3.3 RAID
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
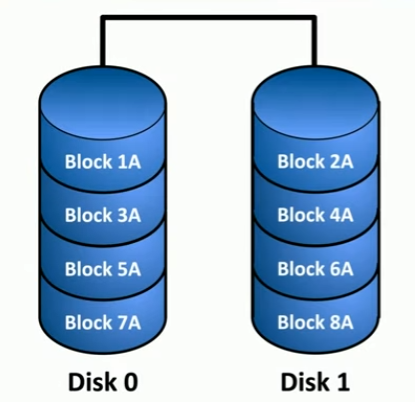
RAID 0
STRIPING; minimum 2 drives, no redundancy.
- Data is "split" evenly between the two drives.
- performance increase; does not provide redundancy because data is split in half, not copied
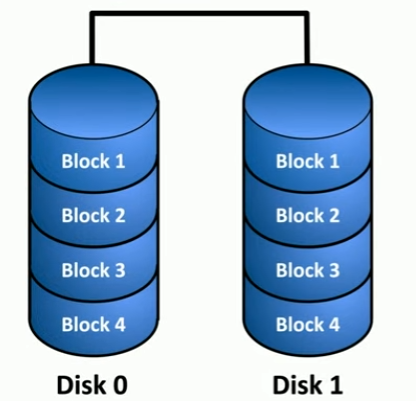
RAID 1
MIRRORING; minimum 2 drives, redundancy.
- data is duplicated across both drives
- need twice as much storage for same amount of information
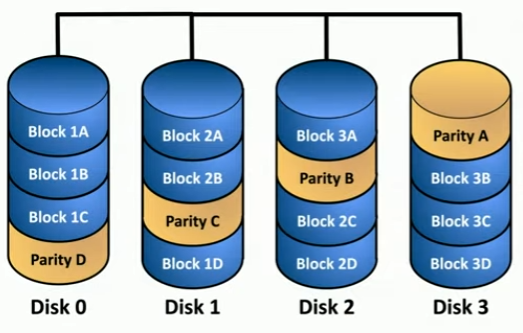
RAID 5
STRIPING WITH PARITY; minimum 3 drives, redundancy.
- data is split across different drives (like R0) but now there’s an additional disk that holds ‘parity’ data to rebuild data in case one drive is lost
- or, parity data can be split across all disks so all - 1 drives can be used to rebuild data
- may slow performance
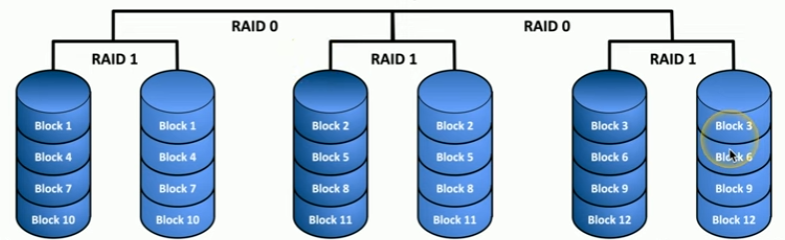
RAID 10 (1+0)
STRIPE OF MIRRORS; minimum 4 drives, redundancy
- mirror all of our RAID 0 arrays; have a copy of each striped drives where data has been split
- speed of striping, redundancy of mirroring
Is RAID a backup?
RAID maintains uptime/availability; it’s NOT a backup
Parity block
Fault tolerance method used to rebuild data from other drives if one drive has failed; used in RAID 5
RAID 0
Minimum 2 drives, no redundancy
RAID 1
Minimum 2 drives, redundancy
RAID 5
Minimum 3 drives, redundancy
RAID 10
Minimum 4 drives, redundancy