C3 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter (Combined)
1/41
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Ion
An atom or group of atoms that has gained or lost one or more electrons
+1
The ion group 1 elements form
+2
The ion group 2 elements form
-2
The ion group 6 elements form
-1
The ion group 7 elements form
Ionic Bonding
Chemical bonding that results from the electrical attraction between cations and anions.
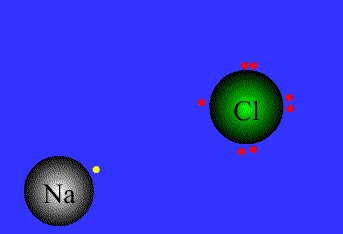
Cation
A positively charged ion.
Anion
A negatively charged ion.
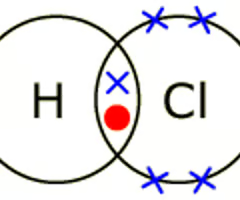
Dot and Cross
The diagram used to show bondin
Ionic Bonding
Happens between metals and non-metals.
Giant Ionic Lattice
The structure formed by ionic compounds.
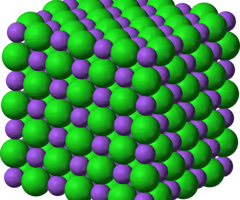
Ionic Compound Properties
-High Melting / Boiling points
-When solid it can't conduct electricity
-Dissolve easily in water
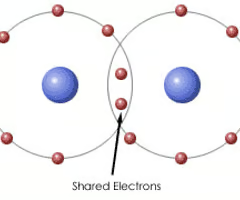
Covalent Bonding
A bond formed when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons
Non-metals
The element type that bonds covalently
H₂
H-H
Cl₂
Cl-Cl
O₂
O=O
N₂
N≡N
H₂O
H-O-H
Polymers
Long chains of repeating units. Lots of small 'units' link together to form a long molecule.
Giant Covalent
A type of bond where lots of atoms are bonded by shared electrons. High melting/boiling points.
Electricity
Not usualy conducted by giant covalents
Diamond
A hard allotrope of carbon.
Graphite
A allotrope of carbon that is made of layered sheets of hexagons.
Metallic Bonding
The chemical bonding that results from the attraction between metal atoms and the surrounding sea of electrons.
Electricity and Heat
What metals conduct
Alloys
mixtures composed of two or more elements
Solid
This state of matter has strong forces holding particles in place.
Solid
This state of matter has vibrating particles.
Liquid
This state of matter has weak forces holding particles in a set shape
Liquid
This state of matter has a definite volume but not a definite shape
Gas
This state of matter has very weak forces holding particles together.
Gas
This state of matter has an indefinite shape and volume.
Gas
In this state of matter particles move constantly with random motion.
(s)
Solid
(l)
Liquid
(g)
Gas
(aq)
Aqueous (dissolved in water)
Melting
Solid to liquid
Boiling
Liquid to gas
Condensing
Gas to liquid
Freezing
Liquid to solid