econs mixed economy system
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Mixed economic system
An economic system that combines the use of free market economic system with some government planning and control to determine the allocation of resources in the economy
Ownership of resources and decision making is split between private and public sector
Types of government intervention
Direct government provision
Regulations (which includes price control )
Indirect tax
Subsidies
Nationslization
where government takes over ownership of private sector companies or industries
Direct government provision
refers to government producing and supplying goods and services directly to people
Affects consumers not producers (subsidies)
Using money collected from taxes (take from consumer) or borrowing ( need to pay back money to borrower)
Supplied “free of charge” to people or charge a price at a subsidised rate (merit good) —> lack of public good
Direct provision is used to correct which market failures
lack of public good (eg. Government directly provides streetlamp , national defence )
Under production of merit goods and goods with high external benefits (goal : increase supply of merit good)
Abuse of monopoly power (government may nationalise industries that provide essential services such as public utilities like water , aircon ,electric to prevent private sector monopolies from restricting supply and raise prices)
Advantages of direct provision
Directly increase supply of public goods and merit goods that are either underproduced or not produced in a free market
nationlization may directly prevent private firms from abusing their monopoly power
More people (low income consumers) can consume the good at lower prices or free of charge
Ensure that essential services will still be provided even if it is making a loss
Can protect or increase employment by providing jobs for people
Disadvantages of government provision
Opportunity cost may be high (choosing to spend more on one good may mean less spending on other important areas)
Government may increase taxes in order to provide the good “free of charge” or at a subsidised price —> greater tax burden for people
If government borrows money to fund the production —> debt burden will increase
Government may be inefficient and produce poorer quality goods —> gov is non profit motivated - > little incentive to be efficient and cut cost and quality of goods and services may be poor
Regulations (including price control)
regulations are legal rules made by a government to control the behaviour of the people and firms , or control the way something is done
If people and firms fail to comply —> they may have to pay fines or be imprisoned
Aim:to produce a more socially desirable outcome by controlling the forces of demand and supply in a regulated market
examples of regulations
The ban on consumption or production of certain products
Making the use of certain foods compulsory
Setting certain minimum standards for goods and services that producers/consumers must follow.
Government regulations may include setting price controls such as
Maximum prices (price ceiling )
Minimum prices (price floor)
Regulations are used to correct the following market failures
Over consumption of demerit goods and activities with high external cost (price floor)
Under production of merit goods and goods with high external benefits (price ceiling)
Abuse of monopoly power
Over consumption of demerit goods and activities with high external cost , how does regulation correct this market failure
eg. 1 : ban smoking at certain places / ban sake of alcohol after certain hours , to decrease consumption / production of demerit goods
Eg. 2: ban littering / single use plastics / restricting amount of pollutants firms can release into environment / environmental regulations , to decrease negative externalities (harmful spillover effects)
Eg 3 : setting price floor (higher price ) on sale of alcoholic drinks , to reduce consumption of demerit goods
Underproduction of merit goods and goods with high external benefit , how does regulations correct this market failure
compulsory basic education / vaccination —> to increase consumption of merit goods (lower prices )
Abuse of monopoly power , how does regulations affect this market failure
to prevent firms from exploiting consumers ( restricting supply + raising prices ) government can
Set a minimum acceptable service standard (eg, product safety , product quality , delivery time)
Set a maximum price (price ceiling) that the firm can charge
Advantages of regulations
Total ban / restrictions are quite effective in correcting the market failure directly
Simpler to implement (compared to indirect tax / subsidies )
Disadvantages of regulations
High monitoring cost —> government needs to allocate extra resources to monitor behaviour and enforce the law —> OPP cost —> resources could be used in other areas
Regulations that restrict / ban production may force many companies to shut down —> unemployment may increase
Complying with health and safety regulations , environmental regulations and other regulations will cause higher cop, lesser supply , more expensive (higher prices)
Reduces freedom of choice
Penalty is too low = people and firms may not comply with regulations
Compulsory education / vaccinations may not be effective if the poor cannot afford to pay for the good
Price control (under regulations ), price ceiling definition
A legal maximum price on a good ser by the government that is below the market equilibrium price
(Price too high, set lower)
Why does the government set a price ceiling
to make certain essential goods affordable to the poor
To prevent monopoly firms from overcharging consumers
*never on luxury goods
Eg, food price control (essential food, rice , bread) / rent control
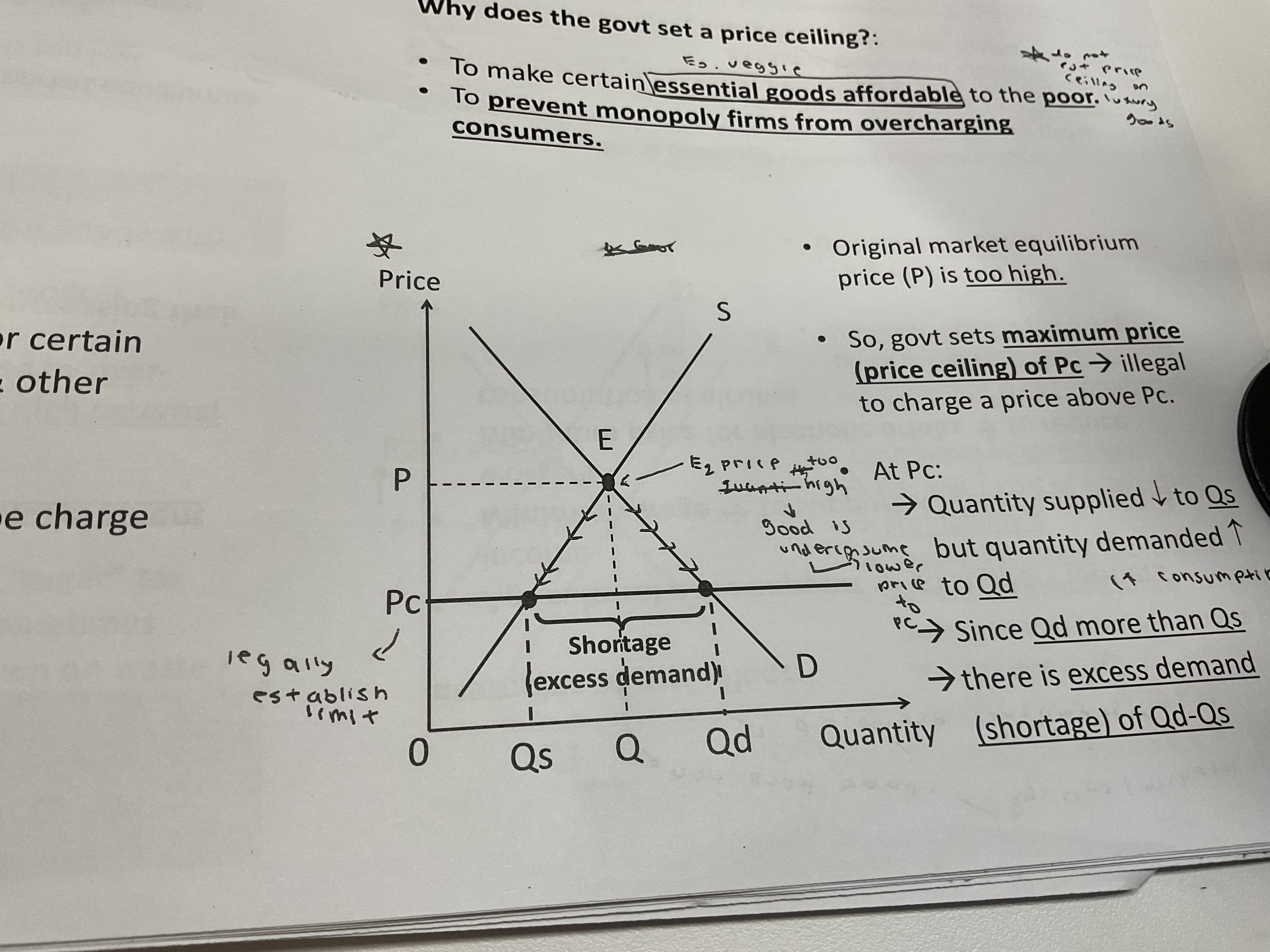
Why do governments need to put a price ceiling
Original market equilibrium price is too high
So government sets maximum price / price ceiling and it is illegal to charge a price above price ceiling
At price ceiling = quantity supplied decreases , but quantity demanded increases
Now, quantity demanded is more than quantity supplied
There is excess demand , causing a shortage
What is a price floor
A legal minimum price on a good set by the government that is above the market equilibrium price (raise price)
Why does government set price floor
Support producers / workers by increasing their income they received
Reduce consumption of demerit goods / goods with high external cost by increasing the price paid
Examples of price floor
Eg 1 : agriculture price support : to support farmers income
Eg 2: minimum wage : to support wages of low skilled workers
Eg 3 : minimum price for alcoholic drinks : to reduce consumption of alcohol
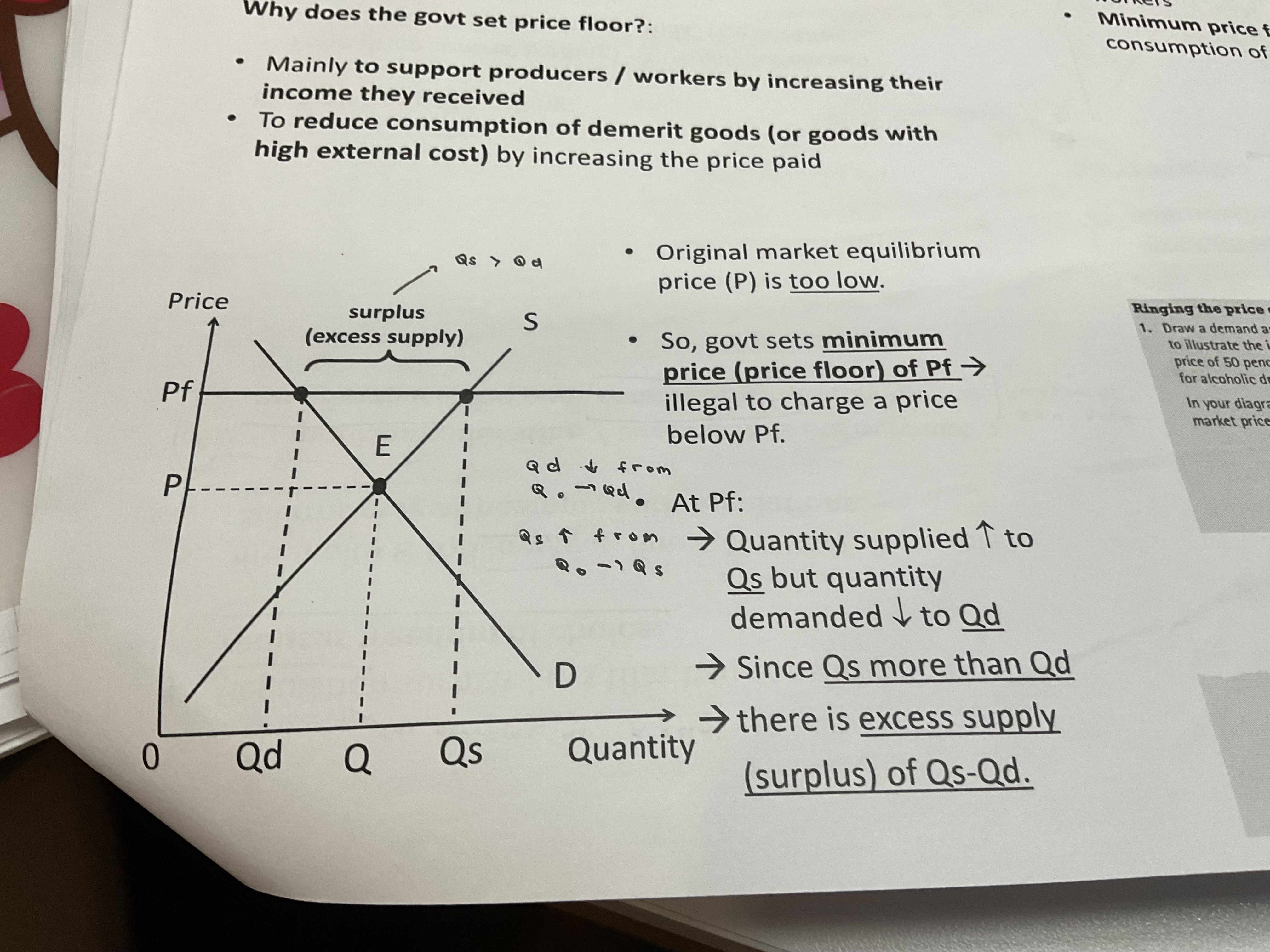
Why do governments set price ceiling
original market equilibrium price is too low
So government sets minimum price / price floor , illegal to charge a price below price floor
At price floor , quantity supplied increases but quantity demanded decreases
Hence, quantity supplied is more than quantity demanded
Causing a surplus, excess supply
Advantages of price floor
Disadvantages of price floor
Indirect taxes
Taxes imposed on goods and services
Used to correct the market failure caused by overconsumption of demerit goods and activities with high external cost
Eg cigs/alcohol
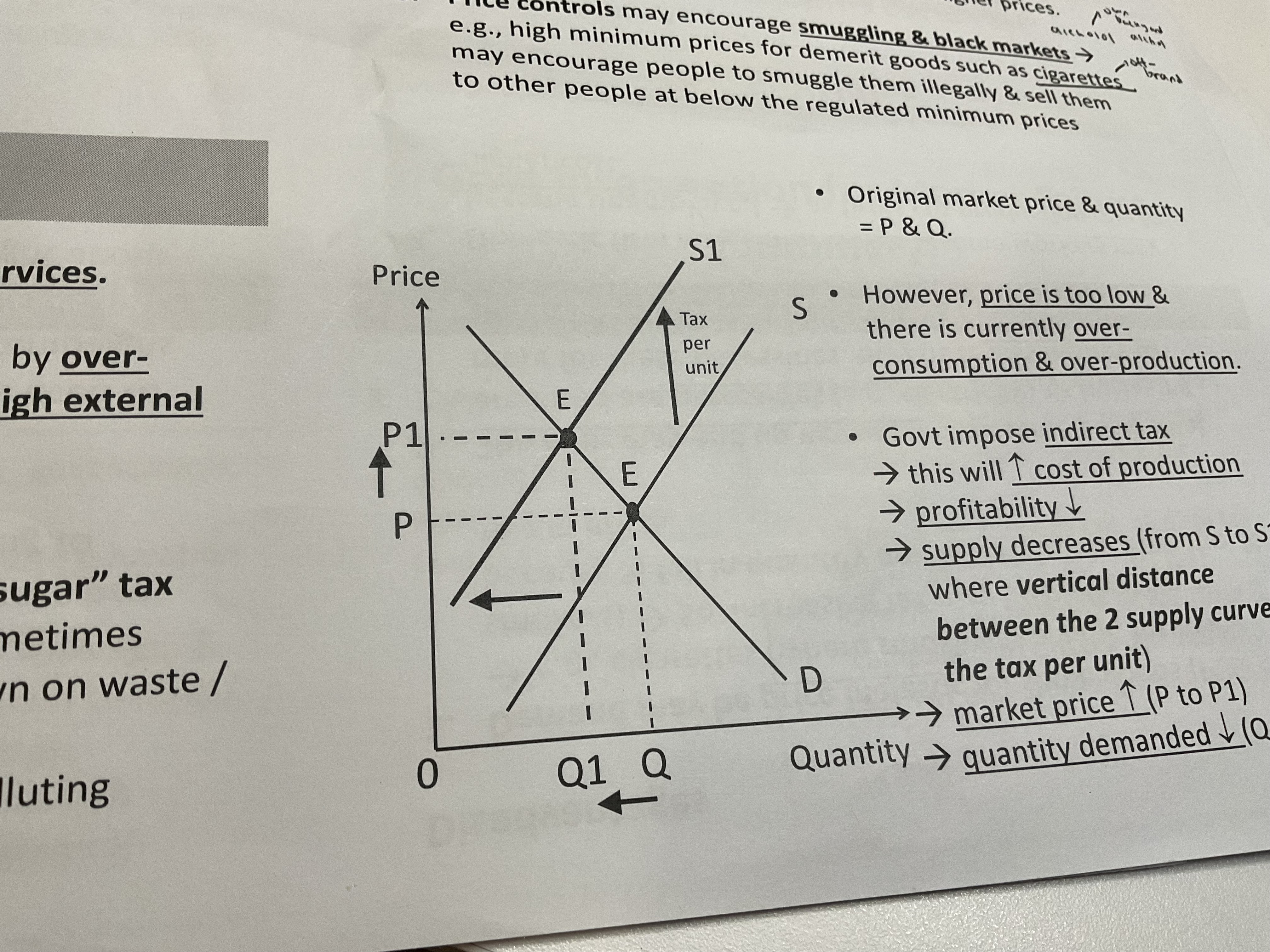
Why does indirect tax lower quantity demanded
when price is too low, there is over consumption and production of the good
Government imposes indirect tax to increase cop and reduce profitability for firms , decreasing supply for S-S1
Between S-S1 —> vertical distance between the 2 supply curves is the tax per unit
Market price increases from P -P1
quantity demanded decrease from Q -Q1
Advantages of taxes
Can help internalise the externality —> making consumers / producers pay for the harm / damage that they are causing to others
Government collects tax revenue —> can be used to finance government spending eg. To pay for campaigns to educate people about harmful effect of demerit goods or the external costs brought about by their activities
Disadvantages of tax
Demand may be price inelastic for some goods (PED<1) , Eg.cigs —> increasing tax may be ineffective as a percentage fall in quantity demanded is less than the percentage rise in price
The poor may end up worse off —> so, eg goods that are taxed are necessaries —> by paying more for these necessities , they have less money to spend on other necessities
domestic firms may suffer losses and some workers may become unemployed —> as firms cut production due to higher cost
Subsidies
A payment made by the government to producers to help reduce cost of production
can be used to correct market failure caused by underconsumption of merit goods and activities with high external benefits
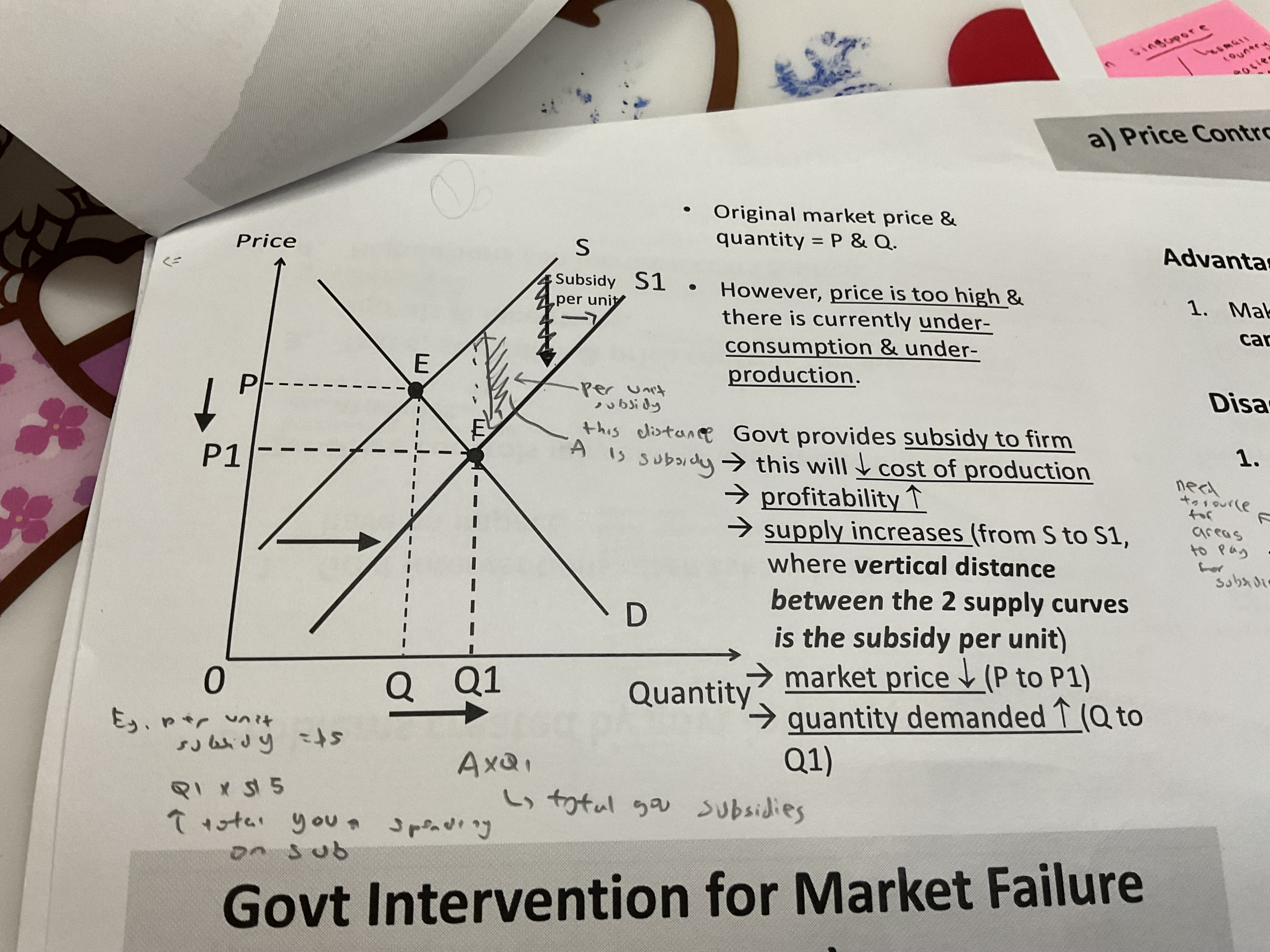
How does subsides solve market failure
Original price is too high so there is an underconsumption and underproduction of goods
Government provides subsidies to the firm to reduce cost of production, increase profitability and causes supply to increase from S-S1
Vertical distance between 2 supply curves = subsidies per unit
Market price falls from P-P1
Quantity demanded increases Q-Q1
Advantages of subsidies
Makes the goods more affordable —> more poor people can now afford to consume the good
Disadvantages of subsidies
Opportunity cost may be high —> giving more subsidy on one good may mean less spending on other important areas
Government may have to increase taxes to pay for subsidies —> raise tax burdens for consumers / taxpayers —> they have less income to satisfy other wants —> opportunity cost for taxpayers
Government may over subsidies —> good becomes too cheap —> overconsumption —> wastage of resources
Advantages of government in a mixed economy
can help overcome many problems of a market economic system and correct the various types of market failure
Disadvantages of government in a mixed economy
Government intervention takes a long time to agree and have an impact
Price controls may encourage smuggling and black markets
Taxes and subsidies and price controls can distort price signals ( price can’t change) and incentives
Regulations can increase cost and price
Public sector organisations may be inefficient or poor quality
Cause conflict of interest
Some government intervention may be based on political or personal choices
(All these lead to inefficient allocation of resources )
due to problems created by government intervention ,
Many countries are trying to reduce the size of the public sector and increase the role of market economic system
How to reduce government intervention and increase the role of markets in the mixed economic system
Privatisation
Cutting taxes and public spending
Deregulation
Privatisation def
Where government sell or transfer state owned enterprises and public sector activities to private sector firms
De regulation
Removing regulations ( including price control)
Advantages of increasing the role of markets in mixed economic system
Reduces problems created by government intervention = increase efficiency = cut cost =lower prices and improve quality of products produced
Increase in economic welfare when resources are efficiently allocated
Government intervention is only needed in
Certain essential areas
Not in essential areaS
Greater role of free market in resource allocation decisions