Theme 2 Edexcel A-Level Economics (A)
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Gross Domestic Product
The value of all the goods and services produced within an countries borders in a year
Gross National Product (GNP/GNI)
Value of all goods and services produced by citizens of a country in a year (GDP - Remittances to abroad + Remittances from abroad)
Limitations of GDP as a measure of economic output
- Different calculation methods
- Doesn't include black market
- Doesn't represent changes in product quality without changes in price
- The Informal Economy (home labour, unpaid work) not included
- Population increases can lead to falsely higher GDP
Limitations of GDP as a measure of standards of living (6)
- Wealth is not spread equally
- Per Capita is a better measure
- Higher GDP doesn't necessarily mean higher real income: inflation
- Real GDP is after inflation
- GDP doesn't account for non-financial improvements, such as environment and community
- HDI is a much better measure of changes to living standards
What are limitations of GDP when comparing economies?
Needs PPP (such as the Big Mac Index), due to different prices in different countries, so doesn't reflect change in real welfare.
Real GDP Forumla
Real GDP = Nominal GDP / GDP deflator
GDP Deflator is the base year (100) plus the level of inflation compared to the base year (9.7%)
Value vs Volume
Value is the numerical value of goods and services, where as Volume is the quantity produces
What are the main macroeconomic objectives off an economy?
Trade balance (B.O.P. at equilibrium)
Inflation control
Government budget balance
Employment low
Redistribute Income
Sustainable growth (Environment protected, resource protection)
How is National Happiness measured in the UK?
National Well-being Dashboard
World Happiness Report (UN)
Human Development Index (HDI)
What does the National Wellbeing Index Measure?
Relationships, Wealth, Health, Environment, Education
What does the HDI index measure?
Life Expectancy, Education and Income
What is the Easterlin Paradox?
The idea that happiness is not proportional to income. After reaching a certain point, the gain in happiness is not correlated to an increase in income. Despite massive increases in wealth, those in countries with extensive economic growth do not feel happier than 50 years ago.
What are two other theories about happiness and wealth?
International comparisons show that countries have little difference in average happiness
Richard Layard noted than within an economy, happiness depends on relative income and wealth. We are only happier when we feel better off than those we compare ourselves.
Inflation Definition
A sustained increase in the average price level of a country
What is used to measure inflation?
CPI - not including housing, composed of 750 goods that change every year, weighted by proportion of income
RPI - same as cpi, includes housing
Deflation vs Disinflation
Deflation is a sustained decrease in the average price level in an economy, disinflation is a decrease in the rate of inflation
Inflation Formula
(Price index in current year - Price index in base year) / Price index in base year
Decimal answer, so *100
Causes of inflation
Cost-push and Demand-pull
Explain Demand-pull inflation
If there is excessive spending (PLASTIC) in an economy (due to increase in C, I, G, or (X-M)) and the economy is reaching productive capacity (full employment of FOP), then there is a pressure for prices to rise to a greater level (rationing function).
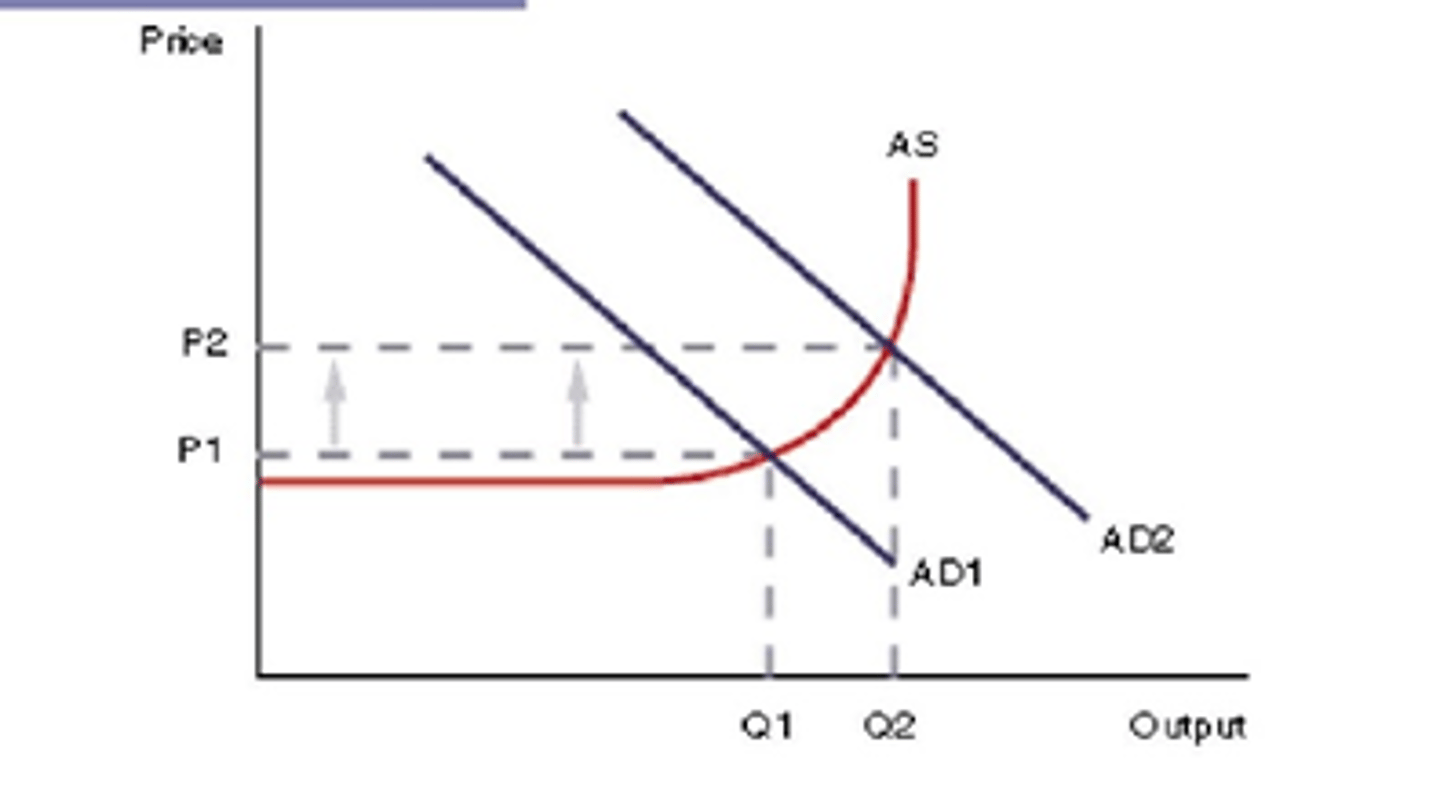
Explain Cost-push inflation
Where the costs for firms producing goods and services increase, so there is a decrease in supply (PTSCO). Could be government taxation, increased wage pressures, or import price increases (weak £).
COR that lead to D.P. inflation
rising property price -> Increased consumer wealth -> demand pull inflation
rapid expansion of money and credit -> cheaper loan finance for consumers -> greater spending -> risk of D.P. inflation
COR that lead to C.P. inflation
depreciating exchange rate/raised energy prices/rise in minimum wage -> more expensive imports -> costs of production go up -> raised prices for consumers
Effects of inflation on consumers
Shoe Leather Costs - the costs of reducing cash holdings during times of high inflation
Real Income Decreases
Real savings decrease - when inflation rate exceeds interest rates, savers lose out
Borrowers cheaper
Effects of inflation on producers
Costs of production increase (wages, materials), so less internationally competitive
Cost of changing prices
Animal spirits decrease - firms will spend less on investment
Causes uncertainty - the nemesis of physical good manufacturers
Effects of inflation on the government
Pressure to increase interest rates, increases government budget deficit, leads to national debt.
Higher tax revenue as nominal income values go up
Effects of inflation on workers
Fall in real incomes
Redundancies
What is unemployment
People in the labour force, who are willing and able to work, actively seeking a job but cannot get one (at the going wage rate)
What is underemployment
Those currently in work, but who are not utilised by firms to their full potential (skills or part-time), and are being underused as a factor of production
Who in the population are considered economically inactive
Those of the working age population who are not in employment nor actively seeking it.
Student, the ill, the retired or claimants are examples.
Formula for unemployment rate
No. unemployed people / No. in the Labour Force
Decimal answer, so *100
How is unemployment measured, and what are their pros/cons?
The Labour Force Survey (LFS) is conducted using a sample of 60,000 households. It is reliable and inclusive, but subject to proxy responses.
The Claimant Count is measured by recording those claiming the J.S.A. or are claiming benefits. It is easy to collect, but is exclusive of much of the population so not representative.
How does the business cycle affect Claimant Count compared to LFS?
During periods of boom, there will be more confidence among the unemployed, so less people will choose to claim benefits.
What are the 5 types of unemployment?
- Cyclical
- Structural
- Seasonal
- Frictional
- Real Wage
What is the cause of Cyclical Unemployment?
A slowdown in the economy - general lack of demand for goods and services - leading to mass lay-offs and business closure. Can be resolved by increasing AD.
What is the cause of Structural Unemployment?
Where specific industries suffer due to a lack of demand or profitability. This can be due to international competition or footloose TNCs outsourcing elsewhere. Can be resolved by supply-side policies
What is the cause of Seasonal Unemployment?
Seasonal work, such as tourism industry, are based on time of year, so many are unemployed during the off-season periods.
What is the cause of Frictional Unemployment?
People who have left a job, and are not 'between jobs', actively seeking a role.
What is the cause of Real Wage Unemployment?
Where real wages are set above the market equilibrium, so there is excess supply of labour that cannot be afforded at the minimum wage level.
Can be resolved by Trade Unions or a decreased Minimum Wage.
Effects of unemployment on individuals
- Reduced disposable income
- Reduces living standards
- Further unemployment due to lower profits (positive feedback cycle)
Effects of unemployment on firms
- Increase productivity (output per worker) to keep their job
- Less jobs, so less overall production possible
- Reduction in F.O.P.
- Large pools of labour to hire
- Falling profits due to lower consumption
Effects of unemployment on the government
Government loses out on tax income, as incomes fall
Effects of unemployment on the economy
Negative multiplier effect
- Local factory closure
- Lost jobs
- Lower spending in the region
- Less tax revenue (VAT/Income)
- Less reinvested into economy
- Further reduced output (emigration)
Social effects of unemploymet
- Increased poverty
- Reduced National Happiness
- Increased crime
- Worsening health
- Relationship risks
(Basically all things that contribute to the National Wellbeing Dashboard)
What are the two components of the Balance of Payments?
Capital and Financial Account
Current Account
What is the current account?
A record of a country's dealings with the rest of the world, composed of:
- Trade in goods and services
- Net Primary Income
- Net Secondary Income
What is Net Primary Income?
The net return from financial assets abroad, including profits and interest + remittances into the UK.
What is Net Secondary Income?
A record of all other financial dealings, money transferred by individuals and the government.
What is a current account defecit/surplus?
Where the components of the current account into the country are less/greater than those out of the country.
What causes a current account defecit?
- High inflation
- Low productivity
- Import-lead growth (high spending on imports does mean that country is prosperous)
Can a country run on a current account defecit?
Yes, but only if they can attract capital + financial flows into the country. These can compromise short-term (stock market investments) or long-term (Foreign Direct Investment). This stabilises the Balance of Payments.
Globalisation has meant that goods are more available, so S.O.L. can increase with deficit.
Why is a current account deficit bad?
- Reduces Aggregate Demand (AD), and has a negative multiplier effect on jobs and living standards.
- Less competitive in export sectors on FX
What does the significance of the current account (defecit/surplus) depend on?
1. The cause of the current account deficit
2. Is it economic cycle based (long/sort term)
3. Can there be sufficient FDI to keep a stable B.O.P.
What is Aggregate Demand?
Demand for all goods and services produced in an economy.
AD = C + G + I + (X-M)
C = 60%
I = 20%
Think of all components in the context of AD when applying C.O.R.
Why does the AD curve slope downwards?
Inverse relationship between the price level and real GDP:
- Real incomes rise as the price level falls
- Falling prices make foreign alternatives less attractive
- If inflation is low, then a reduction in interest rates will increase export consumption and depreciation of currency
(WPIDEC)
What factors determine Consumer Spending? (6)
1. Real disposable income
2. MPS and MPC
3. Wealth Effect - those with greater wealth have greater levels of consumption
4. Interest rates
5. Credit availability
6. Consumer confidence
How are MPS and MPC calculated?
Marginal, meaning for each extra...
MPS = change in savings / change in income
MPC = change in consumption / change in income
What is Investment?
Gross investment - all spending on capital goods
Net investment - gross investment - replacement cost of existing capital (capital consumption)
What factors influence Investment?
- Animal Spirits
- Access to cash (credit/retained profit)
- Stage in economic cycle
- Influence of supply side policies
- Demand for exports
- Interest rates:
High interest rates make the return on investment (present value) of investments more expensive.
What composes Government spending?
1. Transfer Payments: benefits paid to individuals, grants/subsidies, money abroad
2. Current Government Spending: state goods and services like education and health
3. Capital Spending: new investments the government makes (infrastructure)
What influences Government spending?
- The trade cycle, as spending is higher during a recession to increase AD
- Fiscal Policy, as expansionary fiscal policy that increases spending (cuts taxes)
- Age Distribution of Population: An ageing population, as in the UK, requires huge amounts to pay the state pension every year to all pensioners.
What is Austerity?
Contractionary Fiscal Policy: decreasing government expenditure, and increasing taxes to try and have a budget surplus
What influences the Net Trade balance?
- Real incomes (domestic vs abroad)
- Exchange rates (SPICED, WPIDEC)
- Protectionist policy (tariffs, quotas) lead to increased prices
- Elasticity of imports and exports
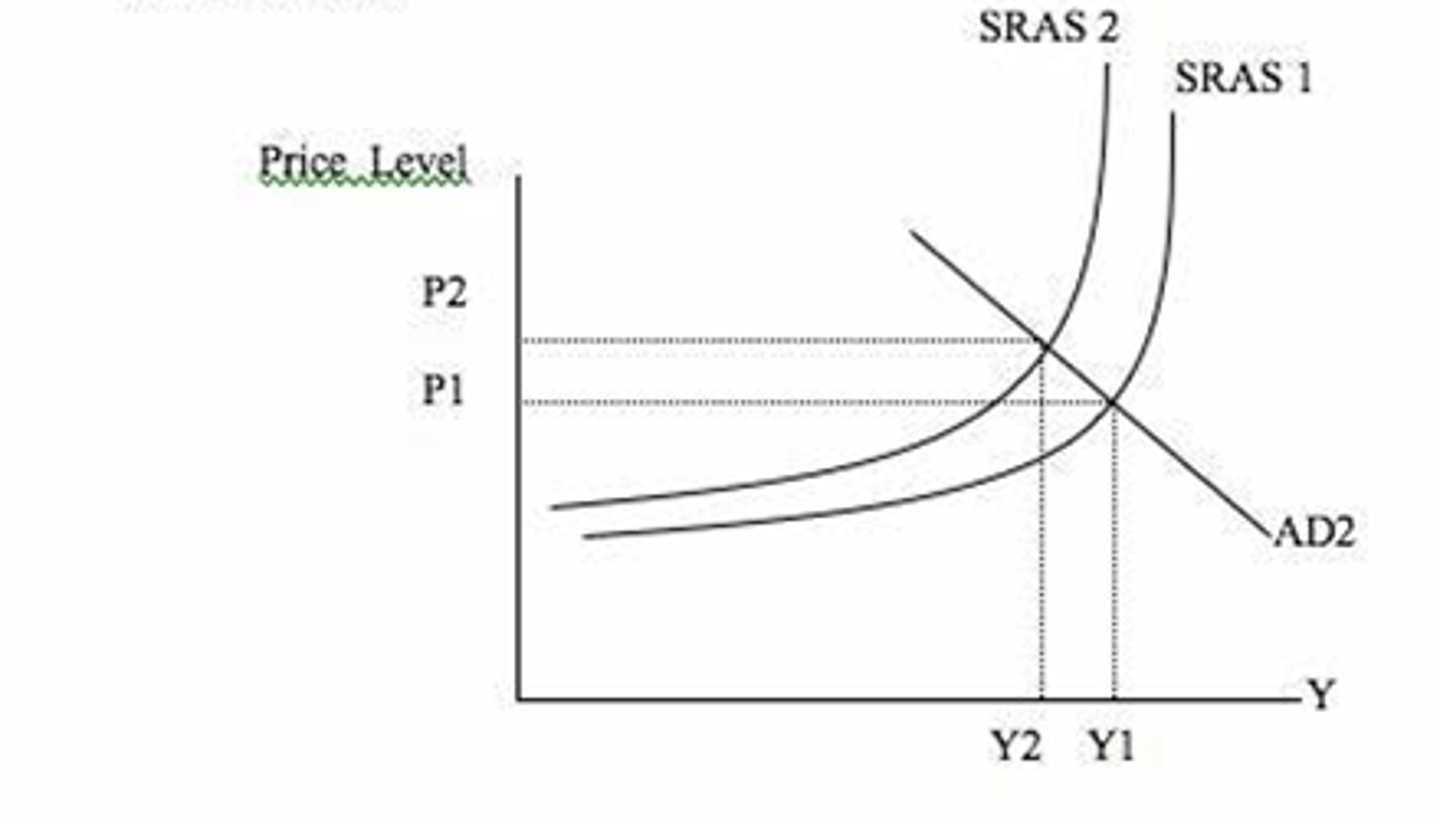
What are the types of Aggregate Supply to consider?
Short-run Aggregate Supply (SRAS)
Over a limited period of time, supply of goods and services.
Linear diagram
Limited factor mobility or opportunity to increase output
Long-run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
Neo-classical and Keynesian approach
What causes shifts in SRAS?
Costs:
- Labour
- Materials
- Regulation/Taxation
- Energy
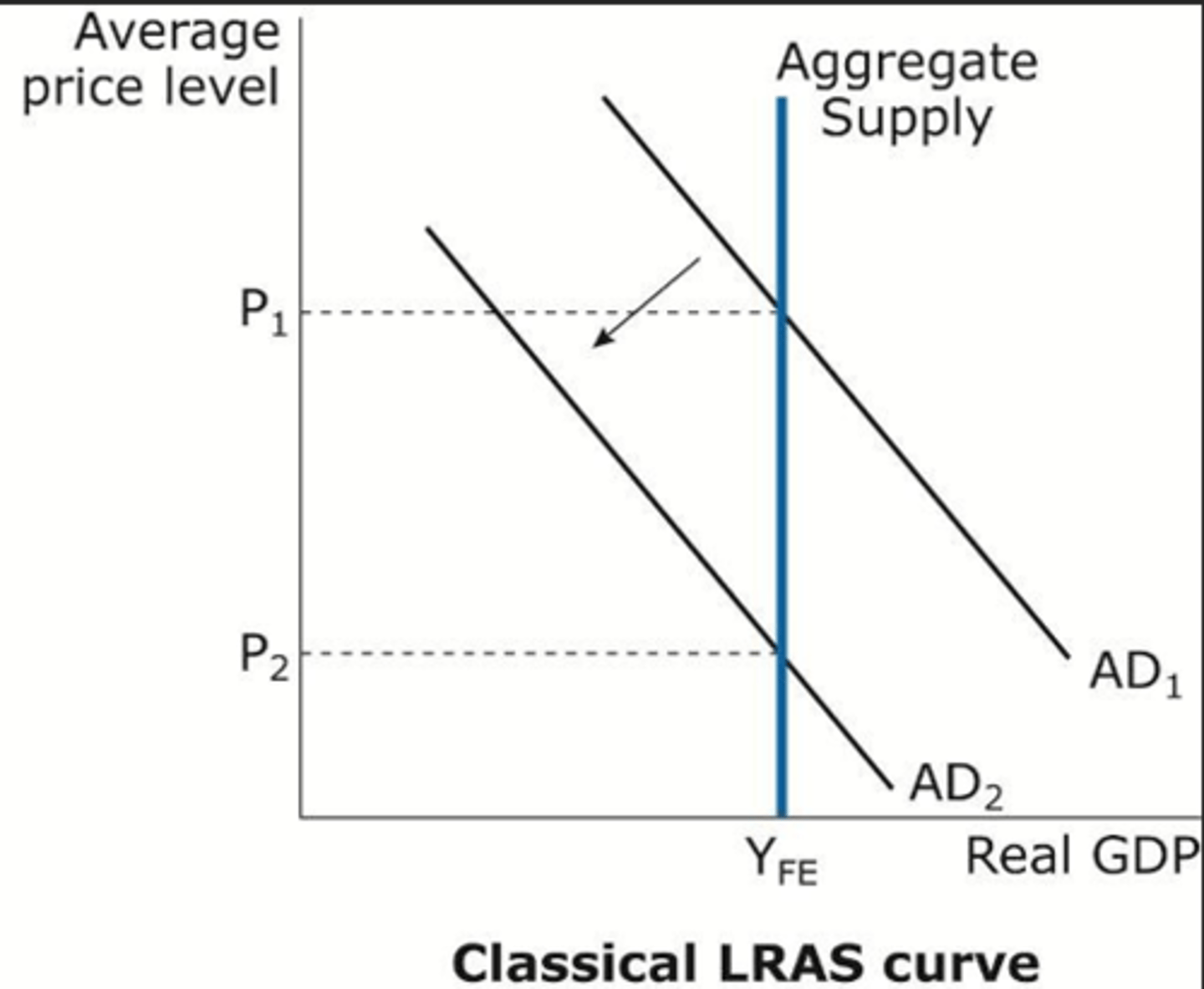
Explain Classical Economist view of LRAS
Classical economist:
- Perfectly inelastic supply curve at the Full Employment (YFE) output
- Economic output is determined by supply-side factors
- In the long-run, the economy tends towards full employment
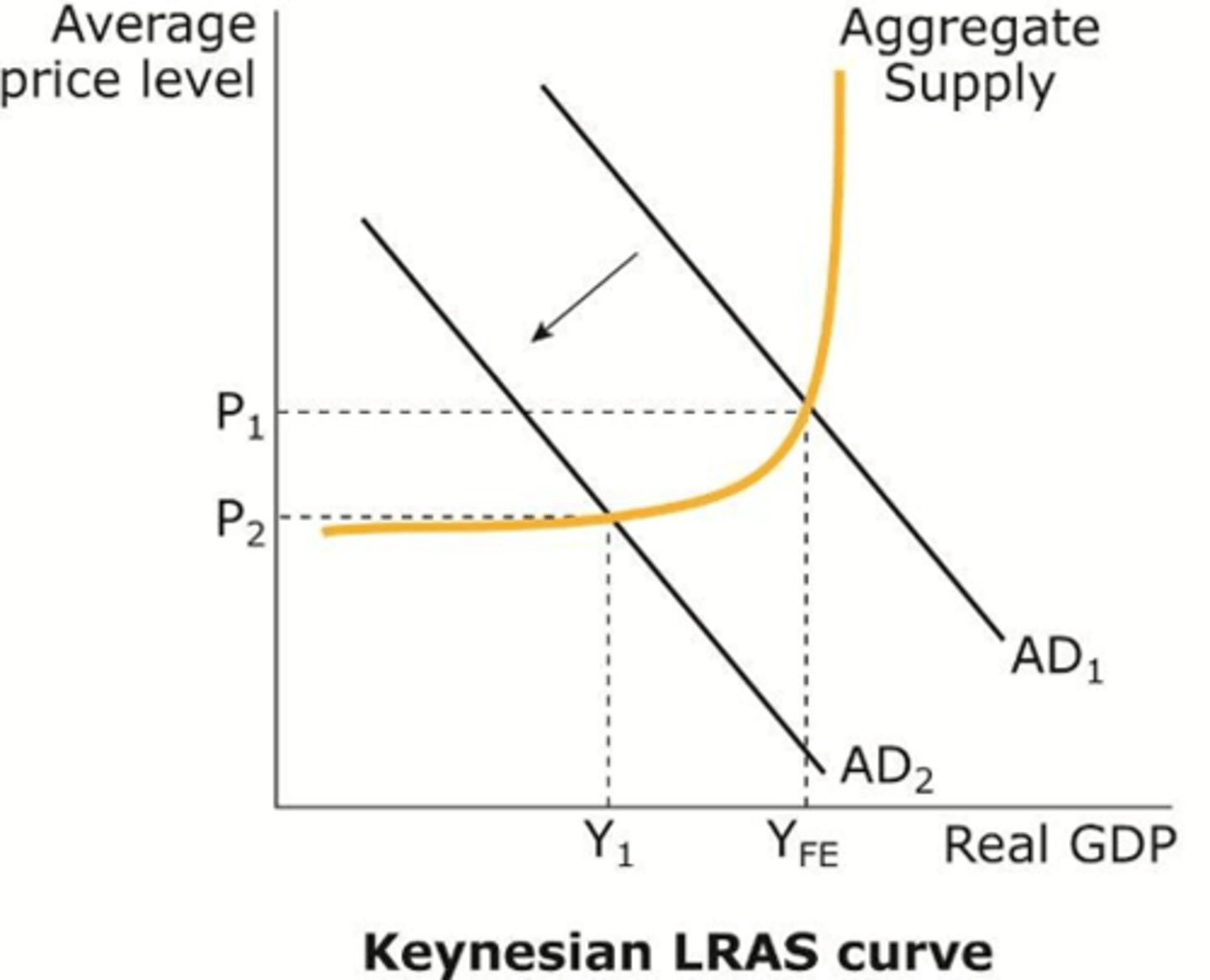
Explain Keynesian Economist view of LRAS
Keynesian Economist:
- At lower levels of growth and demand, factors of production can be acquired at a relatively low rate
- Only when factors of production become in short supply (usually due to increased demand) will firms have to pay more
- Supply will become inelastic at this point
What factors shift LRAS?
- Quality and quantity of F.O.P.
This includes better technology and innovation, more motivated labour, increased investment and new resources
- Increased efficiency
- Immigration of labour
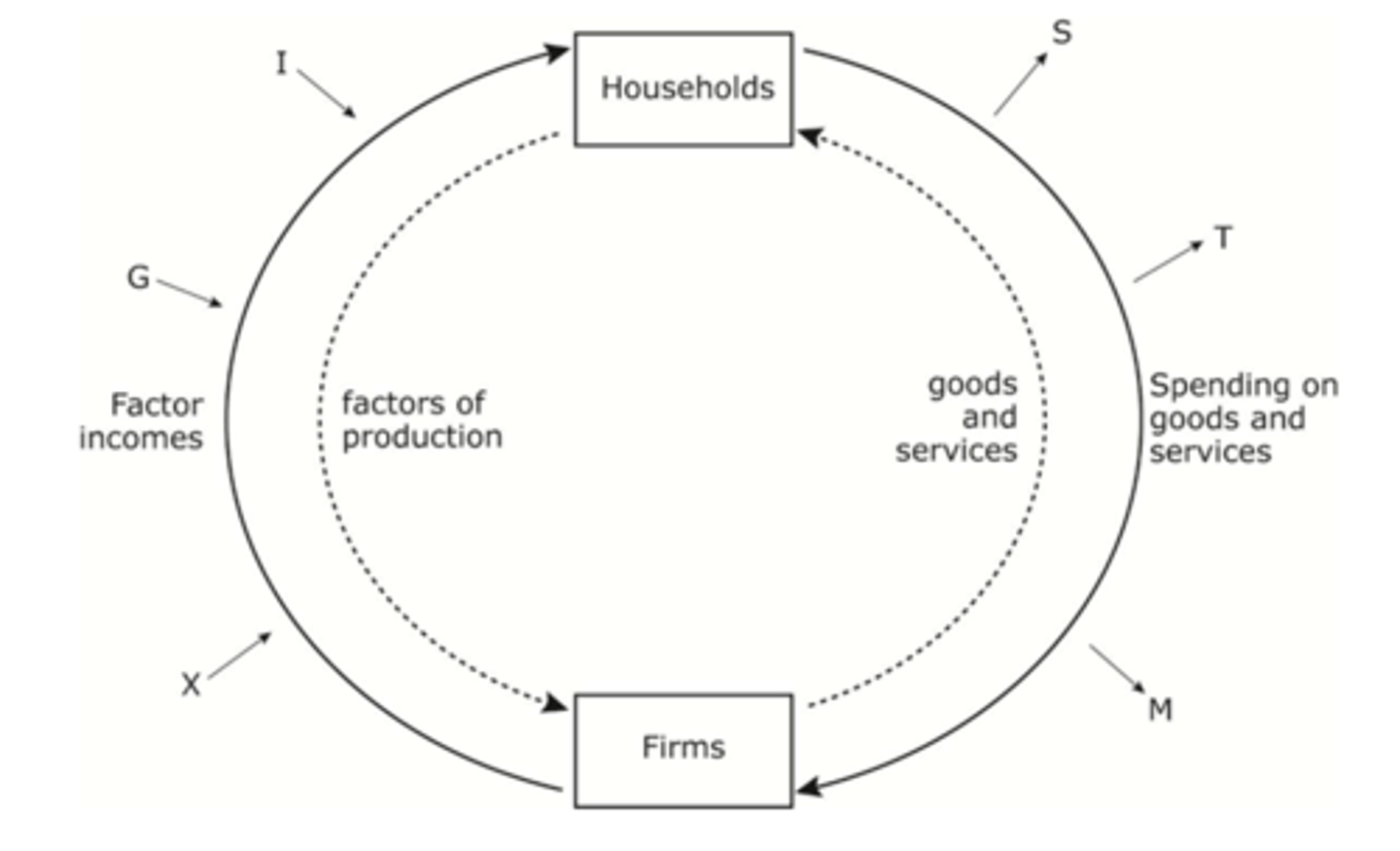
What is National Income?
The circular flow of income diagram, that shows movement of money into and out of the economy, and flows between firms and households.
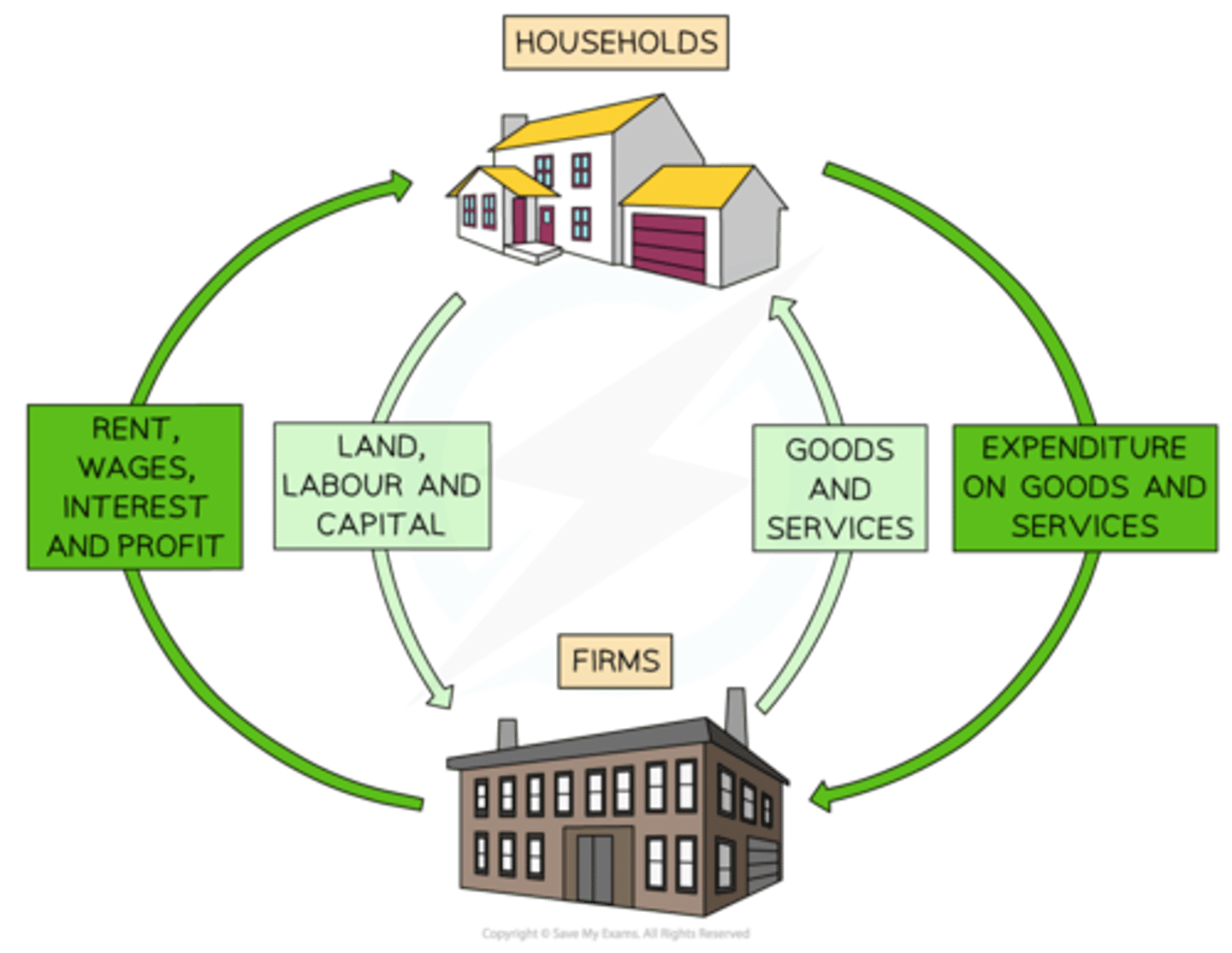
What are the inputs and output between firms and consumers?
To firms:
- Labour, Capital, Land, Entrepreneurship
- Payments for goods and services
To consumers:
- Wages, Dividends, Rent
- Goods and services
What are inputs and outputs called in the circular flow of income, and what are they?
Injections
- Government spending
- Investment (foreign)
- Export revenue
Withdrawals
- Savings
- Taxation
- Imports
When injections > withdrawals, this represents economic growth (increase in GDP)
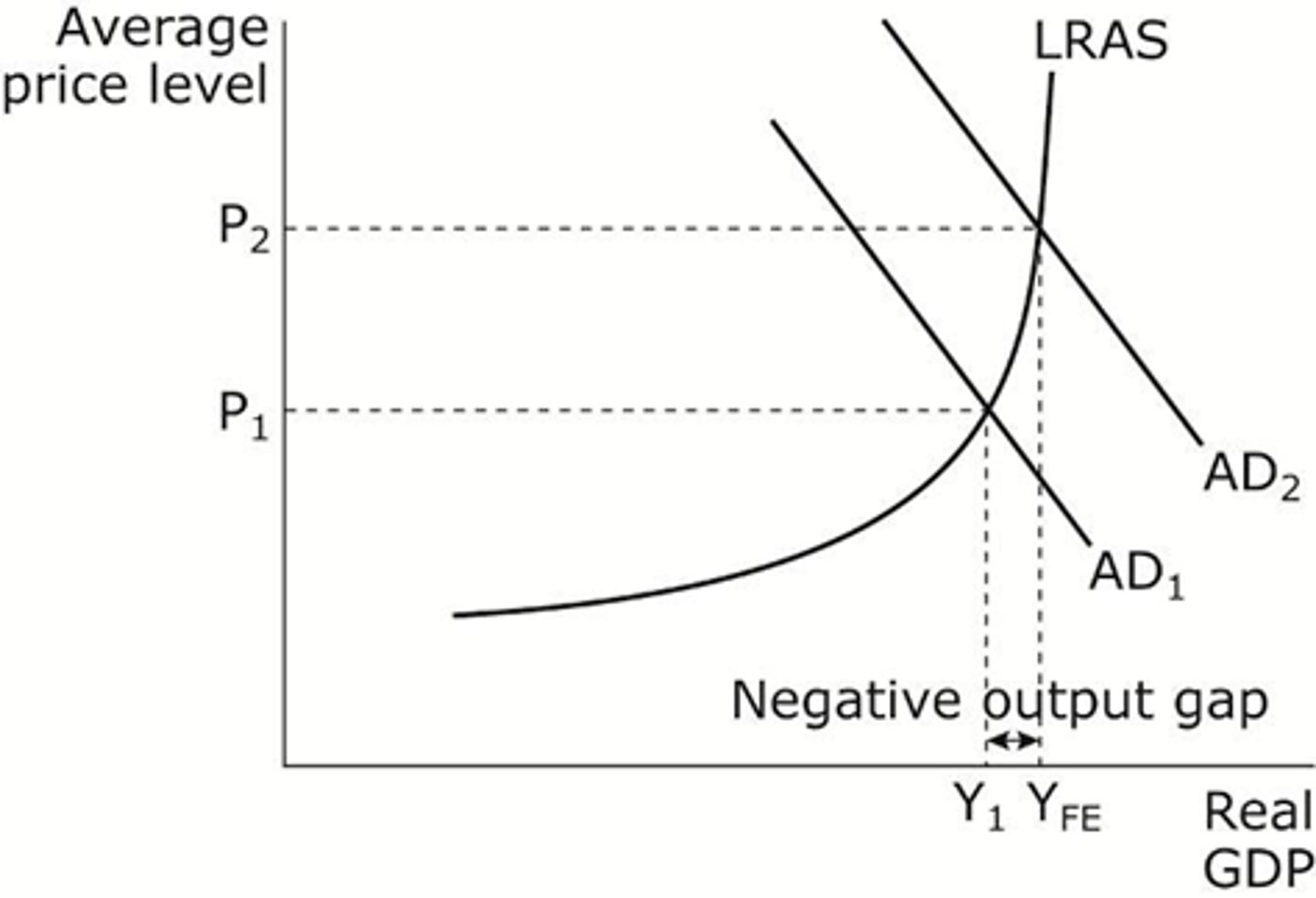
What is the equilibrium called on a SRAS/LRAS curve?
Short/long-run Real National Output Equilibrium
Diagram explanation for changes to LRAS or SRAS Diagrams
1. Describe the intitial position of equilibrium, and its meaning in context (LRAS/SRAS)
2. Describe the shift, what causes the shift and how it effects the price level
3. Describe the new equilibrium, its position relative to other curve and how it bring output close/further
4. Comment on Keynesian vs Classical view
What is the Multiplier?
The ratio of how an injection into the economy results in a further change in real income.
What is the Multiplier formula?
1/MPW (Withdraw) or 1/(1-MPC)
The MPW is derived from:
- MPS (Save)
- MPT (Taxation)
- MPM (Import)
Example of Multiplier Effect
Money is raised from exports
Increase in wages for workers
Increased consumption by workers on goods and services
Leads to a second round increase in AD
This is a multiplier effect on an injection
What factors effect the multiplier effect?
All those that influence tax, imports and savings:
- Interest Rates
- Exchange Rates
- Fiscal policy objectives (austerity)
- Quality of goods produced
- Immigration
What is short-run economic growth, and what causes it?
A change in one or more components of AD, that results in an increase in AD, shown by a shift right on an AD/AD diagram, or a movement closer to the PPF.
Export lead growth is where (X - M) is high.
What affects how much short-run growth can occur?
- The components of AD
- The multiplier that effects the economy after an increase in AD
- How close AD already is to Y(FE), full employment, as bottlenecks in the economy occur, and/or inflationary pressures arise
What is long-run economic growth, and what causes it?
A shift right in LRAS caused by an increase in the quality or quantity of factors of production, which includes better technology, higher productivity, new natural resources or better levels of education (LLCE)
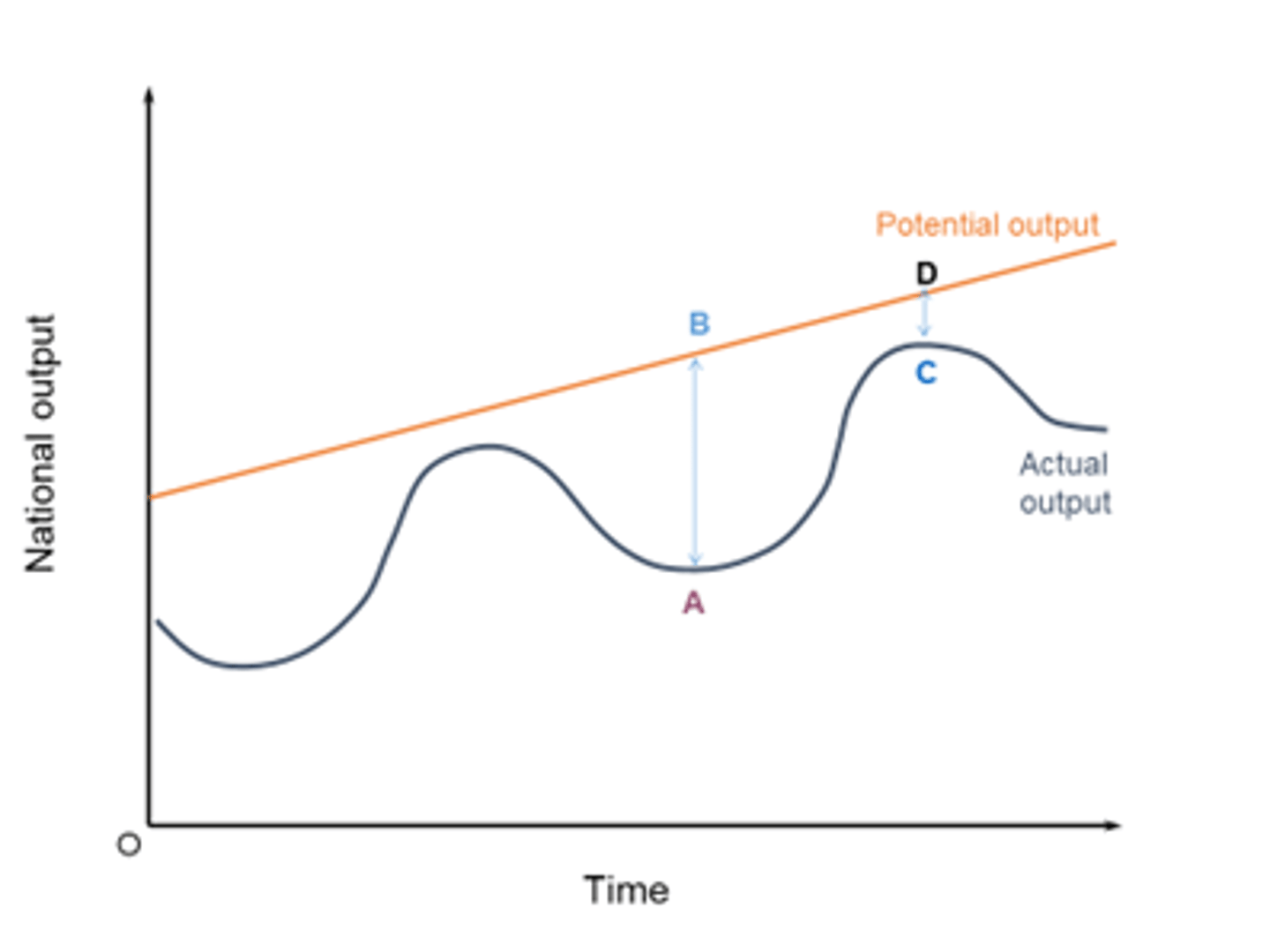
What is the difference between actual and potential growth?
Actual growth is an increase in GDP, whereas potential growth is an increase in the productive capacity of the economy.
What is an Output Gap?
The difference between real and potential GDP. The distance between Y1 and YFE. Classical economists believe they are only possible in the short-term.
Explain a Positive Output Gap?
- A positive output gap is where the real output is greater than the long term productive potential of the economy
- This is not sustainable growth, and likely highly inflationary
- Caused by working overtime
Explain a Negative Output Gap?
- A negative output gap is where real output is less than potential output, so the point of production is inside the PPF.
- The economy is operating with spare capacity
- Keynesian economists believe a N.O.G. can occur in short- and long-run
Draw the trade cycle, labelling all lines and turning points.
Remember: Actual growth rate vs Trend growth rate
Label the Ooutput gaps.
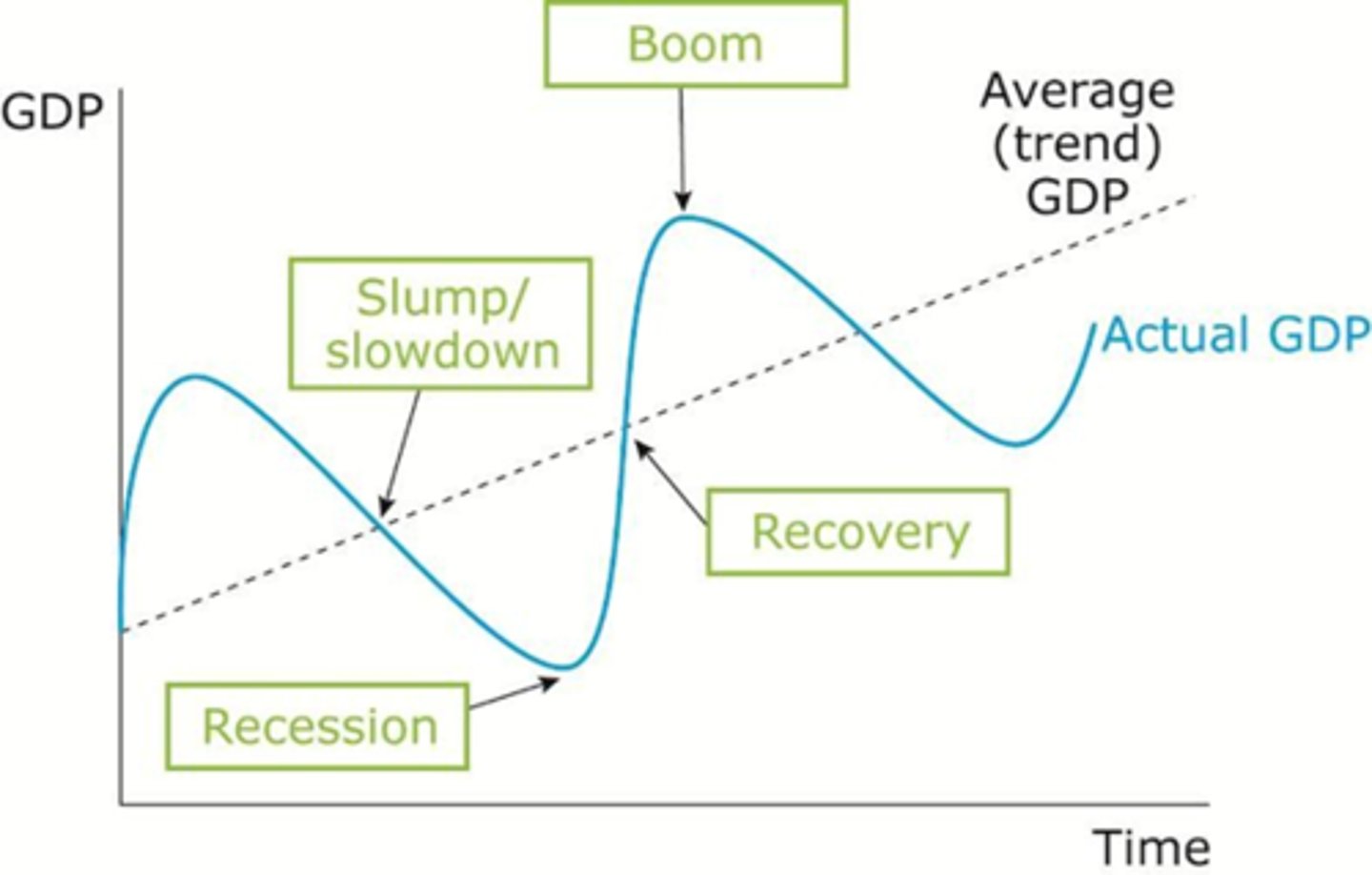
Recession Definition
Two consecutive quarters of negative economic growth
Characteristics of a slowdown
High unemployment
Lower national happiness
Falling tax revenues
Increased benefit payments
Improving B.O.T.
Low inflationary pressure
Characteristics of a recovery
Rising inflationary pressure as approaching the Boom
Near full employment
Higher tax revenues
Greater level of imports (trade deficit)
Benefits of Economic Growth
- Higher standards of living (SOL)
- Higher tax revenues
- Increased business confidence
Costs of Economic Growth
- Inflationary pressure, decrease in real income
- Greater demand for imports
- Demand-pull inflation
- Negative externalities
- Inequality
What is the purpose of Demand-side Policy?
To shift Aggregate Demand (AD) by influencing the factors that comprise it.
What is fiscal policy?
Manipulation of government spending and taxation to influence AD. This is done by the Central Government and present it at the annual budget meetings.
Types of fiscal policy
Expansionary - combatting slowdown in GDP by raising G and cutting T
Contractionary - used to try and avoid inflationary pressures and issues by too fast GDP growth, increasing T, decreasing G
Discretionary policy encompasses both of these as they are deliberately to expand or contract the economy.
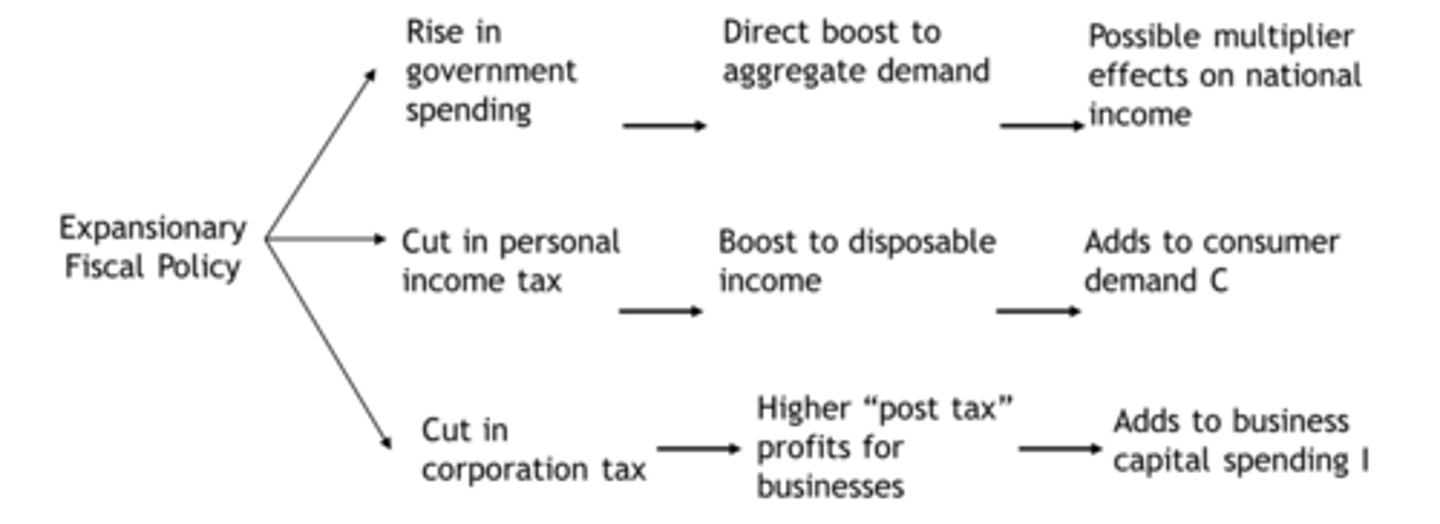
Potential impacts of expansionary fiscal policy
- Crowding Out - where government activity in a sector causes a shift in supply (reduced investment)
- Inflationary pressures
- Increased national debt (continued budget defecit)
- Reliance on businesses/household on subsidies or benefit payments
An increase in government spending requires cash, so more borrowing demand, commercial interest rates rise, borrowing more expensive.
What does the effectiveness of fiscal policy depend on? (evaluation)
- What increased government spending is used for
- Whether financial markets increase costs of lending
Side effects of fiscal policy changes
- Increased corporation tax reduces retained profits, and therefore decreases AD
- Lower income taxes incentivise employment
What is monetary policy?
Manipulation of the money supply by the central bank to influence AD. This is done through adjusting interest rates, invoking Quantitative Easing, or by using a managed exchange rate.
What are the effects of expansionary monetary policy?
Policies aimed at increasing AD
- Low interest rates:
Cheaper mortgages, Less savings, cheaper domestic borrowing
Increase in consumption
Cheaper industrial borrowing, increased confidence
Increase Investment
Underlying assumptions for the effects of expansionary monetary policy
· Mortgage interest rates do not always follow base rate changes
· If confidence is low people and firms will not borrow
· Time Lag of information means implemented too late – 2 years
· Depends on the size of the multiplier
Effects of QE
Increased price of bonds (high demand)
Greater wealth in consumers and banks that own them
Increased Consumption
Increased cash availability
Reduced cost of borrowing
Increased Investment
Negative effects of QE
Increased wealth inequality of bond price increases
Many may not want to borrow