Marine Ecology Exam 1
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
Physical _______________ can play a disproportionate role in limiting the distribution of organisms, and can set the __________ of where organisms can live.
environmental extremes
outer limits
Physical environment alters _____________ for many ecological processes.
Interaction strength
Physical Drivers (6)
light regime
temperature regime
hydrodynamic regime
chemical regime
mechanical disturbance
gradients & rates of transfer
Interactions between physical context and species occur at _______________. Variability of conditions across _______ and _______.
several spatial scales
space and time
Biomechanics
How the flow of water affects the body of an individual
Molecular diffusion
Quantifies the rate at which particles disperse from areas of higher to lower concentration
What is molecular diffusion influenced by?
Temperature
Viscosity
Particle size
How does viscosity affect marine ecological processes?
How animals move/sink
How drag affects seaweed or coral shapes
Seawater’s viscosity changes with ________ and _______, which in turn influences organism ______ and _______ use.
temperature and salinity
behavior and energy
Specific Heat
How much heat you need to raise 1 g of a substance by 1 degree
Reynolds Number
Relative importance of inertial & viscous forces and consequences of their relative importance
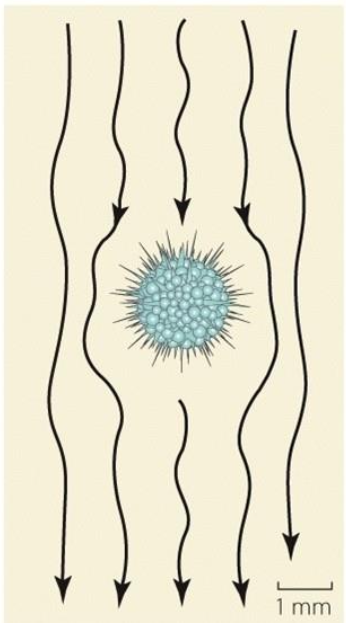
Does this organism have a high or low Reynolds number? Why?
Low
Environment is very viscous
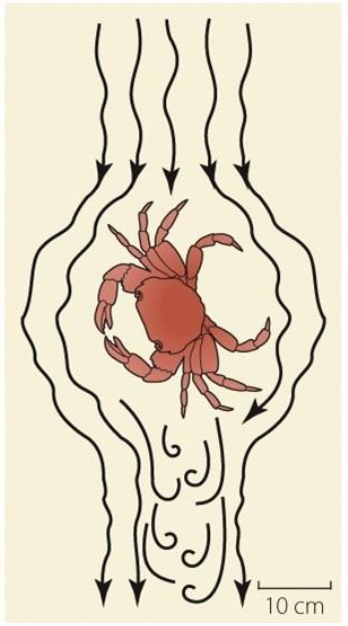
Does this organisms have a high or low reynolds number? Why?
High
Environment is very fluid
What are the 3 key forces?
Drag
Lift
Shear
What is drag?
The force that acts opposite the direction in which the organism moves
How does drag affect motile and sessile organisms?
Sessile: can cause dislodgment/breakage
Motile: takes more energy and streamline to reduce drag
What is lift?
A force that acts in a direction perpendicular to the flow and is upward in most situations. Results from lower pressure on the top than bottom.
What is shear?
How much the water moves at different speeds along the height of an organism
Turbulisors
Used by pelagic fish to delay boundary layer separation. Use at the widest point of their body to induce turbulent flow
What is a boundary layer?
Distance over which the object reduces the free stream velocity
What is the boundary layer influenced by?
Size, rugosity, flow speed, fluid density and viscosity
Fast currents ______ the thickness of boundary layers, whereas weak currents _________the thickness of boundary layers.
reduce
increase
What is Benthic boundary layer?
Large-scale boundary layer over the sea floor
What is momentum boundary layer?
Forms around each object/organism
What is the diffusion boundary layer?
Thin viscous layer very close to each object/organism where there is very little fluid motion and diffusion/conduction are the only transport mechanisms.
Organisms exchange heat, gases, and nutrients with their environments via _______
Gradients
Gradients can be created by (2)
Organism
Shaped by environment
Exchange happens without a gradient (T or F)
False
Heat flows from ______ to ______ areas
warmer to colder
Intertidal organisms face temperatures __________ higher than surrounding area
10-15 degrees
Greater flow _______ DBL and _________ mass transfer, which can enhance various biological processes
reduces
enhances
Particle flux =
flow velocity x concentration
If flow velocity is too high, prey capture/retention is _________
compromised
If flow velocity is too low, a _______ concentration of food is required to achieve the same flux
higher
Increasing turbulence can ________ the detection range and probability response by both predator and prey
decrease
What is dispersal?
Movement of individuals of a population away from their native habitat
Roughly ____% of all marine organisms have a biphasic life cycle and produce planktrophic propagules
80%
Dispersal among populations links them together is called a __________
metapopulation
What is important about dispersal?
Some populations act as larval sources, sustaining others
Species distribution range
Colonization of new habitats
What are the biological determinants of dispersal spread?
Pelagic larval Duration
Larval feeding/behavior
Adult behavior
What are the oceanographic determinants of dispersal spread?
Temporal variation in ocean conditions
Habitat patchiness
Retention vs immigration
What are the ecological determinants of dispersal spread?
Selection for/against immigrants
Population size
3 Basic modes of larval development
Direct
Lecithotrophic
Planktotrophic
Direct larval development
No larval stage
Internally brooded
Lecithotrophic larval development
non-feeding larval stage
Do not require food to complete development
Short PLD
Planktotrophic larval development
Feeding larval stage
Incapable of completing development w/o feeding
Long PLD
Direct: Larval mortality
Protected eggs
High survival rate
physical/chemical defenses
Lecithotrophic: Larval mortality
physical/chemical defenses
intermediate survival rate
Planktotrophic: larval mortality
Few defenses
low survival rate
Episodic regions of enhanced shear and vertical velocities such as _____, ______, ______. Accumulate passive, buoyant particles and weakly swimming organisms
Fronts, eddies and upwelling zones
Increased primary productivity and concentrated food biomass may ______ larval development and _____ PLD
accelerate and shorten
For actively swimming larvae, temporally varying patches of prey may _______ survivorship and _______ aggregation.
enhance and promote
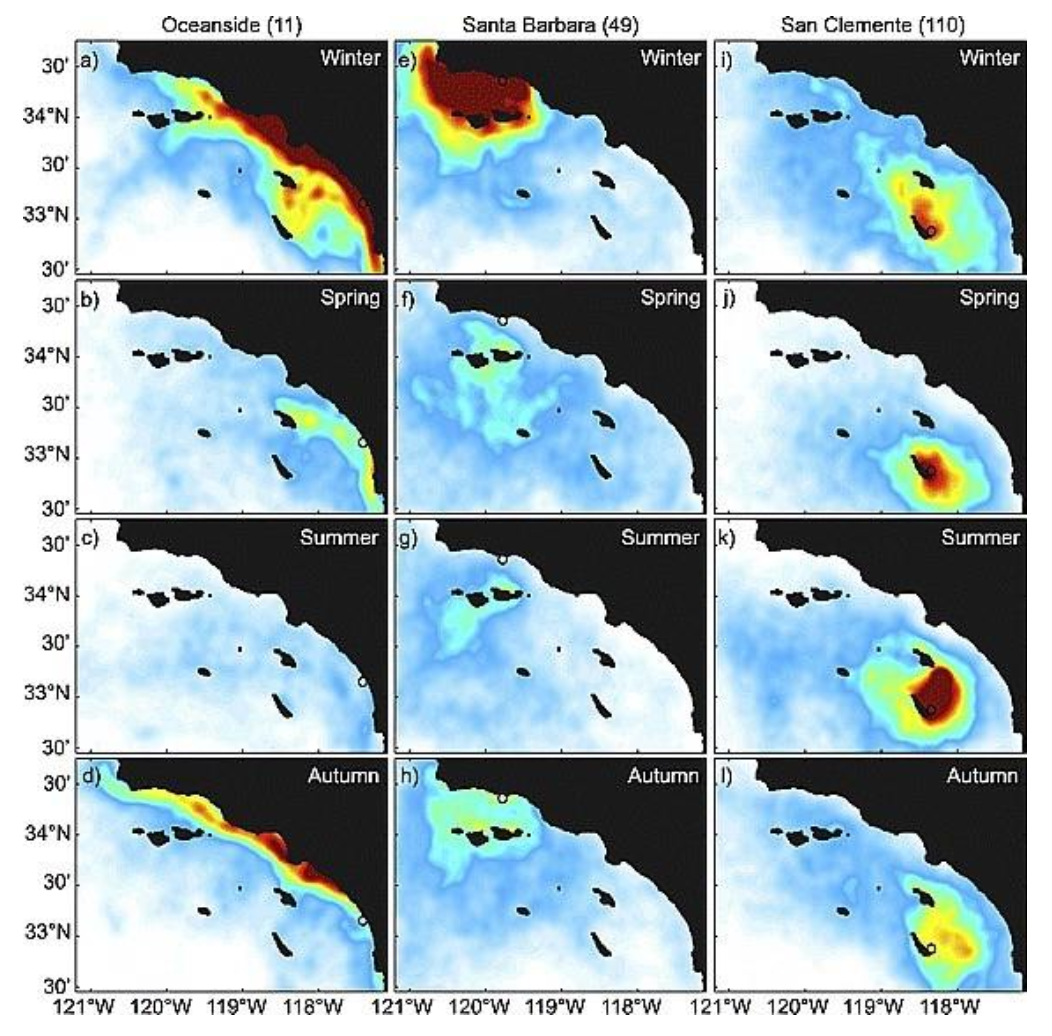
Davidson current dominates in the _______
winter
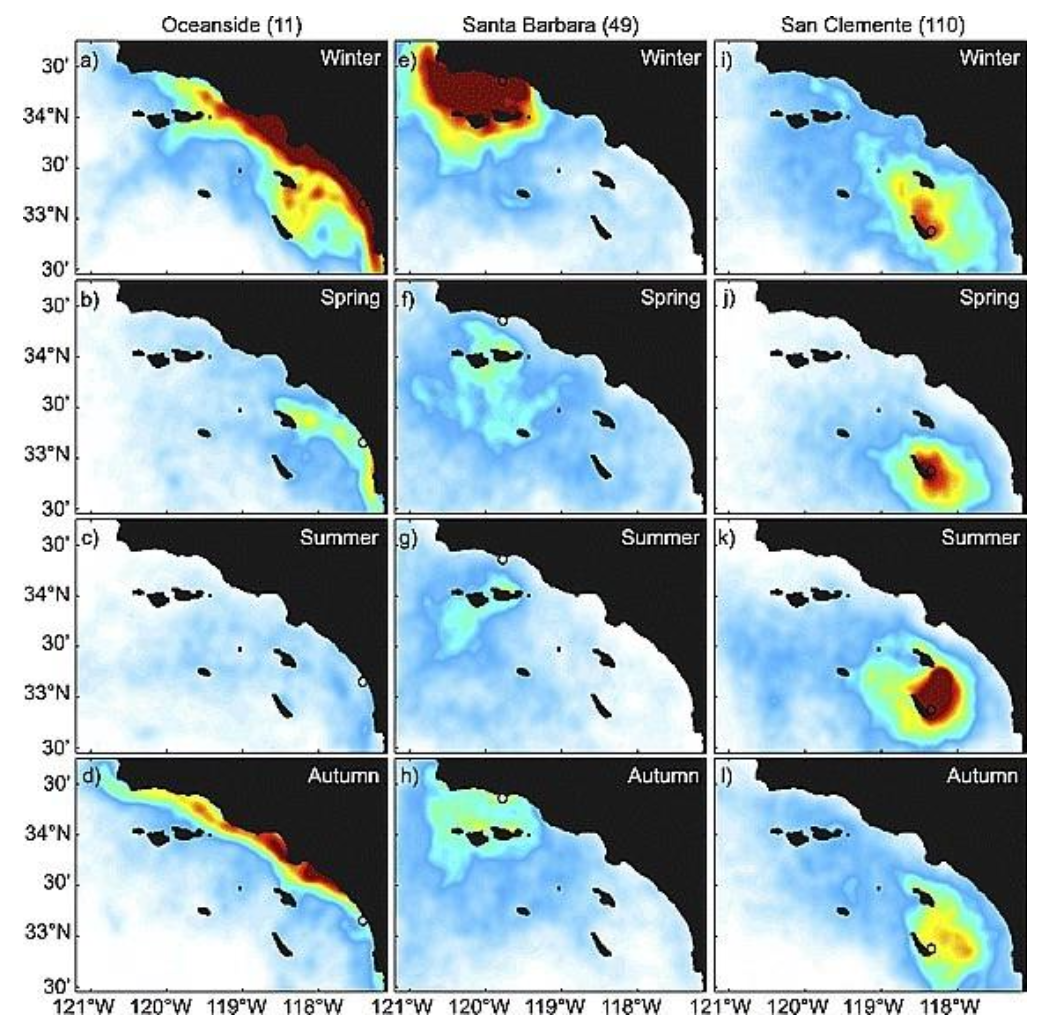
Coastal upwelling dominates in the _________
Spring
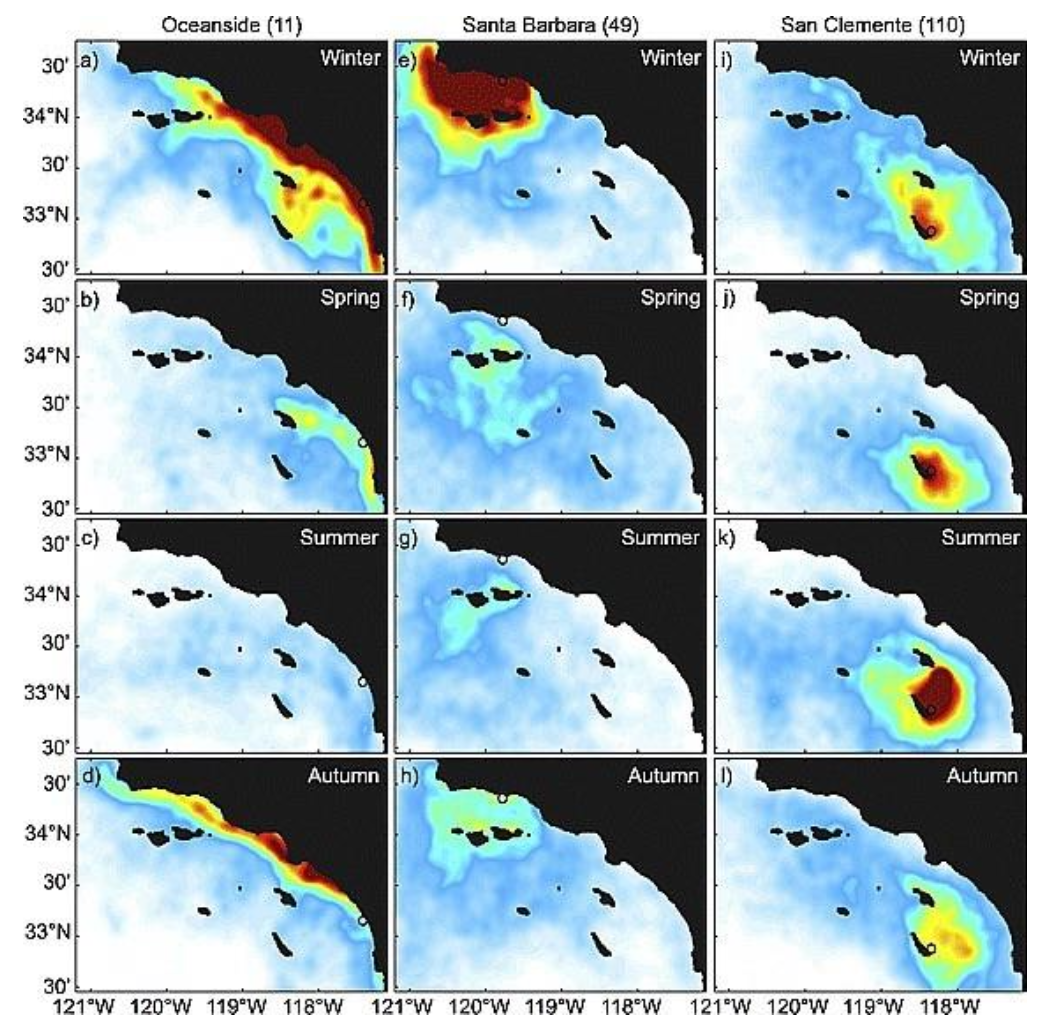
Eddies & recirculation gyres dominate in the ________
Summer
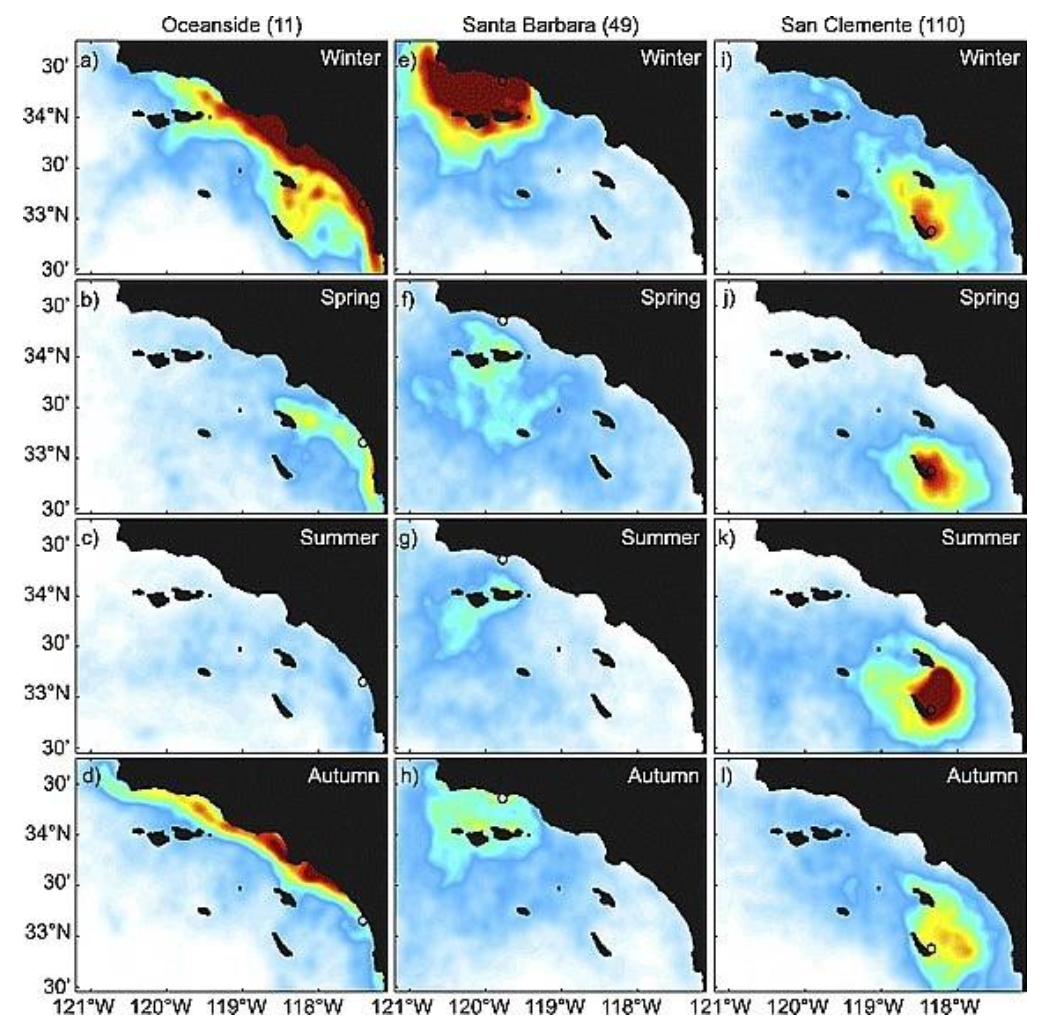
Relaxation of winds and upwelling occur in the ______
Fall
Isolated patches = local retention, what kind of population?
Closed
Continuous patches = more immigration, what kind of population?
Open
What factors influence larval retention?
low PLD
Ocean currents
Habitat patchiness
Locally-sources individuals sometimes survive and reproduce better than immigrants due to ____________, which reduces effective connectivity even when dispersal is high
local adaptation
Benefits of MPAs?
Adult & larvae spillover
Population spillover
Intertidal
Between the tides
Littoral means
shore
What is semidiurnal tide?
2 high tides & 2 low tides
What is mixed tide?
Two high and two low unequal tides
What is diurnal tide?
1 high tide, 1 low tide
Types of intertidal communities (5)
Rocky intertidal
Soft sediment
Estuaries
Salt Marshes
Mangroves
Extent of gradient between ocean & land will often be determined by _______
wave size
What causes zonation in intertidal communities? (3)
Physical limitations
Settlement patterns
Biotic limitations
What is the most likely physical factor determining zonation?
Tides
What are physical factors? (4)
Tidal cycle
Wave action/exposure
Temperature/UV
Substrate types
Pacific Coast has more _______ intertidal communities while the Atlantic coast has more ________ sediment intertidal communities
rocky
soft
Define Littoral zone
Between the highest and lowest spring tides
Define Supralittoral zone
splash/highest zone
dominated by periwinkle snails & lichens
Define midlittoral zone
Upper limit: barnacles
Lower limit: kelp
Upper midlittoral
Only covered by water at high tide
Dominated by: algae, barnacles & periwinkle/turban snails
Middle midlittoral
Regularly covered by water
Dominated by: rock weed, mussels, turban snails & barnacles
Lower midlittoral
Usually submerged, only exposed at very low tides
Dominated by: algae, sea anemones, stars & urchins
What is the SST year round in HI ocky intertidal?
24-28 degrees
What is HI’s zonation?
Supralittoral
Mid-intertidal
Lower intertidal
What are physical adaptations in intertidal? (7)
Aggregate, seek shelter, orient away from sun
Evaporative cooling
Light color
Sculpture, thick & ribbed shells
Heat shock proteins & antifreeze
Strong attachment
Flexibility
Rapid reattachment
Upper limits are determined by ____ factors
physical
Lower limits are determined by ______ factors
Biological
The __________ is the portion of the fundamental niche to which an organism is restricted by factors such as predation, competition, pathogens, etc.
Realized niche
Keystone species concept
Species whose effect on its community is disproportionately much greater than its abundance alone
Top down control
______ plays a major role in structuring some biological communities
Disturbance
Equilibrium
Absolute and relative abundance of sp remains constant and is balanced by intra-and interspecies interactions
Nonequilibrium
There is a balance of absolute and relative abundance globally, but locally, equilibrium is prevented by periodic stochastic disturbances
Intermediate disturbance theory
Local populations are not in equilibrium, but are disrupted by disturbances
Higher disturbance =
Lower chance of secondary & late succession/colonization