anatomy module 2
1/268
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapters 10-15
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
269 Terms
myocyte
muscle cell; muscle fiber
sarcolemma
the plasma membrane of the muscle fiber
sarcoplasma
the cytoplasm of a muscle fiber
sarcoplasmic reticulum
ER of a muscle fiber
functional characteristics of all muscle
contractibility: ability to shorten and generate force
excitability: ability to respond to stimuli by producing electrical signals
extensibility: ability to stretch without being damaged
elasticity: ability to return to its original length/shape following distension
functions of muscle
movement
posture and joint stabilization
open/close body passages
thermogenesis
thermogenesis
contracting skeletal muscles produce heat
voluntary/involuntary; shivering
contracting smooth muscles also helps prevent heat loss
goosebumps, dartos muscle
connective tissue components of skeletal muscles
sheaths of CT hold skeletal muscle tightly together in parallel alignment so they can generate force as a whole
provides elasticity
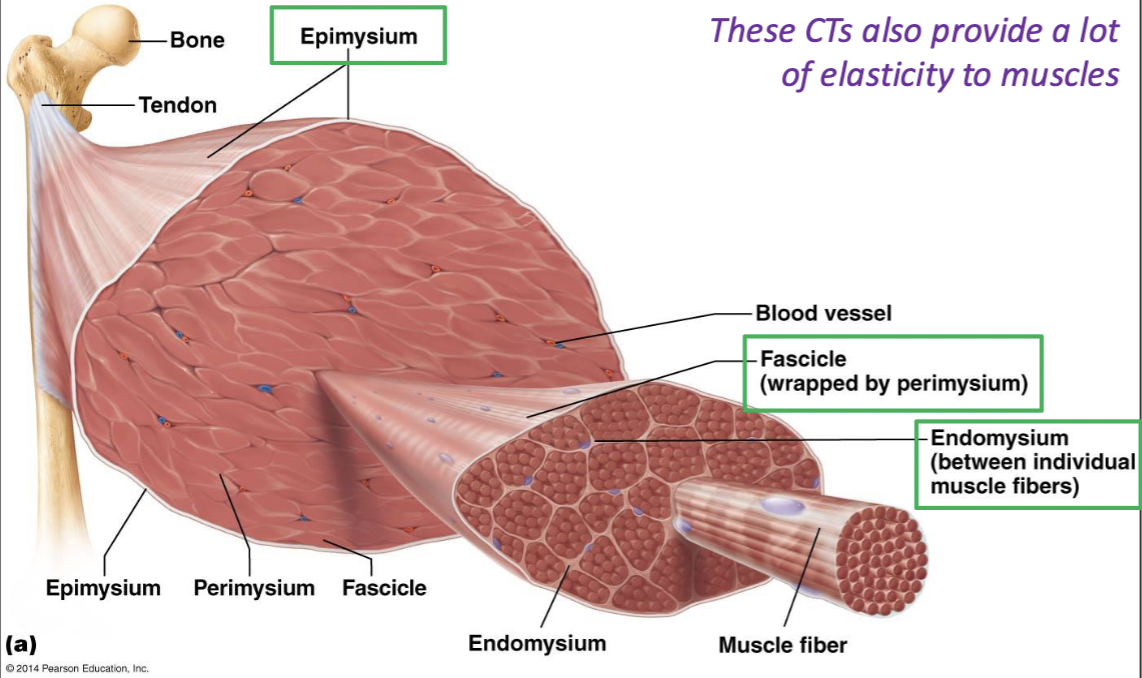
epimysium
connective tissue around the whole muscle
fascicle
bundle of muscle fibers
wrapped by perimysium
endomysium
betwen individual muscle fibers
tendons
CT attachment of a skeletal muscle to a bone’s periosteum
continuous with all 3 CT sheaths of muscle beyond the length of the fibers
aponeurosis
broad, flat tendon
origin
attachment of muscle on the stationary/less moveable bone
insertion
attachment of muscle on the mobile/more moveable bone
direct attachment
connective tissue very short
muscle may appear to be attached to the bone
less common
indirect attachment
connective tissue forms tendons/aponeurosis
common
strains vs. sprains
strains: muscle and/or tendons
sprains: ligaments
nervous innervation of muscle
each muscle is typically innervated by a single nerve which branches extensively within the CT sheaths
each axon making up the nerve synapses with multiple muscle cells
blood supply of muscles
each muscle is typically supplied by a single artery which branches extensively within the CT sheaths
capillary networks within the endomysium are wavy in resting muscle to allow for extensibility
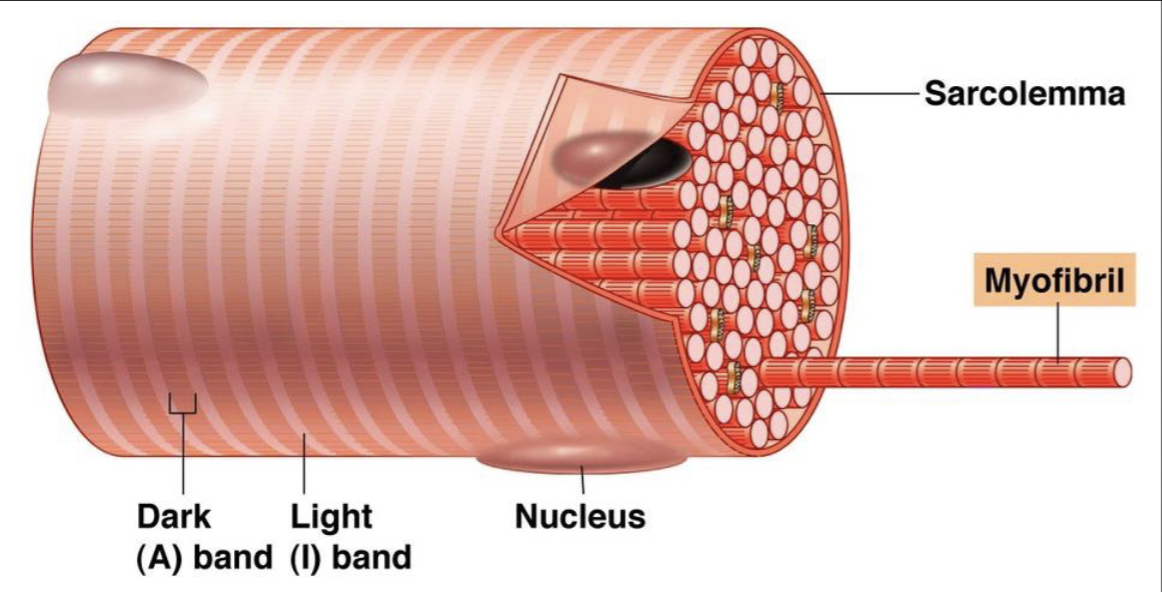
skeletal muscle fiber striation
due to the organization of proteins found within muscle cells
myofibrils
specialized contractile organelles
specific for myocytes; allow muscles to contract
made up of three types of proteins
contractile, regulatory, structural
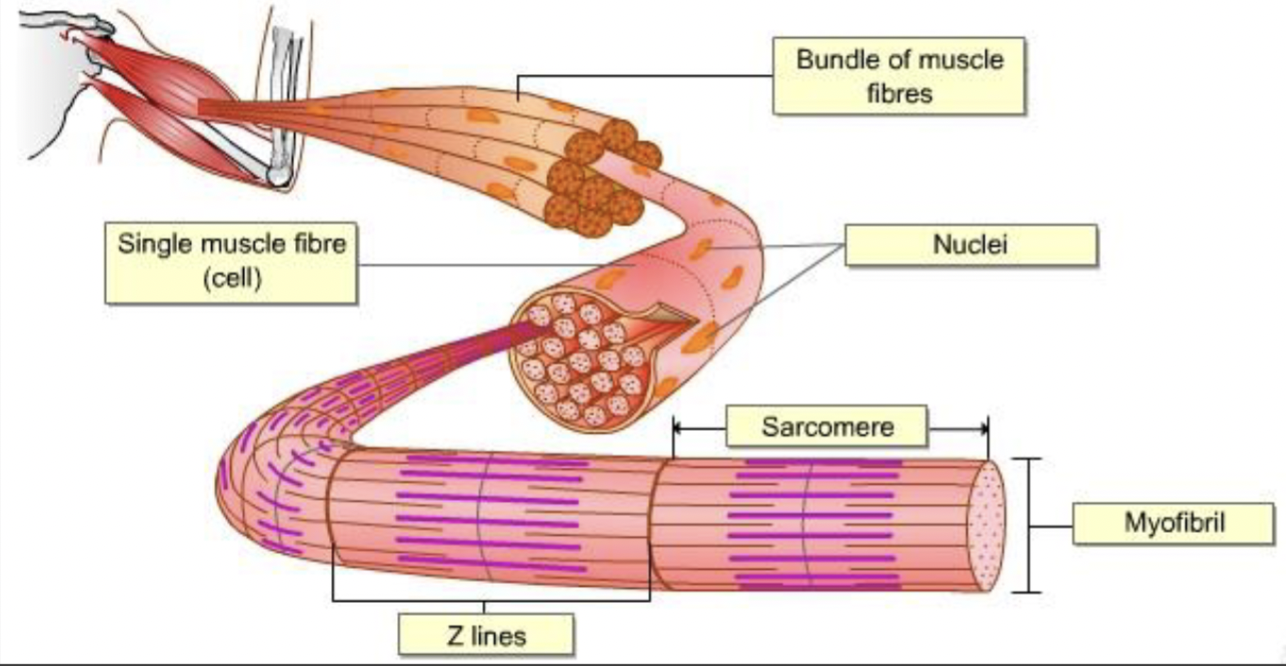
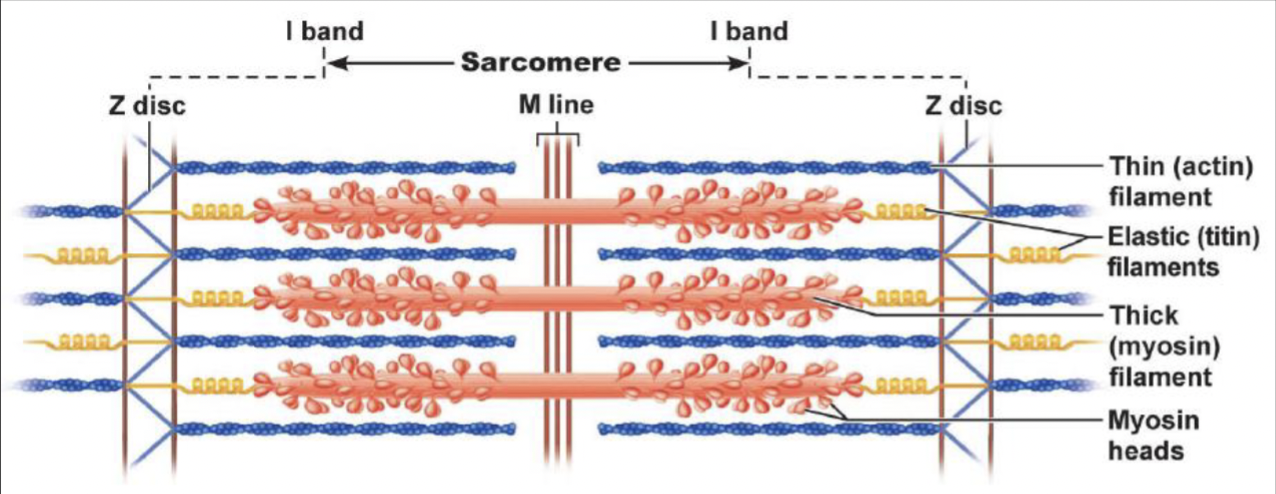
sacromere
the basic contractile unit of muscle
several units make up the myofibril
contractile proteins
actin and mysoin myofilaments
do the work; occur in all cells
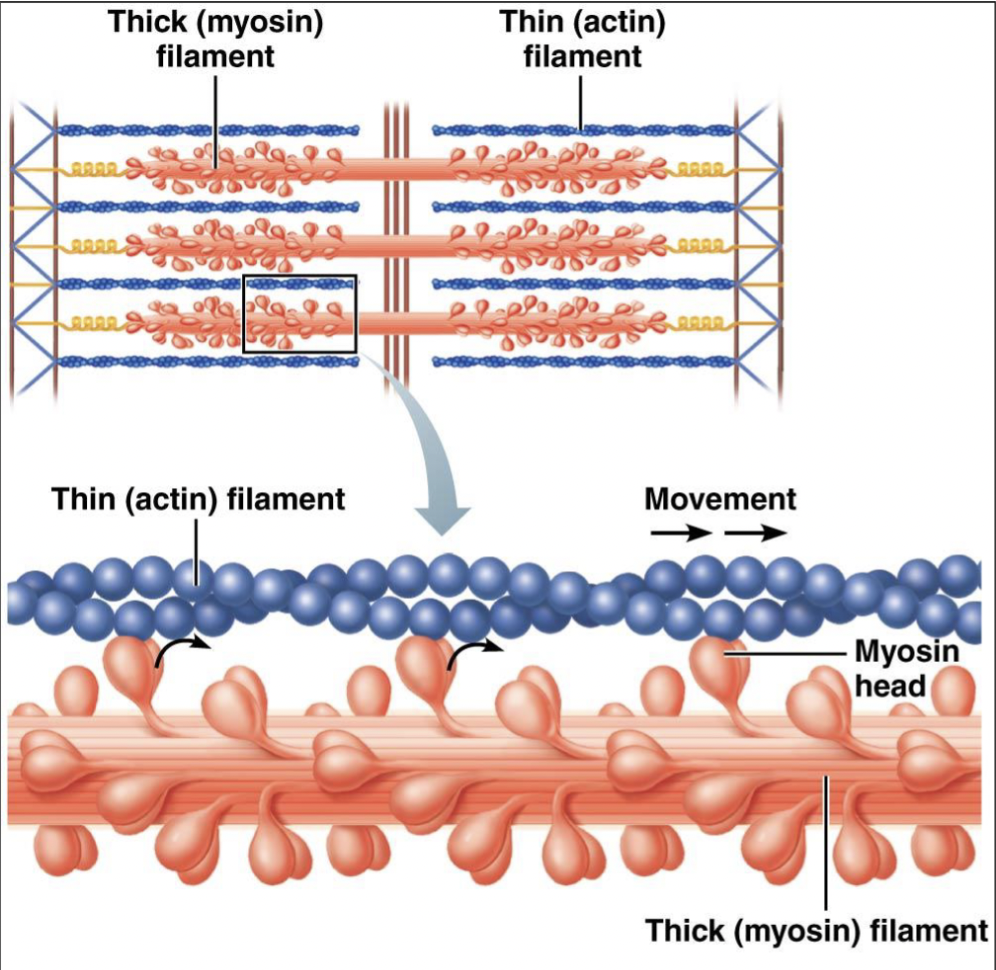
thin filament
actin, tropomyosin, troponin
actin attached to Z disc; extends to center
actin molecules arranged in a double helix
each actin molecule has a myosin-binding site for the myosin head
thick filament
many myosin molecules
tethered to Z disc by titin
provides slack
myosin heads attach to actin in the thin filaments, then pull thin filaments inward
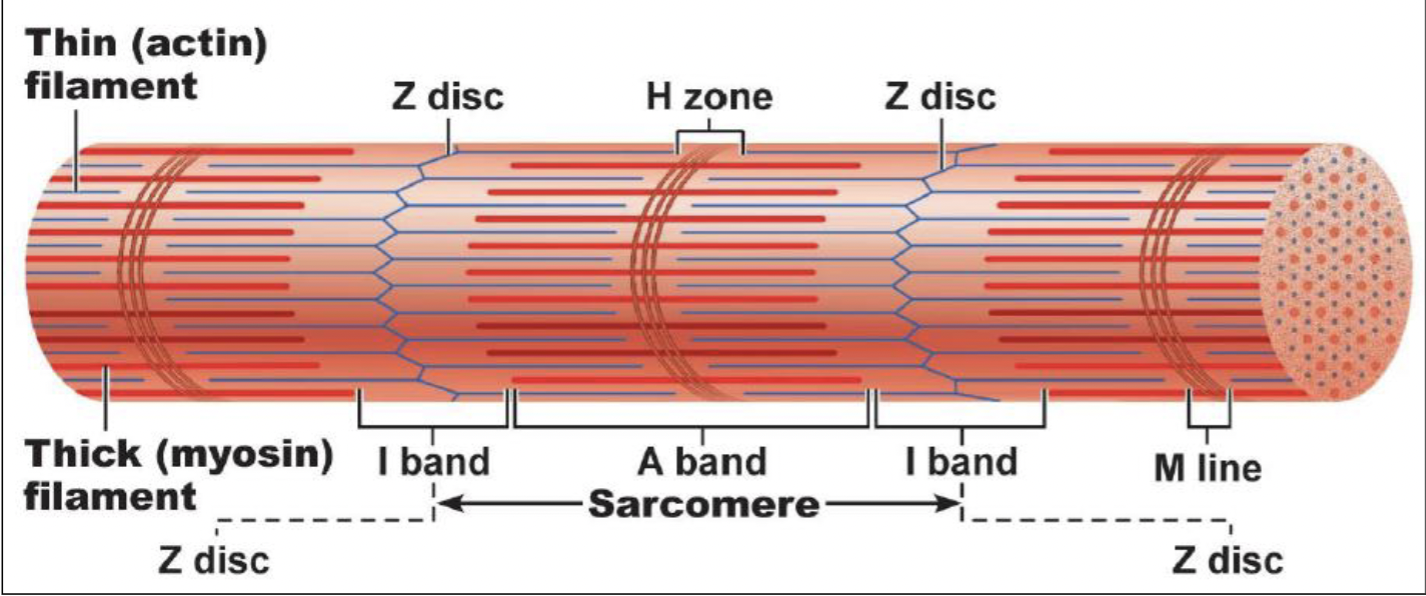
actin and myosin arrangement in sacromere
Z disc (line): separates sacromeres
A band: entire length of thick filament
M line: center of the sacromere
I band: thin filament only
H zone: thick filament only
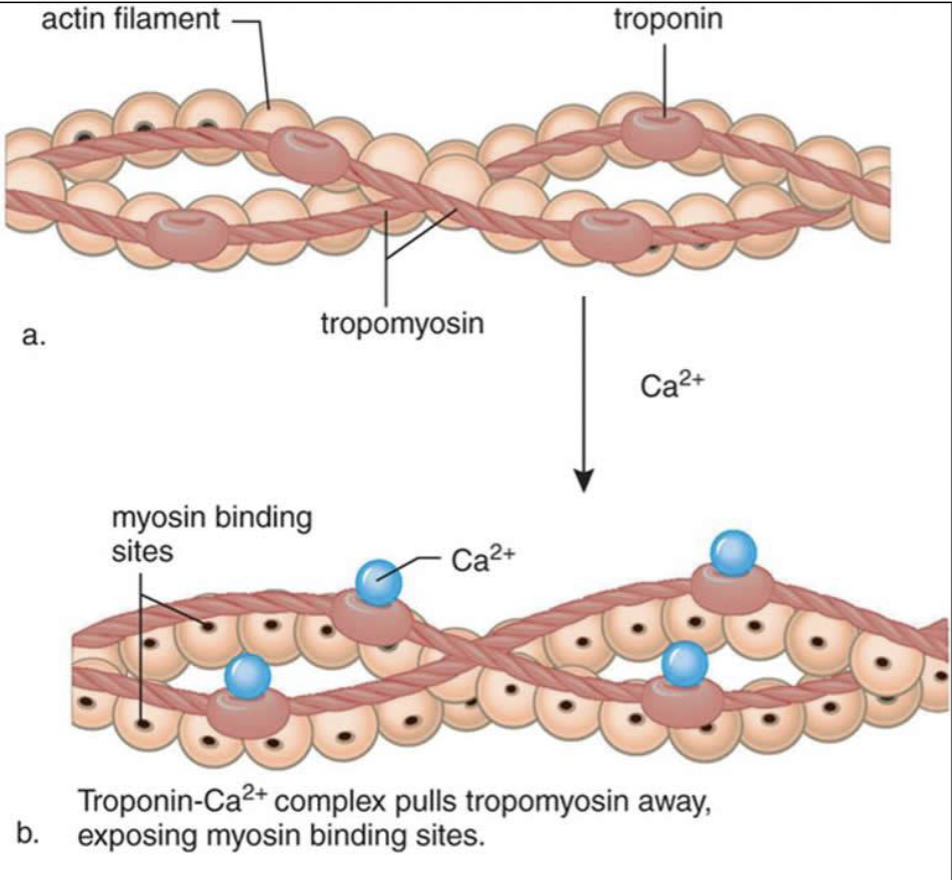
regulatory proteins
tropomyosin: covers myosin-binding sites
troponin: holds tropomyosin strand together
when calcium ions bind to troponin, it changes its shape, pulling tropomyosin off the binding site
structural proteins
titin: inside sacromere; anchors myosin to Z disc
allows for extensibility
dystrophin: at the ends of the myofibril to keep it in place
sarcoplasmic reticulum
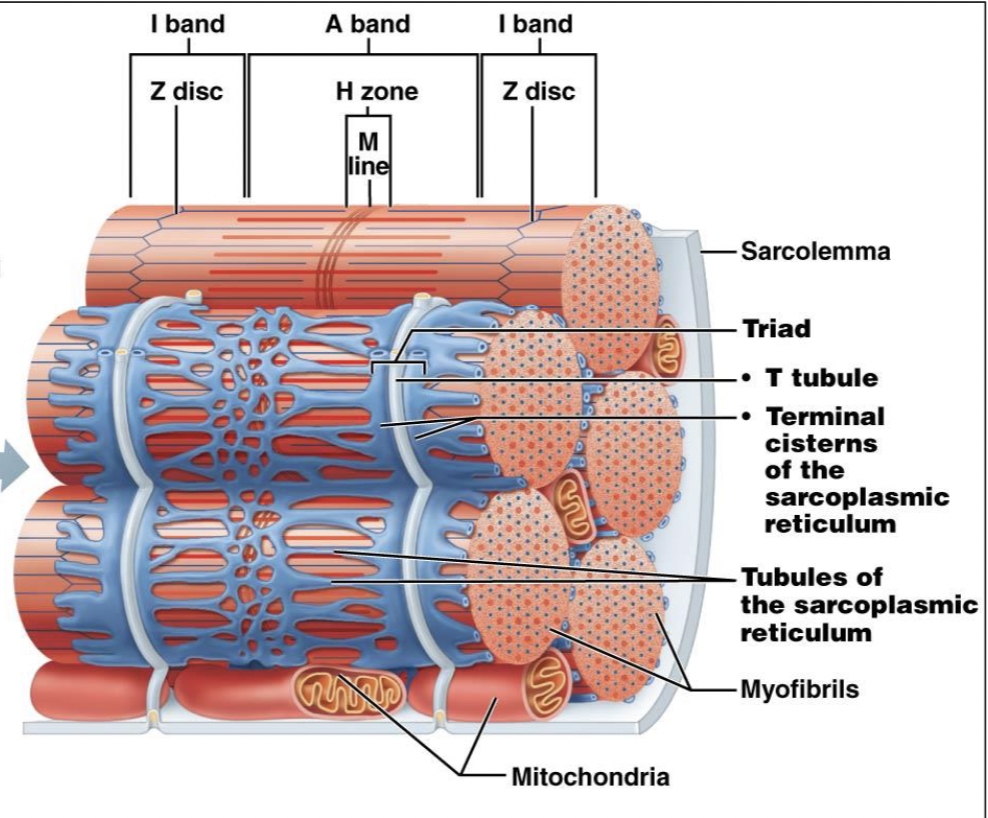
T-tubule
invagination of sarcolemma
carries an electrical impulse from surface membrane deep into muscle fiber
tubules of the SR
network of tubules that regulate calcium ion levels and where electrical signals travel down
terminal cisterns of the SR
the tubules of the SR coming to an end
where calcium ions are stored and released
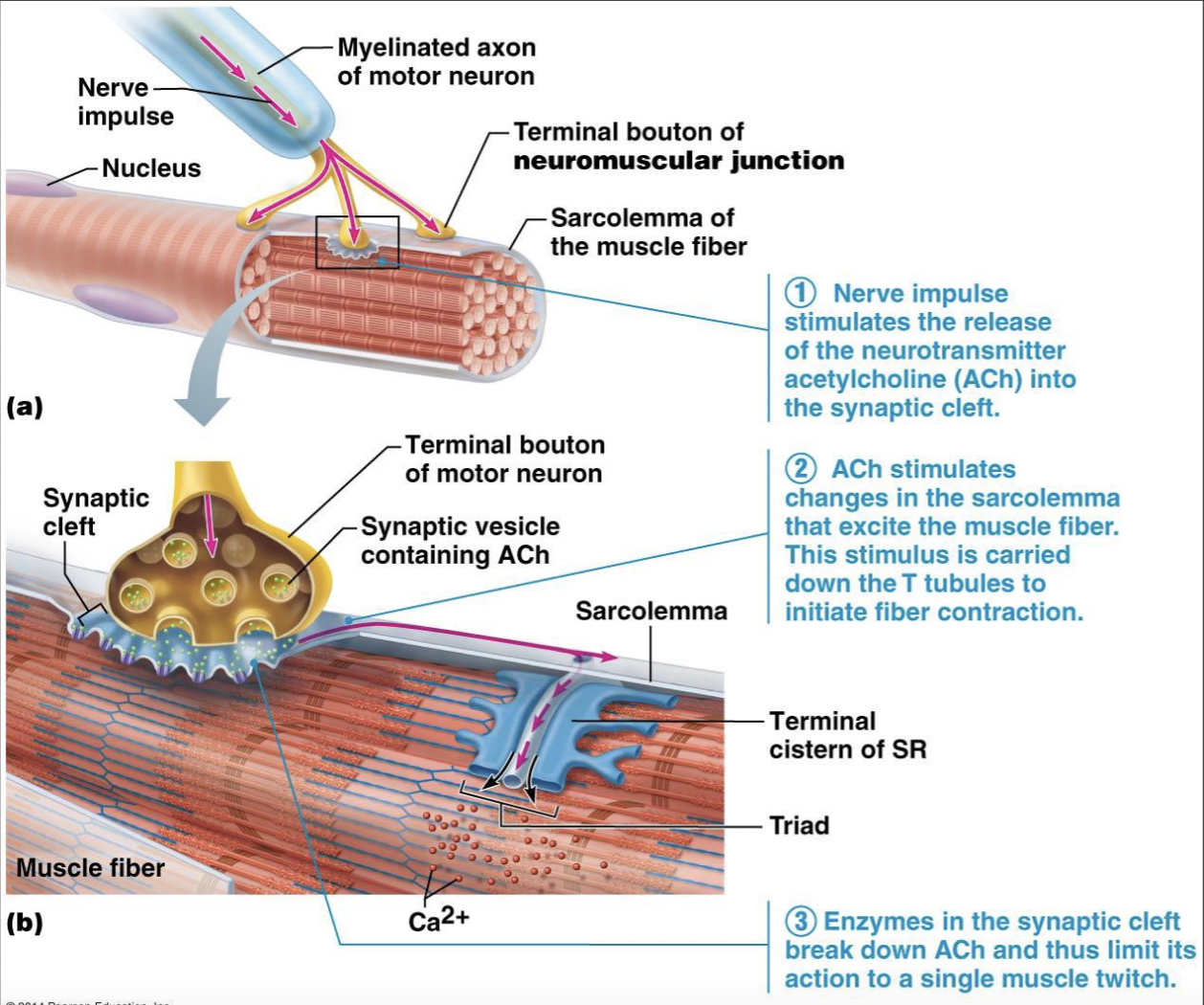
sliding filament mechanism of contraction
Ca+ released from terminal cisterns SR and binds to troponin → troponin is released from tropomyosin → tropomyosin on actin rolls over → myosin heads bind and pivot to pull the thin filaments inward
change in filaments during contraction
do not change in length; only amount of overlap changes
A-band doesn’t change
motor unit
one nerve fiber and all the muscle fibers innervated by it
branches out to a number of fibers
each muscle fiber is supplied by only one motor neuron
one fiber will not be innervated by multiple nerves
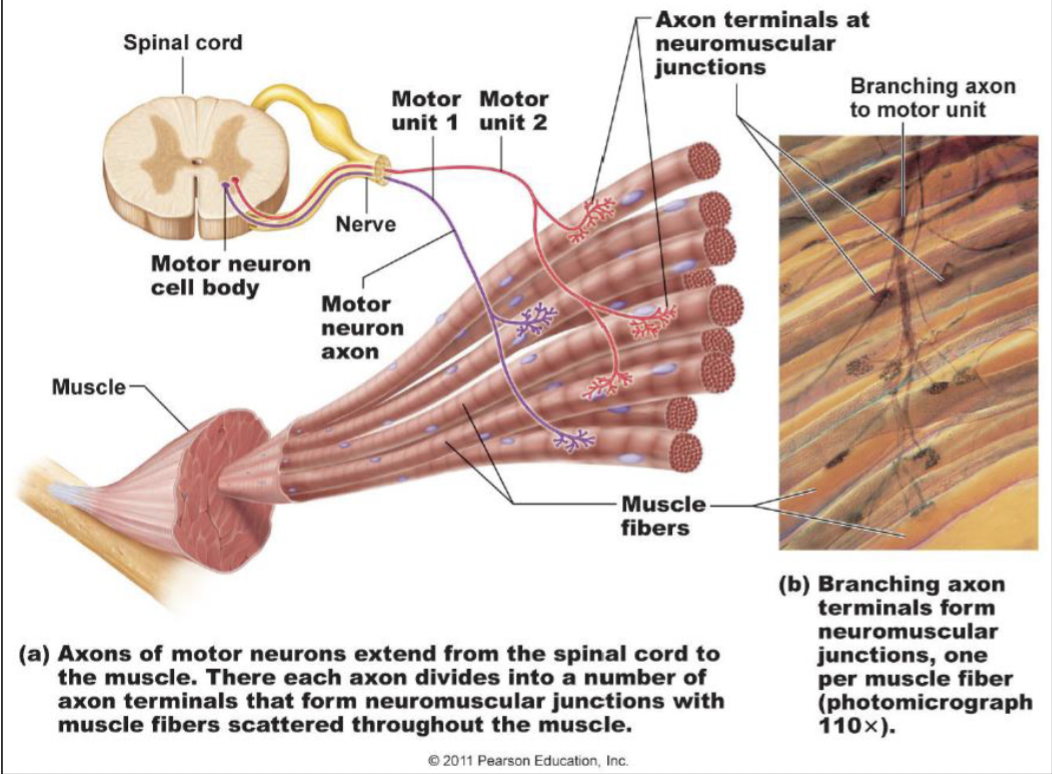
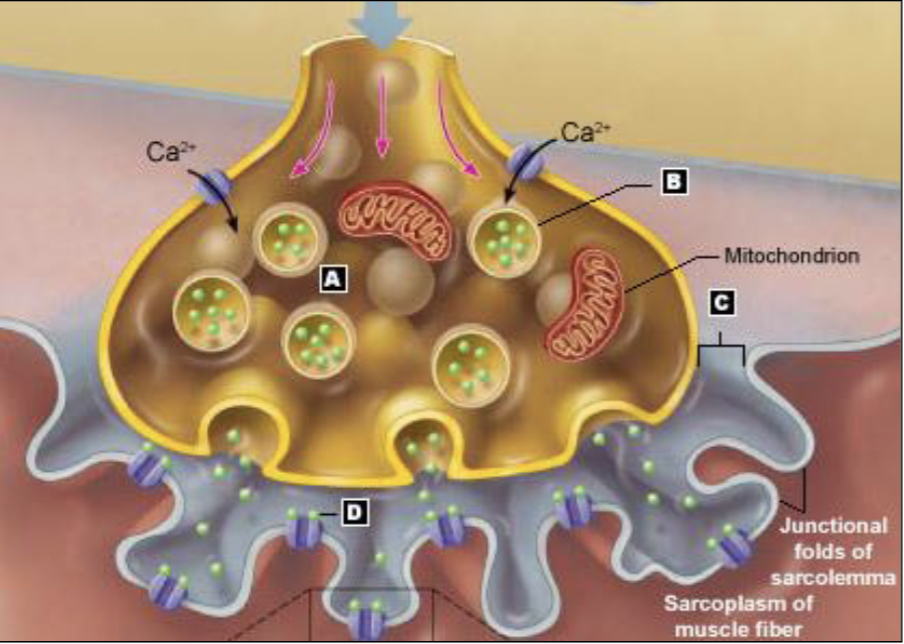
the neuromuscular junction (NMJ)
communication site b/w neuron and muscle cell
three main components of the NMJ
axon terminal: aka terminal bouton
junctional folds of the sarcolemma: increase surface area for more receptors
synaptic cleft: space b/w folds and axon terminal
nerve impulse to movement
LOOK AT NOTES FOR AFTER #3!!!!!
skeletal muscle fiber types
slow oxidative type I
fast ox-glycolytic type IIa
fast-glycolytic type IIb/IIx
slow oxidative type I characteristics
myoglobin content: high
contraction velocity: slow
metabolic process for ATP production: aerobic
fatigue resistance: high
color: red
fiber diameter: small
slow oxidative type I function
maintaining posture and endurance activities
constant states of contraction
fast ox-glycolytic type IIa characteristics
myoglobin content: high
concentration velocity: fast
metabolic process: aerobic + anaerobic
fatigue resistance: intermediate
color: pink
fiber diameter: intermediate
fast ox-glycolytic type IIa function
walking, sprinting
fast-glycolytic type IIb/x characteristics
myoglobin content: low
contraction velocity: fast
metabolic process: anaerobic
fatigue resistance: low
color: white
fiber diameter: large
fast-glycolytic type IIb/x function
rapid, intense movements of very short duration
more force (bc of large fiber)
arrangement of fascicles in muscles
within a fascicle, all muscles fibers are parallel to one another
arranged differently in various muscles
arrangement reflects function
longer fibers: greater range of motion
shorter fibers: greater strength
fascicles and muscles shapes
strength of a muscle and the direction of its pull are determined partly by the orientation of its fascicles
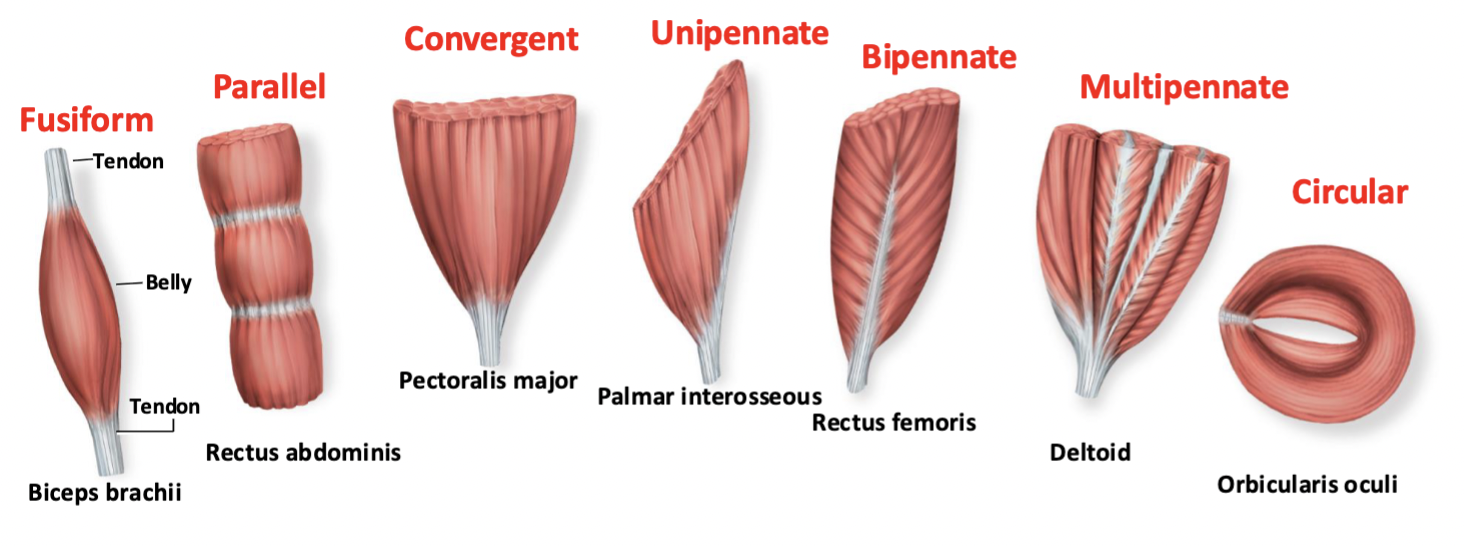
circular
fascicles arranged in concentric rings
always found around external body openings (sphincters)
convergent
origin is broad and the fascicles converge toward a tendon of insertion
pennate
short fascicles that attach obliquely (angulary) to a tendon that runs the length of the muscle
parallel
fascicles run parallel to the long axis of the muscle
fusiform and straplike (sartorius)
lever systems
effort: force being produced by contracted muscle
based on insertion point
load: external weight/body part; resistance
fulcrum: pivot/fixed point; where movement stems from
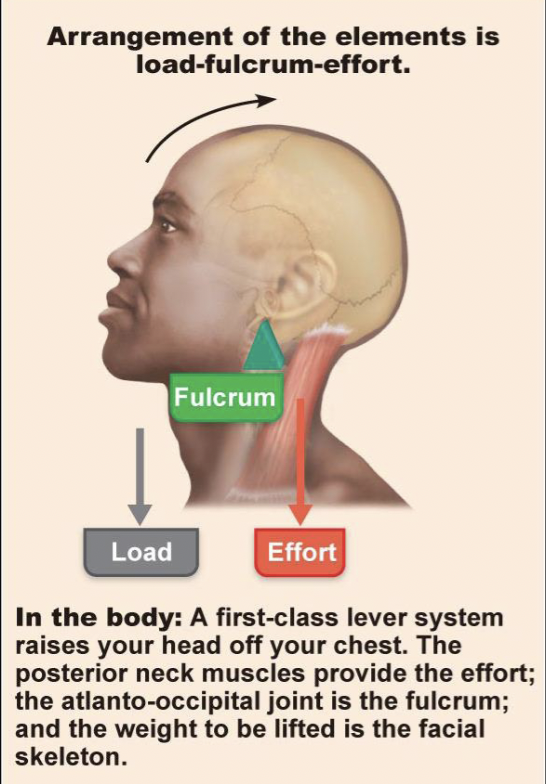
first class lever
fulcrum in the middle
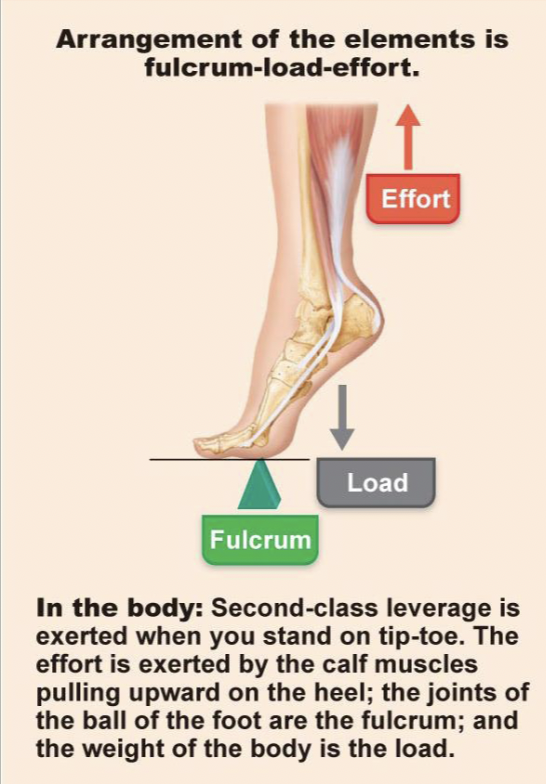
second class lever
load in the middle
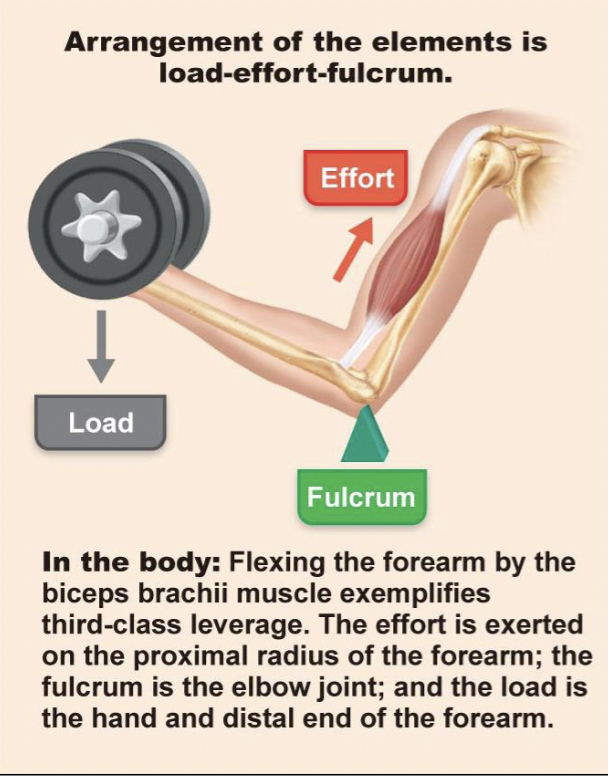
third class lever
effort in the middle
muscles actions and interactions
a muscle that crosses a joint, acts at that joint
muscles only pull
muscles that produce opposite actions lie on opposite sides of a joint
agonist: contracts to cause an action
antagonist: stretches and yields to the effects of the agonist
synergist
acts to assist an agonist by adding extra force or reducing undesirable movements
canceling out unwanted movements
fixators: fixes a bone in place
naming skeletal muscles
named according to several descriptors
location, shape, size, fascicle arrangement, location of attachments, number of origins, action
often, multiple criteria are used
flexion
a muscle that crosses on the anterior side of a joint
extension
a muscle that crosses on the posterior side of a joint
abduction
a muscle that crosses on the lateral side of a joint
adduction
a muscle that crosses on the medial side of a joint
muscle compartments of the limbs
fascial compartments group muscles of similar origin and function
most compartments are innervated by a single named nerve
fascia
connective tissue separating compartments
anterior brachial compartment
muscles: coracobrachialis, brachialis, biceps brachii
action: flexion of shoulder and elbow
innervation: musculocutaneous nerve
posterior brachial compartment
muscles: triceps brachii, anconeus
action: shoulder and elbow extension
innervation: radial nerve
anterior antebrachial compartment
muscles: superficial, intermediate, and deep flexors
action: flexes wrist and fingers
innervation: median or ulnar nerve
ulnar innervates pinky and half of ring finger
posterior antebrachial compartment
muscles: superficial and deep extensors
action: extends wrist and fingers
innervation: radial nerve
anterior thigh compartment
muscles: quadriceps femoris
action: knee extension and hip flexion
innervation: femoral nerve
posterior thigh compartment
muscles: hamstrings
action: knee flexion and hip extension
innervation: tibial nerve (portion of sciatic nerve)
medial thigh compartment
muscles: adductors
action: hip adduction and medial rotation, and slight knee flexion
innervation: obturator nerve
anterior leg compartment
muscles: tibialis anterior, EHL, EDL, fibularis tertius
action: dorsiflexion, inversion, extension of toes
innervation: deep fibular nerve
lateral leg compartment
muscles: fibularis longus and brevis
action: plantar flexion and eversion
innervation: superficial fibular nerve
superficial posterior leg compartment
muscles: gastrocnemius and soleus
action: knee flexion and plantar flexion
innervation: tibial nerve
deep posterior leg compartment
muscles: tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, popliteus, flexor hallucis longus
action: plantar flexion, knee flexion, toe flexion
innervation: tibial nerve
compartment syndrome
when muscles swell from trauma/overuse, pressure in the compartment increases
compressed vessels → ischemia, swelling
ischemia: blockage of blood flow
compressed nerves → pain or numbness
can require a fasciotomy
the nervous sysem
master controlling and communicating system
rapid and specific signals
immediate responses
employs electrical signals and chemical means to send messages from cell to cell
endocrine system
communicates by means of chemical messengers (hormones) secreted into the blood
slow acting
3 overlapping functions of the nervous system
sensory function
integration function
motor function
sensory function
sensory receptors monitor changes inside and outside the body
integration function
CNS receives and interprets sensory input and makes a decision for action
motor function
motor neurons elicits responses by activating effector organs
divisions of the nervous system
central nervous system
peripheral nervous system
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
integrative and control centers
peripheral nervous system
all nervous tissue outside the CNS
cranial and spinal nerves that can have sensory or motor functions
connects the CNS to the rest of the body
divisions of the PNS
sensory (afferent) division
motor (efferent) division
sensory division
somatic and visceral sensory nerve fibers
conducts impulses from receptors to the CNS
motor division
motor nerve fibers
conducts impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles and glands)
systems of the motor division
somatic nervous system
automatic nervous system (ANS)
somatic nervous system
somatic motor (voluntary)
conducts impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles
automatic nervous system
visceral motor (involuntary)
conducts impulses from the CNS to cardiac muscles, smooth muscles, and glands
divisions of the automatic nervous system
sympathetic division
parasympathetic division
sympathetic division
mobilizes body systems during activity
fight or flight response
parasympathetic division
conserves energy
promotes house-keeping functions during rest
rest and digest
nervous tissue
composed of neurons (excitable) and neuroglia (non-excitable)
special characteristics of neurons
conductivity: able to send electrical signals from one body part to another
called action potentials/nerve impulses
extreme longevity: neurons can live and function for a lifetime
do not divide: cannot replace themselves if destroyed
few exceptions
high metabolic rate: require constant supply of O2 and nutrients
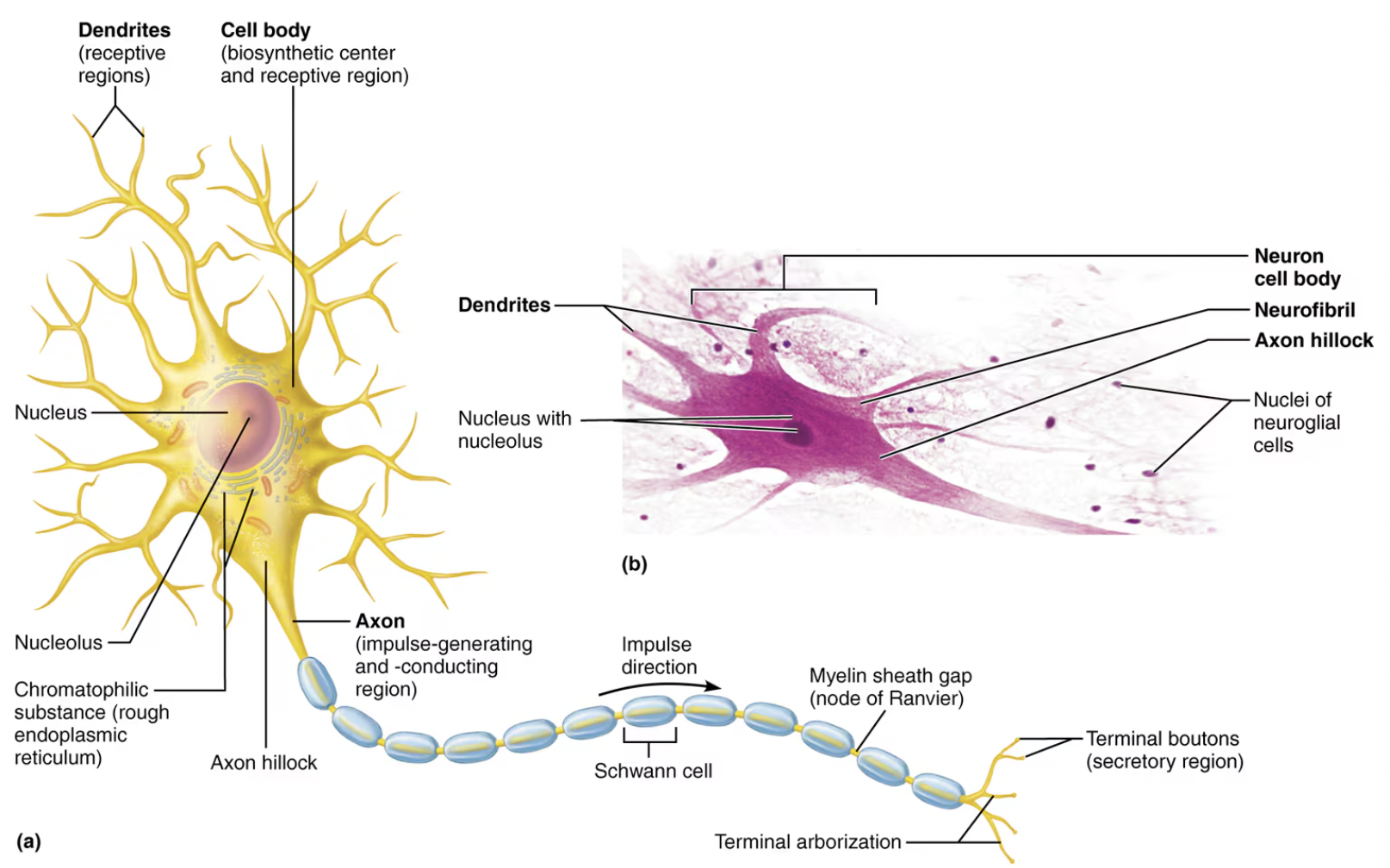
the basic neuron