1.3 - Contemporary Psychology
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Psych
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Eclectic model
An approach that pulls together multiple ways examining / schools of psychology for a particular problem or question
biopsychosocial approach
recognizes three equally important aspects of human mental processes and behavior: biological, psychological, and social.
levels of analysis
Various ways of examining the same psychological phenomenon.
No one perspective provides the one and only answer,
levels of analysis when considering aggression
The complex layers of influence are best appreciated when combined to examine how they interact.
biological approach - suggests that aggression is related to the amount of testosterone in the system
culture - influence violence
experiential factors - such as learning can increase or decrease aggression
The Biological & Evolutionary Perspective
assumes that human behavior can be explained and predicted using biological processes.
builds on work from Charles Darwin and considers evolutionary factors, natural selection & heritability
Neuroscience - studies the connection between behavior and the body, brain and nervous system
The biological perspective uses a variety of research approaches, including the study of genetics, activity of individual brain cells, and patterns of activation across the brain over time.
This is made possible through new tools such as complex imaging techniques, including …
positron emission tomography (PET)
functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
positron emission tomography (PET)
a neuroscience imaging technique that uses radioactive glucose to indicate areas of activity in the brain
functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
a noninvasive brain imaging technique that uses powerful magnets and radio equipment to produce detailed images of the soft tissue in your brain.
heritability
how much of a characteristic can be linked to genetics as opposed to the environment
natural selection
the process by which organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and reproduce more successfully than those less adapted.
Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic Perspective
A family of theories originated by Freud that focuses on unconscious motivation and childhood experiences
unconscious mind
According to Freud, thoughts, memories, feelings, and wishes that reside outside of awareness.
The Behavioral Perspective
The study of learning based on directly observable actions.
Assumptions
All behaviors are learned from our environment.
The behaviourist approach argues we are born as a blank slate (tabula rasa) and our experiences (stimuli) shape our actions.
Only observable, measurable behavior is worthy of study – no reference to internal mental states, since those cannot be objectively seen or measured.
Animals and humans learn in the same ways, so behaviorists carry out experiments on animals and extrapolate the results to humans.
Psychology should be scientific and objective therefore behaviorists use mainly laboratory experiments to achieve this.
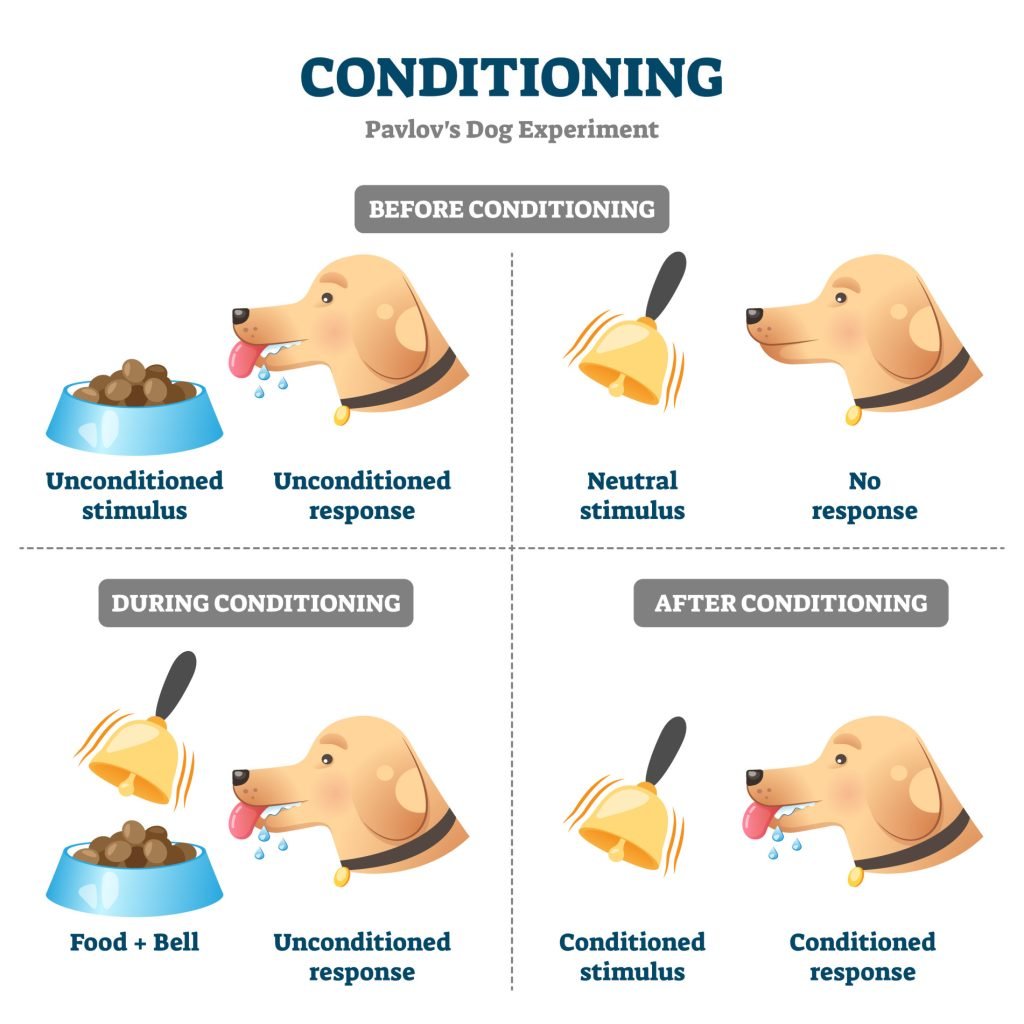
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning - a type of learning that occurs through association.
Pavlov’s Experiment - demonstrated classical conditioning by showing that dogs could learn to associate a neutral stimulus (like a bell) with food, eventually salivating at the sound alone.
Humanistic Psychology
emphasizes the study of the “whole” individual, rejecting the idea of breaking down human behavior and experience into smaller components, instead advocating for holism.
Assumptions
Every person has their own unique way of perceiving and understanding the world, and the things they do only make sense in this light.
This approach is not objectivity as the other approaches; its aim is to understand people’s subjectivity.
People are self-determining, they have free will they can make choices about the way they think and act.
self-actualization
the innate desire to achieve one’s full potential, becoming everything one is capable of becoming.
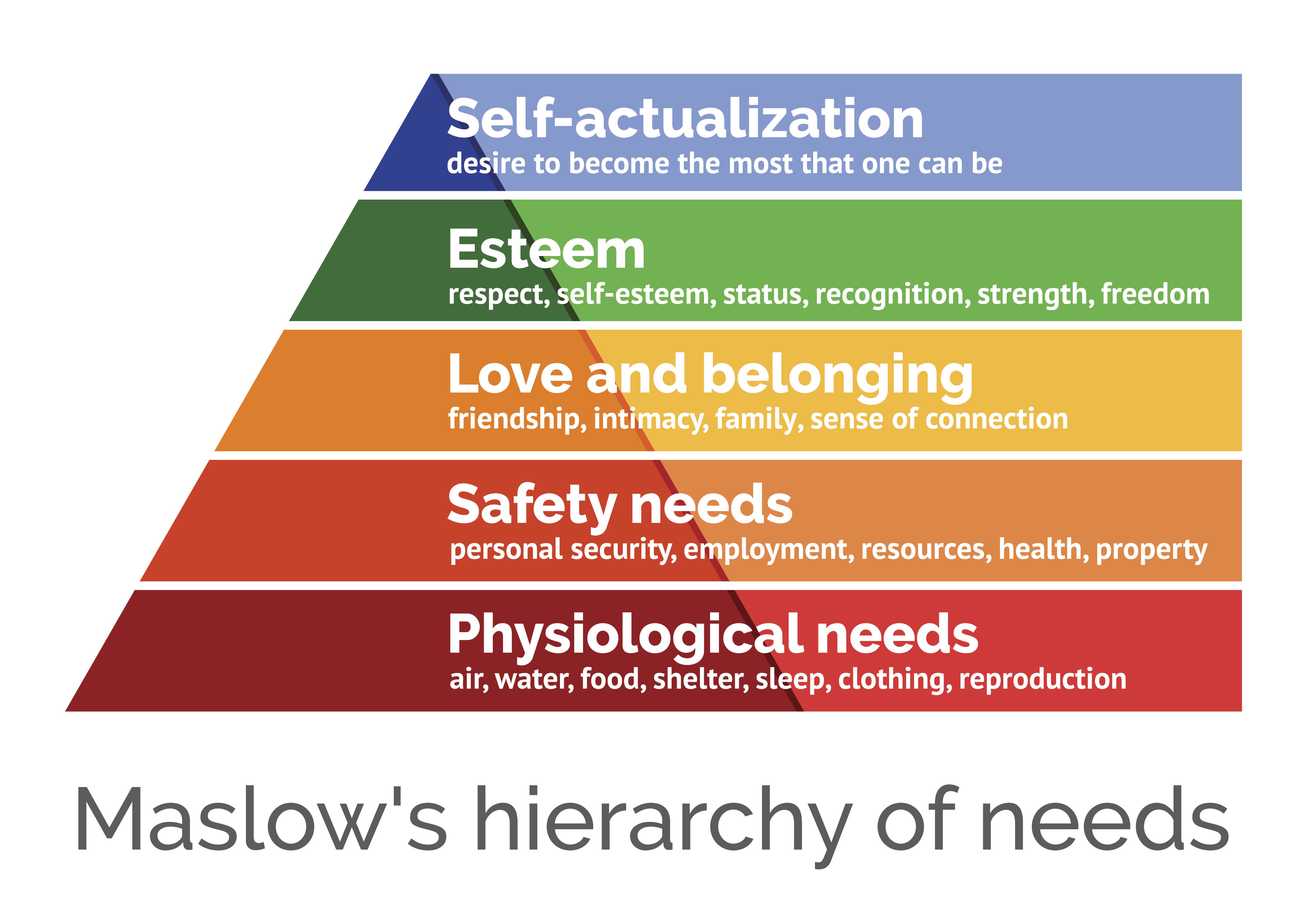
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
before an individual can achieve self-actualisation, other basic “deficiency needs” at lower levels must be met.
The hierarchy is typically ordered from bottom to top as follows:
Physiological Needs: Basic survival needs such as food, water, and sleep.
Safety and Security Needs: The need to feel safe and out of danger, including having a home, employment, and good health.
Love and Belonging Needs: The need for friendship, intimacy, and acceptance by others.
Self-Esteem Needs: The need for confidence, achievement, and being respected by others.
Humanistic psychology can be seen in positive psychology, …
a branch of psychology that emphasizes the constructive features of human strength and healthy living rather than sickness and pathology.
The Cognitive Perspective
emphasizes the internal processes of thought that help us make sense of the world. (the mind is like a computer)
Assumptions
The main assumption of the cognitive approach is that information received from our senses is processed by the brain and that this processing directs how we behave.
These internal mental processes cannot be observed directly, but we can infer what a person is thinking based on how they act.
Cognition
All types of thinking, including knowing, remembering, reasoning, deciding, and communicating.
cognitive neuroscientists
A scientist who studies brain action as it is linked to thought, perception, and language.
The Sociocultural Perspective
school of psychology that emphasizes the way that social and cultural elements in the world (or environment) influence behavior and mental processes.
Social Psychology focuses on how our thoughts, feelings and behaviours influence and are influenced by others (includes Social Learning Theory)
Cross-Cultural Psychology examines and compares behaviors and mental processes between different cultures
a check on ethnocentrism
ethnocentrism
Believing that your own group is superior to others and should be the standard by which other cultures are judged.
social learning theory
explains how people learn behaviors, attitudes, and emotional reactions through observing and imitating others.
basic research
A type of research concerned with expanding knowledge, even if the knowledge has no practical application.
applied research
research driven by a need to solve a specific problem.
2 main professional organizations in psychology
The American Psychological Association (APA)
The Association for Psychological Science (APS)
Which contemporary perspective’s primary aim is to explain the impact of natural selection on behavior and mental processes?
A. The biological perspective
B. The behavioral perspective
C. The evolutionary perspective
D. The humanistic perspective
C
Didier’s therapist says that Didier is anxious because of unconscious conflicts. His therapist is using the _____ perspective to explain his anxiety.
A. biological
B. psychodynamic
C. evolutionary
D. humanistic
B
Roberta’s therapist says she is anxious because of underactive neurotransmitters in her nervous system. Roberta’s therapist is using the _____ perspective to explain her anxiety.
A. humanistic
B. behavioral
C. biological
D. cognitive
C
Ian is studying the levels of testosterone in the body as they rise and fall during the year. He is investigating this in order to expand knowledge. This research is known as _______ research.
A. applied
B. basic
C. anecdotal
D. eclectic
B
Which of the following are settings in which you are likely to find a psychologist?
A. Private practice
B. Hospitals
C. Industry
D. Schools
E. All of the above
E
Psychologists have developed focused specializations of research and practice, with specialty subfields including …
including clinical, counseling, industrial/ organizational, education, developmental cognitive, social, and personality.