REMOTE SENSING MIDTERM UNIT 1
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Electromagnetic Theory: The source of energy in passive remote sensing
Passive RS: no energy sent for illumination, measure “natural” energy
Sun (Thermonuclear fusion on the surface of the sun) provides the most obvious electromagnetic energy source
Most energy is reflected and we measure it (we use: infrared, visible light, ultraviolet)
Electromagnetic theory: How energy interacts with the atmosphere and land surfaces (overview)
The energy from the sun is radiated from atomic particles, reflects off or is absorbed then re-remitted by Earth’s surface, travels through the atmosphere and is detected by Remote Sensing systems and sensors.
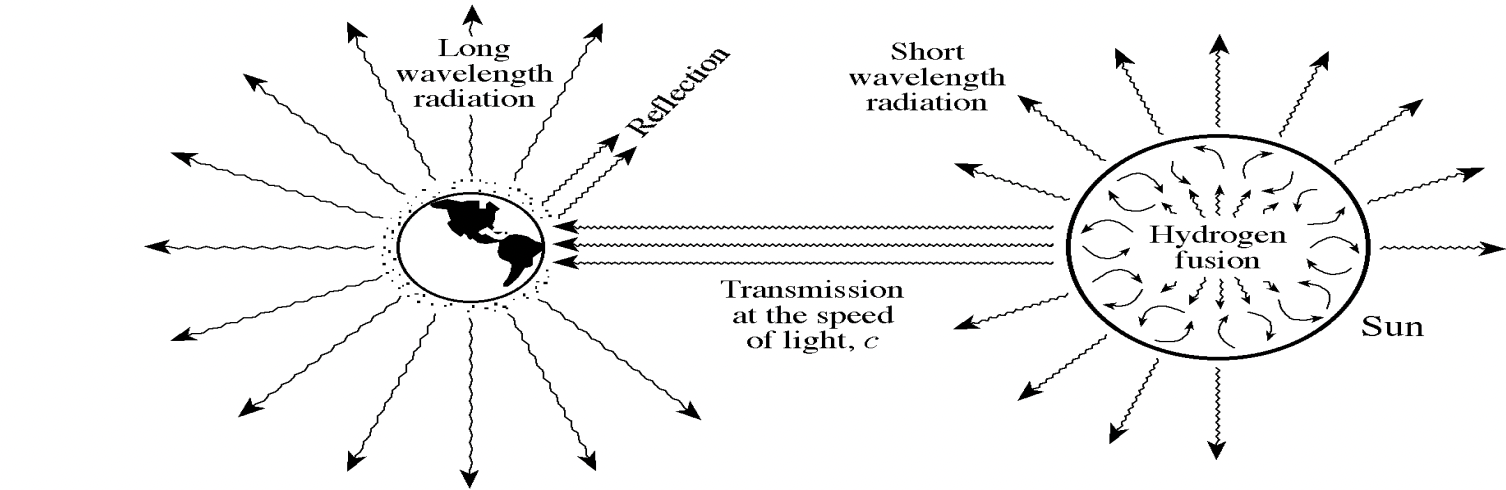
What type of energy transmission can occur in a vacuum? Why is this relevent?
Radiation: the region between the Earth and the Sun is a vacuum
In what ways does energy interact with features on the Earth’s surface / Atmosphere? List and define 4
Earth’s Surface
Refraction: When medium light is passing through are different densities, the light can bend when it passes from one to another
Absorption: Radiant energy is absorbed and converted into other forms of energy.
Reflectance: MOST IMPORTANT radiation that causes our eyes to see colors, causes infrared film to record vegetation, and allows radar images of the earth to be created
Atmosphere
Scattering: When light passes through the atmosphere, atmospheric particles make energy change its normal trajectory
Absorption: Radiant energy is absorbed and converted into other forms of energy. (see absorption band / atmosphere close down)
Negative energy interaction with the atmosphere
Absorption:
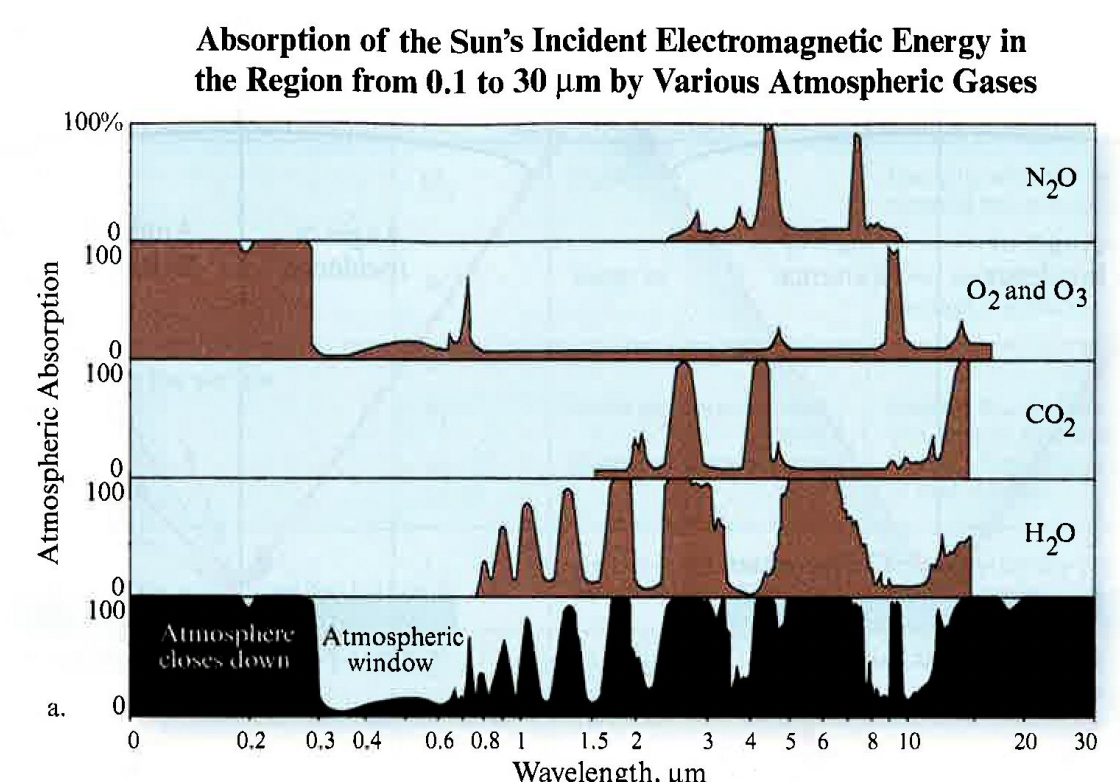
An absorption band is a range of wavelengths (or frequencies) in the electromagnetic spectrum within which radiant energy is absorbed by substances such as water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2 ), oxygen (O2 ), ozone (O3 ), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
The cumulative effect of the absorption by the various constituents can cause the atmosphere to close down in certain regions of the spectrum. This is bad for remote sensing because no energy is available to be sensed.
Radiant flux and its importance
Definition: the total amount of radiant energy (electromagnetic radiation) emitted, reflected, transmitted, or absorbed by an object per unit of time, measured in Watts (W) per second
Importance: By carefully monitoring the exact nature of the incoming (incident) radiant flux in selective wavelengths and how it interacts with the terrain, it is possible to learn important information about the terrain.
What do we measure in Remote sensing?
reflected radiation / incoming radiation per wavelengths/bands (what proportion of the incoming radiation is reflected?)
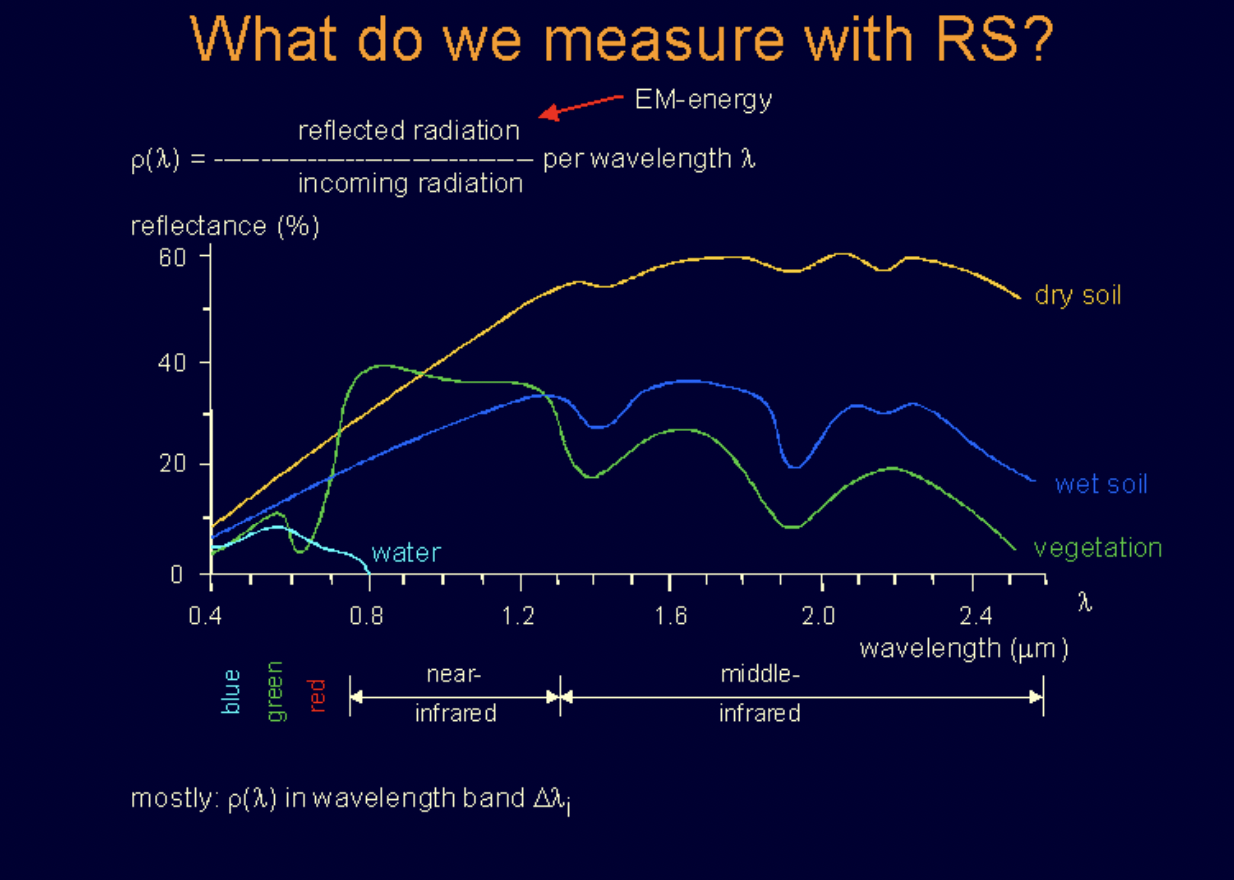
What is a spectral signature?
the unique pattern of electromagnetic radiation reflected, absorbed, or emitted by a material, across different wavelengths, allowing for the identification and classification of materials on Earth's surface
Questions to ask yourself when given a reflectance (y axis) by wavelength (x-axis) plot
Consider the wavelength in which the greatest difference between the reflectance of two objects occurs
Consider what wavelengths it absorbs
Consider what wavelengths it reflects
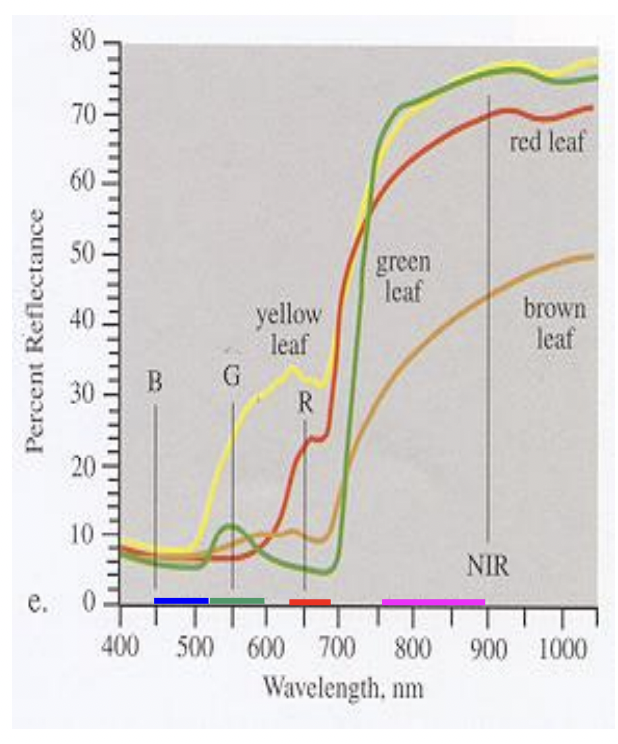
Interpret
Reflectance spectra of vegetation
Chlorophyll reflects higher Green and Infrared, but absorbs more Red
NDVI is (IR-R)/(IR+R); range is – 1 to +1 -
NDVI of an actively photosynthesizing leaf is, e.g. (72-22)/(72+22) = 0.53
Electromagnetic Theory: The role of remote sensing instruments in capturing and analyzing energy
(Radiance and Digital Numbers)
(Spectral Bands)
(Spectral Signatures)
Remote sensing instruments detect and measure electromagnetic radiation interacting with Earth's surface. These instruments capture energy at different wavelengths to analyze surface properties.
Radiance and Digital Numbers
Radiance is the amount of energy detected by the sensor, which depends on the radiation reflected, emitted, or scattered from the surface.
The digital number (DN) in a remotely sensed image represents the measured radiance, where higher DN values indicate higher radiance.
Spectral Bands
A spectral band is a specific range of wavelengths that a sensor can detect.
Different materials reflect and absorb energy differently across spectral bands, allowing for classification of land cover, vegetation health, water bodies, and more.
Energy Interactions & Analysis
Remote sensing instruments analyze energy based on spectral signatures, which are unique patterns of reflectance for different materials.
Sensors like multispectral and hyperspectral instruments collect data in multiple spectral bands for detailed analysis.
Draw plot that explains Remote sensors and Digital Numbers
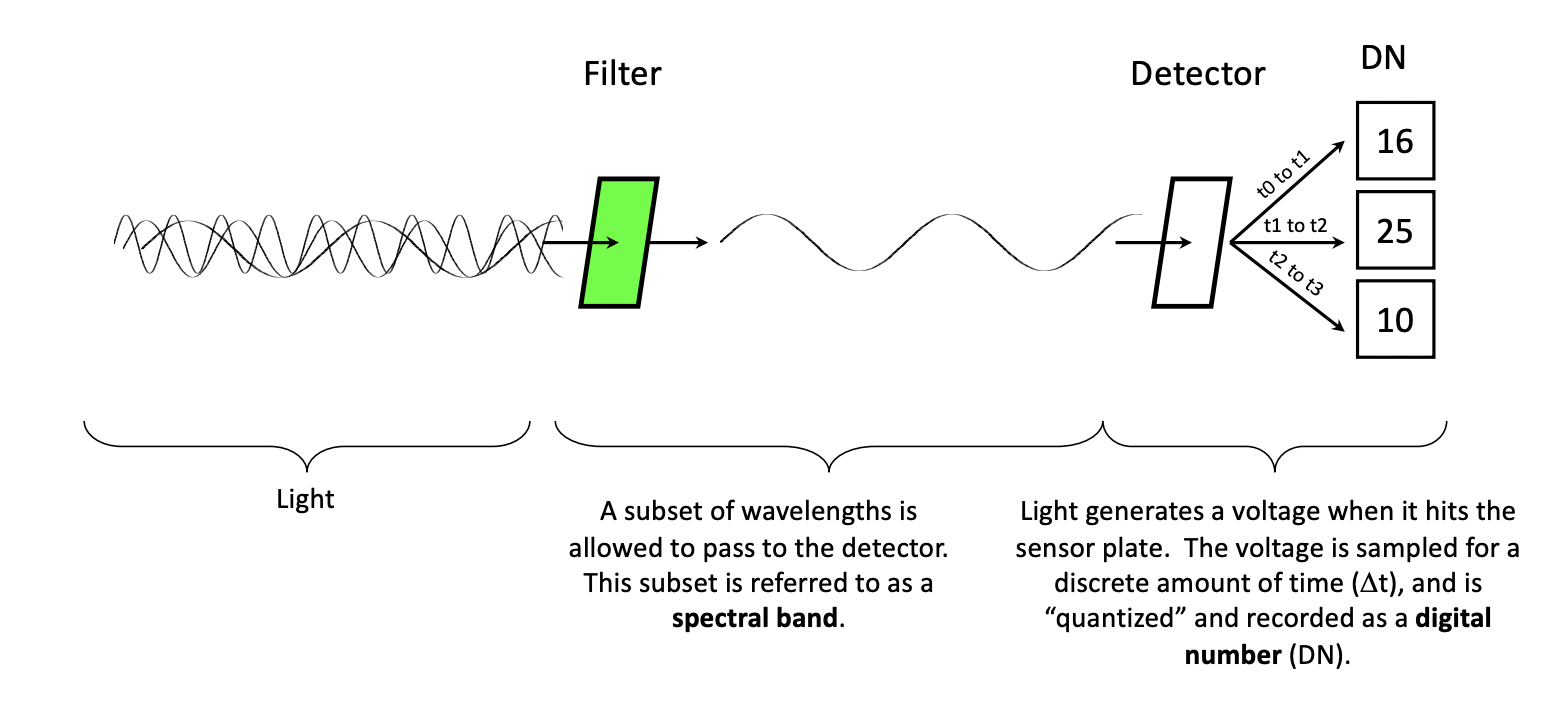
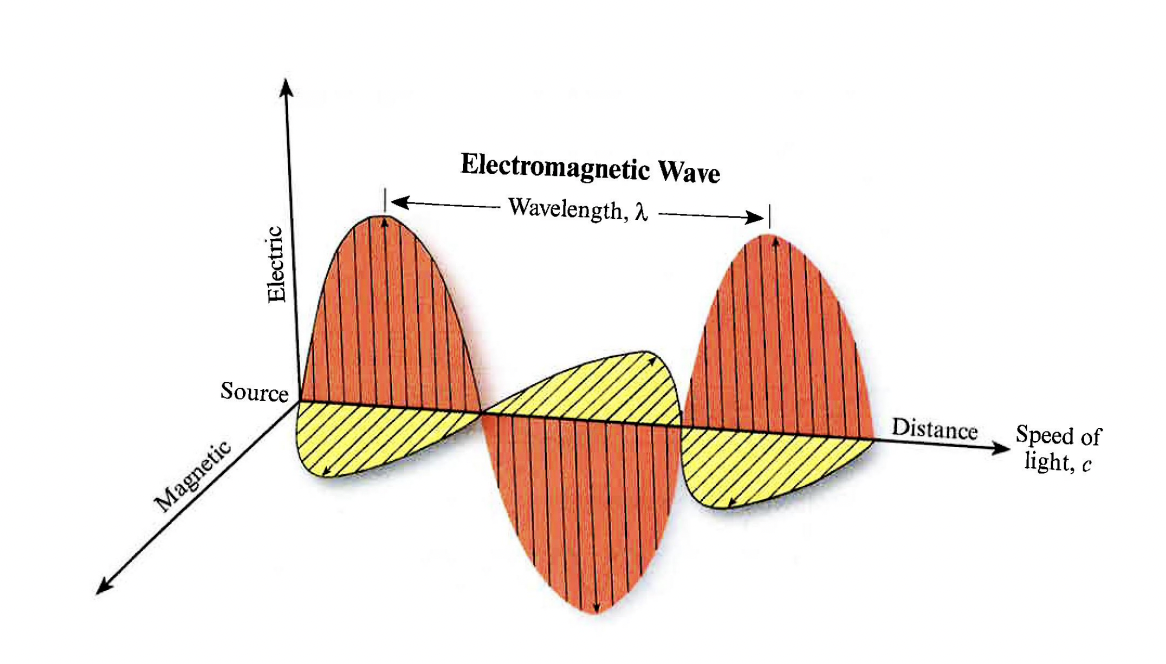
Explain this Model (Electromagnetic Theory)
Electromagnetic wave: Two fluctuating fields, electric and magnetic, which are vectors and right angles perpendicular to direction of travel
Wavelength: distance between two wave peaks in an electric wave
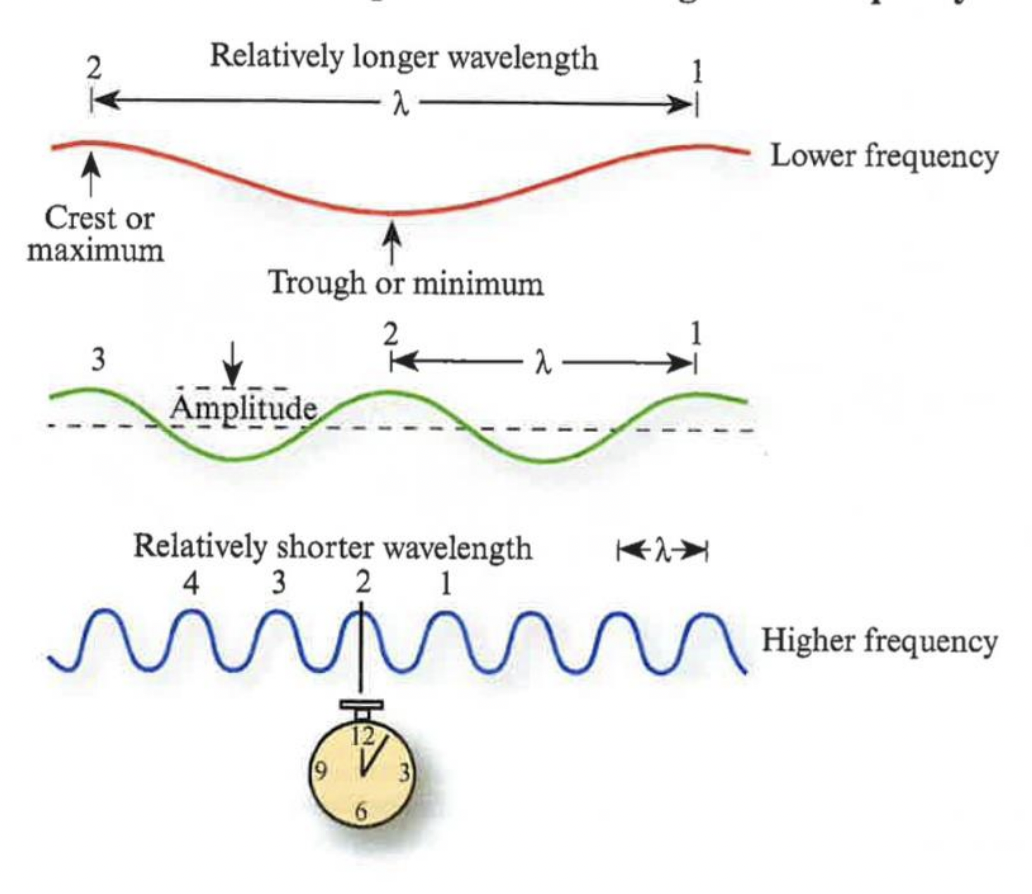
Explain this plot (Electromagnetic Theory)
Frequency is inversely proportional to wavelength
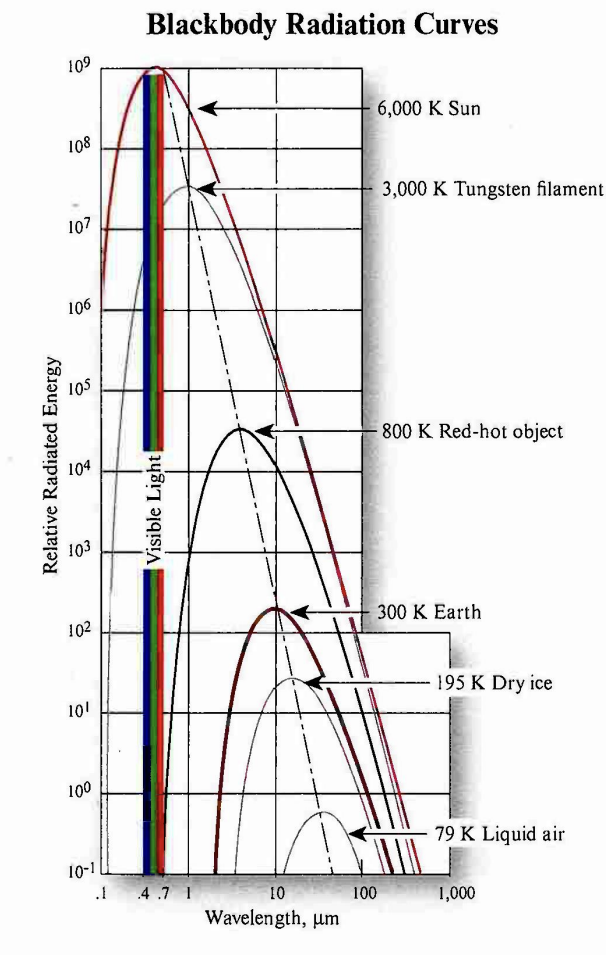
Explain this plot (Electromagnetic Theory)
A Blackbody: It's an ideal object that absorbs all radiation that hits it and emits radiation perfectly.
Temperature & Emission: Hotter objects emit more radiation and at shorter wavelengths (higher energy).
Shape of the Curve: The curve shows intensity (how much energy is emitted) at different wavelengths.
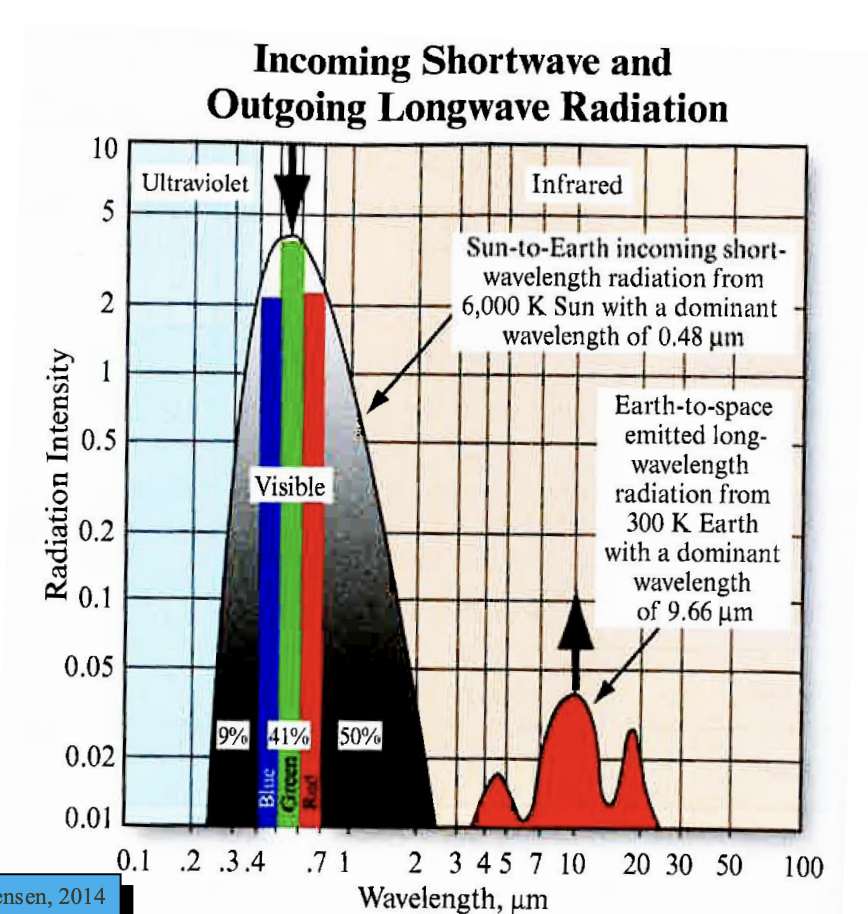
Explain this plot (Electromagnetic Theory)
The Sun approximates a 6,000 K blackbody with a shorter dominant wavelength (green light). It produces 41% a lot of its energy in the visible region from 0.4 - 0.7
Earth approximates a 300 K blackbody with a longer dominant wavelength
Remote sensor detectors can be made sensitive to energy in the nonvisible regions of the spectrum
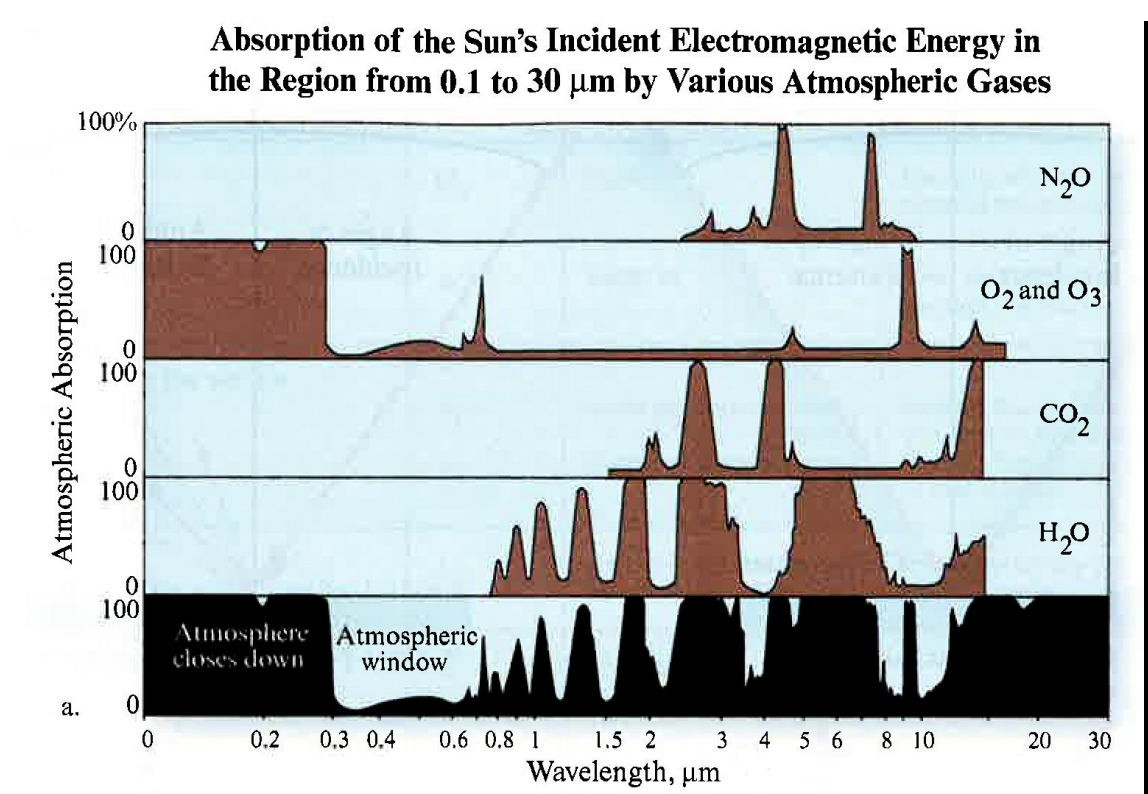
Explain this plot
An absorption band is a range of wavelengths (or frequencies) in the electromagnetic spectrum within which radiant energy is absorbed by substances such as water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2 ), oxygen (O2 ), ozone (O3), and nitrous oxide (N2O).
The cumulative effect of the absorption by the various constituents can cause the atmosphere to close down in certain regions of the spectrum. This is bad for remote sensing because no energy is available to be sensed.
wavelengths for visible light
red
green
blue
(0.4-0.7)
Blue = 0.4 - 0.5
Green = 0.5 - 0.6
Red = 0.6-0.7
wavelengths of NIR
(.75 - 1)
draw the plot to show how satellites receive EMR
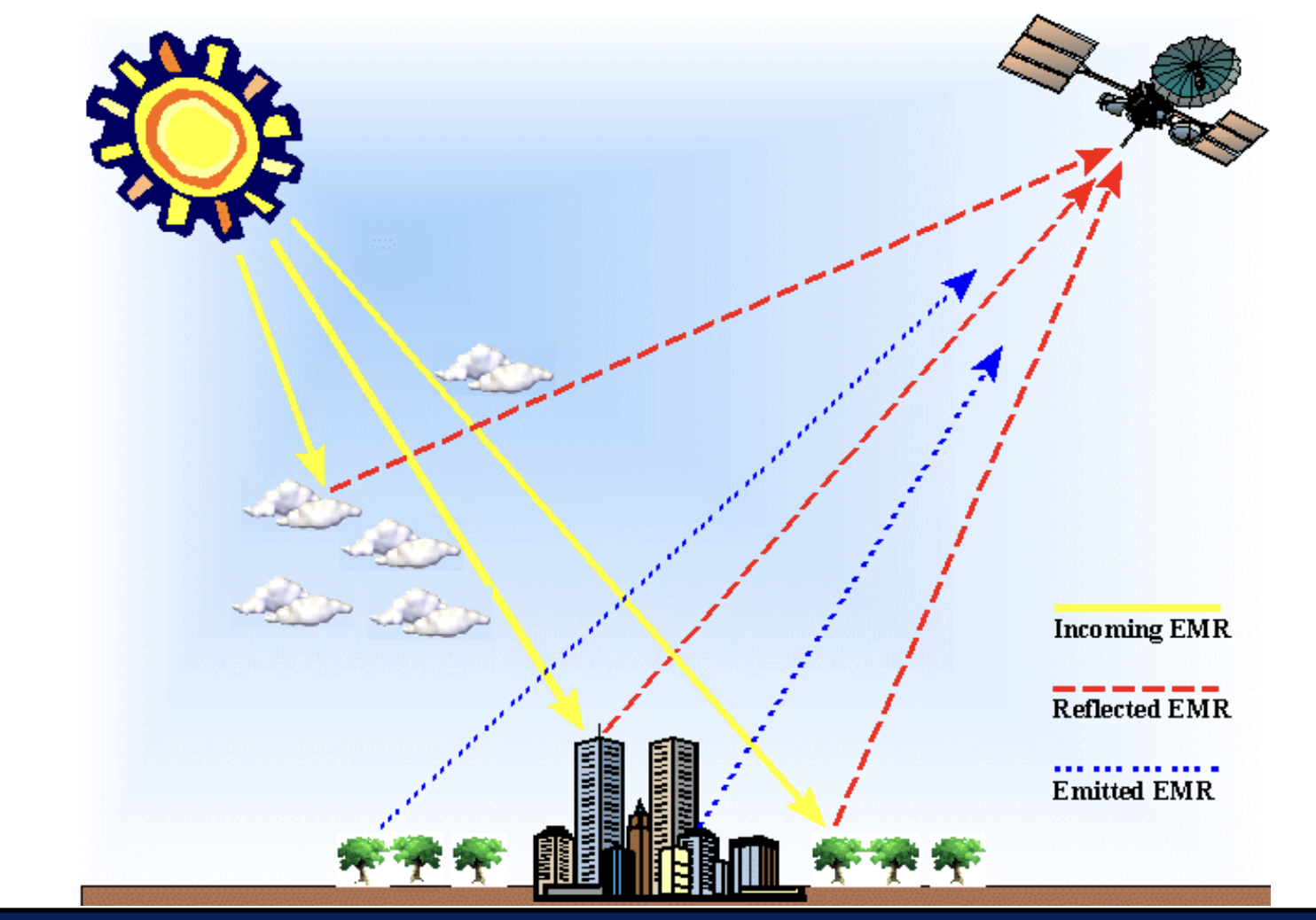
active vs passive remote sensing
Passive RS: Measures naturally emitted or reflected energy from the Earth's surface. (Sun, Earth energy)
Active RS: Emits its own energy (e.g., a laser or microwave signal) and measures the reflection.