2. Redox Reactions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What occurs in a redox reaction?
electrons move from the substance being oxidized to the substance being reduced
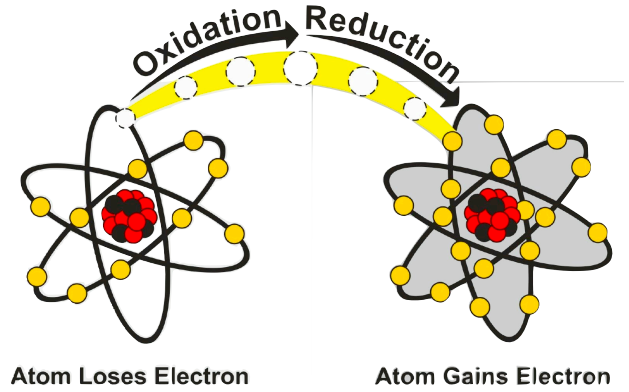
What are Half-Reactions?
a chemical equation that represents one part of a redox reaction
can help show change/ transfer of electrons
eg. Cu(s) Cu2+ (aq) + 2e-
Ag+ (aq) + e- Ag (s)
ELECTRONS ARE ADDED TO EITHER SIDE TO BALANCE CHARGES AND THE AMOUNT LOST IN ONE HALF-REACTION MUST BE GAINED IN THE OTHER HALF-REACTION
What is important to remember about electrons in Redox Rxns?
electrons are added to either side to balance charges
# electrons lost in one reaction must be gained in the other
What are the steps to solving Redox Rxns?
Assign oxidation states to determine which atoms are being oxidized and which are being reduced
Write half-equations for oxidation and reduction as follows:
balance the atoms other than H and O
balance each half-equation for O by adding H2O
as needed
balance each half-equation for H by adding H+
as needed
balance each half-equation for charge by adding
electrons to the sides with more positive charge
check that each half-equation is balanced for
atoms and for charge
Equalize the number of electrons in the two half-equations by multiplying each appropriately
Add the two half-equations together, cancelling out anything that is the same on both sides
Oxidizing Agent
substance that gains electrons (being reduced)
brings about oxidation of the other reactant
Reducing Agent
substance that is losing electrons (becomes oxidized)
brings about reduction of the other reactant
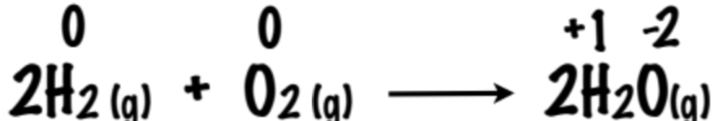
Apply the terms of Redox and Agents to the reaction presented:
Hydrogen is oxidized
Oxygen is reduced
H₂ is the reducing agent
O₂ is the oxidizing agent.
Whether a species acts as an oxidizing or as a reducing agent depends on…
what it is reacting with
What do relative strengths of agents depend on?
depends on their tendencies to lose or gain electrons
more reactive metals lose electrons more readily so they are stronger reducing agents)
How can one test relative strengths of Reducing Agents?
see if a metal can reduce ions of another metal in solution
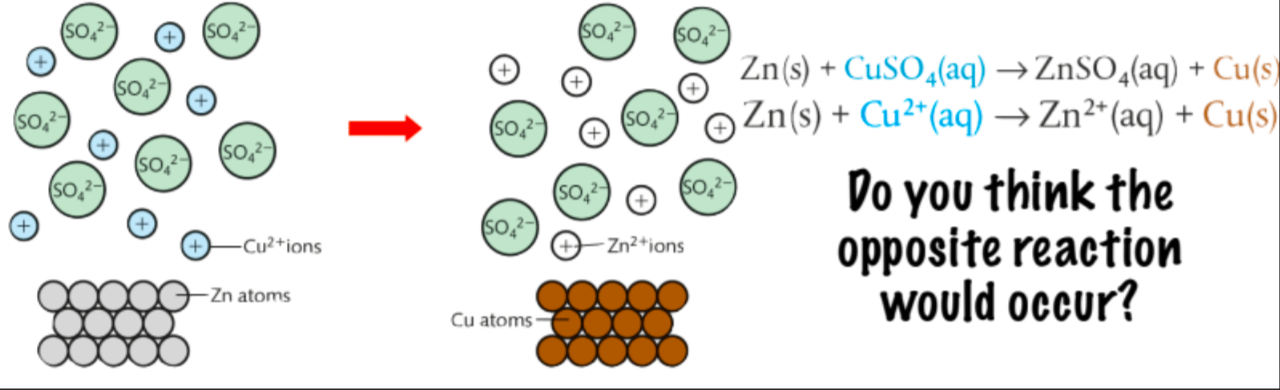
the opposite reaction (Cu kicking Zn off) would not happen as Zn is more reactive
Tell me about the Activity Series
tool that enables us to predict whether a redox reaction between a metals and the ions of another metal is feasible
found by testing different displacement reactions together