Skeletal System Pathology
1/160
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
161 Terms
Total Bones in Body
206
Total Axial Bones
80
Total Appendicular Bones
126
Compact Bone
cortical bone, dense outer layer of bone tissue, provides strength and support to skeleton
Cancellous Bone
spongy/trabecular bone; bone tissue that is porous and honeycomb-like structure; located at ends of long bones, vertebrae, ribs, skull, and pelvic bones; house bone marrow
Trabeculae
thin bony rods and plates that form spongy porous structure within cancellous(spongy) bone; house red bone marrow
Osteoblasts
cells that form new bones and grow/heal existing bones; turn proteins into new tissue
Osteoclasts
bone-resorbing cells that break down old or damaged bone
Primary Ossification
occur before birth in long shaft of bones(diaphysis)
Secondary Ossification
occur after birth in ends of long bones(epiphysis)
Synarthroses
immovable joint; examples include radioulnar, tibiofibular, skull sutures
Amphiarthroses
slightly movable, joints between vertebral bodies
Diarthroses(Synovial)
freely movable; shoulder and hip jts
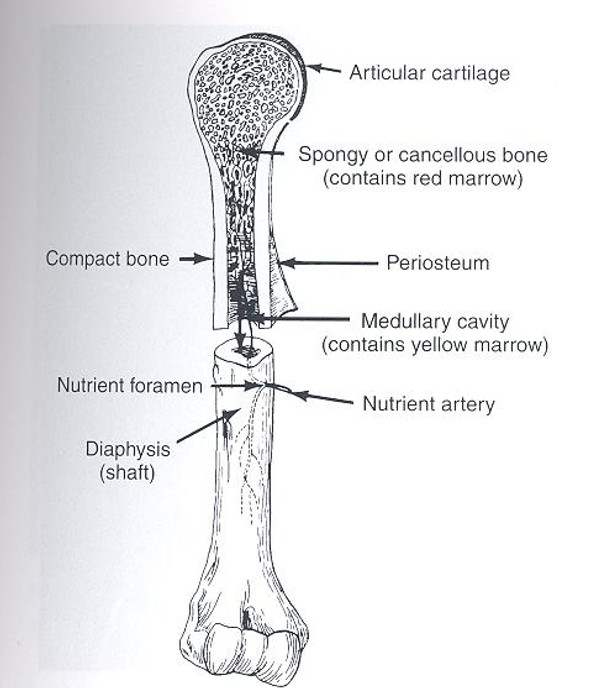
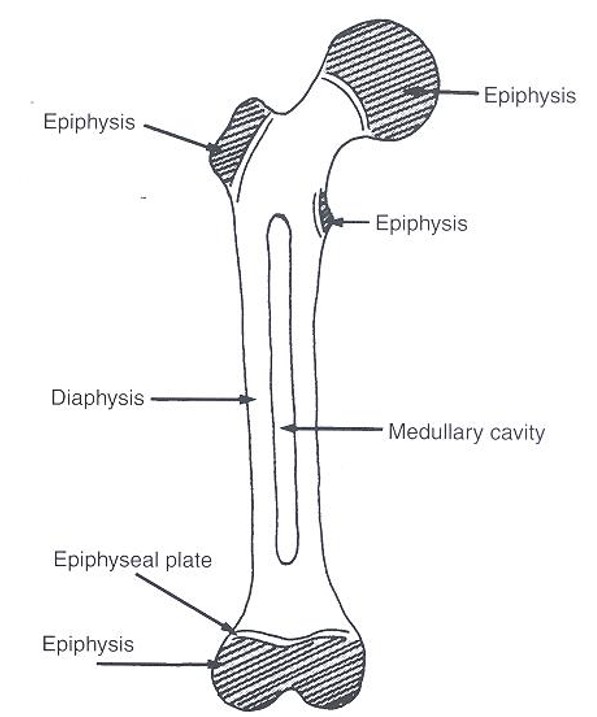
Diaphysis
long cylindrical shaft of long bone; composed of cortical bone and medullary cavity
Epiphysis
expanded end of long bones; made of cancellous bone and covered by thin layer of compact bone
Metaphysis
wider part of long pone located between diaphysis(shaft) and epiphysis(end)
Bone Materials
Long Bone Parts
Skeletal MRI
best for soft tissues/jts(knee and shoulder)/bone marrow; modality of choice for detection and staging soft tissue tumors in extremities
Skeletal CT
1.show cortical bone best
2.helical/spiral used to explore bone tumors due to its high contrast
3.quantitative evaluate bone mass loss especially within vertebral bodies of spine
Nuclear Medicine
modality of choice in detection/staging of metastatic disease; shows metabolic reaction of bone to disease process and more sensitive; good for traumatic/inflammatory diseases
Positron Emission Tomography(PET)
primarily used to diagnose and stage metastatic disease; also used for back pain or child abuse fx’s; dx of osteomyelitis/trauma/inflammatory and degenerative arthritis/avascular necrosis/osteonecrosis of mandible/condylar hyperplasia/metabolic bone disease/Paget disease
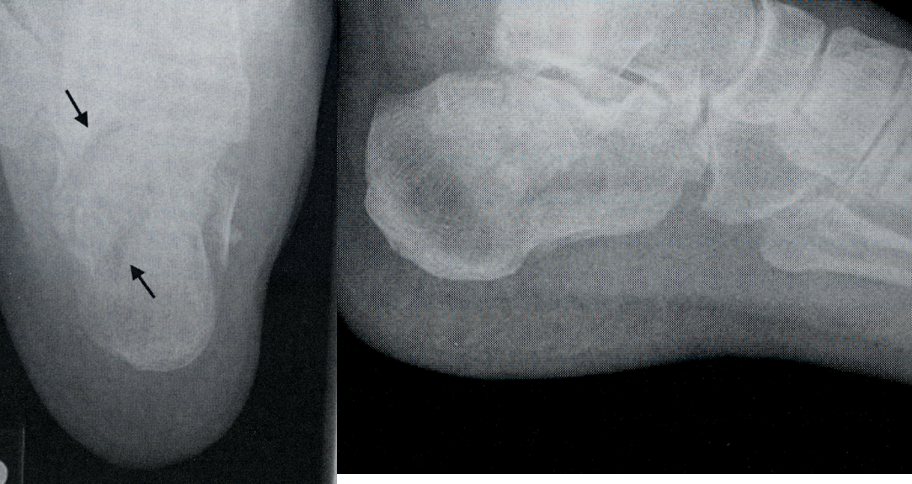
Osteogenesis Imperfecta(Brittle Bone)
1.congenital and autosomal dominant
2.RA seen as bowing, fx’s, and lack of density
3.require decreased exposure factors
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Brittle Bone Disease Types
osteogenesis imperfecta congenita and osteogenesis imperfecta tarda
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita
present at birth; present as multiple fxs at birth that heal only to give way to new fxs causing limb deformities and dwarfism and eventually death
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Tarda
fxs appear years after birth and generally stop once adulthood is reached; some cases a hearing disorder persists due to osteosclerosis(formation of abnormal connective tissue in auditory ossicles)
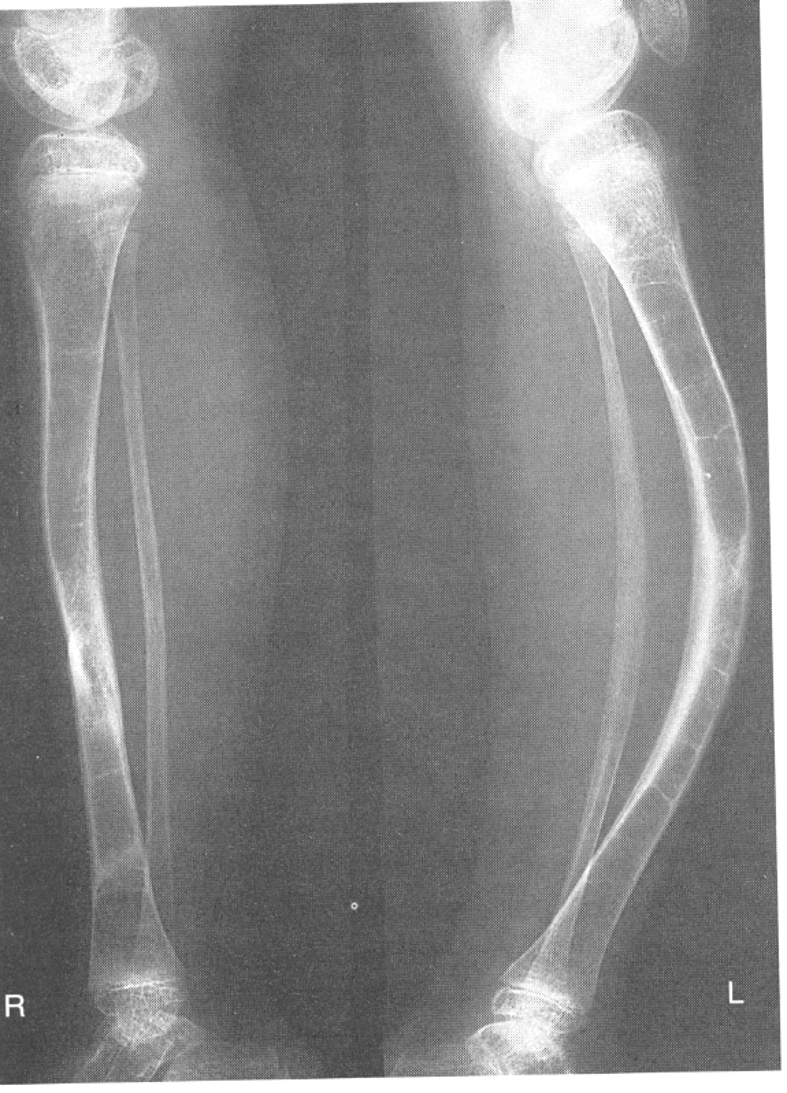
Achondroplasia
1.failure of cartilage at epiphysis in long bones to convert to normal bone; seen as normal trunk size and short extremities
2.RA see short long bones
3.Dx with bone age studies to indicate normal vs abnormal bone growth
4.autosomal dominant gene
Achondroplasia
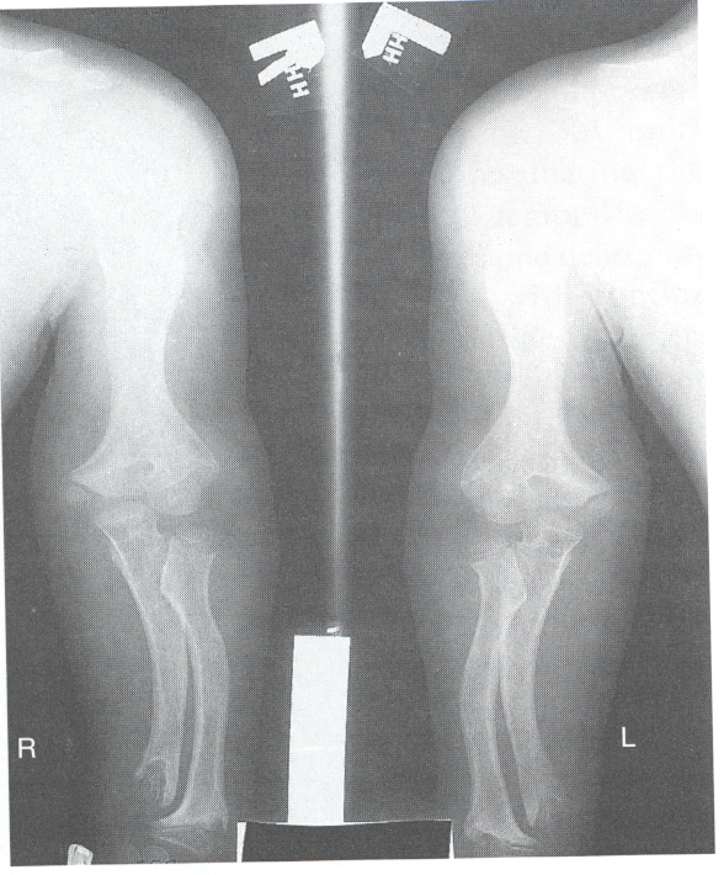
Most Common Inherited Disorder of Skeletal System
achondroplasia; results in bone deformity and dwarfism; occur in 1 in 15,000-40,000 newborns
Achondroplasia Manifestations
extreme lumbar spine lordosis, bowed legs, bulky forehead with midface hypoplasia and narrowing of foramen magnum within the skull(neural compression)
Achondroplasia Tx
llizarov procedure that attempts to lengthen shortened limbs; corticotomy of limb then attachment of llizarov fixator(2 circular frames that surround limb/wires/rods); allow for growth of 1mm per day
Bone Age Radiographic Studies
used to monitor patient with growth hormone(GH) deficiency; images analyzed to compare chronologic age with radiographic bone age using: atlas matching method(Greulich & Pyle 1950s) or point scoring system(Tanner & Whitehouse 1960s)
Osteopetrosis(Marble Bone)
1.increased bone density and defective contour of bones
2.effects long bones, spine and pelvis
3.requires increased exposure
4.2 types(Craniotubular Dysplasias and Albers-Schonberg)
Osteopetrosis
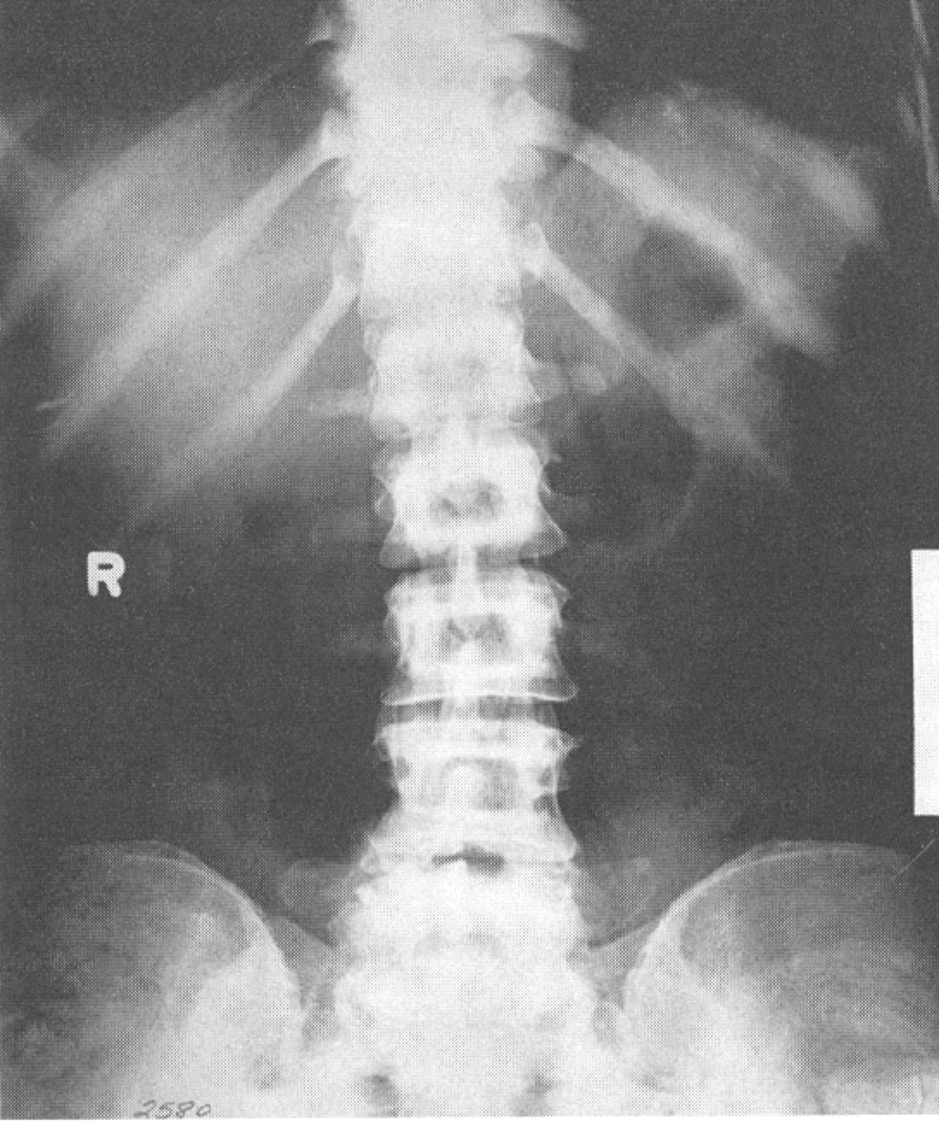
Craniotubular Dysplasias
effect cranium and long bones; autosomal recessive
Albers-Schonberg Disease
most common type of osteopetrosis; autosomal dominant; cause sclerotic bone with abnormal bony contour along with increased bone density and mass
Syndactyly
webbed toes
Polydactyly
extra fingers or toes
Talipes (Clubfoot)
inverted feet, unable to bear weight, most common in males
Talipes
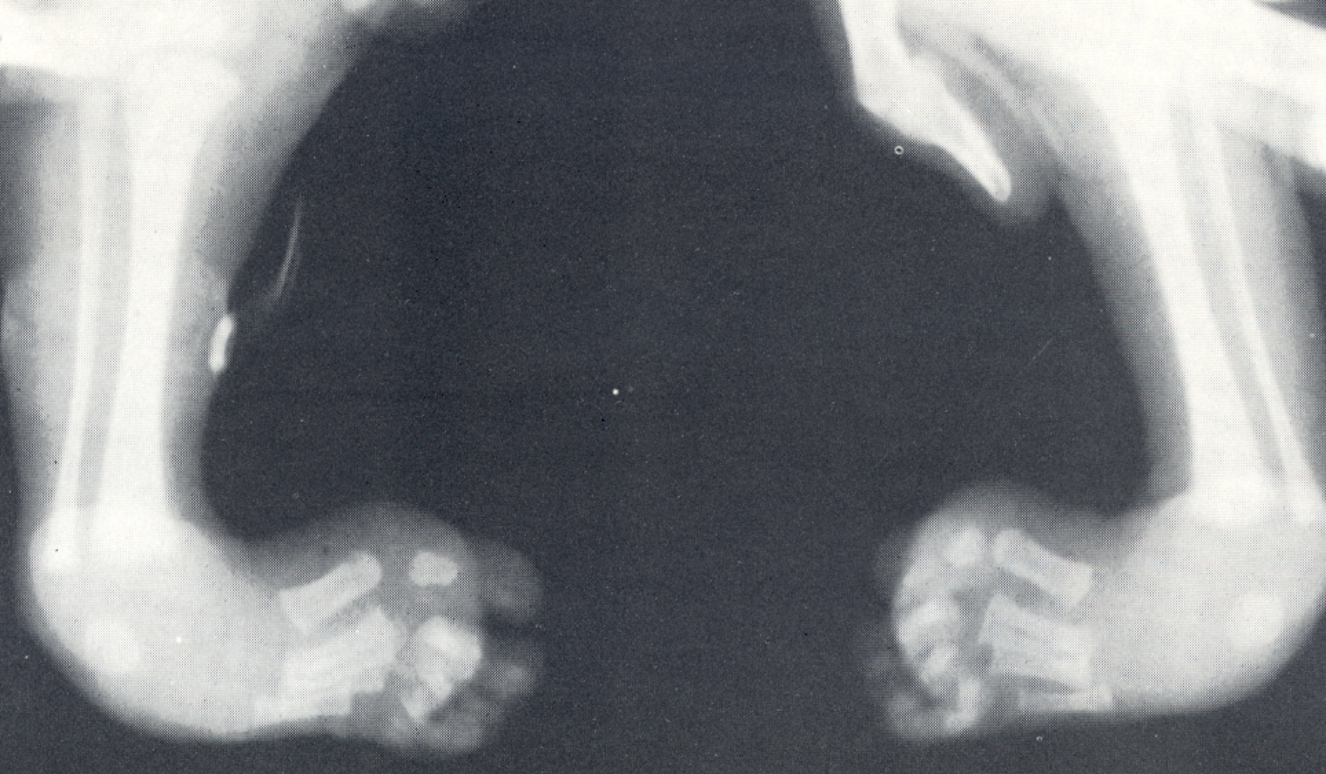
Talipes Dx/Tx
dx using Kites position; corrected through splinting
Scoliosis
lateral curvature of spine along with twisting of the spine; most common in females and undetected until adolescence; leads to leg length discrepancies/arthritis/cardiopulmonary complications/postural changes due to compensating for curve or pain
Scoliosis Projections
4(PA standing, standing lt/rt bending, recumbent PA) or AP and lateral standing 1-2in below crest included
Ferguson Method
uses multiple images to help distinguish primary from compensatory curve in scoliosis(only secondary curve will change when foot elevated); PA standing and second with foot on 3-4in block on convex side of primary curve
Scoliosis
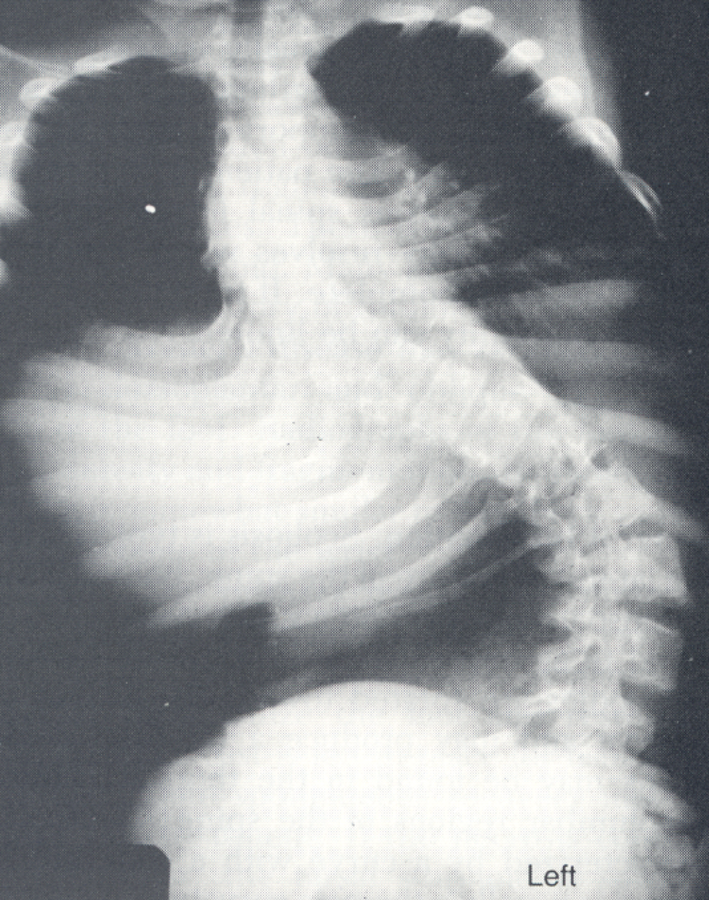
Transitional Vertebrae
vertebra takes on appearance of vertebra on each side of major spinal division; most common between thoracic and lumbar
Transitional Vertebrae
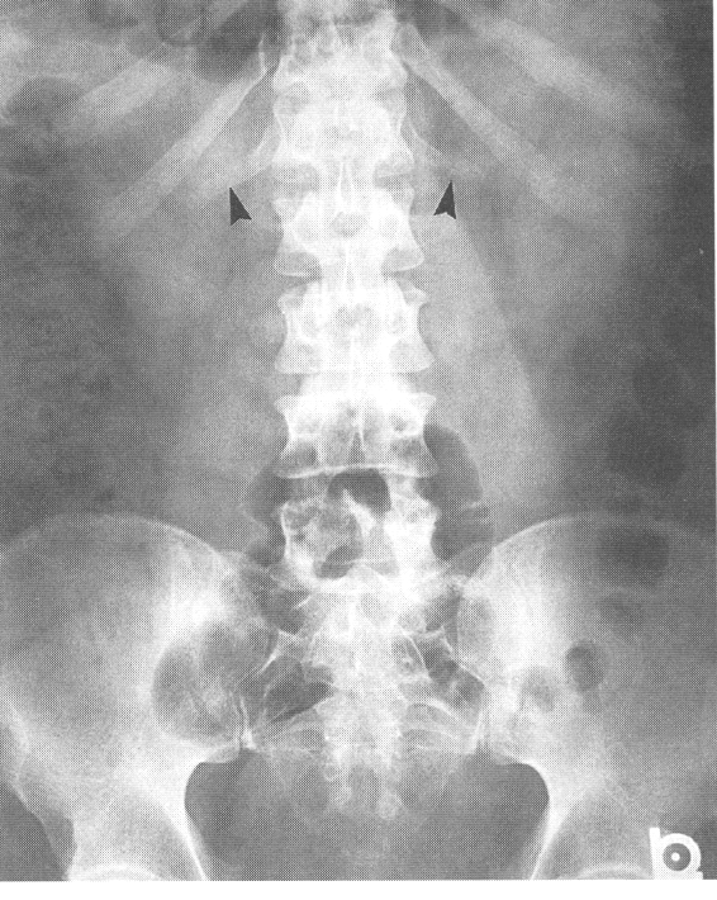
Spina Bifida
1.incomplete closure of vertebral arch
2.most often in lumbar spine
3.RA see no spinous process in back, best seen in AP projection
Spina Bifida
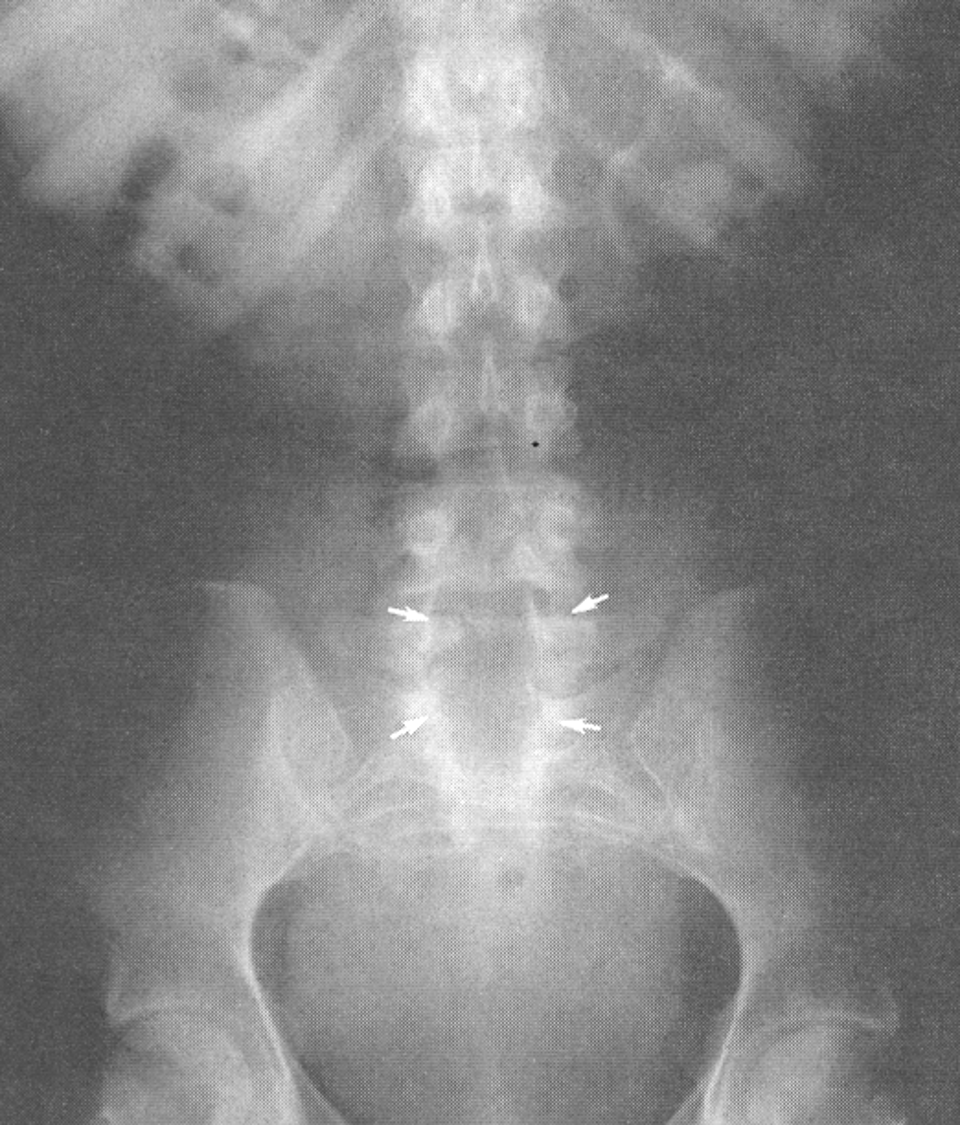
Spina Bifida Occulta
failure of fusion of two laminae, visible radiographically, spinal cord or nerve root may be involved leading to varying degrees of paralysis
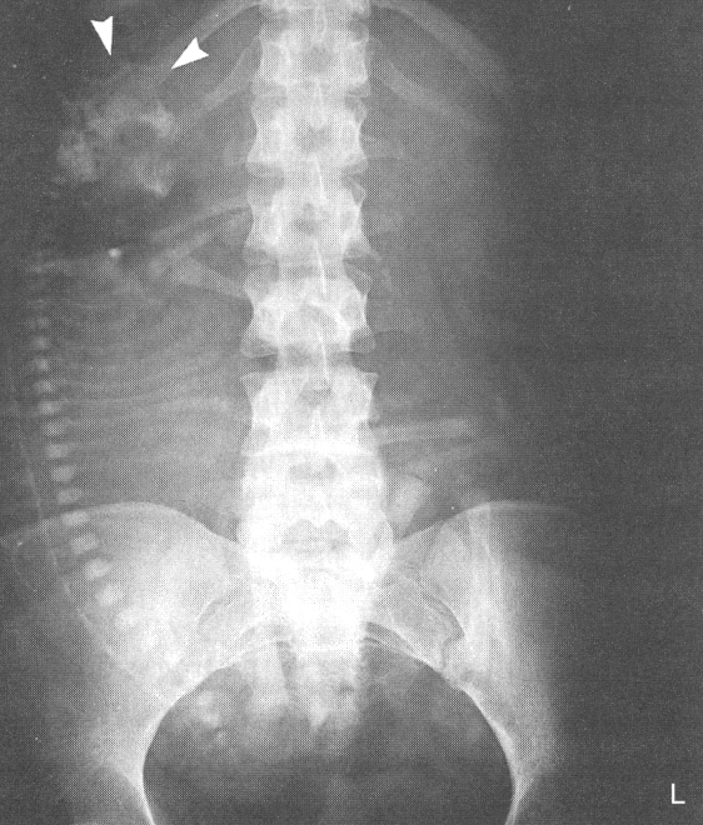
Anencephaly
lack of brain or cranial vault, may have normal facial bones, death shortly
Anencephaly
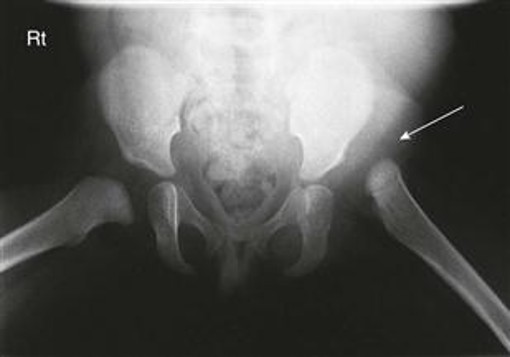
Developmental Dysplasia of Hip
acetabulum does not completely form and head of femur is displaced superiorly and posteriorly; occurs in 1 in 1000 births mostly in males and typically associated with other diseases like cerebral palsy
DDH Dx/Tx
dx using sonography of cartilage in early life and later with radiographs; treated with immobilization through casting or splinting of affected hip to allow acetabulum to grow and form normal joint; if untreated leads to uneven limb length/hip muscle weakness/uneven gait
Developmental Dysplasia of Hip
Osteomyelitis
infection of bone and/or bone marrow with pathogenic bacteria through blood or penetrating injury; acute or chronic; indicated by dull pain/heat in affected area/intermittent low grade fever
Hematogenous Osteomyelitis
develops at the ends of long bones; in children affects distal femur/proximal tibia/humerus/radius; in adults affects vertebrae secondary to bacteremia through genitourinary tract/soft tissue/respiratory infections
Osteomyelitis Dx
MRI(detect 3-5 days after onset) and nuclear medicine exams of choice; RA see dense bone(sequestrum) surrounded by decreased density(involucrum) but does not show until after 10-14 days
Osteomyelitis
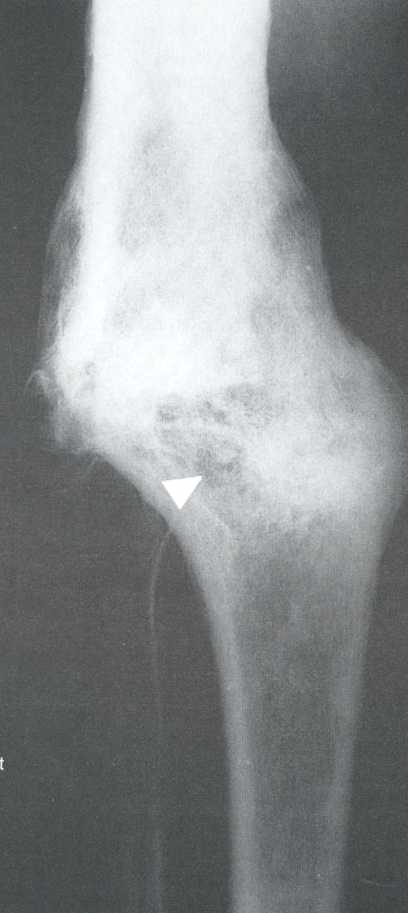
Osteomyelitis RA
due to constriction of periosteum the blood vessels and thrombose leading to bone necrosis within 24 to 48 hours but not visible until 10-14 days later when new periosteal bone repair occurs that is visible radiographically
Osteomyelitis RA and MRI
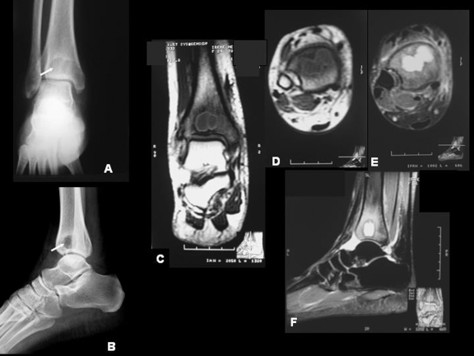
Pott’s Disease
1.tuberculosis of the bone caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis
2.chronic inflammatory disease
3.commonly effects hip, knee, spine
4.RA see worm-eaten appearance
5.starts in epiphysis and may involve articular cartilage and joint space; may result in softening and collapse of vertebrae
Pott’s Disease
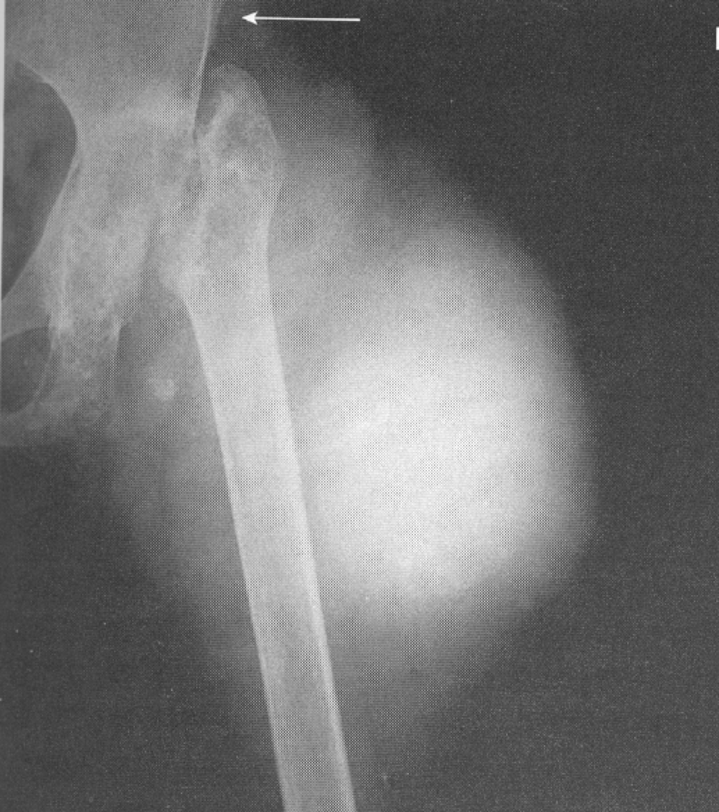
Degenerative Arthritis
effects articular cartilage
Inflammatory Arthritis
effects synovial membranes
Infectious(Acute) Arthritis
1.caused by pyogenic bacteria(S. aureus, streptococci, Neisseria gonorrheae)
2.infection by entering joint through break in skin or adject infection
3.RA see increased joint space with bony destruction
4.treatment with antibiotic therapy
5.sympotms include rapid onset of pain, redness, swelling of affected joint, fever
6.dx with blood analysis and synovial fluid from infected area
Psoriatic Arthritis
1.inflammatory condition of rheumatoid like destructive process that predominantly affects DIP joints of hands and feet
2.cause psoriasis of skin
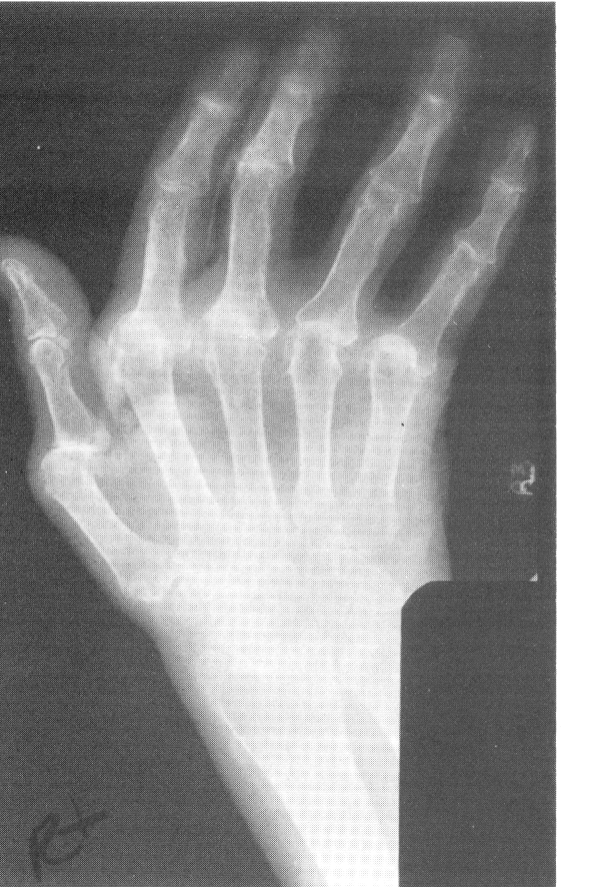
Rheumatoid Arthritis
1.inflammatory disease with adult onset 30-40 years old, 3x more in women
2.cause overgrowth of synovial membranes
3.effects peripheral joints of hands and feet first
4.RA see ankylosing of joints and dislocation
5.requires increased exposure
Ankylosing Spondylitis
1.arthritis of spine that cause inflammation in joints and vertebrae
2.adult onset 20-40 years
3.RA see bamboo spine/rigid fused spine
4.requires increased exposure
5.may be hereditary
Osteoarthritis(Degenerative) Arthritis
1.degenerative joint disease effecting cartilage
2.Primary: normal deterioration of joint
3.Secondary: result of trauma or other disease conditions
4.RA see narrowed joint space and possible osteophytes
5.Tx with NSAIDS, exercise, and surgery
6.requires decreased exposure
7.MOST common arthritis and asymptomatic until 50s
Gouty Arthritis
1.results from increase in uric acid salts in joint spaces
2.inherited metabolic disease
3.effects metatarsophalangeal joint
4.associated with radiolucent kidney stones
Spondylosis
arthritis of spine causing degeneration of joints and vertebrae; caused by general wear and tear of spine
Ankylosing Spondylitis
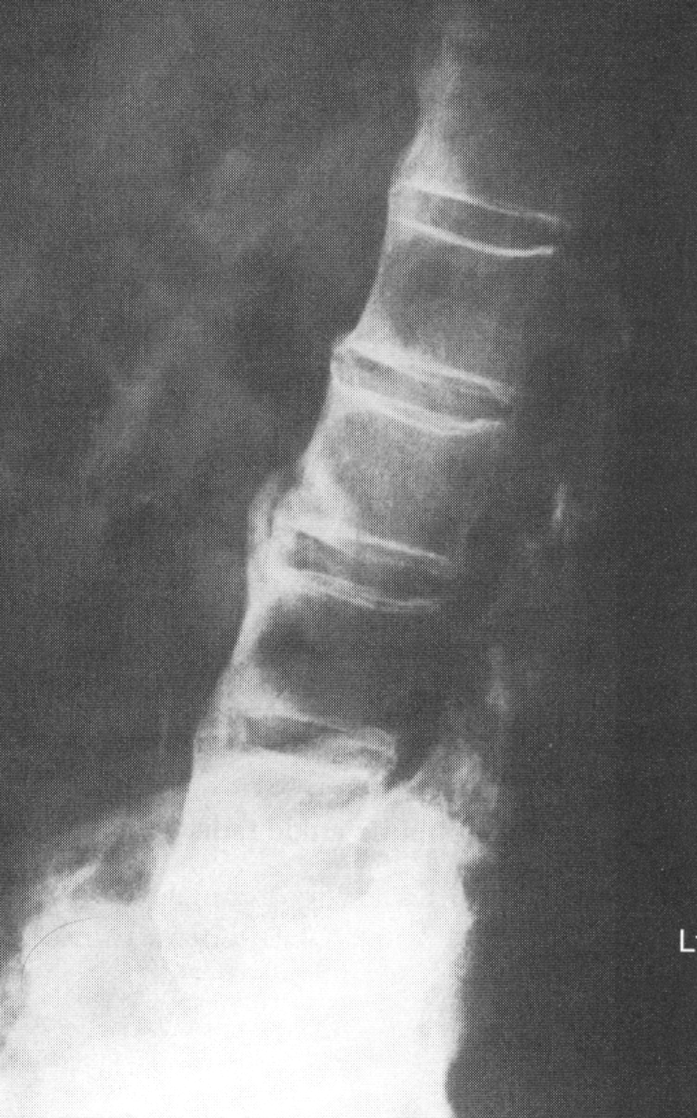
Degenerative Arthritis
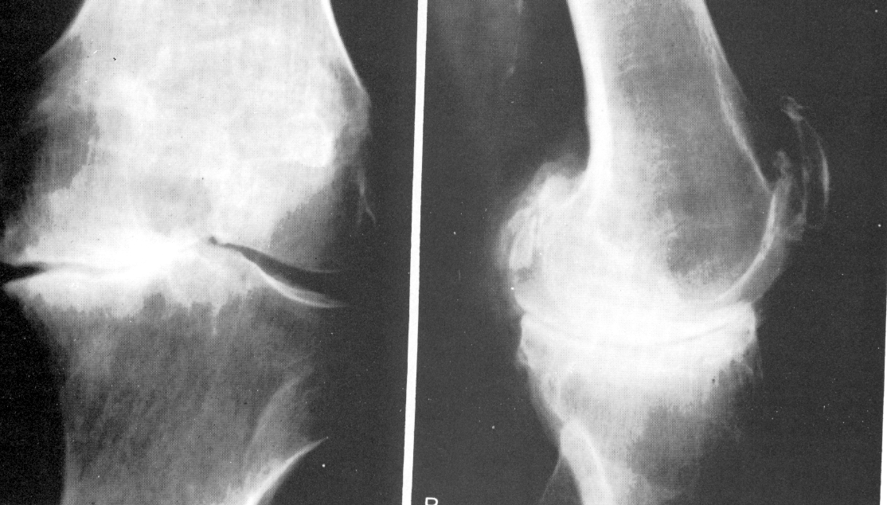
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Tenosynovitis
inflammation of tendon and synovial membrane enclosing it
Bursitis
inflammation of bursae
Ganglion Cysts
cystic swelling connected with a tendon sheath in joint space
Tendon
specialized connective tissues that attach muscle to bone; enclosed in synovial sheath
Bursae
sacs lined with synovial membrane found in locations where tendons pass over bony prominences
Joint Disease Dx
MRI is the modality of choice due to its ability to show soft tissue structures, especially good for arthrography
Osteoporosis
1.abnormal decrease in bone density due to lack of osteoblastic activity
2.primarliy in post-menopausal women due to hormones or dietary factors
3.RA see compression fx’s in spine with osteopenia
4.requires decreased exposure factors
5.best dx with DEXA of hip or spine or QCT
6.tx with calcium, vitamin D, biphosphates(fosomax)
Osteoporosis
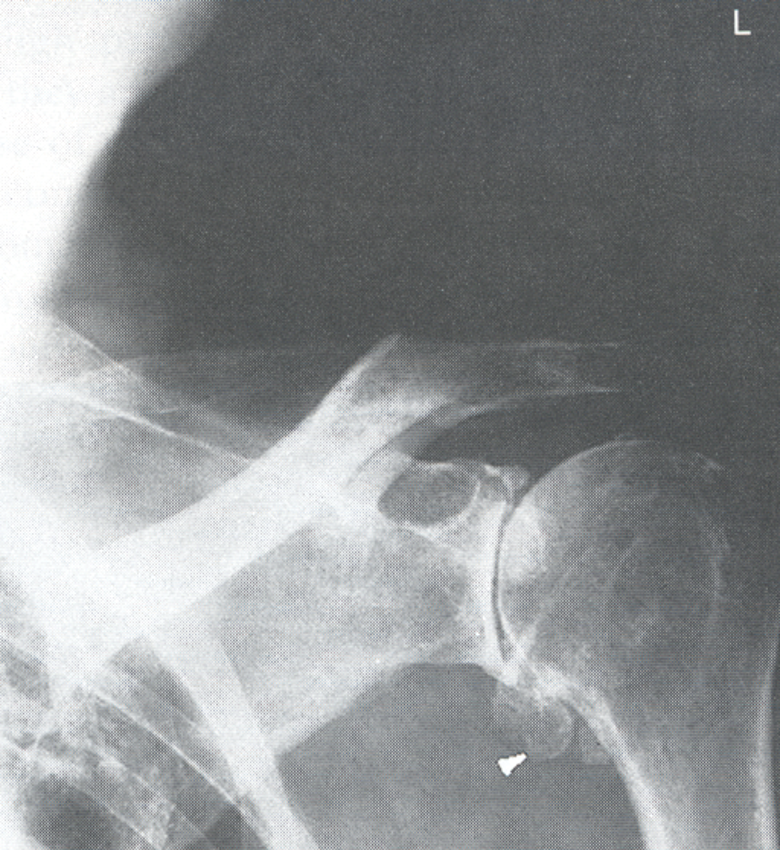
Osteomalacia
1.failure of bones to calcify
2.occures due to inability to absorb calcium, vitamin D, phosphorus
3.known as Rickets if occurring before growth plate closure
4.Dx with lab tests
5.RA see osteopenia with bands of radiolucency in bone(pseudofractures) similar to osteoporosis
6.requires decreased exposure
Osteomalacia
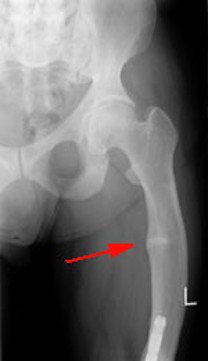
Rickets Disease
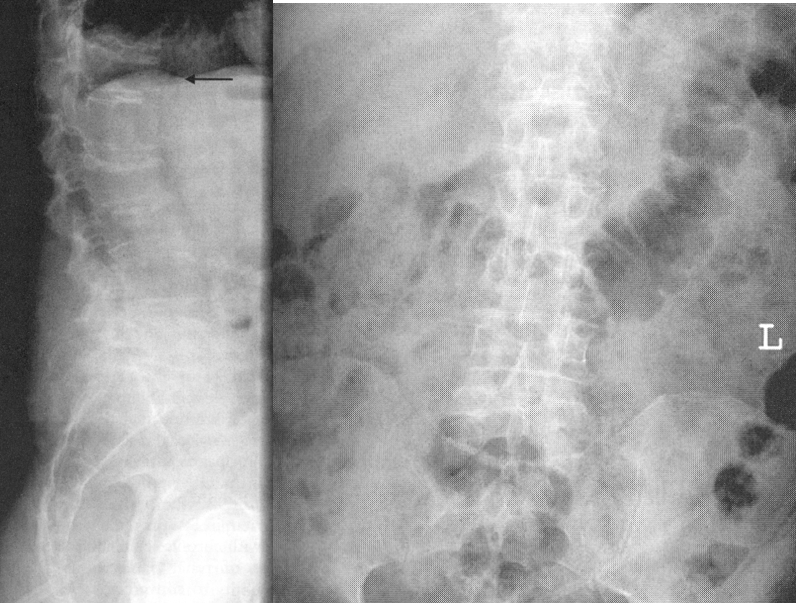
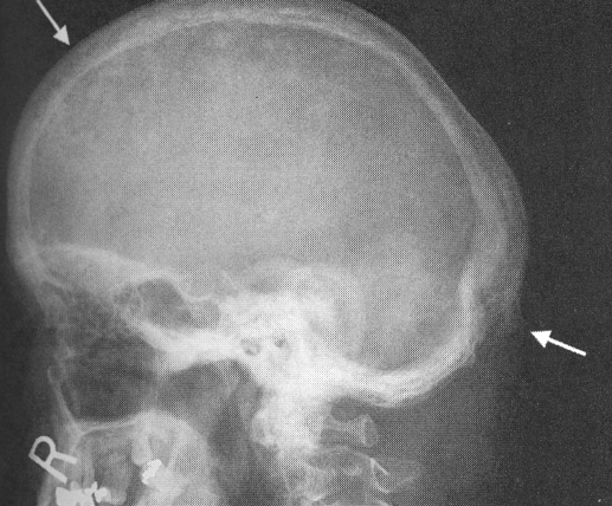
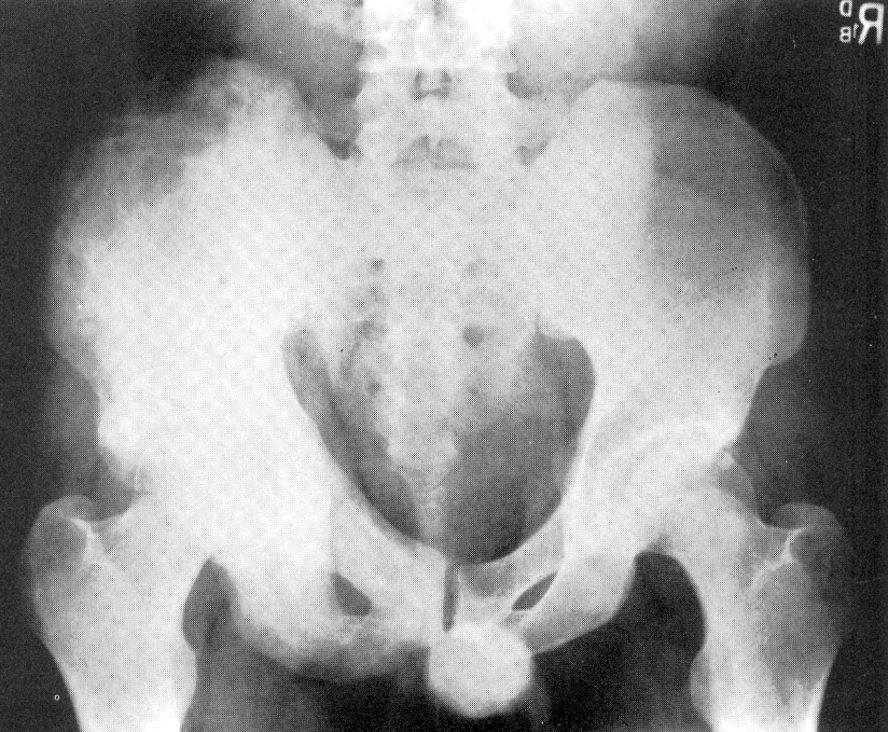
Osteitis Deformens(Paget’s)
1.metabolic disorder of bony destruction(osteolytic stage) and over-replenishment(osteoblastic stage) with poorly mineralized bone
2.etiology unknown
3.occurs in pelvis, spine, skull, long bones and leads to fractures and nerve impingement
4.effects mostly men
5.RA see mixed areas of radiolucent and radiopaque densities
6.requires increased exposure
Paget’s Disease Skull
Paget’s Disease Pelvis
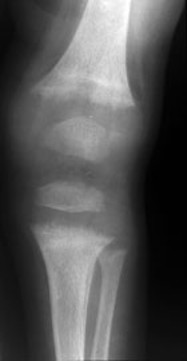
Occult Elbow Fx
posterior or supinator fat pads visible
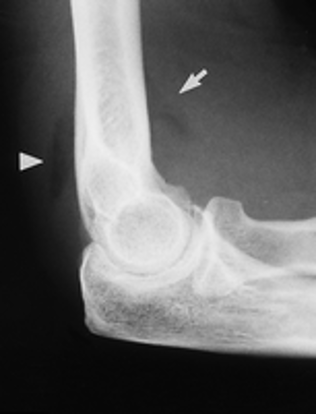
Occult Fracture
not visible on normal radiograph but indicated by posterior or supinator fat pads(not normally seen) on lateral elbow
Boxers Fracture
firth metacarpal fx due to blow to or with hand
Boxers Fx
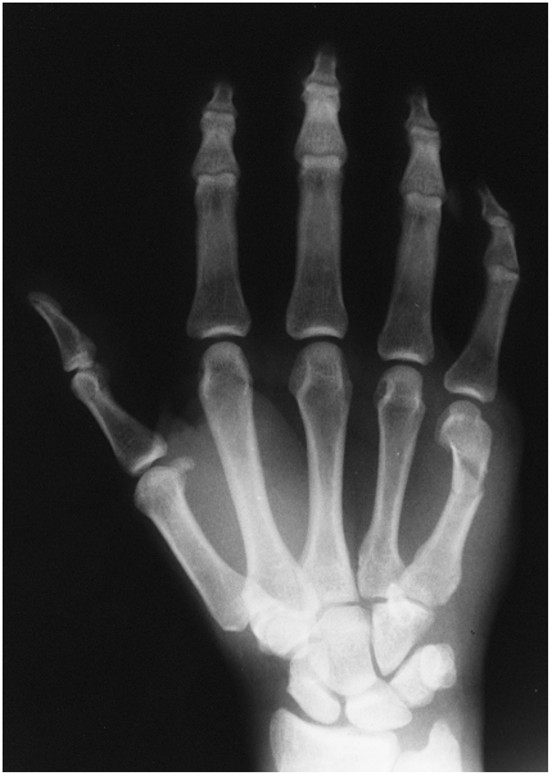
Impacted Fx
Bennet Fracture
fracture and dislocation of first carpometacarpal joint
Impacted Fracture
fractured bone ends jammed into cancellous tissue of another fragment
Comminuted Fracture
fracture in which bone is splintered or crushed(not complete)(
Comminuted Fx