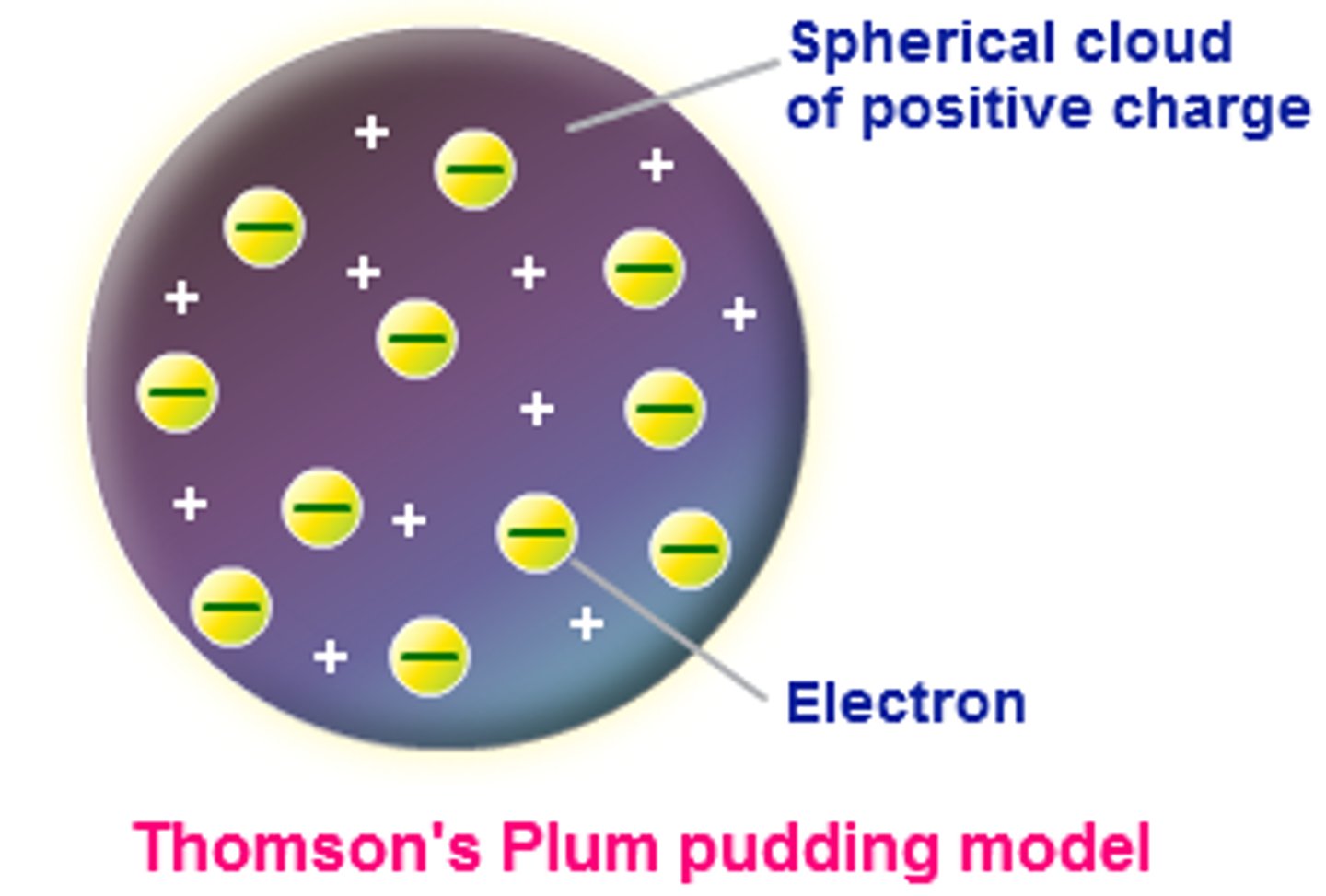
J.J. Thomson's Raisin Bun Model
•Materials, when rubbed, can develop a charge difference.
•This electricity was called "cathode rays"
•The rays have a small mass and are negatively charged.
•These negative subatomic particles (electrons) were a fundamental part of all atoms.
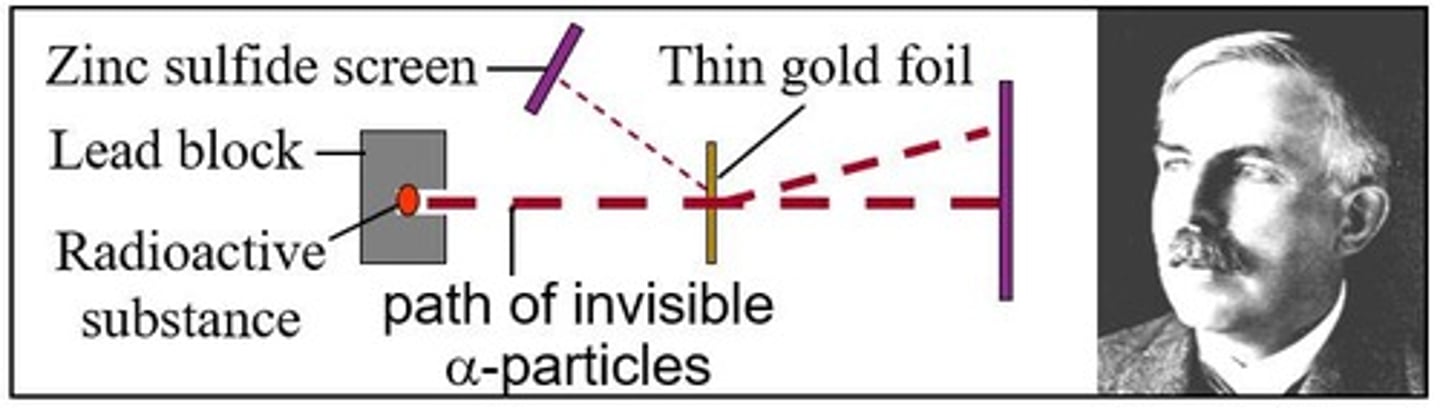
Rutherford's Nuclear Model experiment
•Rutherford shot alpha (α) particles at gold foil.
•Most particles passed through; atoms are mostly empty.
•Some positive α-particles deflected or bounced back!
•Thus, a "nucleus" is positive (protons) & holds most of an atom's mass.
Rutherford says electrons orbit the nucleus like
Planets around the sun

James Chadwick
•Found that the observed masses of the nuclei were not the same as the sum of the masses of the protons; must be another
•He concluded that a nucleus must contain positively charged protons AND uncharged particles called neutrons.

Excited state
Electron state when it absorbs energy and jumps to a higher energy level.
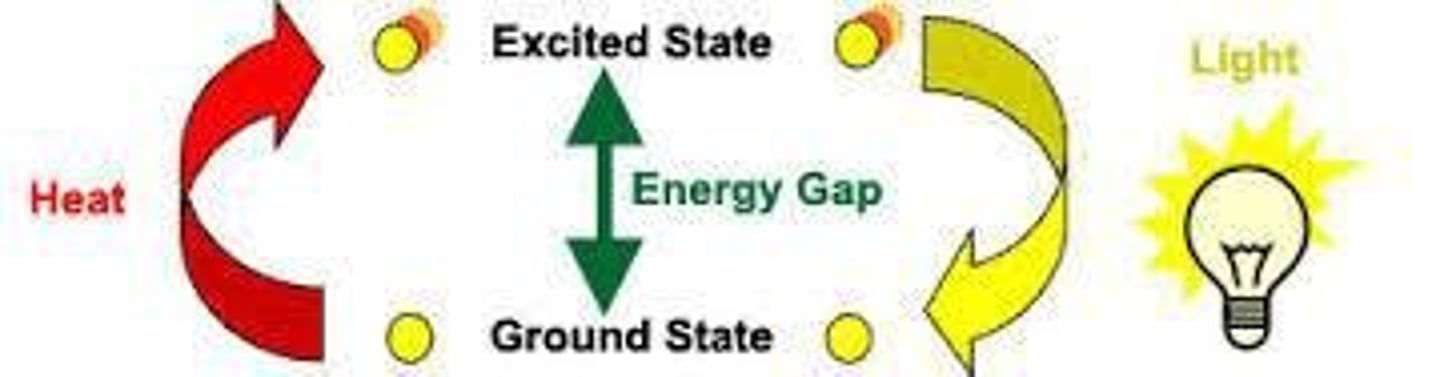
Ground state
•Energy level when an electron is most stable
•Does not release energy
Planck suggested that energy is
Given off in little packets of energy, or quanta (aka photons).

Planck's constant
6.6262 x 10^-34 J-s
Photoelectric Effect - Early 1900s
•When light was shone on a metal, electrons were emitted from that metal.
•Light was known to be a form of energy, capable of knocking loose an electron from a metal
•Therefore, light of any frequency could supply enough energy to eject an electron.
Photons
A particle of EM radiation having no mass and carrying a quantum of energy.
Bohr says electrons orbit the nucleus in
Energy levels
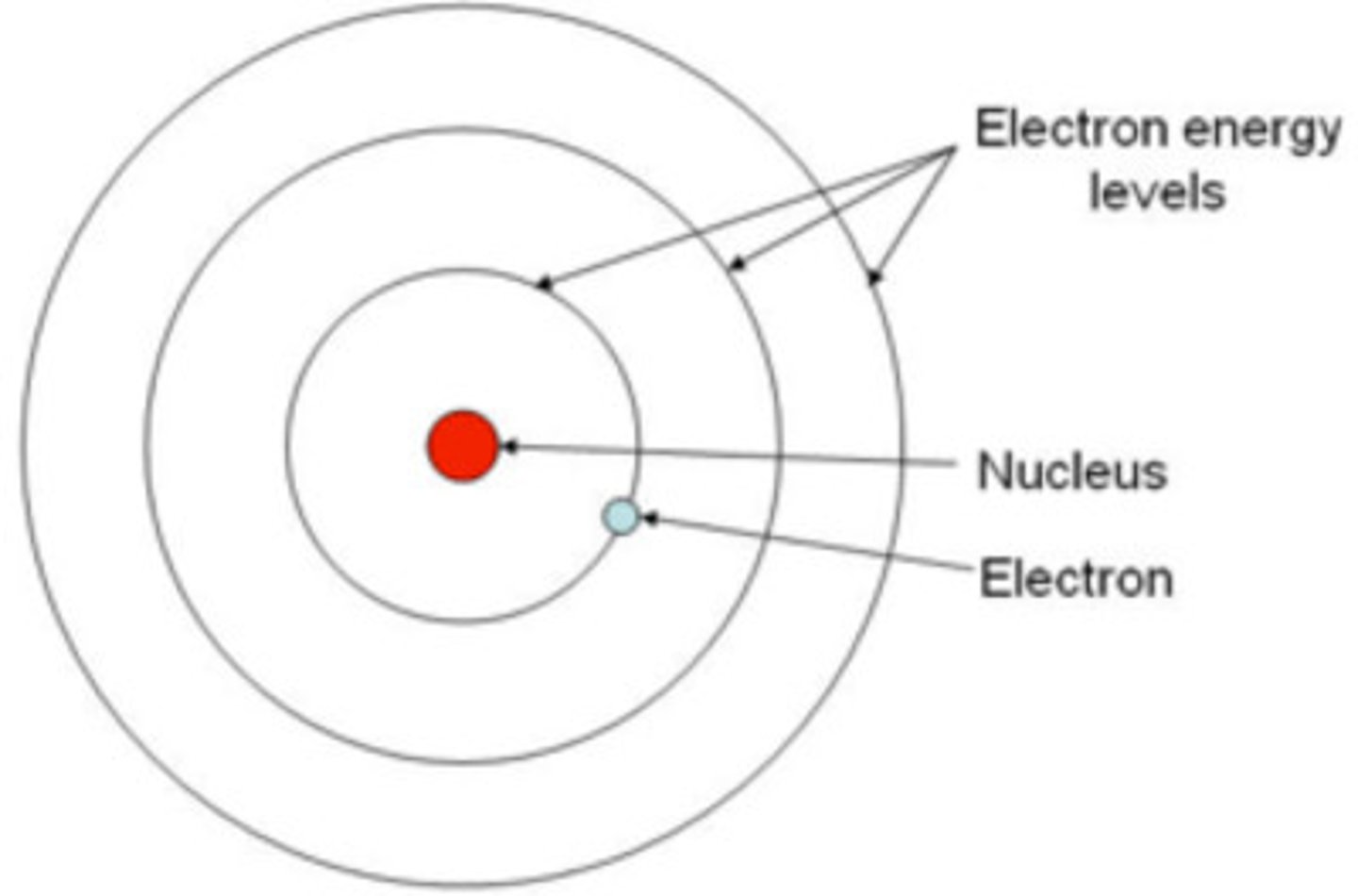
Quantized energy levels
An electron can travel indefinitely within an energy level without losing energy; energy is quantized.
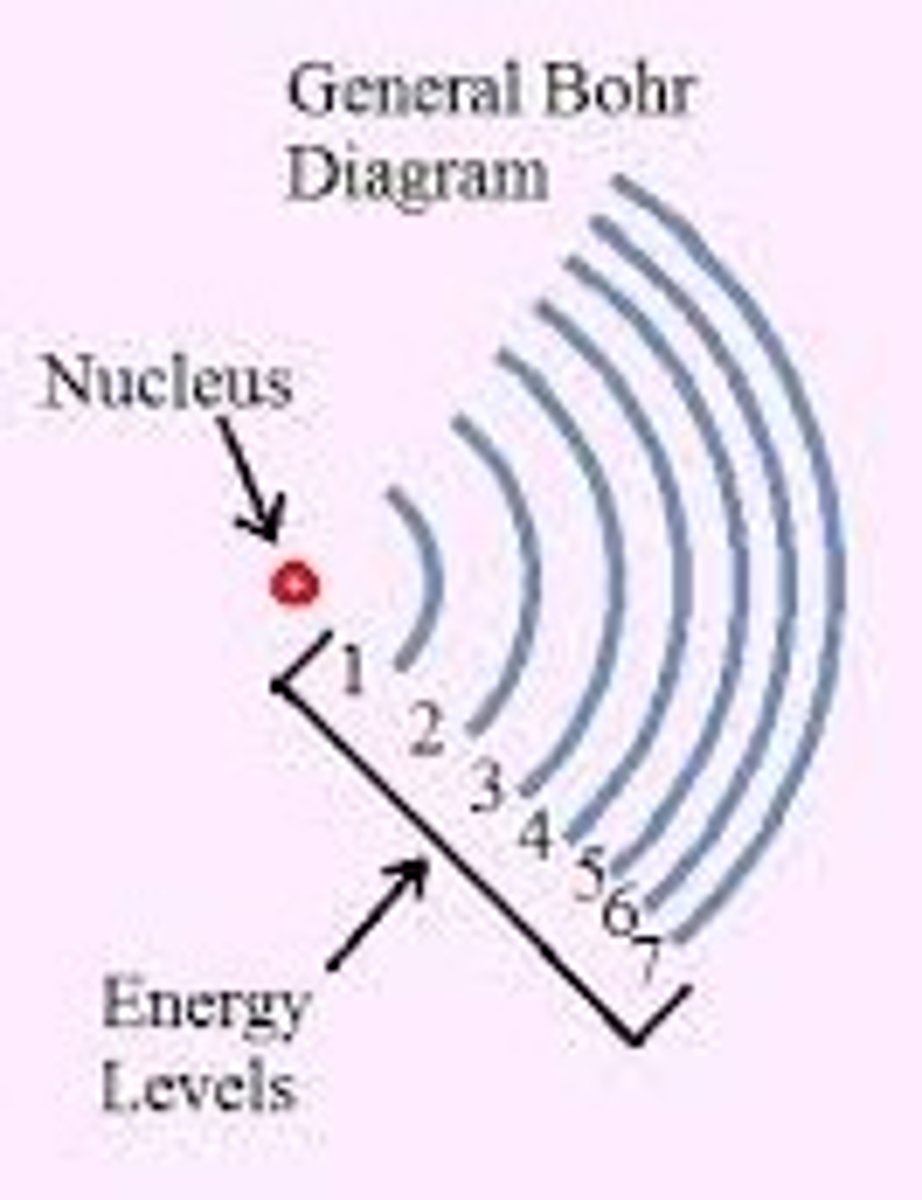
Energy level relation to distance
The farther from the nucleus, the higher the energy level.
Louis de Broglie
Theorized that electrons should move in a wave-like pattern.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
It is impossible to know both the position and momentum of a subatomic particle simultaneously.
Quantum Mechanical Model
The model used today, developed from contributions of Schrodinger and Heisenberg.
Minimum frequency for ejection
An electron must be struck by a single photon with minimum frequency to be ejected.
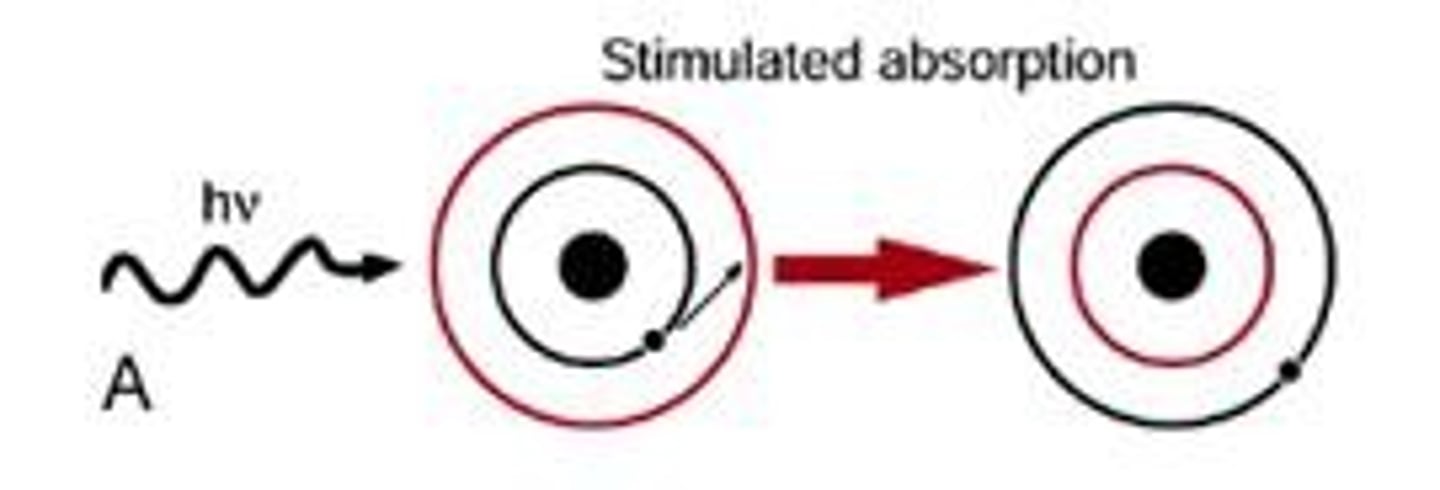
Energy absorption
An electron can move to a higher shell if it absorbs a specific quantity of energy.
Energy loss
An electron can move to a lower shell if it loses energy.
Distinctive glow
Each element has its own frequencies of color, so it emits its own distinctive glow.
Electromagnetic radiation (EMR)
Radiation that has a dual wave-particle nature.
Energy is absorbed by matter only in
Whole numbers of photons.
Schrodinger's contribution
Extended de Broglie's idea that electrons act like waves.
Electron cloud
The region of space where an electron is likely to be found.
Energy levels and electrons
Electrons cannot exist between energy levels.
Aristotle date
350 BC
Democritus date
400 BC
Dalton Billiard Ball Model date
1805

J.J. Thomson's Raisin Bun Model date
1897
Rutherford's Nuclear Model date
1911
James Chadwick date
1932
Photoelectric Effect date
1900s
Bohr's Planetary Model date
1913
Atomic Theories order
1805 John Dalton
1897 Thomson
1911 Rutherford
1913 Bohr
What did Dalton theorize
•All matter is made of atoms.
•Atoms of an element are identical.
•Each element has different atoms.
•Atoms of different elements combine in constant ratios to form compounds.
•Atoms are rearranged in reactions, but are not created nor destroyed.

Robert Millikan experiment
•They used oil drops to determine the charge of an e-
•The fall of the charged oil drops due to gravity could be stopped by adjusting voltage across two charged metal plates
•They calculated the charge from the voltage and the mass of the drop
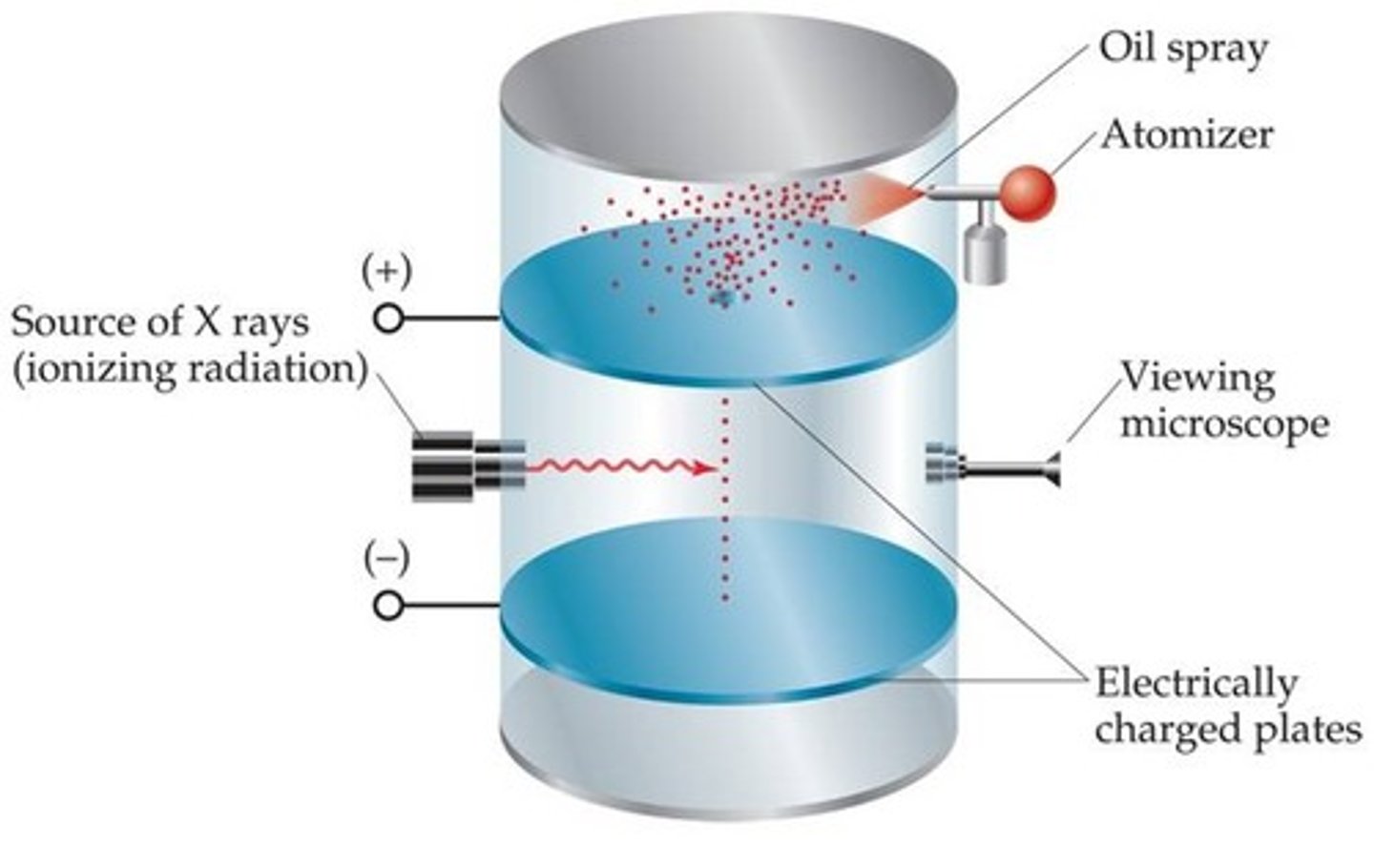
Mass of e-
Using the oil drop experiment and the charge of charge-to-mass ratio from Thomson, Millikan found the mass of e- was 9.11 x 10 -31 kg
Rutherford and his colleagues bombarded a thin foil of gold with a beam of alpha particles and then onto a fluorescent screen.
Small amounts were deflected; 99.9% passed straight through unaffected.
What are limitations to Rutherford's Model?
•Orbiting electrons should emit light, losing energy in the process
•This energy loss should cause the electrons to collapse into the nucleus
•However, matter is very stable, this does not happen
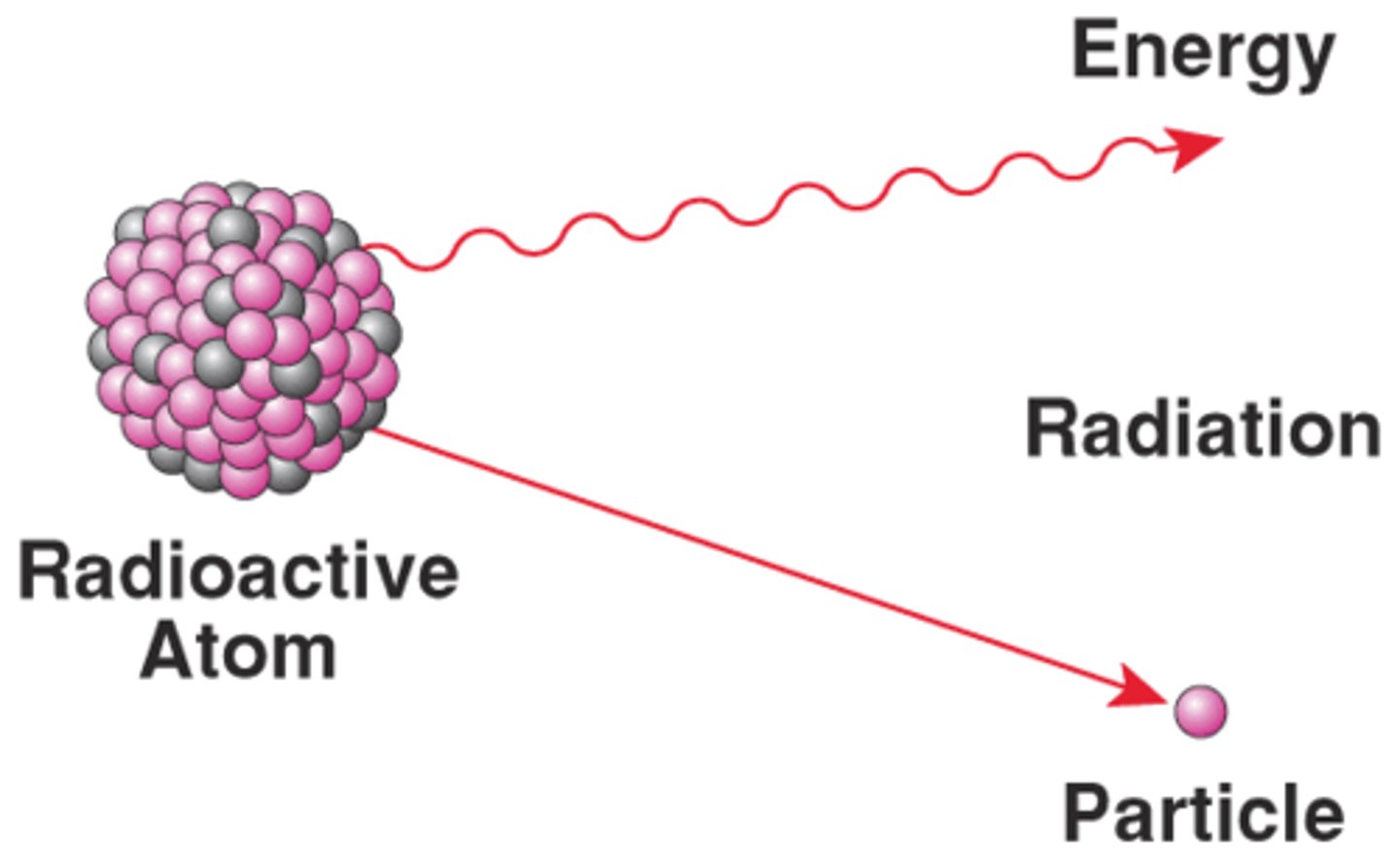
Radioactivity
•Spontaneously emit radiation energy, particles, or waves that travel through space or substances
•Also the decay of the nucleus of an atom
•First proposed by Rutherford - he discovered the alpha particle and named the beta particle and gamma ray
Henri Becquerel - 1896
Discovered a piece of uranium produced an image on a photographic plate- this meant that unstable atoms can give off smaller particles!

Alpha particle
Positively charge. Large in comparison. Essentially a Helium Nucleus (as proved by Rutherford)
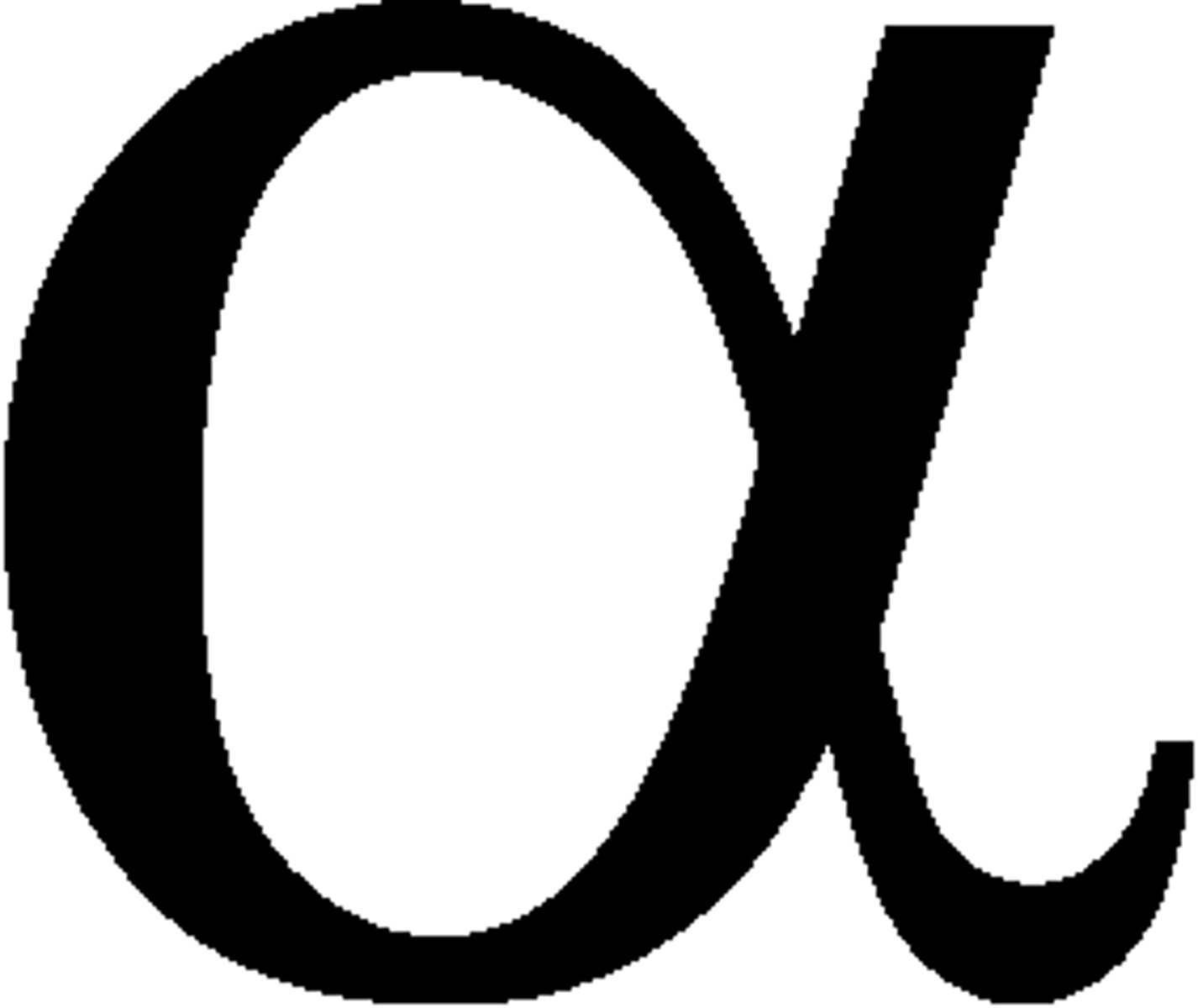
Beta particle
Negatively charged. Light. (later to be shown as electrons)
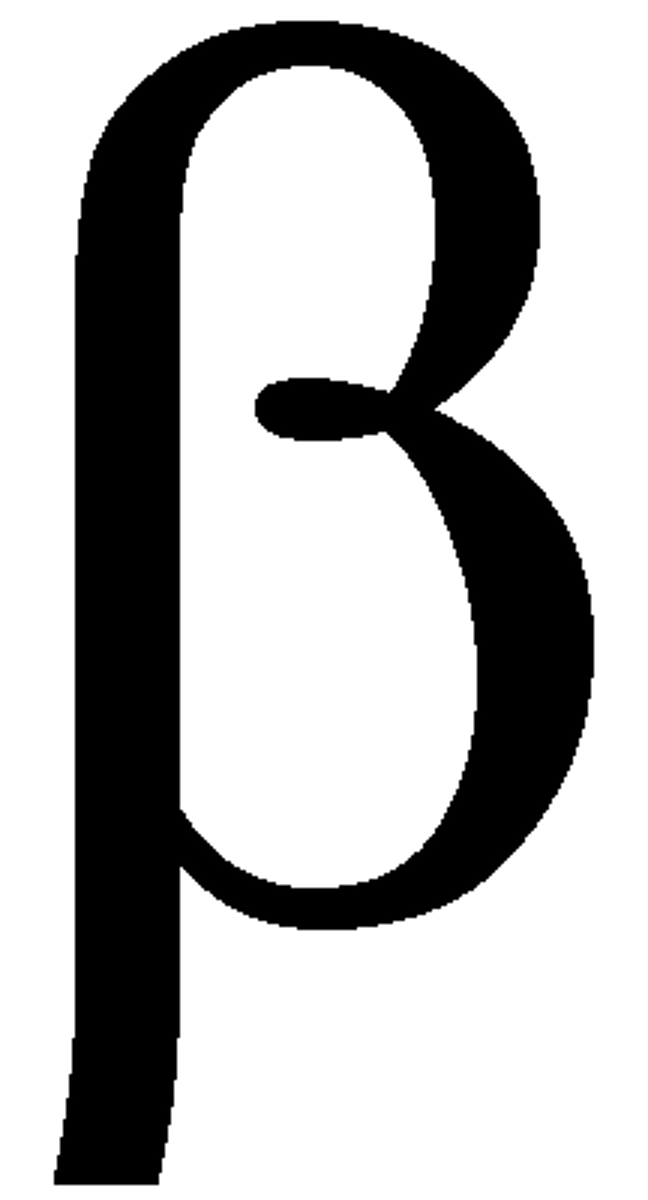
Gamma rays
Neutrally charged. No mass - Energy.

Rutherford's work suggested that
•All of the atom's positive charge, together with most of its mass, is concentrated in the centre.
•Alpha particles which travel close to the nucleus are strongly deflected
•The degree of deflection depends on how close it approaches.
Brief idea of Rutherford's Model
•He envisioned an atom that had a positively charged nucleus in the centre.
•The atom was mostly empty space.
•An he deemed it reasonable that electrons orbit this nucleus like planets orbit the Sun.
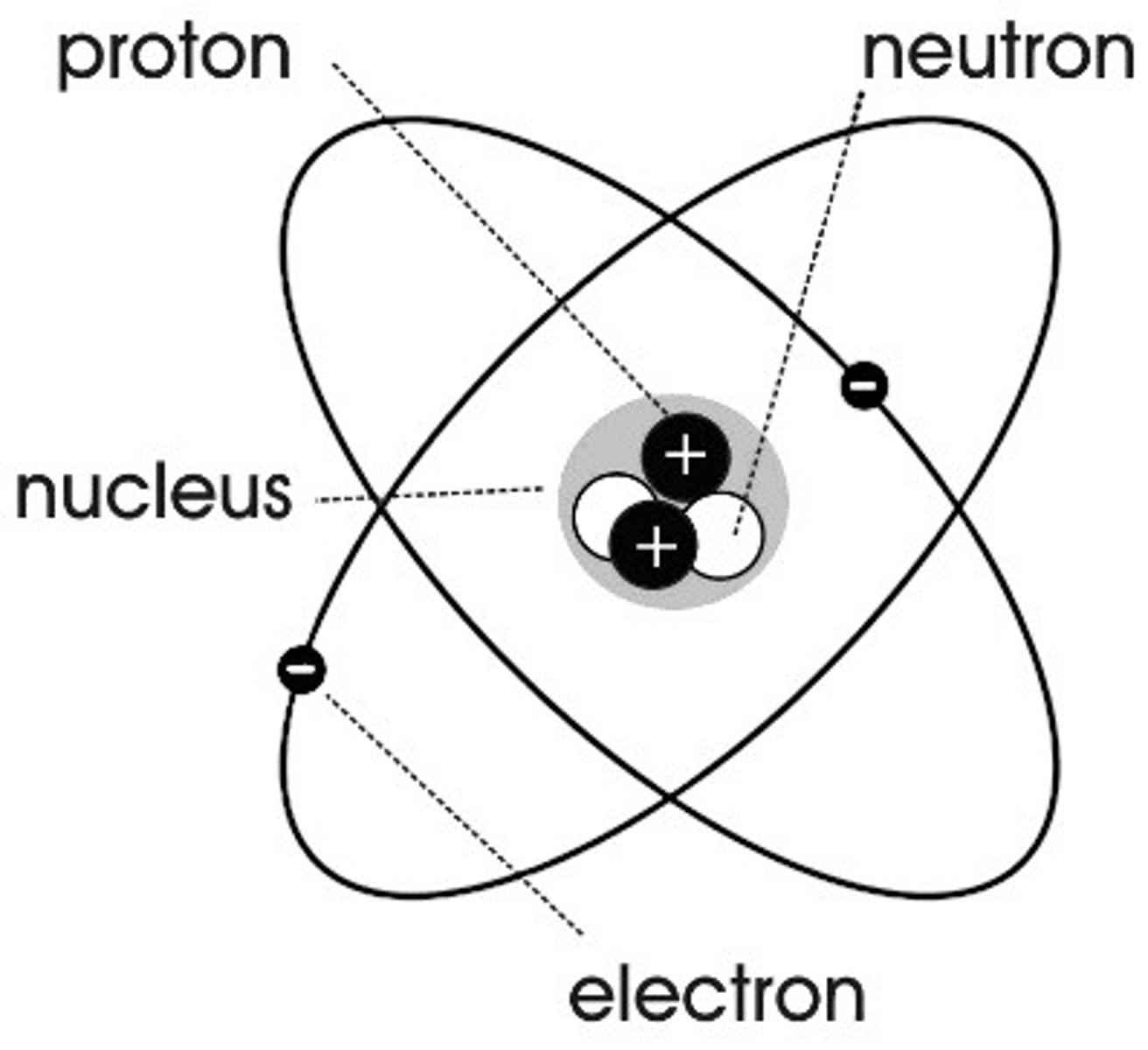
Rutherford's model could not explain
•What held the protons together in the nucleus.
•The origins of emission spectra of gases could not be explained.
•Why the electrons did not lose energy as they orbited
4 characteristics of light
Frequency, wavelength, amplitude, speed
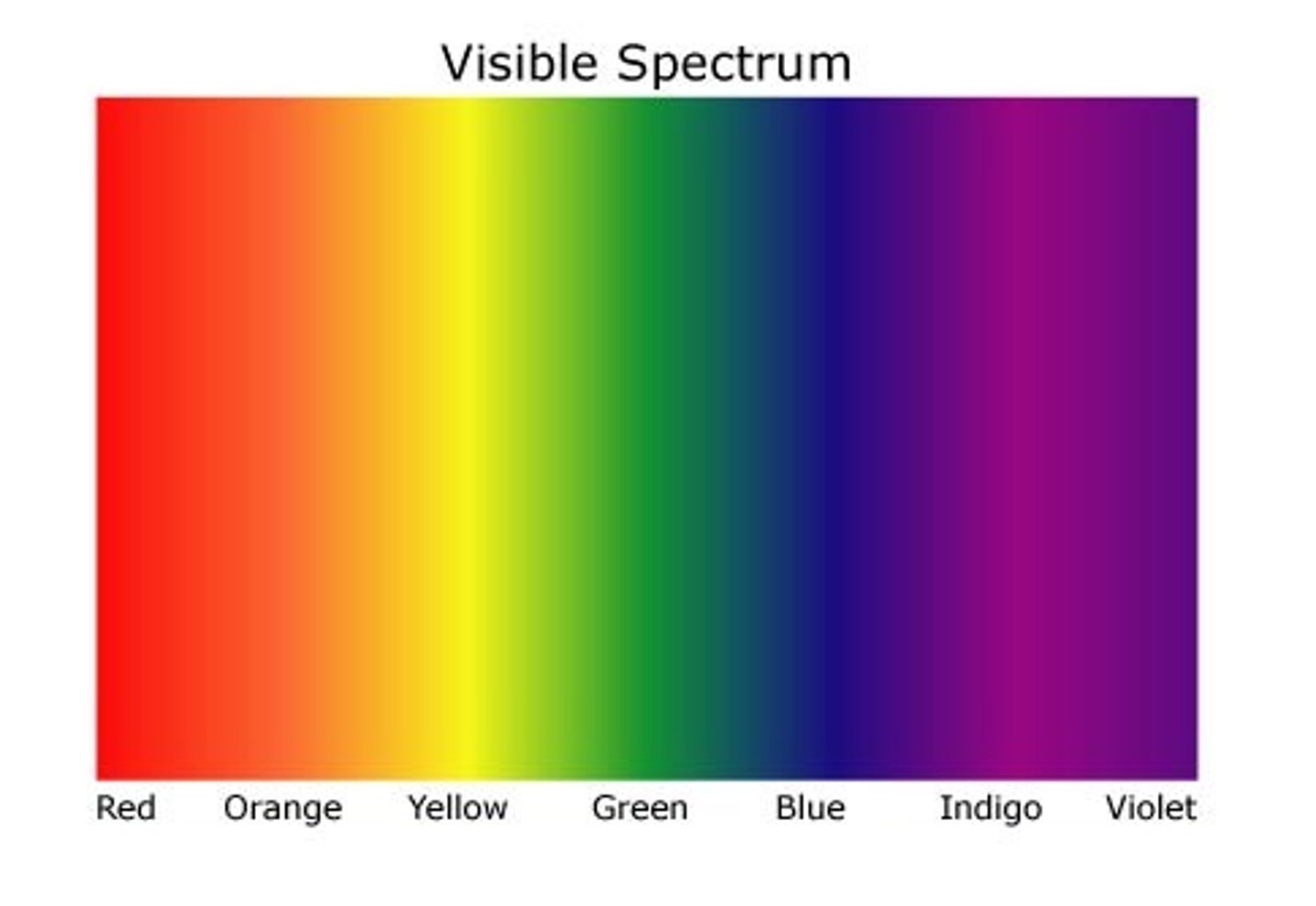
When an electron loses energy
•It drops back to its ground state energy level
•Releases energy in the form of light
•Each element has a specific line spectrum

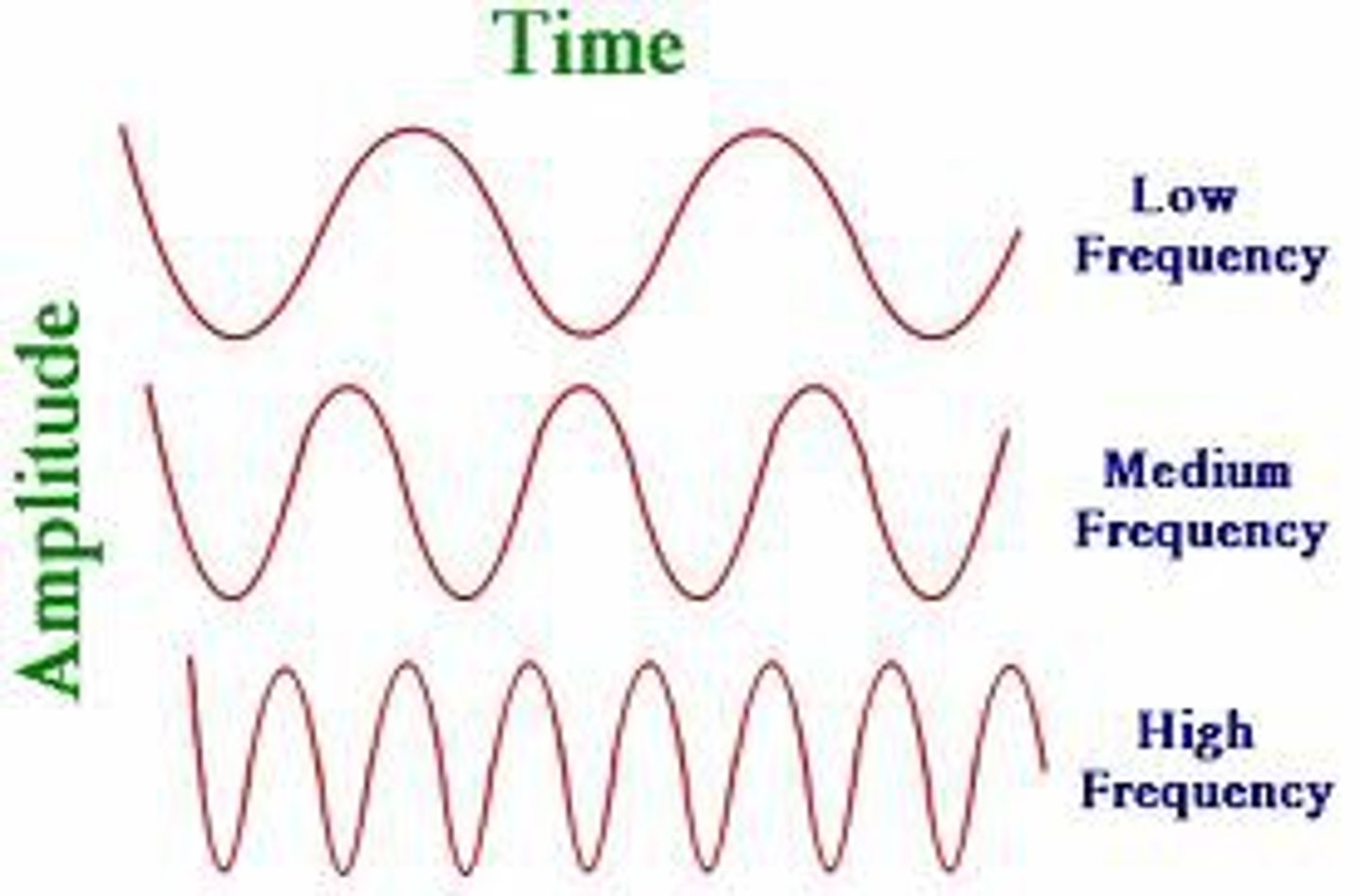
Frequency
•How fast the wave oscillates.
•Measured by the # of times a light wave completes a cycle of up and down motion per sec.
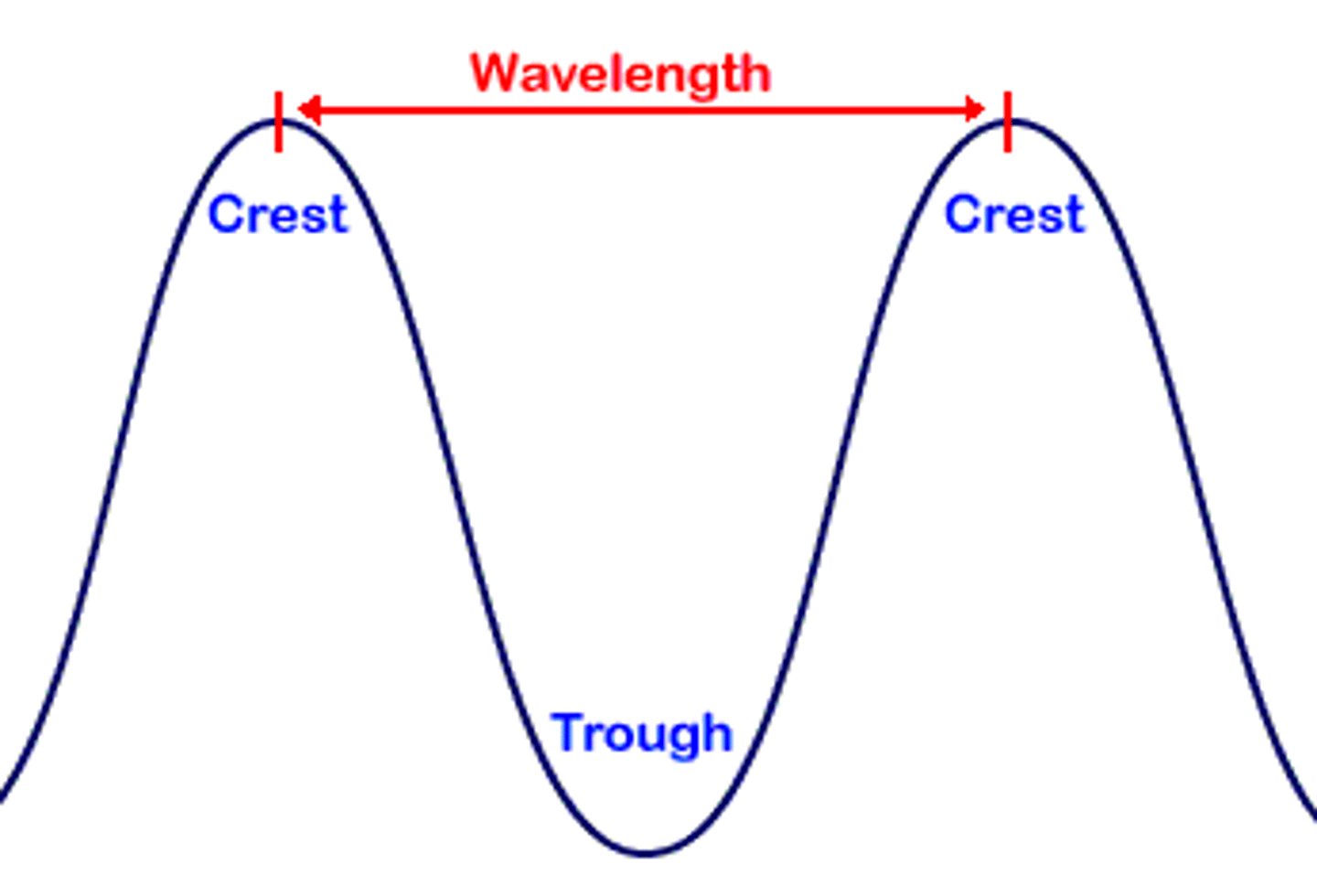
Wavelength
•The distance between successive crests of the wave.
•The distance that the wave travels as it completes one full cycle of up and down motion
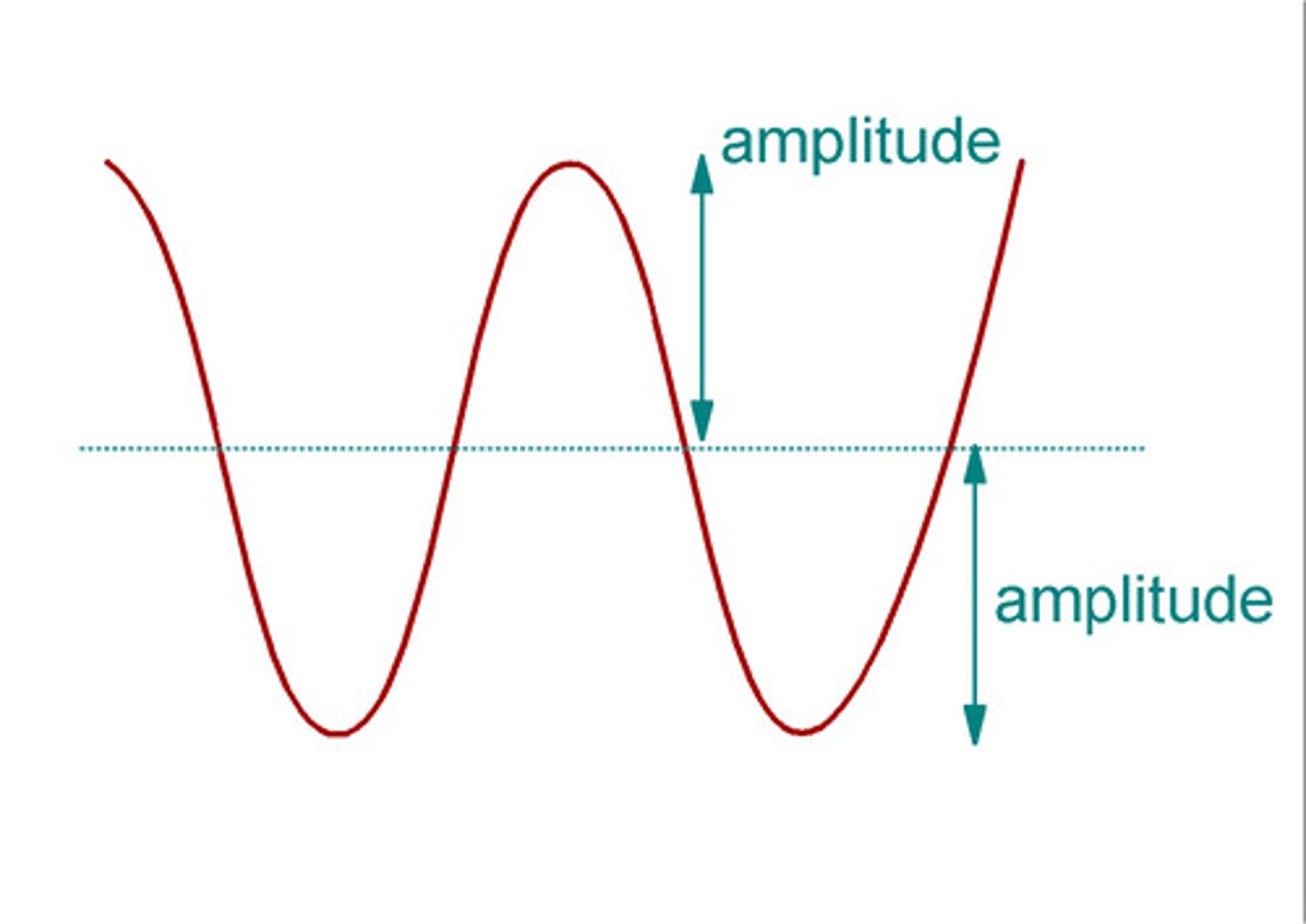
Amplitude
Is the height of the wave measured from the origin to its crest, or peak
Speed
•Regardless of its wavelength, each type of EMR moves through space at a constant speed: 3.00x10^8 m/s
•Nothing can go faster than light (in a vacuum)
Waves transfer ?
Energy from one place to another

The brightness, or intensity of light depends on the __________ of the light wave.
Amplitude
The shorter the wave the
Higher the frequency
The energy in wave form that is absorbed or emitted by atoms, is
Restricted to specific quantities (quantized)
Planck's formula
E=hv where E is energy of photon, v is frequency and h is Planck's constant
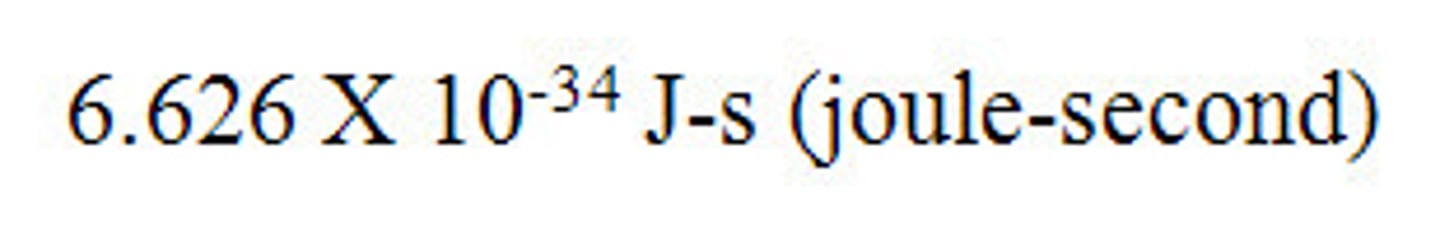
Planck's hypothesis
An object can only gain or lose energy by absorbing or emitting radiant energy in QUANTA
Einstein discovered EM radiation is
Wave and particle
Einstein's work in the photoelectric effect
•Electromagnetic radiation is absorbed by matter only in whole numbers of photons
•In order for an e- to be ejected, the e- must be struck by a single photon with minimum frequency
When all the electrons in an atom are in the lowest possible energy levels
Ground state
Bohr's Planetary Model- What happens when one of an atoms electrons absorb energy in the form of photons
•It becomes excited
•If enough energy is absorbed the electron can make a quantum leap to the next energy level, if there is room
When the electron returns to a lower energy state the energy is released in the form
A photon, which we see as visible light

The energy of the photon determines
Wavelength or color
