Chapter 2 Theorems/Info - Matrix Algebra
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This covers all of the important theorems and ideas from chapter 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Theorem 1 - Matrix addition & Scalar Multiplication Laws
Let A, B, C be matrices of the same size and let r, s be scalars:
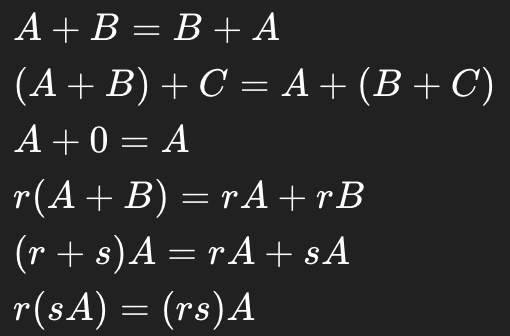
Invertible Matrix
An n x n matrix A is invertible if there exists C such that: CA = I and AC = I
This guarantees:
The inverse is unique
Denoted A-1
Theorem 4 - The Invertibility Test
For A = [a b ; c d],
A invertible ad - bc doesn’t equal = 0
Guarantees:
det A doesn’t = 0
Explicit inverse formula exists
Theorem 5 - Unique Solution to Ax = b
If A is invertible, then for every b ∈ Rn
Ax = b has the unique soltuion x = A-1b
“Solve Ax = b without row reducing” - use A-1b
Theorem 6 - Algebra of Inverses
Products of invertible matrices are invertible
Order reverses in inverses
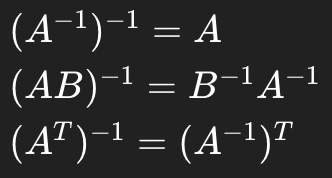
Theorem 7 - Row Equivalence & Inverses
A is invertible if A = In
Row reducing [A I] gives [I A-1]
Fast invertibility check
Algorithm for computing A-1
Subspace Test
A set H ⊂ Rn is a subspace if:
0 ∈ H
Closed under addition (stay in the set)
Closed under scalar multiplication
“Is this a subspace? check all three
Column Space
Col A = Span {a1,…,an}
Col A ⊂ Rm
Always a subspace
Theorem 12 - Null Space
Nul A = {x : Ax = 0}
is a subspace of Rn
Solutions of homogeneous systems form a subspace
Basis
A basis is a leneraly independent set that spans the subspace
Guarantee:
The coordinates are unique
Theorem 13 - Pivot Columns Form a Basis
The pivot columns of A form a basis for Col A
Ignore non-pivot columns completely
Dimension
dim H = number of vectors in any basis of H
Guarantee:
All bases have the same size
Rank
rank A = dim(Col A) = # pivot columns
Theorem 14 - Rank-Nullity Theorem
If A has n columns,
rank A + dim(Nul A) = n
Instantly connects pivots and free variables
Theorem 15 - Basis Test
If H is p-dimensional:
Any linear independent set of p vectors in H is a basis
Any spanning set of p vectors in H is a basis
Invertible Matrix Theorem
For A ∈ Rnxn, the following are equivalent:
A invertible
A = In
n pivots
Ax = 0 has only trivial solution
Columns of A are linearly independent
Applications of IMT
Equivalent to invertibility:
Columns of Rn
Ax = b has a solution for all b
x → Ax is one to one and onto
AT is invertible
CA = I or AD= I for some matrix
Prove one → you get all