Chapter 3 : Movement in and out of Cells
1/36
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
In which states are molecules able to diffuse?
Diffusion occurs in all states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas.
Molecules in liquids and gases are constantly moving and bumping into each other.
This means that they tend to spread out more than solids
In order for the cell to carry out the many chemical reactions it needs to, substances must enter and leave the cell.
In what 3 ways does this happen?
Diffusion
Osmosis
Active Transport
net movement
overall or average movement
particles
Particles are tiny units of matter that make up everything in the universe.
They can be classified as atoms, molecules, ions, or subatomic particles like protons, neutrons, and electrons.
kinetic energy
energy of moving objects
concentration gradient
an imaginary ‘slope’ from a high concentration to a low concentration.
A difference in concentration between 2 areas
diffusion
The net movement of the particles of a gas or a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration as a result of their random movement.
PASSIVE ENERGY PROCESS → no energy needed
osmosis
the net movement of water down a concentration gradient from an area of high concentration of water molecules to an area of low concentration of water molecules (through the cell membrane)
Active Transport
the movement of substances against a concentration gradient and/or across a cell membrane, using energy.
What are the factors affecting the rate of diffusion?
surface area to volume ratio
temperature
concentration gradient
How does temperature affect the movement rate of substance into and out of cells?
As temperature increases the particles have more kinetic energy and are moving around faster
in a given time more diffusion will occur
Eventually increased temperature ruptures the plasma membrane & denatures the enzymes
this kills the cell.
How does concentration gradient affect the movement rate of substance into and out of cells?
The higher the concentration gradient of a substance the faster the rate of diffusion
This is only if the substance can cross the plasma membrane (osmosis/water)
when there is a big difference between the number of particles in one place vs. in another, diffusion will happen much faster than if they are already spread out
How does surface area to volume ratio affect the movement rate of substance into and out of cells?
A higher ratio increases the rate of substance movement in and out of cells due to more surface area for exchange.
a cell with a bigger surface area but similar volume will have a faster rate of diffusion
What happens if the surface area to volume ratio is too small?
1) Living cell can not get nutrients for respiration and growth.
2) Living cells can not remove waste before toxins build up.
3) Cell size is limited by diffusion.
What do Dissolved substances have to pass through to get into or out of a cell?
partially permeable membrane
Diffusion is one of the processes that allows this to happen
All living cells rely on diffusion to live.
What do they use it for?
Getting raw materials for respiration (dissolved substances and gases)
Removing waste products (eg. from respiration)
Plants use of photosynthesis (raw materials in, waste products out)
Diffusion and Breathing
Where does gas exchange take place in the lungs?
CROSS-SECTION THROUGH AN ALVEOLUS
Alveoli are the tiny air sacs at the end of the bronchioles, in which gas exchange occurs.
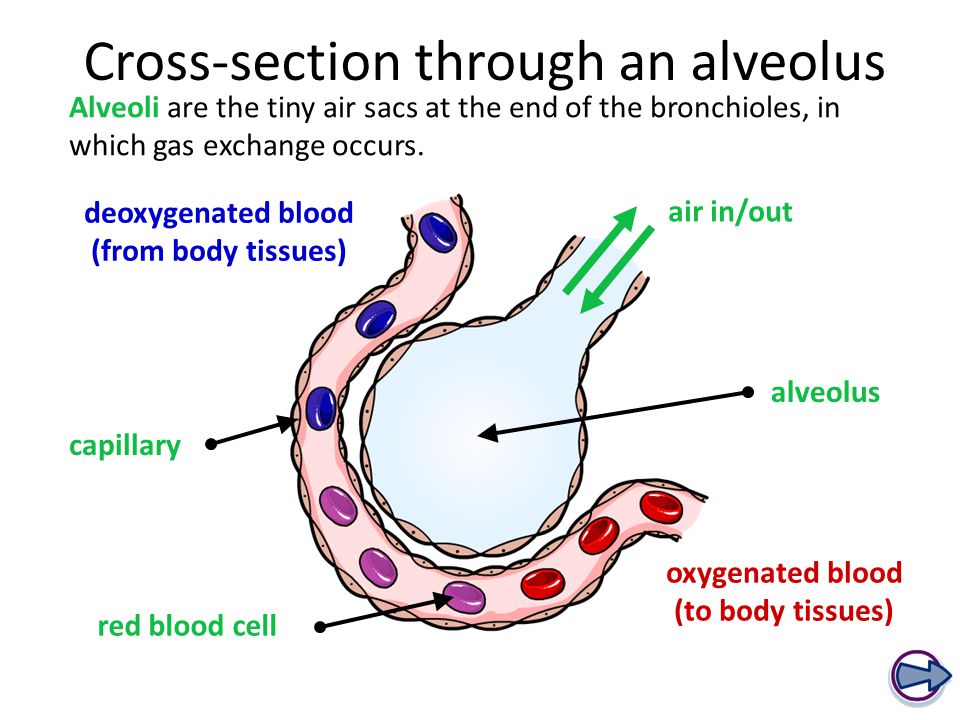
How are alveoli adapted?
They are very thin – only one cell thick.
They are covered by a network of fine capillaries, enabling gases to pass almost directly between the lungs and bloodstream.
They are moist, encouraging gas molecules to easily dissolve.
They have a large combined surface area, allowing large amounts of gases to be exchanged with each breath.
Diffusion and Digestion
Digestion breaks down large food molecules into smaller molecules such as glucose, amino acids and fatty acids that can be easily absorbed.
Small food molecules are usually absorbed in the small intestine, diffusing across the intestine wall and into the bloodstream.
How is the small intestine adapted for diffusion?
Villi INCREASE THE OVERALL SURFACE AREA of the small intestine, thus increasing the volume of substances which can be absorbed by diffusion.
The villi and microvilli result in a LARGE SURFACE AREA, for maximum absorption.
The villi also give a GOOD BLOOD SUPPLY to absorb the nutrients.
Diffusion and Nerve Impulses
A synapse is a junction between two neurons across which electrical signals must pass.
Neurotransmitter molecules diffuse from vesicles towards the neurotransmitter receptors, moving from an area of high concentration to low concentration.
Diffusion and the Placenta
The placenta is an organ that develops in the uterus during pregnancy.
The umbilical cord connects the placenta to the fetus.
It enables nutrients and oxygen to pass from the mother to the fetus by diffusion, and waste substances to diffuse from the fetus back to the mother.
What is the Placenta able to keep out?
What is is it unable to stop?
The placenta can stop certain molecules and bacteria from diffusing through
It is unable to stop many harmful substances such as alcohol, chemicals and some types of virus from diffusing through, reaching the fetus.
Photosynthesis and diffusion
carbon dioxide + water → oxygen + glucose
Carbon dioxide diffuses in through the stomata
Oxygen and water diffuse out of the stomata
During photosynthesis, the level of CO2 is low inside the leaf
This creates a big concentration gradient so CO2 diffuses into the cell
Defining active transport
Sometimes substances move into cells from low to high concentration. This is called active transport.
Active transport needs energy to make it happen.
How do molecules move along the concentration gradient during active transport?
Molecules move against the concentration gradient with the help of energy from ATP, using carrier proteins in the cell membrane.
Substances can move passively in and out of cells by diffusion until the concentration on both sides of the cell membrane reaches
an equilibrium
Why is it important for plants to use active transport?
Minerals enter a root cell by active transport.
The plant uses energy to move minerals up the concentration gradient from the soil into its root cells.
Active transport in humans
During digestion, the villi in the small intestine absorbs the soluble nutrients. Over time, the concentration of nutrients in the villi reaches an equilibrium with the concentration in the gut.
Active transport is used to continue the transport of the small amounts of remaining nutrients against the concentration gradient.
Dilute solutions
high concentration of water molecules.
concentrated solutions
low concentration of water molecules.
During osmosis, water molecules diffuse from where to where?
During osmosis, water molecules diffuse from pure water or dilute solution to more concentrated solutions.
hypotonic solution
a lower solute concentration compared to the cell (turgid)
This causes water to move into the cell, potentially leading to cell swelling or bursting.
isotonic solution
A solution with the same concentration of solutes as the cell. (flaccid)
It maintains cell shape and size by preventing water movement in or out.
hypertonic solutions
a higher solute concentration compared to the cell. (plasmolyzed)
This causes water to move out of the cell, leading to cell shrinkage or crenation.
In order to remain healthy, what do animal cells need to maintain?
Animal cells need to maintain an isotonic water balance.
This means that the water concentration both inside and outside the cell are equal.