Human Bio Exam 3
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
Joints
articulating - bone to bone contact point
Classification of Joints (articulations)
Classification based on structure
Fibrous joints
dense connective tissues connect bones
bones in close contact
Cartilaginous joints
hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage connect bones
boney joints may form when fibrous or cartilaginous joints ossify
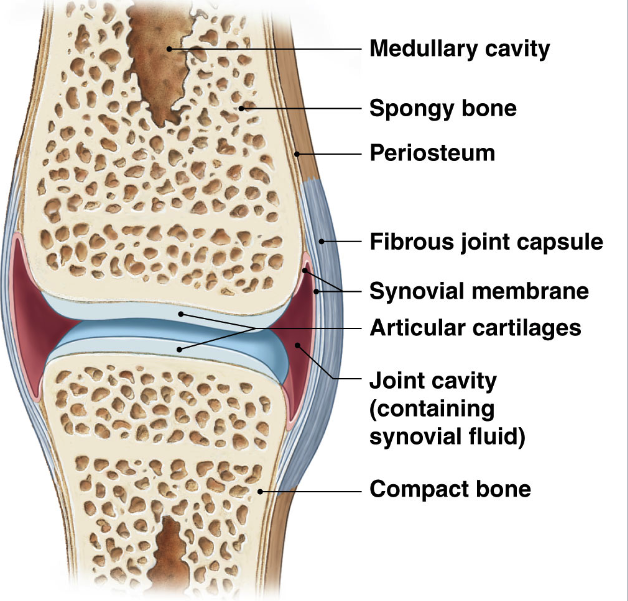
Synovial joints
most complex
joint capsule
synovial fluid
reinforcing ligaments and cartilage
Classification based on function
Synarthrotic joints → fibrous & cartilaginous
immobile
Amphiarthrotic joints → fibrous & cartilaginous
slight mobility
Diarthrotic joints → synovial
free mobility
Synovial Joints: General Structure
Articular cartilage → reduce friction
only on articulating surface
watery matrix
similar to hyaline cartilage
joint capsule
fibrous outer layer:
dense connective tissue connecting to periosteum
synovial membrane:
inner surface, areolar tissue and incomplete epithelium.
produce synovial fluid
synovial fluid
produced by synovial membrane
within joint cavity
viscous
lubricant, shock absorption, nutrient distribution
Accessory Structures of Synovial Joints
meniscus/ menisci
fibrocartilage: additional layer between articulating bones
shock absorption
subdivide cavity, channel fluid, alter shape of articulating surface
Fat pads
adipose covered by synovial membrane
protect articular cartilage
packing material
Bursa
pockets of synovial fluid surrounded by membrane
reduce friction at site of tendon and ligament attachment
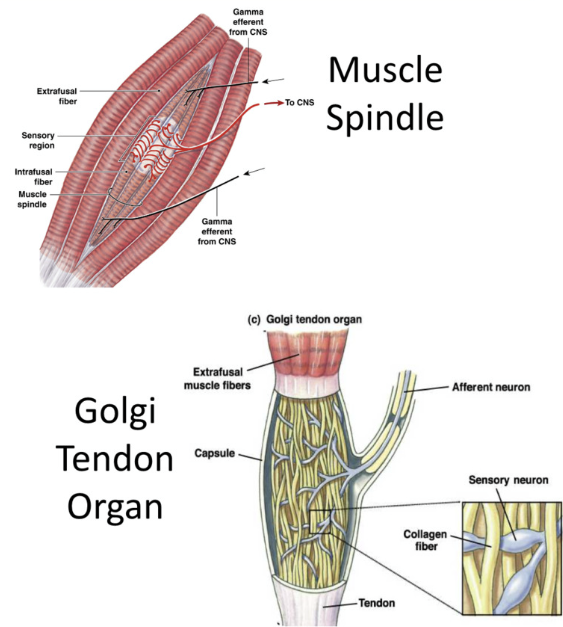
Proprioceptors
Monitor position and movement of skeletal muscle and joints
muscle spindles
specialized muscle fibers throughout a muscle (neighbor regular muscle cells)
sarcomeres on either end of a regoin without filaments (wrapped by sensory neurons
respond when muscle is stretched
golgi tendon organs
sensory dendrites interwoven among collagen fibers of tendons
provide info about contraction of tendons
tendon stretch→ squeeze sensory dendrites → inform brain of activation
Joint capsule receptors
mechanoreceptors found on sensory dendrites in joint capsule
found in synovial membrane
responds to pressure, stretch, and movement
eg pacinan corpsucles and ruffini endings
Ligaments and Tendons
ligaments attach bone to bone
more flat
slightly less dense
tendons attach muscle to bone
more round
more dense
attach via fibrocartilage transition to periosteum
dense regular connective tissue
thick parallel bundles of collagen
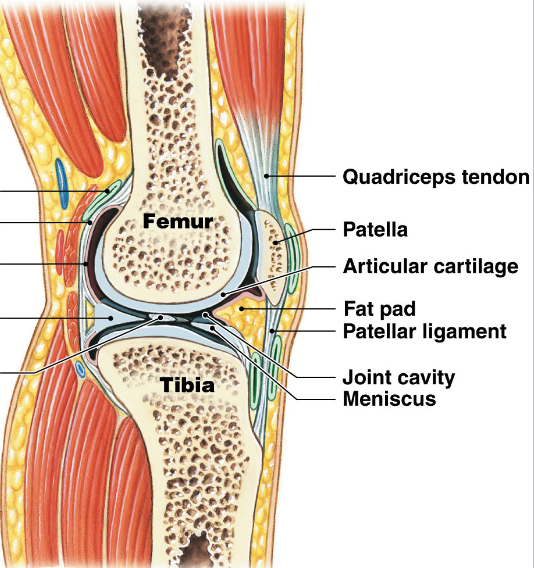
Accessory structures of knee
medial and lateral menisci
fibrocartilage pads between femur and tibia
fat pads
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
femur to tibia
limit anterior/posterior movements
medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
stabilize knee in standing position
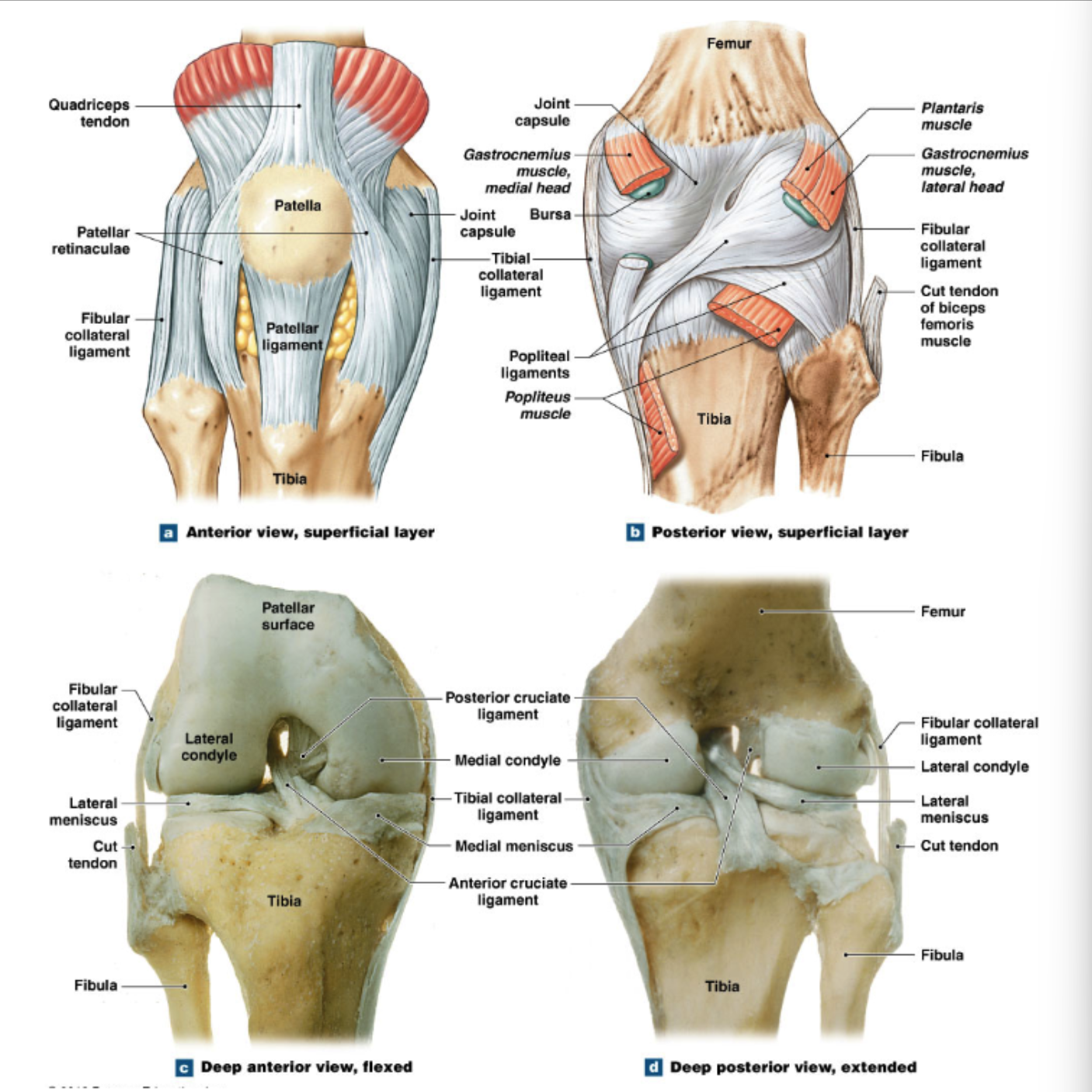
Unhappy triad of injuries
tears/rupture of all 3:
ACL
MCL
lateral meniscus
caused by string force outside of knee when foot is stationary
treatment: ACL tear commonly requires a graft
Divisions of nerous system
Central Nervous system
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System
All nervous tissue other than CNS
Nerves: transmit information to and from CNS
Cranial and Spinal Nerves
Cranial Nerves
arise from brain
12 pairs on each side → 24 total
Spinal Nerves
arise from spinal cord
31 pairs
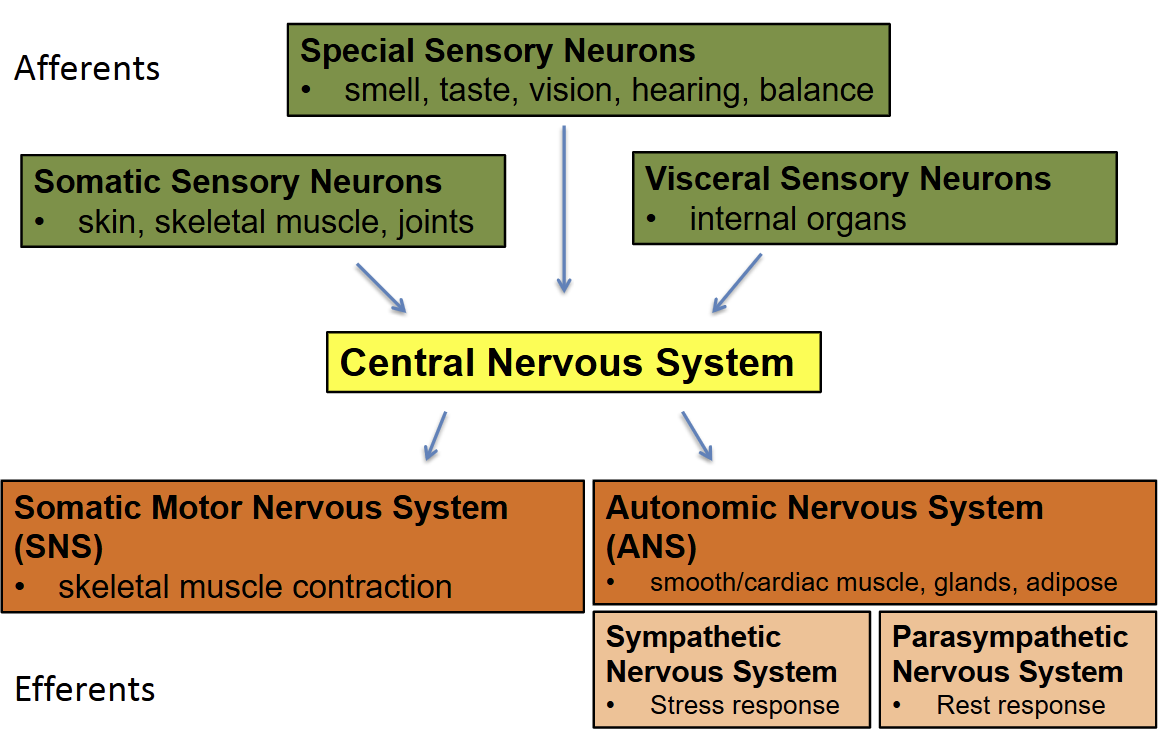
Organization of Peripheral Nervous System
Afferent → CNS → Efferent
Afferents (sensory) accepting
Somatic Sensory Neurons: skin, skeletal muscle, joints
Special Sensory Neurons: smell, taste, vision, hearing, balance (vestibular sense)
Visceral Sensory Neurons: internal Organs
→
Central Nervous System
→
Efferents (motor) enacting
Somatic Motor Nervous System (SNS):
skeletal muscle contraction
controlled
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)/ Visceral Nervous System:
smooth/cardiac muscle, glands, adipose
uncontrolled
Sympathetic Nervous System
Stress Response
Parasympathetic Nervous System
rest and digest response
Functions of Spinal Cord and Nerves
Transmission of sensory information to brain (afferent/sensory)
Transmission of motor information from brain (efferent/motor)
Generation of spinal reflexes REVIEW EARLY
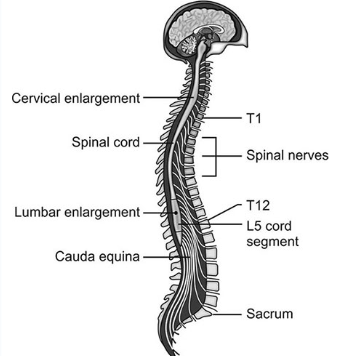
Gross Anatomy of Spinal Cord
leaves cranium at foramen magnum → extends into vertebral canal
true spinal cord ends at L2 vertebra
Spinal cord in adult ends at level of 1st lumbar vertebra
cervical enlargements:
supplies nerves to arms
lumbar enlargement:
supplies nerves to legs
conus medullaris:
tapering of spinal cord to a point below lumbar enlargement
Filim Terminale (not neuronal):
connective tissue that connects conus → coccygeal ligament (full length of vertebral column)
for stabilization
Cauda equina:
bundle of spinal nerve roots and filim terminal within vertebral canal from ~ L2 - S5
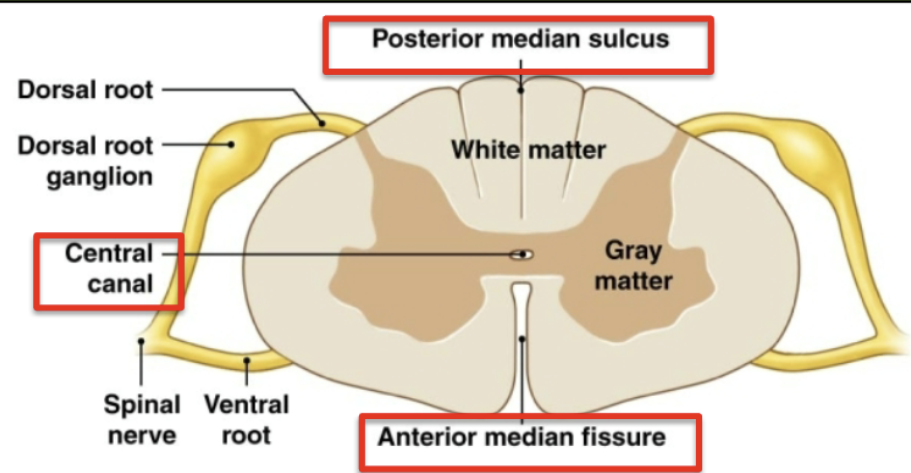
Cross Section of Spinal Cord
posterior median sulcus in front
little groove
anterior median fissure at bottom
larger groove
Central canal
filled with CSF
Inner gray Matter:
abundance of cell bodies/dendrites (inner, deep)
Outer white matter:
abundance of myelinated (and some unmyelinated) axons (outer, superficial)
Roots → where spinal nerves communicate with spinal cord
Ventral roots:
Efferent (motor) pathways: carry information away from CNS → periferal targets
Dorsal Roots:
Afferent pathways: carry sensory information from periphery → CNS
from spinal cord into dorsal
ganglion: collection of cell bodies of peripheral nervous system
Ventral root join with dorsal root → form spinal cord
Organization of White and Gray Matter
Gray Matter:
cell bodies + dendrites
organized into nuclei = collection of cell bodies in CNS
dorsal horns: (sensory)
somatic and visceral sensory nuclei
process/ relay sensory information
ventral horn: (motor)
efferent
somatic motor nuclei
integrate / relay motor information
Lateral horns: (motor)
thoracic and lumbar only
visceral motor nuclei
White Matter
organized into columns
anterior, posterior, and lateral columns
each column contains tracts
Tracts = bundles of axons with similar structure and function
relay info up and down spinal cord.
Commissures: both white and gray, axons which cross sides
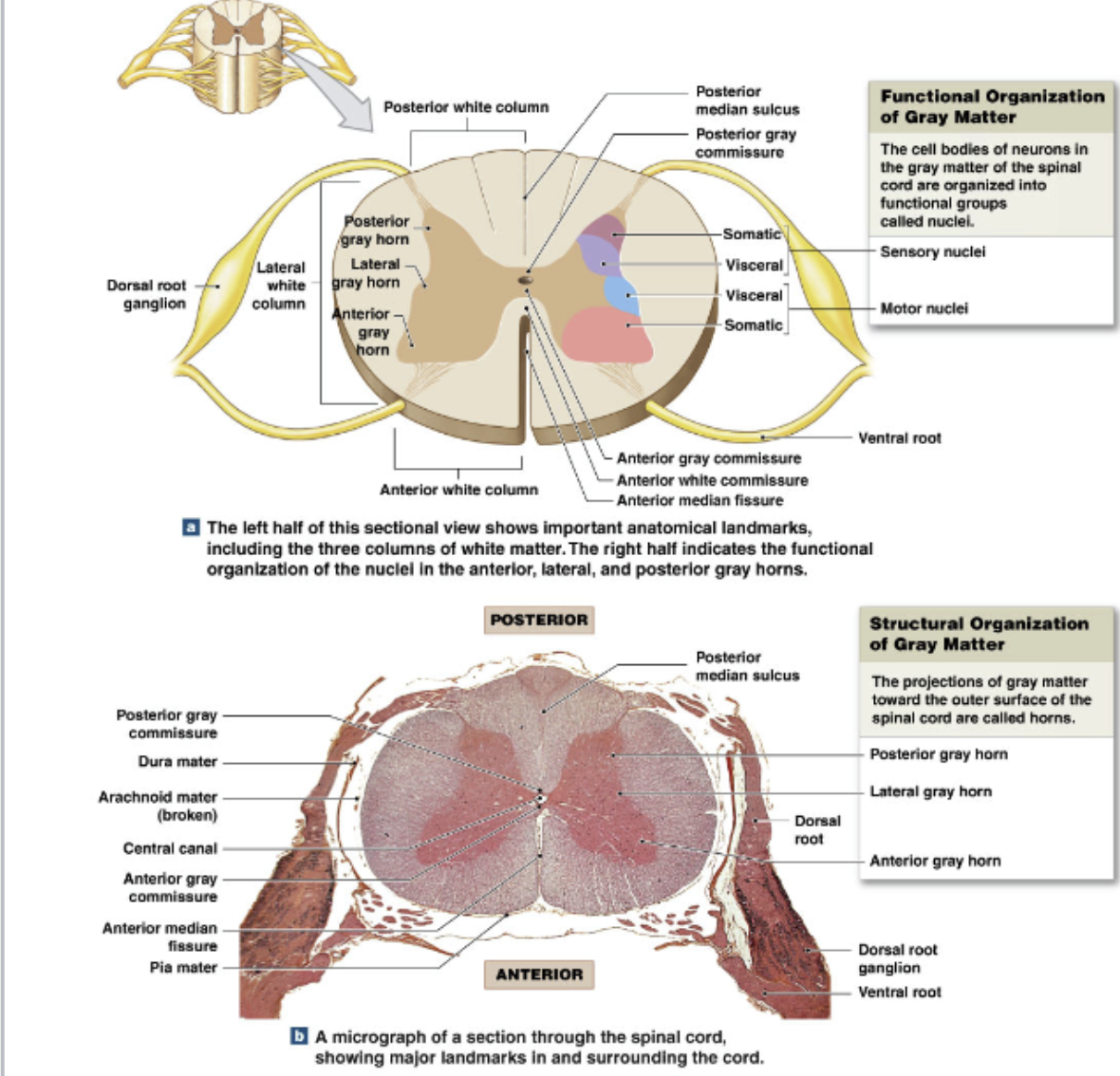
Associated Structures: Meninges
Function: provide structural support, shock absorption, house blood vessels
Epidural space:
between vertebrae and dura mater
areolar and adipose tissue
Dura mater
outer layer
dense collagen fibers longitudinally along SC
Arachnoid mater
thin epithelial membrane
connected to subarachnoid space (has cobweblike structure)
Pia mater:
inner layer
collagen and elastin
physically attached to nervous system
Meningitis
inflammation of meninges
disrupt flow of CSF
damage neurons in affected areas
Epidural Anesthesia and Spinal Taps
Epidural Anesthesia
Administration of anesthetics to epidural space within lumbar region of vertebral column
Pain reducing effect only on nerves in that area
Lumbar Puncture/ spinal tap
sampling of CSF
Reducing CSF pressure
Site: subarachnoid space within lumbar region of vertebral column
Spinal Nerves and Spinal Cord
31 pairs of spinal nerves (junction of dorsal and ventral roots)
innervate neck, truck, upper, and lower limbs
grouped by level and numbered
Cervical Nerves: C1-C8
Thoracic Nerves: T1-T12
Lumbar Nerves: L1-L5
Sacral Nerves: S1-S5
Coccygeal Nerve: Co
Most exit vertebral column via intervertebral foramina
Dermatomes
Area of skin innervated by nerve fibers of a particular pair of spinal nerves
Shingles: variant of chicken pox
attacks neurons within the dorsal root of spinal nerves
painful rash and blistering
follows the dermatomes of affected spinal nerve
Structure of Peripheral Nerves
Nerves contains axons of many individual neurons
Endonurium
perinurium
isolates fascicles
endoneurium
in fascicle, isolate axons.
spinal nerves are mixed nerves
contain efferent + afferent fibers (motor information + sensory information)
branch at later points
Branches (Rami) of Spinal Nerves
spinal nerves branch into
dorsal branch (ramus) of spinal nerve
small
innervates narrow strip of muscles
heads back torwards
Ventral branch (ramus) of spinal cord
large innervates lateral and anterior trunk and limbs
sensory info happens along vertebral
front = ventral
dorsal = back
Spinal Reflexes
Reflex= rapid, unconscious responses to specific stimuli
reflexes are programed → once activated, produce same response
each reflex follows same 5 step reflex arc → circuitry of single reflex
reflex arc
arrival of stimulus → act
Patelar Reflex
monosynaptic response (1 synapse)
receptor: muscle spindle (proprioceptors)
Sensory Neuron: stretch activates neurons that innervate muscle spindle
Motor Neuron: sensory neuron directly synapses with motor neuron in spinal cord
Effector: muscle fibers in region of spindle contract in response to action potentials from motor neurons
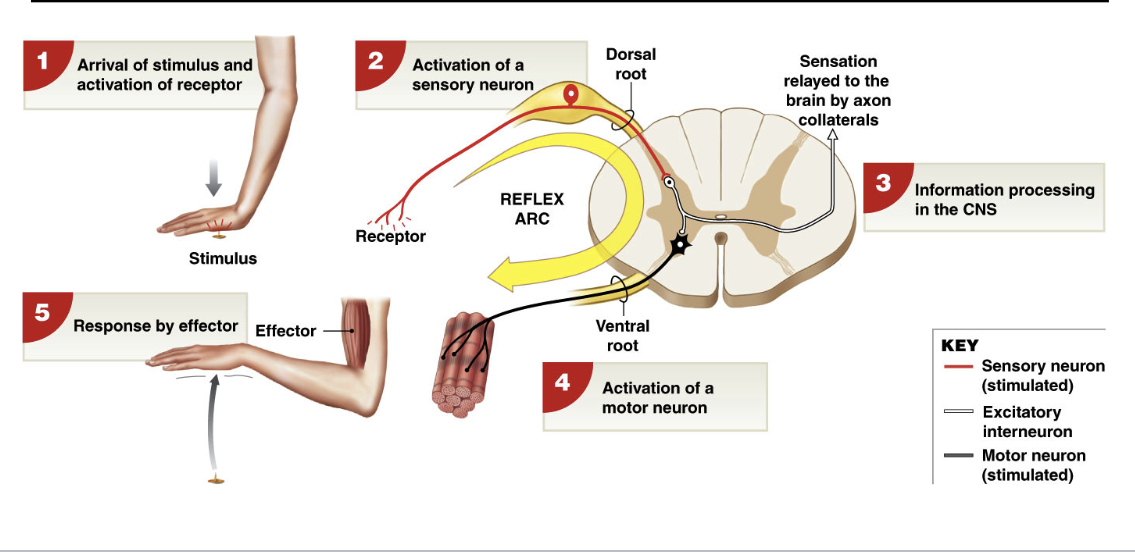
Crossed Extensor Reflex
eztension of the opposite limb
Activation of sensory neuron →
ssstimulation of excitatory motor neurons to extensor muscle on opposite limb
stimulation of inhibitory interneurons to flexor on opposite limb
CONTRALATERAL reflex arc → crosses to other side
note: simple stretch and withdrawal reflexes activate isolateral reflex arcs → same side of the body
Structure and Function of Brain
Embryonic Development of the CNS
nervous system develops from ectoderm
14 days = dorsal streak appears along length of embryo → thickens to form neural plate
18 days: neural plate sinks to form neural groove and neural fold
neural crest cell = ectodermal cells that lie along edge of neural fold
21 days: neural fold fuses along midline → create hallow neural tube
give rise to most neurons and glial cells of CNS (not microglia)
neural crest cells → PNS
neural crest cells separate from neural tube → create longitudinal column of cells
gives rise to meninges and most of PNS
ectoderm → skin and nervous system
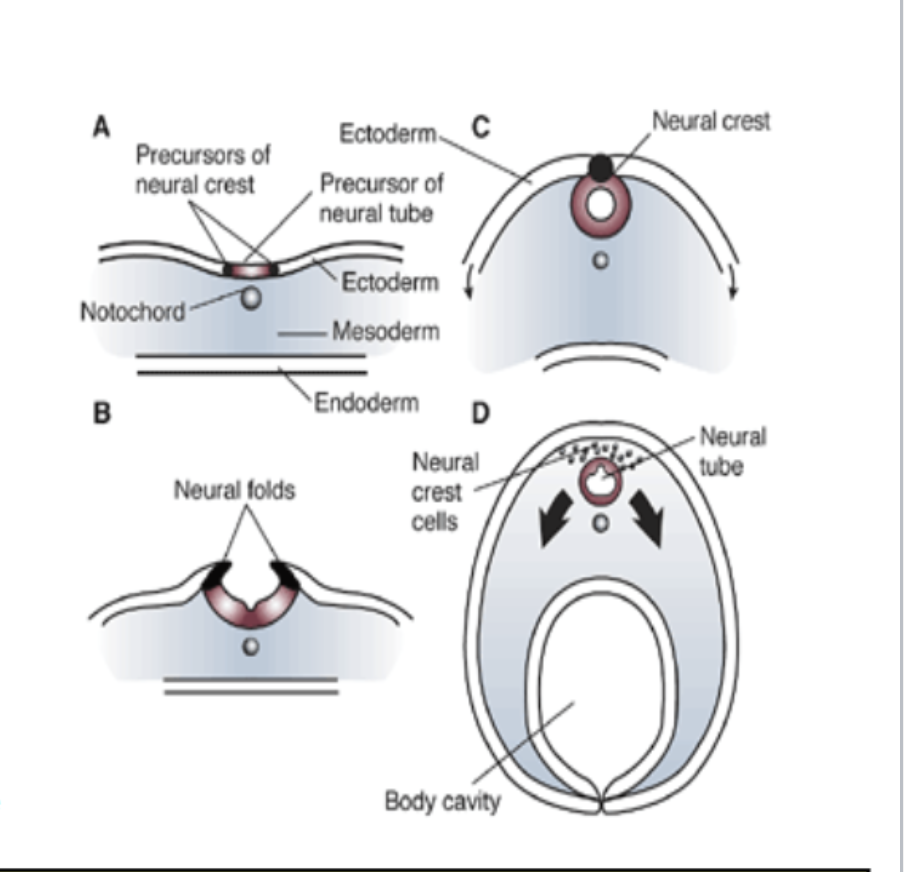
Further embryonic development
Overview of adult brain regions
cerebellum
Pathway of CSF flow
CSF circulates through ventricles, aqueduct, and centra canal
enters subarachnoid space via apertures (holes) within the fourth ventricle that pump csf
CSF is drained into the venous blood (dura sinuses) via arachnoid granulations
entire volume of CSF = 150 mL
CSF is constantly being produced → 500 mL/day
Entire volume of CSF is turned over 3 times/day
Brain stem
includes: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
connects spinal cord to rest of brain → pathway for ascending and descending tracts
site of control for many process that regulate life sustaining function (autonomic)
most cranial nerves connect to brain stem
have cell bodies for most dopaminergic, serotonergic, adrenergic, and cholinergic neurons
→ role in attention/consciousness and habituation, mood, movement, motivation
Medulla Oblongata
pyramids: relay voluntary motor commands from HIGHER centers → spinal cord
olives: relay motor commands from HIGHER centers → cerebellum
Reflex centers of Medulla → receive and integrate input from sensory nerves and other brain regions
cardiac control centers: heart rate, strength of heart contraction
vasomotor control center: blood vessel dilation
respiratory control centers: rate and depth of breathing
Pons
major function → linking cerebellum to higher brain centers and spinal cord
Transverse fibers: link 2 hemispheres of cerebellum
continuation of sensory/motor tracts connecting higher and lower centers and nuclei of cranial nerces
Reflex centers of pons:
2 additional respiratory control centers
mictujhjwehrkuwhrkwehrkehwhrewiuewuke
Midbrain
cerebral peduncles of midbrain: (ventral lateral portion)
location of mostly descending tracts → cerebellum or SC
Tectum of Midbrain (posterior to cerebral aqueduct)
Corpora quadrigemina: process auditory and visual sensations → generate reflex movements (head, body, eyes)
superior colliculus: visual stimuli
inferior colliculus: auditory stimuli
Tegmentum of midbrain (anterior to cerebral aqueduct)
location of structures important for motor control
Red nuclei = connections to cortex and cerebellum → unconscious motor commands
substantia nigra: connections to basal nuclei → normal inhibition of unconscious movement
Cerebellum
Right+ left hemisferes conected by transverse
body position and motor related tasks
integrates senstor
structure:
posterior to pons and medulla
separated in two hemispheres connected by vermis (posterior)
outer gray matter: cerebellar cortex
purkinje cells: extensive dendrites (200,000 synapses) → gray matter of cerebellum → MOTOR CONTROL
inner which matter: arbor vitae
3 large nerve tracts (peduncles) connect cerebellum to other brain regions: superior, middle, inferior
Diencephalon: Thalamus
Sensory process relay station
important function as sensory relay
thalamic nuclei receive a mority of sensory information (except olfaction)
projections to the appropriate sensory cortex
filtering effect → minority of arriving sensory information is passed on
Numerous
Diencephalon: Hypothalamus
Homeostatic regulation of multiple body functions
Nuclei seperately regulate
autonomic functions (influence automatic brainstem functions)
FFF: feeding fighting fucking
Diencephalon: Epithalamus
anterior: poertions
Limbic System
border between diencephalon + cerebrum: nuclei + tracts
c. amygdala
relay between: cerebrum , limbic system, sens
Cerebrum: white + gray matter
gray: cerebral cortex (outside)
White matter: cerebrum
A) association fibers
different regions of the same hemisphere
B) projection fibers
ascending + descending
Grey: basal nuclei → subcortical nuclei
a. caudate nucleus
b. putamen
c. globus pallidus
→ connect with cereb
hemispheric lateralization
Sulci: dividing cerebrum hemispheres
Cerebral cortex functional regions
sensory areas: one for each sense (already filtered by thalamus)
Motor Areas
Association Areas: takes raw data from primary cortex and assigns meaning to ut
Integration Areas: takes info from multiple senses and puts together
Cranial Nerves
KNOW SENSORY MOTOR OR BOTH
I. Olfactory
sensory → smell impulses via olfactory foramina
II. Optic Nerve
V. Trigeminal (MIXED)
wewew
VI. Facial (MIXED)
sensory from taste
VII. Glossopharyngeal
tastes
Somatic Motor Nervous System
efferent neurons
originate in brain, travel to facilitate
decussation
axons of most motor tracts must CROSS THE MIDLINE of spinal cord or brainstem to other side
Corticospinal tract (somatic motor)
voluntary skeletal muscle movement
upper motor neurons descend vuia cerebral peduncles to → pyramids of
Autonomic Motor System (
unconscious maintainance of life support + homeostasis
Hypothalamus: control center for autonomic activity (4 Fs)
→
Motor Pathways: regulate glands, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, adipose
Divisions of ANS: sympathetic (fight or flight)
ANS: parasympathetic (rest and digest)
decreases:
metabikuc rate
Heartrate
blood pressure
increases
Autonomic nervous system working together
SNS and PNS have opposing affects
preganglionic neuron is SHORT
postganglionic neuron is LONG
cell bodies of preganglionic sympathetic neurons originate in lateral gray horns of T1-L2
Travel via Communicating Rami
connect spunal nerves ti sympathetic trunks, contain sympathetic axons
travel to white ramus
(for sympathetic nervous system)
SNS + sympathetic chain ganglia
Pathway for preganglion neuron T1-L2 only
cell body in lateral gray hirn
2 paths:
cell body in sympathetic chain ganglia, follows GRAY ramus to → spinal nerve
SNS + collateral ganglia
pre-gang pathway:
cell body in lateral gray horn
exists spinal cord via ventral root, joins spinal cord
follows white ramus to sympathetic ganglion
SNS + adrenal gland
NO SYNAPSE ON ANY GANGLIA
pre-gang pathway:
exis
80% epinephrine (adrenaline)
20% norepinephrine
Summary of SNS and PNS
Both use acetyl choline
norepinephrine released by post ganglionic fiber is sympathetic nervous system
neuroendocrine found in adrenal glands
epinephrine = more potent form of norepinephrine
spread throughout bloodstream to have wide affect
all alpha and beta receptors recognize norepinephrine and epinephrine
heart has beta receptors
PNS organization:
PREganglionic neuron is LONG
POSTganglionic neuron is SHORT
III. oculomotor → contraction of iris/lens
VII. mucus + saliva production f
IX. saliva production
X. all PNS in thoracic + abdominopelvic cavity
ANS: neuroeffector junction
Neurotransmitters of the ANS
Ach → acetylcholine released by choluinergic neurons
NE relwased nu adrenergic neurons
ALL pregang neurons are cholinergic (PNS, SNS)
parasympathetic pathways
Neurotransmitor receptors
nicotinic receptors:
N1 (skeletal muscle), N2 (postgang)
muscarinic
norepenephrine
(effectors on sympathetic nervous system)i e
Alpha recpetors
Sensory Receptors
goal of each sensory receptor is TRANSDUCTION
general sensory receptors
exterorecreptors: external stimuli
mechanoreceptors: touch, pressure, vibration
thermoreceptors: temperature
nociceptors: pain and itch
proprioceptors: positional and movement of skeletal muscle
muscle spindle, golgi tendon orgon, joint capsule receptors
interoreceptors: internal stimuli
baroreceptors: monitor pressure in hollow organs
chemoreceptors: detect pH, CO2, O2
nociceptors: pain
Specialized Sensory Receptors
vision
photoreceptors
Common Receptors
Mechanoreceptors
ex. tactile/touch receptors, muscle spindle, baroreceptors, mechanoreceptors of inner ear
Ionotropic: Chemically gated ion channels
changes structure of protein to open
ex: nociceptors
Metabotropic: G-protein coupled receptors
ex: photoreceptors, olfactory/taste receptors
General Sensory Pathways: Touch, Pressure, Pain, Temperature
somatic sensory pathways:
First order neuron→ delivers sensory information to CNS (ie: cell body in DRG or cranial nerve)
Second order neuron → cell body of interneuron within spinal cord/brain
Third order neuron → cell body of interneuron within thalamus
synapse on neurons of primary somatosensory cortex
first neuron synapsing on the second neuron travelling up posterior column into medulla oblongata
spinothalamic pathway: anterior tract → crude touch, pressure
spinothalamic PAthways
latera
Proprioceptive input
Proprioceptuve input
first order neuron → synapses in dorsal horn on
sedond order neuron → axons in lateral columns (spinocerebellar pathway) and synapse directly in cerebellum
2 divisions: within lateral column, contralateral and isolateral
does not enter consciousness
both sides cross ober
General sensory pathways: Visceral Input (interoceptors
Visceral Input (interoceptors)
first orfer neuron → axons typically follow pathway od autonomic motor neurons in reverse to spinal cord/cranial nerve
thesoathways are often complex
most major thoracic/abdominal organs send sensory info back via vagus nerve to synapse on
Organization of the retina
layers
pigmented retina:
pigmented epithelial cells
neural retina
photoreceptors (rods and cones) synapse on
→ bipolar cells
→ ganglion cells: axons that make up optic nerve
process starts from back to front
light bounces off back of eye, travel through rods and cones → bipolar cells → ganglion
Photoreceptors
Rods: highly light sensitive (no color)
densely scattered in peripheral retina
Cones: visualize color
3 types: red, green, blue (require more light)
highly concentrated in fovea
specific wavelenths
outer segment: series of membranous disks within photoreceptors
contains the visual pigments
Visual Pigments
absorb photons of light (first step of visual transduction)
found within membranes of outer segments
consist of pigment (retinal)
bound to a protein (opsin)
pigment is always retinal
protein in always opsin
type of opsin determines wavelength sensitivity
1 opsin for rods
1 for each type of cone
visual pigment in rods is rhodopsin
Visual transduction (resting state)
rods in the darkk
chemically gates Na+ channels are open
bound to cGMP
membrane potential: -40mV
continuously releasing neurotransmitter onto biopolar cells
cGMP keeps channels open to let Na+ enter cell to make it less negative
visuawl transduction —> activation
rhodosin is a G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)
step 1
retinal absorbes a photon
converst from 11 cis to 11 trans
acticates opsins
step 2
opsin activates transduction
transucin activates pjospjodoesteraseeeee
cG<P-
olfaction
olfaction and taste are chimical senses; chemical binding a receptor
odorant molecules must be volatile and dissolve through nasal mucosa to reach olfactory epithelium wjcoh contains receptor celod
olfactory recptors
~ 350 human
a receptor can be sensitive to a class or several couses of molecurx
NOT TESTED ON OLFACTORY OSTHESY'
Taste Anatomy
tongue papillae found along edge of tongue
back 1/3 of tongue → hypoglossopalangeal nerve
front 2/3 of tonue → facial nerve
taste buds are also located in soft palate and within epithelium of pharynx
Taste Qualities
each taste cell is responsible to only one taste quality
each taste bud is responsible to all taste qualities
tastants dissolve in saliva and are carried to taste bud through taste pore
qualities
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
others: fat, metallic, calcium, water
flavor is a combination of many senses→ taste, olfaction,
spicy and cooling effects of food are due to activation of pain and temperature receptors on free nerve endings of CN V called chemesthesis (trigeminal sense)
Taste Transduction - salty, sour
salty and sour taste
salt (Na+) and sour (H+) can directly depolarize taste cells via cation pores
H+ and Na+ do not pass through same channels (pores)
sour channel
proton channel
salt channel
epithelial sodium channel (ENaC)
non-sodium specific channels
Taste Transduction - sweet, bitter, umami
sweet, bitter, umami ligands bind GPCRs
2 famililies of taste GPCRs
T1Rs: 3 members
umami - T1R1 and T1R3
sweet - T1R2 and T1R3
T2Rs: 25 members
bitter
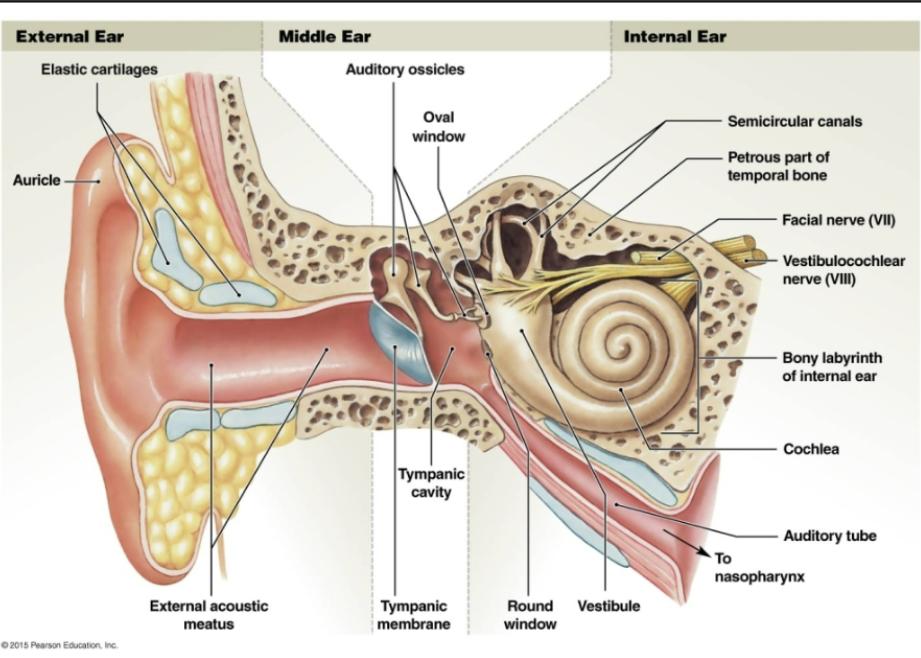
Anatomy of the Ear
NO INFO ON EXAM 3 but on final
anatomy of ear
Equilibium
sound funneled through auriccle into external acoustic meatus
→tympanic membrane (eardrum)
head of snail = vestibule
cochlea = snail shell
antenae = semicircular canals