4.1.8.4 Positive & negative externalities
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are externalities?
third party effects arising from production and consumption of goods/services for which no appropriate compensation is paid.
Where do externalities occur?
outside of the market ie. they affect people not directly involved in the production and/or consumption of a good or service.
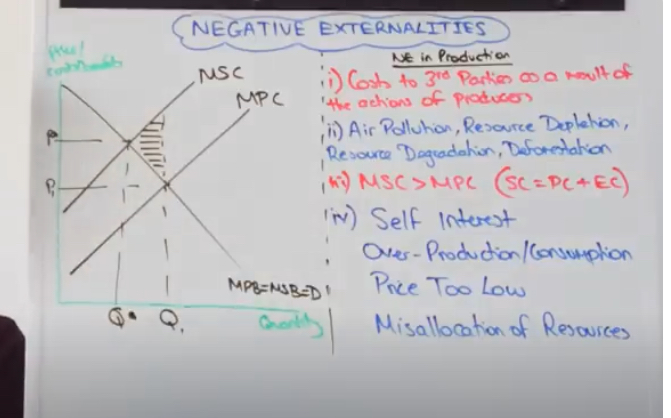
What’s an example of a negative externality of consumption?
A person smoking a cigarette (or eating an egg sandwich) at a bus stop has made a deliberate economic decision to consume a product.
The person standing next to her has not made that decision but is ‘consuming’ the bad smell resulting from the decision made by the other person.
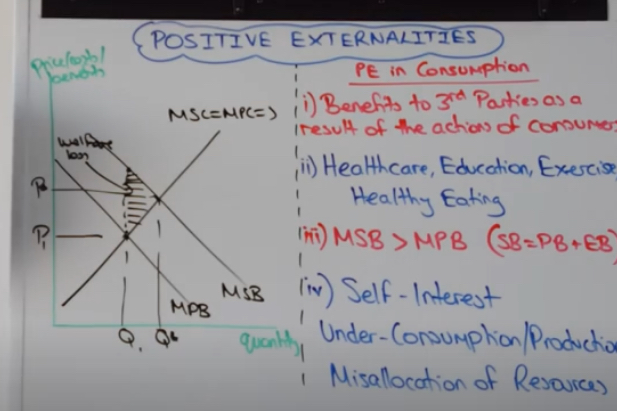
What’s an example of a positive externality of consumption?
A family halfway down my street love their fireworks!
They spend a huge amount on sophisticated fireworks on Guy Fawkes night and put on a great display.
Assuming I enjoy fireworks, their economic decision to consume fireworks counts as a positive externality of consumption for me
What’s an example of a negative externality of production?
Making furniture by cutting down rainforests in the Amazon displaces the indigenous people of the Amazon rainforest.
It also leads to higher global warming as there are less trees to absorb carbon dioxide
What’s a positive externality of production?
A farmer grows apple trees. An external benefit is that he provides nectar for a nearby beekeeper who gains increased honey because of the farmers orchard
What are socials costs?
Social cost = Private cost + External cost
What are private costs?
costs the firm pays to purchase capital equipment, hire labour, and buy materials or other inputs, for a producer of a good/service
What are external costs?
not reflected on firms’ income statements.
costs to society
If social benefit > social cost, then…
product/project is good for society at large.
if private benefit ≯ private cost then…
it will not be worthwhile for an entrepreneur/firm to invest.
What do negative production externalities lead to?
• under-pricing
• over-consumption
• over-production of goods (Excess Supply)
What do Positive production externalities lead to?
over-pricing
under-consumption
under-production (Excess Demand)
What are Negative production externalities & Positive production externalities examples of?
market failure: the market mechanism producing the goods in the wrong quantities.
What are negative externalities in production?
costs resulting from the production process that aren’t paid for by the producer.
Negative Production Externalities Diagram
Without having to pay for externalities, the supply curve is at S1. This is called the private supply curve. It leads to a private equilibrium at (Q1, P1).
Supply curve S2 is the social supply curve. It factors in the external costs and leads to a social equilibrium at (Q2, P2). Notice that price is higher, and quantity is less
vertical gap between the two supply curves represents the external costs.
Positive Production Externalities Diagram
Without gaining the benefit of the externalities, the supply curve is at S1. This is called the private supply curve. It leads to a private equilibrium at (Q1, P1).
A social equilibrium at (Q2, P2) including external benefits, could be achieved, for instance, by government subsidies to incentivise greater production
This time the vertical gap between the two supply curves represents the external benefit. Positive Production Externalities P2 Q2

Why does the market fail and what is done to correct this?
The market (left to its own devices) fails, because the socially irresponsible private equilibrium will be the outcome.
The government can intervene to ‘correct’ the market. It could, for instance, introduce a pollution tax, forcing companies to pay costs equal to the estimated* value of the negative externalities.
This effectively shifts the supply curve back to S2 leading the market to find the social equilibrium.
negative externality of consumption diagram

positive externality of consumption diagram