chemistry c18 and c22 test - rates and energy
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
rate of reaction
change in concentration of a product or reactant per unit time
in a zero order reaction…
concentration does not influence rate as anything raised to the power of 0 is 1
in a first order reaction…
if the concentration is doubled, the rate increases by a factor of 2
in a second order reaction…
if the concentration is doubled, the rate increases by a factor of 2²
2 methods of continuous monitoring of rate
gas collection and mass loss
concentration-time graph of a zero order reaction
straight line with neg gradient, k is equal to gradient, rate does not change through course of reaction
concentration-time graph of a first order reaction
downwards curve with decreasing gradient over time and so decreasing rate, half life of concentration is constant
concentration-time graph of a second order reaction
downward curve steeper at start and tailing off slower
half life (only from concentration-time graph)
time taken for the concentration of a reactant to decrease to half its original value
initial rate
instantaneous rate at start of a reaction when t=0
clock reaction
way of obtaining initial rate by taking single measurement, time from start of experiment measured until a visual change occurs, initial rate is proportional to 1/t, clock reaction repeated several times with diff concs
rate determining step
slowest part of reaction sequence
importance of rate determining step
rate equation only includes species in rate determining step, orders in rate equation match number of species in rate determining step
arrhenius equation
k = e^(-Ea/RT)
logarithmic form of arrhenius equation
ln k = -Ea/R 1/T + ln A
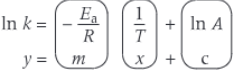
lattice enthalpy
measure of strength of forces between the ions in an ionic solid, involves ionic bond formation from separate gaseous ions, exothermic so enthalpy change always negative
born haber cycle
r1: form gaseous neutral atoms, form ions from gaseous ions, combine ions to form ionic solid, r2: convert elements in standard state directly to ionic lattice
electron affinity
enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms acquires one mole of electrons to form one mole of gaseous negative ions
why are second electron affinities endothermic
second electron is being gained by a neg ion so like charges repel, energy must be put in to overcome this force
what happens when an ionic solid dissolves
ions are hydrated (attracted by polar bonds in water molecule) or solvated (attraction to polar solvent molecules)
standard enthalpy change of solution
enthalpy change when 1 mol of ionic substance dissolves in water to give a solution of infinite dilution
infinite dilution
water is in excess so adding more doesn’t result in anymore heat being absorbed or evolved
what does enthalpy change of solution depend on
lattice enthalpy of solid/dissociation, hydration enthalpy of ions
enthalpy of hydration
enthalpy change when one mol of gaseous ions dissolves in water to form one mol of aqueous ions to form a solution of infinite dilution
entropy
measure of the disorder of a system, a system becomes energetically more stable when it becomesmore disordered, spontaneous reactions go in the direction of increasing entropy
entropy in exothermic reactions
more energy in surroundings, more ways of arranging energy, entropy increases
entropy in endothermic reactions
less energy in surroundings, fewer ways of arranging energy, entropy decreases
delta s of surroundings
-delta H/T
gibbs free energy equation
delta G = delta H -TdeltaS system
how to know if reaction is feasible
if G less than or equal to 0
limitations of predictions made for feasability
gibbs onlt provides info about energetic feasability, activation barrier may be too high for reaction