3.4.3 Monopolistic competition
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
monopolistic
market structure in which there are many firms offering a similar product but with some product differentation e.g. nail salons
characteristics of monopolistic competition
large numbers of small firms
low barriers to entry and exit from industry
products slightly diffeentiated
low degree of market power and some price setting ability
objective of monopolistic competition
to profit maximis so mc=mr
what is the firm with price in monopolistic competition
price maker as they have a differentiated product that is desirable by certain consumers
price maker
firm with market power that is able to manipulate prices in order to change demand
profit in short run
able to make supernormal profit
he AR curve is the demand curve of the firm and it is downward sloping
To sell an additional unit of output, the firm will have to decrease its price
The marginal revenue (MR) curve will fall twice as quickly as the AR
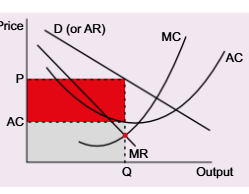
short run profit monopolistic competition diagram
diagram shows output leading to profit maximising price
means firm earns supernormal profit-shown by red rectangle
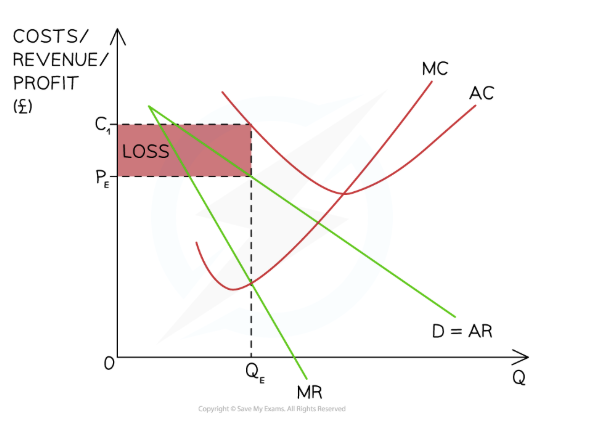
short run loss monopolistic competition diagram
The firm produces at the profit maximisation level of output where MC = MR (QE)
At this level of output, the AR (PE) < AC (C1)
The firm's loss is =
why do supernormal profits become normal in long run
If firms in monopolistic competition make supernormal profit in the short-run, new entrants are attracted to the industry and the number of sellers increases
They are incentivised by the opportunity to make supernormal profit
There are low barriers to entry
It is easy to join the industry
Supernormal profit will be eroded and the firm will return to the long-run equilibrium position of making normal profit
losses to normal profit monopolistic competition in long run
If firms in monopolistic competition make losses in the short-run, some will shut down
The shut down rule will determine which firms shut down
There are low barriers to exit, so it is easy to leave the industry
For the remaining firms, losses will be eliminated and the firm will return to the long-run equilibrium position of making normal profit
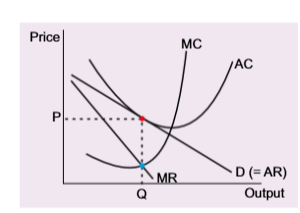
long run monopolistic competition diagram
demand curve shifts left as overall demand split between more firms as more firms
new enetrants will continue to join until
only normal profit is earned,at this point the slopes of the AC curve and demand/AR curve touch tangentially shown by red dot
at this quanity mr =mc blue dot
prices in monopolistic compeition
The short run position of monopolistic competition is basically the same as in a monopoly. However, unlike in a monopoly, new entrants to the market will drive prices down until only normal profit is earned in the long run.
Exactly how long this process takes is important.
If it takes a very long time, the market will resemble a monopoly.
But if it all happens relatively quickly, then the market will be more like a perfectly competitive market.
This is why firms are often willing to spend large amounts of money to try to differentiate their product (e.g. by improving it or by advertising to create a strong brand). The longer a firm can retain its price-making power, the longer it can make supernormal profit.
But unlike in perfect competition, in monopolistic competition the firm is not producing at the lowest point on the AC curve.
These different positions on the AC curve mean that prices in monopolistic competition tend to be higher than in perfect competition.
This is because firms in monopolistic competition need to spend money on differentiating their product (e.g. by advertising) and creating brand loyalty.
Firms in monopolistic competition have also chosen to restrict output in order to maximise profits. This means they don’t benefit from all the economies of scale that they could.
Prices in monopolistic competition tend to be lower than those charged by a monopoly seller.
efficiency in monoolistic competition
not allocatively or productively efficient
dynamically efficient
why is monopolistic competition not productively efficient
not producing at lowest point on ac curve
why is monopolistic competition not allocatively efficeient
equilbrium price greater than mc
why is monopolistic competition it dynamically efficient
differentiated products ans so know innovative products will give them an edge over competitors and enable them to make supernormal profits in short run however sinces firms are small they may struggle to receive finance or have retained profits to invest
example of monopolistic competition fashion
the fashion industry is arguably monopolistically competitive for several reasons. Firstly, due to technological advancements in recent decades the need for conventional brick-and-mortar stores has declined as it has become much easier to create clothing stores online for a fraction of the cost. This has allowed ‘many sellers’ to enter the market, and has significantly lowered ‘barriers to entry’ as the start-up costs for these firms are much lower, and there is some ‘differentiation’ amongst the goods offered by these firms. For example, companies such as Boohoo plc and ASOS are based entirely online and have already taken majority of the market share in the fashion industry as low costs means low consumer prices
example of monopolistic competition airline
n alternative industry that is monopolistically competitive is the airline industry, and there have recently been an influx of ‘budget airlines’ making the market more competitive, e.g. Ryanair, EasyJet and Jet2. These budget airlines are able to offer low prices as they lease their planes as opposed to buying them, which significantly reduces their operating costs.