Micobiology Quiz 2
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
Endospore stain
The purpose is to stain and individualize endospores and differentiate spore-forming cells from non-spore-forming cells
Endospores
Structures that are resistant to heat and chemicals because of a tough outer covering made of the protein keratin. Grow in harsh conditions, such as nutrient loss, temperature, pH, dehydration, UV, or O2 concentrations.
Bacillus anthracis
A bacteria that produces an endospore. Causes anthrax
Common bacteria associated with endospores
Bacillus (aerobic, gram +)
Clostridium (anaerobic, gram +)
What do you need to do during an endospore stain?
When applying the malachite green you need to steam the slide to get the dye into the tough keratin.
What happens to the endospore after the decolorization step in the endospore stain?
The endospore should be green and the vegetative cell should be colorless.
What do you do after the decolorization step in the endospore stain?
Apply safrinin for 1 minute. We use this to stain the vegetative cell. Do not apply heat when doing this step.
Endospore stain
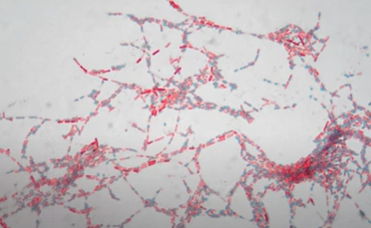
Acid fast stain
Purpose is to stain acid fast bacterial cell walls and differenciate acid-fast bacteria from non-acid-fast bacteria.
Myobacterium
Has a cell wall made up of 60% mycolic acid, which acts as an adherence factor. This adherence factor protects bacteria from phagocytic digestion, dehydration, and chemicals.
What do you need to do during an acid fast stain?
You need to apply carbolfuchsin to the slide and steam it for 5 minutes.
What do you do after the decolorization step in the acid-fast stain?
Counterstain with methylene blue for 1 minute to stain non-acid-fast bacteria. Do not apply heat.
Pink
What color will acid-fast bacteria be at the end of the acid-fast stain?
Blue
What color will non acid-fast bacteria be at the end of the acid-fast stain?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
An acid-fast bacteria. Causes tuberculosis.
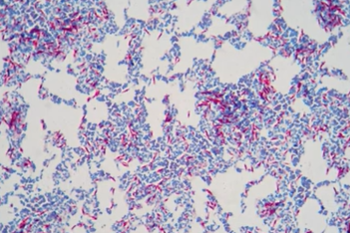
Acid fast stain
Phenol red broth test
Used to determine if bacteria can metabolize a specific carbohydrate.
Durham tube
Tests for gas production.
Phenol red broth composition
Peptones
Sodium chloride (salt balance)
Carbohydrate (substrate)
Phenol red (pH indicator)
Peptones
Partially digested proteins. Used as a food source for general growth.
Phenol red
A pH indicator
Yellow = acidic
Red/orange = neutral
Magenta/pink = alkaline
What does a yellow color with growth mean in the phenol red broth test?
It means the bacteria was able to metabolize sugar. This is a positive result because it turned the solution acidic.
What does a pink color with growth mean in the phenol red broth test?
It means the bacteria were unable to metabolize sugar but used peptones as food. This is a negative result because it turned the solution basic.
What does no growth mean in the phenol red broth test?
This means the results are inconclusive.
Why must a readout be done within 24-48 hours after inoculation in the phenol red broth test?
Readout must be done between 24-48 hours after inoculation, because all the sugars will be used up, lowering the pH if you leave it too little. If you wait too long, the bacteria will start using the peptones for food, which would produce alkaline products, raising the pH.
Chemically defined media
When we know the exact chemical composition of the media.
Fastidious organisms
Organisms that require many growth factors provided in chemically defined media.
Complex (undefined) media
Contain extracts and digests of yeast, meat, or plants. The chemical composition varies batch to batch. Used to culture a variety of bacteria. EX. nutrient broth and nutrient agar.
Agar
A complex polysaccharide derived from seaweed. It is used as a solidifying agent for culture media in Petri plates, slants, and deeps. It is generally not metabolized by bacteria (bacteria do not eat it). It liquifies at 100 °C and solidifies at 40 °C.
Non-saccharolytic
Bacteria are those that do not metabolize sugars.
Caesin
A protein that is partially digested by the pancreas. Used in the phenol red broth for the phenol red broth test.
Oxidation Fermentation Test
Purpose is to determine whether bacteria oxidizes and/or ferments glucose
What do you use for the OF test?
Use a needle to inoculate.
OF test composition
Pancreatic digest of casein (provides food for general growth)
Sodium chloride (salt balance)
Agar (thickening agent, determines motility, and creates anaerobic environment)
Bromothymol blue (pH indicator),
Dipotassium phosphate (buffer, keeping the pH constant)
Bromothymol blue
A pH indicator.
Yellow = acidic
Green = neutral
Blue = alkaline
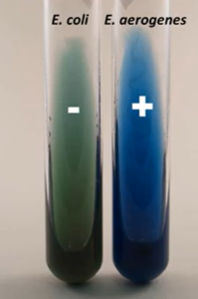
OF Test
+Oxidation
-Fermentation
Strict oxidizer of glucose. This means the bacteria is an obligate aerobe
OF Test
+Oxidation
-Fermentation

OF test
+Oxidation
+Fermentation
Oxidizer and fermenter of glucose. This means the bacteria is a facultative anaerobe. So it grows with or without O₂, but better with O₂.
OF test
+Oxidation
+Fermentation

OF test
-Oxidation
-Fermentation
Non-oxidizer and non-fermenter of glucose. This means the bacteria is non-saccharolytic: doesn't use sugar, but uses proteins aerobically.
OF test
-Oxidation
-Fermentation

How many tubes are inoculated in the IMViC test?
3 tubes are inoculated in this test.
What does “I” stand for in the IMViC test?
Indole
What does “M” stand for in the IMViC test?
Methyl red
What does “V” stand for in the IMViC test?
Vogues-Proskaur
What does “C” stand for in the IMViC test?
Citrate
Indole production test
Used to determine whether bacteria can produce indole from tryptophan (an amino acid). Uses tryptone broth.
What is the substrate in the indole production test?
Tryptophan (an amino acid)
What enzyme is used in the indole production test?
Tryptophanase (endoenzyme)
What are the products of the indole production test?
Indole
Ammonia
Pyruvate
Why can’t you use the pH indicator for the readout of a indole production test?
Ammonia is a base and pyruvate is an acid, so they cancel each other out. This means you won’t be able to detect a change in pH.
What is the reagent in the indole production test?
Kovac Reagent detects the presence of indole. It is not a pH indicator.
Indole production test negative result
Stays yellow which means no indole is present.
Indole production test positive result
Turns pink which means indole is present.
Indole production test
MRVP test
Used to determine whether bacteria ferment glucose into mixed acids or acetoin. Glucose is the substrate for both tests.
What is the substrate in the MRVP test?
Glucose
What is the enzyme in the MRVP test?
Various endoenzymes
What are the products of the MRVP test?
For MR, it is stable mixed acids (decreased pH). For VP, it would be acids at 24 hours and acetoin at 48 hours.
What is the reagent for the MR part of the MRVP test?
Methyl red
What is the reagent for the VP part of the MRVP test?
VPA and VPB.
Methyl red
A pH indicator. It turns pink/red if the pH decreases; this is a positive result due to the pH dropping below 4.4.
VPA and VPB
A reagent that will turn pink/red if acetoin is present; this is a positive result due to the pH rising above 4.4. Not a pH indicator.
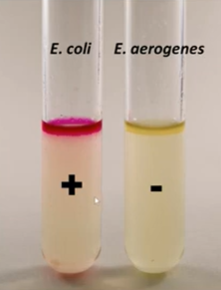
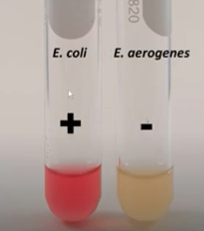
MR test positive result
Turns pink/red because it produces mixed acids, decreasing the pH.
MR test negative result
The color was yellow because the acids were not produced. Also means the pH was greater than 4.4.
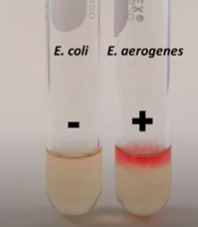
VP test positive result
Turns pink/red because it produces acetoin, raising the pH
VP test negative result
If the color is not red, this means acetoin was not produced.
MR test
VP test
Citrate Utilization Test
Used to determine whether bacteria can utilize citrate as a sole carbon source.
Citrate Utilization Test composition
This is a defined media
Sodium citrate: The sole source of carbon - organisms need carbon to make ALL macromolecules
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate: Source of nitrogen; if organisms can use citrate as a sole carbon source, it will also break down ammonium phosphate as well for basic products
Dipotassium phosphate: Buffer - to keep the pH constant
Sodium chloride: Salt balance
Agar: A solidifying agent.
Bromothymol blue: pH indicator. Yellow = acidic, Green = neutral, Blue = alkaline.
Sodium citrate
The sole source of carbon - organisms need carbon to make ALL macromolecules
Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate
Source of nitrogen; if organisms can use citrate as a sole carbon source, it will also break down ammonium phosphate as well for basic products
Bromothymol blue
pH indicator used for the citrate utilization test. Yellow = acidic, Green = neutral, Blue = alkaline.
What is the substrate in the Citrate Utilization Test?
Citrate and ammonia phosphate
What is the enzyme in the Citrate Utilization Test?
Citrate permease and citrate lyase. They are both endoenzymes.
What are the products of the Citrate Utilization Test?
Ammonia and ammonium hydroxide. These are indirect products of the citrate metabolism.
Citrate Utilization Test positive result
The pH will rise or bacteria will grow because the bacteria utilize the citrate as a sole carbon source. This will turn it blue OR green with growth
Citrate Utilization Test negative result
Green with no growth. This is because the bacteria did not utilize the citrate as a sole carbon source.
What do you use to inoculate in the Citrate Utilization Test?
You use a needle to inoculate in this test. This way you don’t transfer too much bacteria.
Citrate Utilization Test