Eye Complaints & Evaluation (Exam 3)
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Visual Acuity PE
-Do each eye individually (OD, OS)
-Recorded as 20/___
-Best done with glasses
Pupils PE
-Important if suspecting a neurologic problem
-Checking:
-Size of each in bright & dim light
-Response to light
-Response to near
-Marcus Gun Swinging flashlight test: Assess for afferent pupillary defect (presence indicates difference between 2 eyes)
Extraocular Motilities PE
-Important if there is a complain of diplopia
-Perform H motility test to determine if there is a specific EOM that is affected
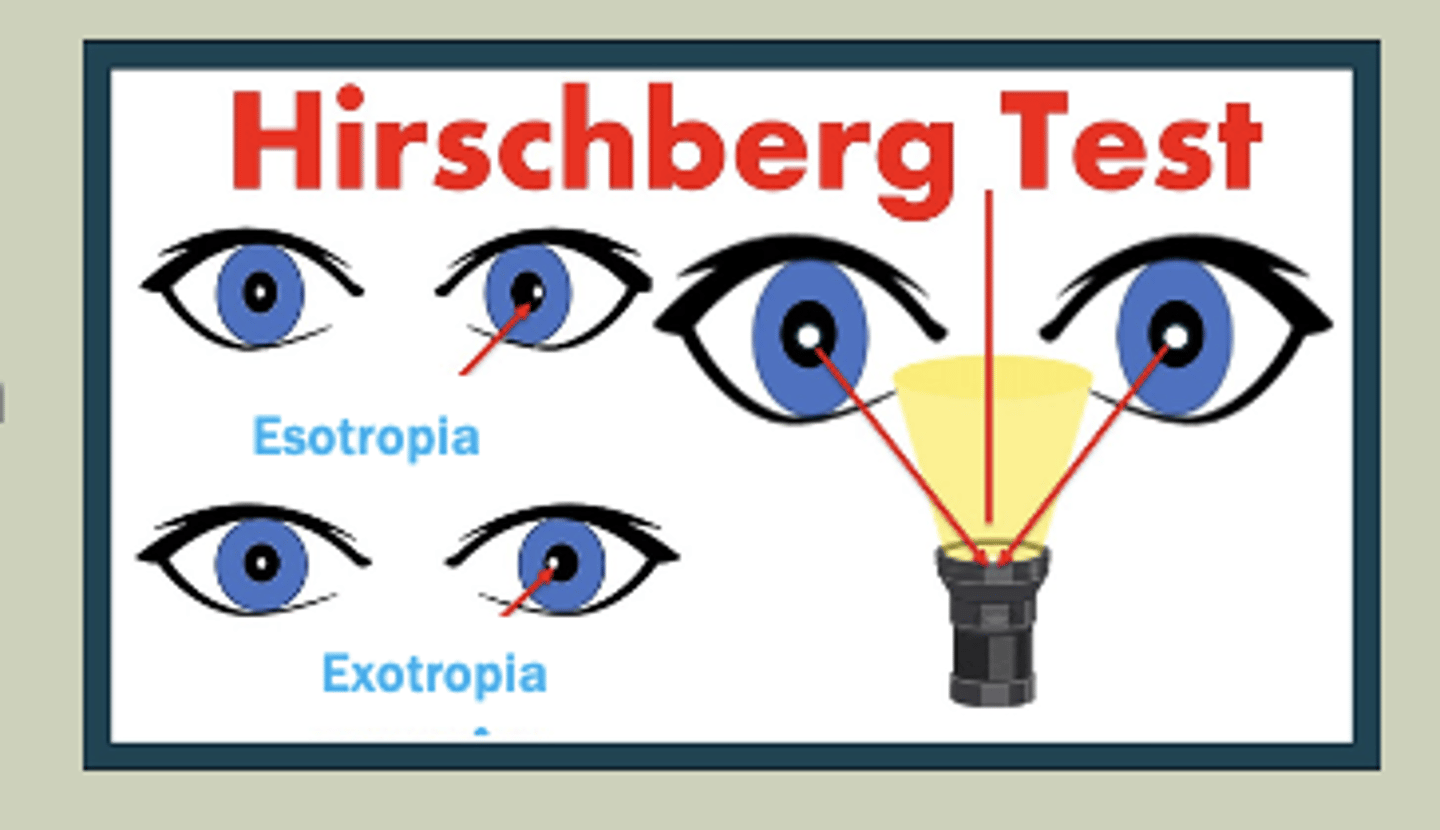
Eye Alignment PE
-Have pt look at light that is equally projected between 2 eyes
-Look for symmetry at the reflected reflex on cornea
-If reflex is temporal: Esotropic
-If reflex is nasal: Exotropic
Palpating Pre-Auricular Lymph Nodes PE
-Important with complaint of conjunctivitis
-(+) indicates viral conjunctivitis
Intraocular Pressure (IOP) PE
-Helpful if considering pt is in acute angle closure
-Tactile pressure
-Tonopen: Anesthetic; tap center of cornea until IOP is measured; Looking for IOP of -21mmHg or less
Slit Lamp Biomicroscopy
-Allows for increased magnification
-More specific location of lesions/abnormalities
Gross Inspection PE
-Make sure to pull eyelids up/down
-pt look in all directions
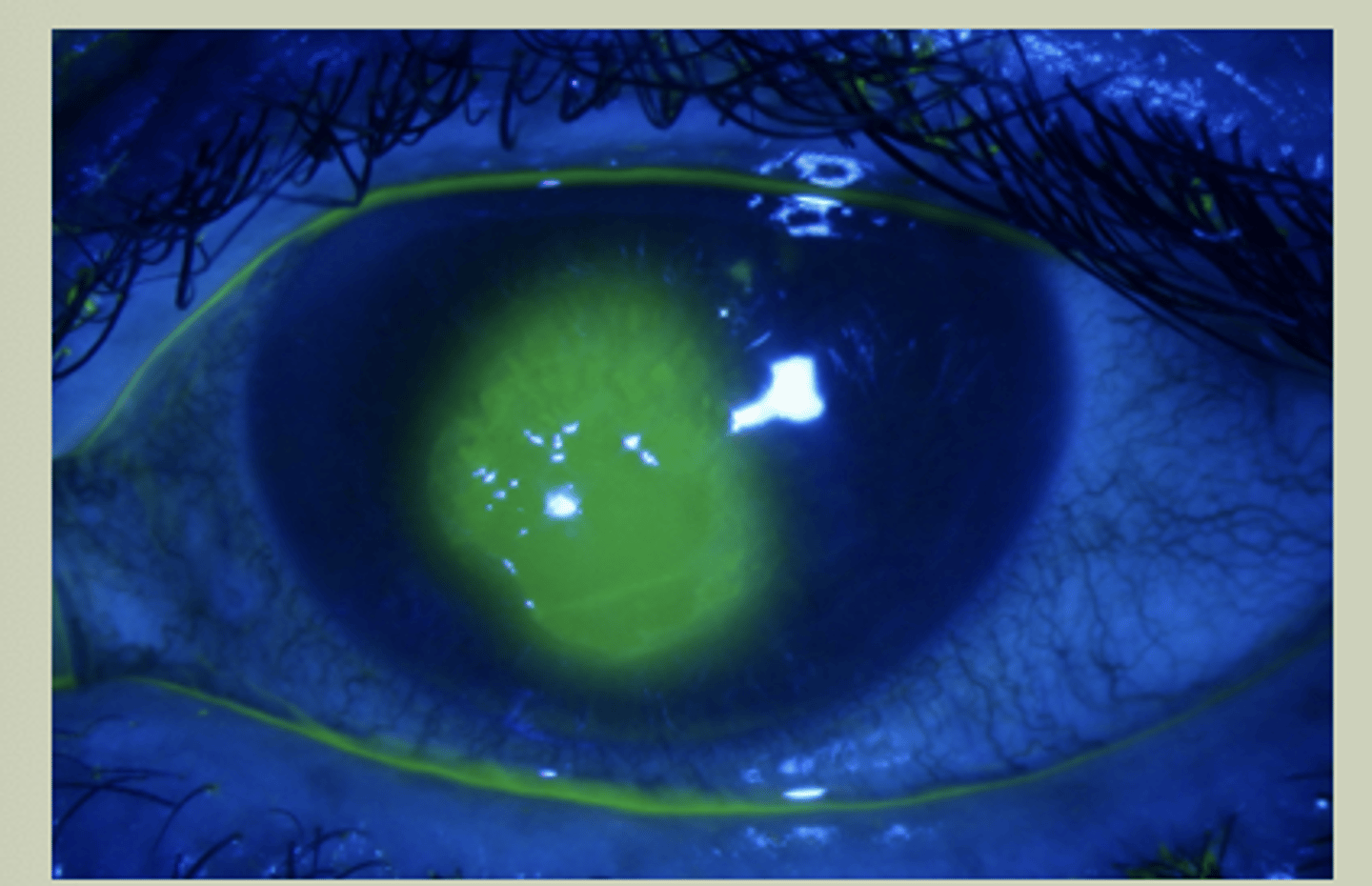
Corneal Fluorescein (FI)
-Will pool in areas of corneal defects
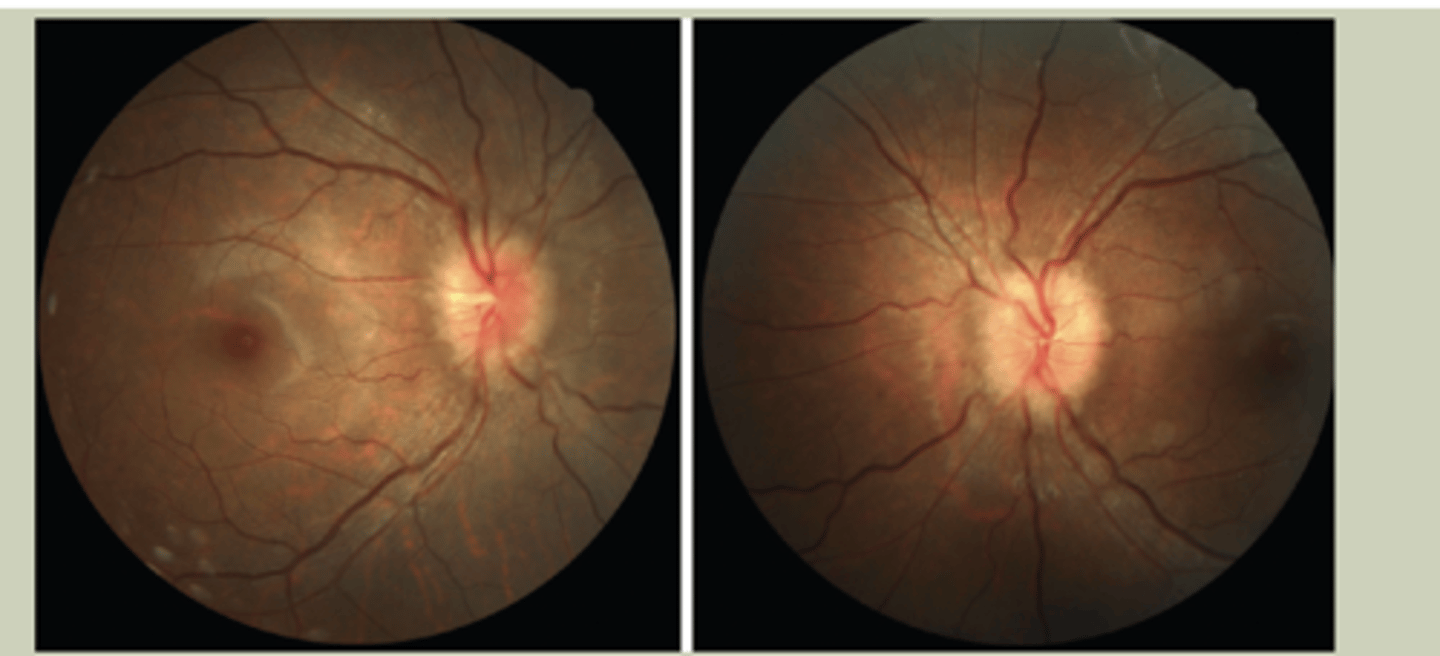
Posterior Segment Assessment
-Can be dilated or undilated
-Direct Ophthalmoscopy (DO)
-Optic Nerve Head: Flat, elevated, blurred disc margins, C/D ration
-Retina: Presence of blood, exudates, or other abnormalities
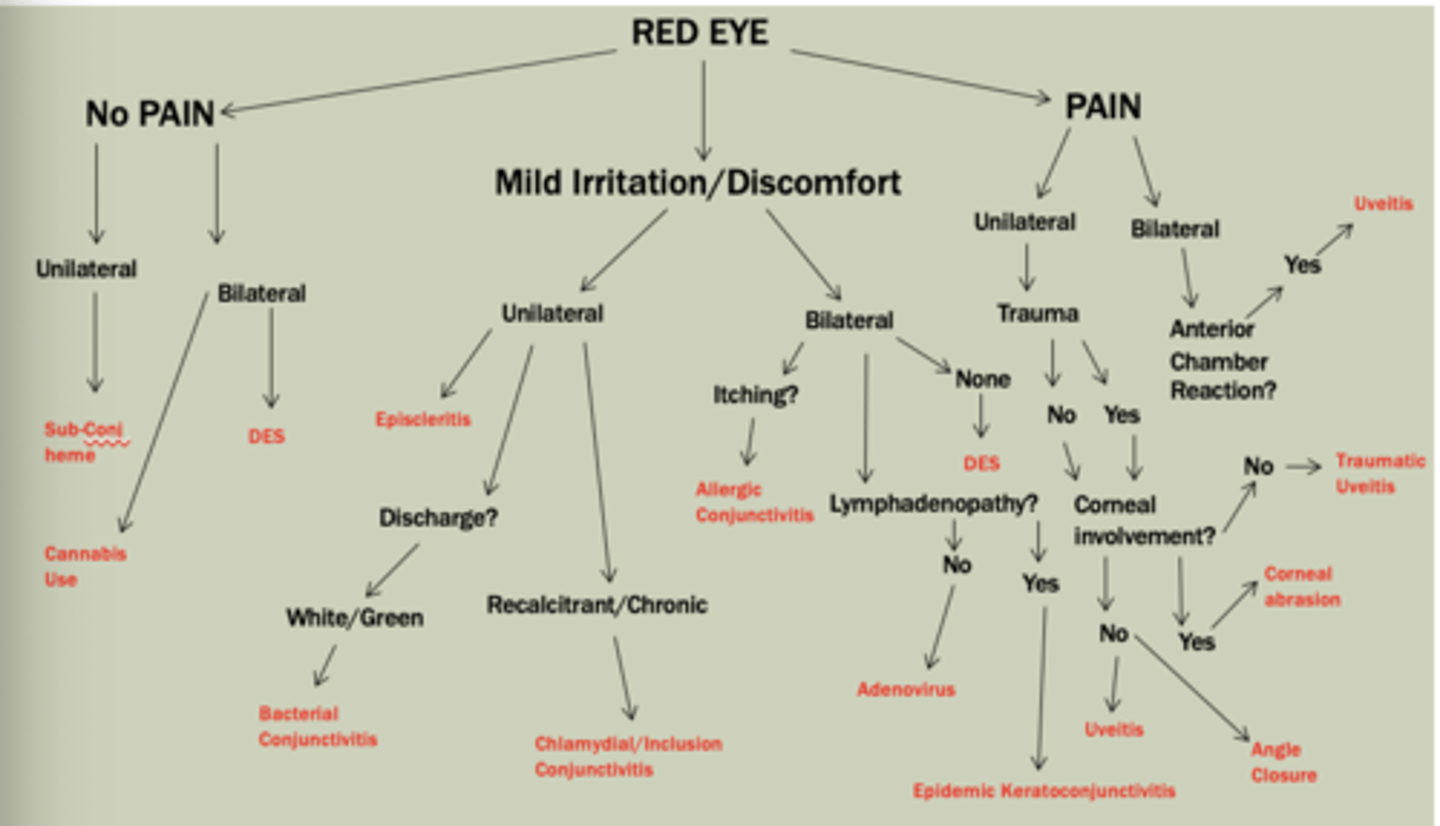
Red Eye Differentiation
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
-Unilateral, pain-less red eye, usually sectoral
-Blood beneath conjunctiva, may have chemotic appearance
-Etiology: Valsalva; bleeding disorder; antiplatelet meds (Aspirin, Clopidogrel, warfarin, plavix- DO NOT advise to stop using)
-Typically, self-resolves within couple weeks
Dry Eye Syndrome
-Multifactorial disease of tears and ocular surface
-Eye discomfort, visual disturbance & tear film instability
-Etiologies: Evaporative (MC) tear evaporate too quikcly; & Aqueous Deficient is lack of production from lacrimal gland
-Dryness, mild pain, foreign body sensation, redness
-Signs: Injection/hyperemia, lid disease, debris in tear film
-TX: refer to eyecare for chronic management
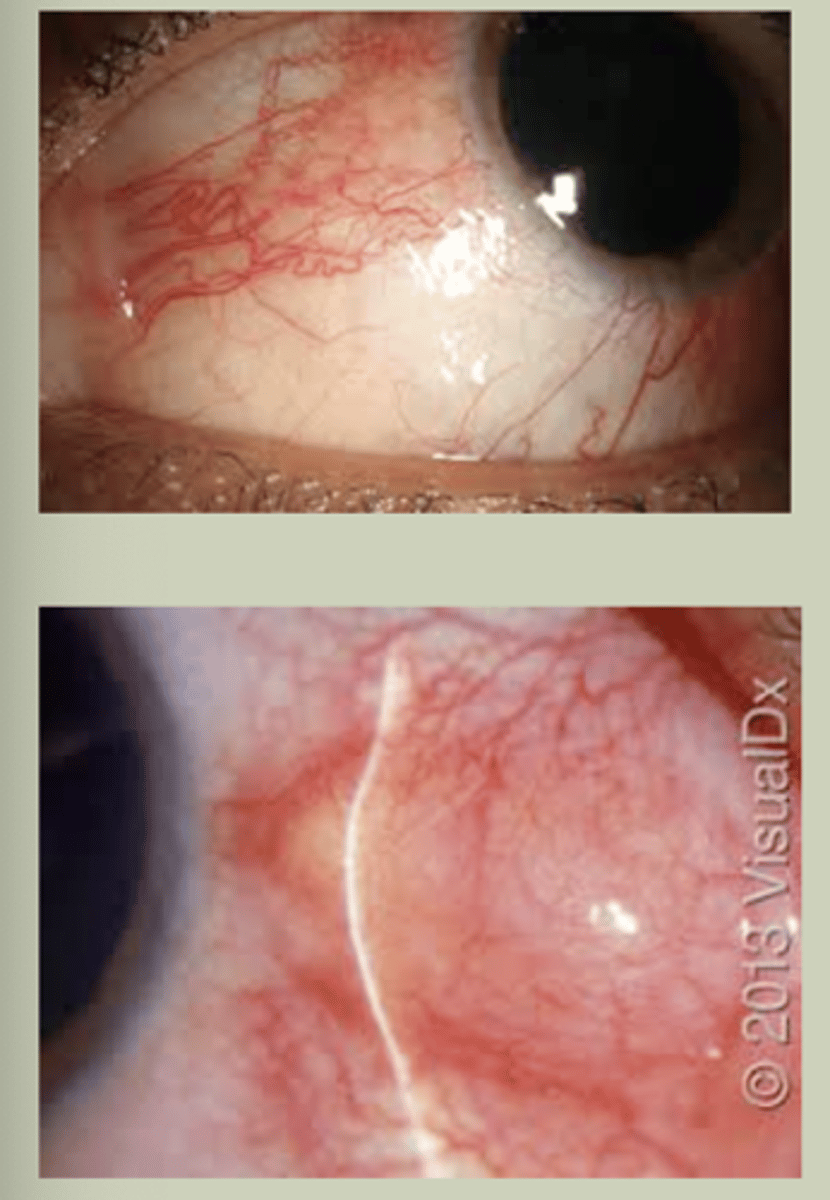
Episcleritis
-Sectoral redness, unilateral
-Mild irritation, discomfort, prickly sensation in eye
-Does not cause change in vision
-Progressing cases can indicate collagen-vascular disease
-Refer to ECP for TX & management
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
-Unilateral with variable colored discharge
-Signs/SX: Unilateral red eye with white/green discharge
-TX: Topical ABX, refer to ECP
Simple Bacterial Conjunctivitis MC Cause
-S. Aureus
Gonococcal Conjunctivitis MC Cause
-N. Gonorrhea
-Hyperacute onset, severe discharge, pre-auricular lymphadenopathy
-Ask about urethral discharge
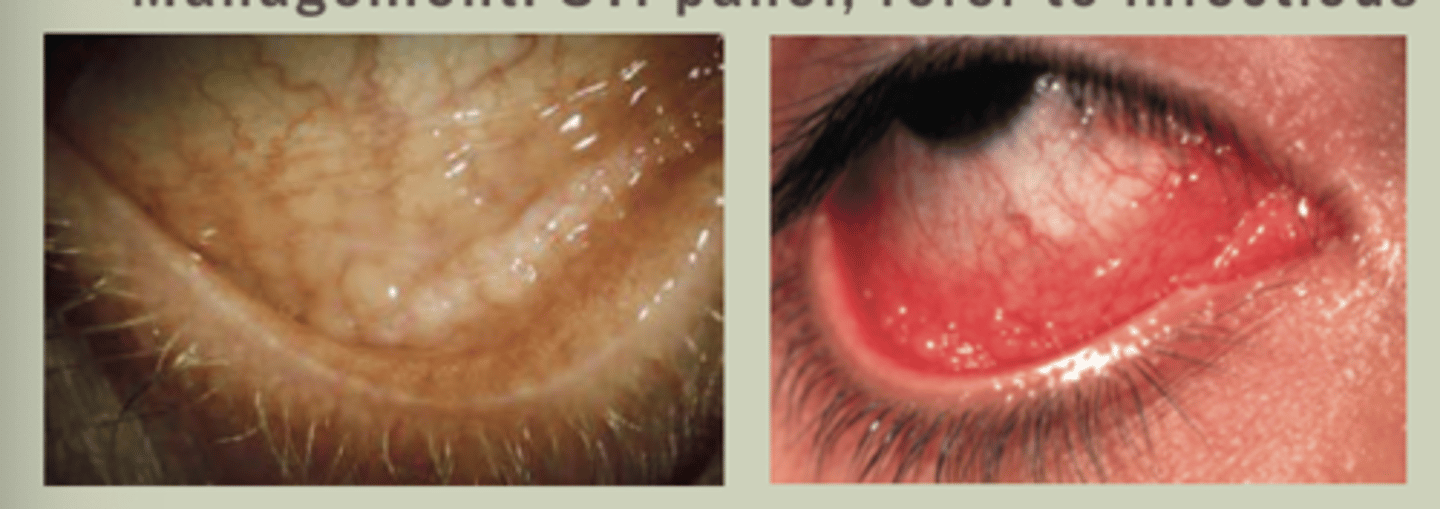
Chlamydia/Inclusion Conjunctivitis
-Unilateral, chronic red with marked inferior follicles
-Trachoma Serotypes A-C; Adult inclusion is D-K
-Usually dx of exclusion
-TX: 1g azithromycin PO
-Management: STI panel, refer to ID
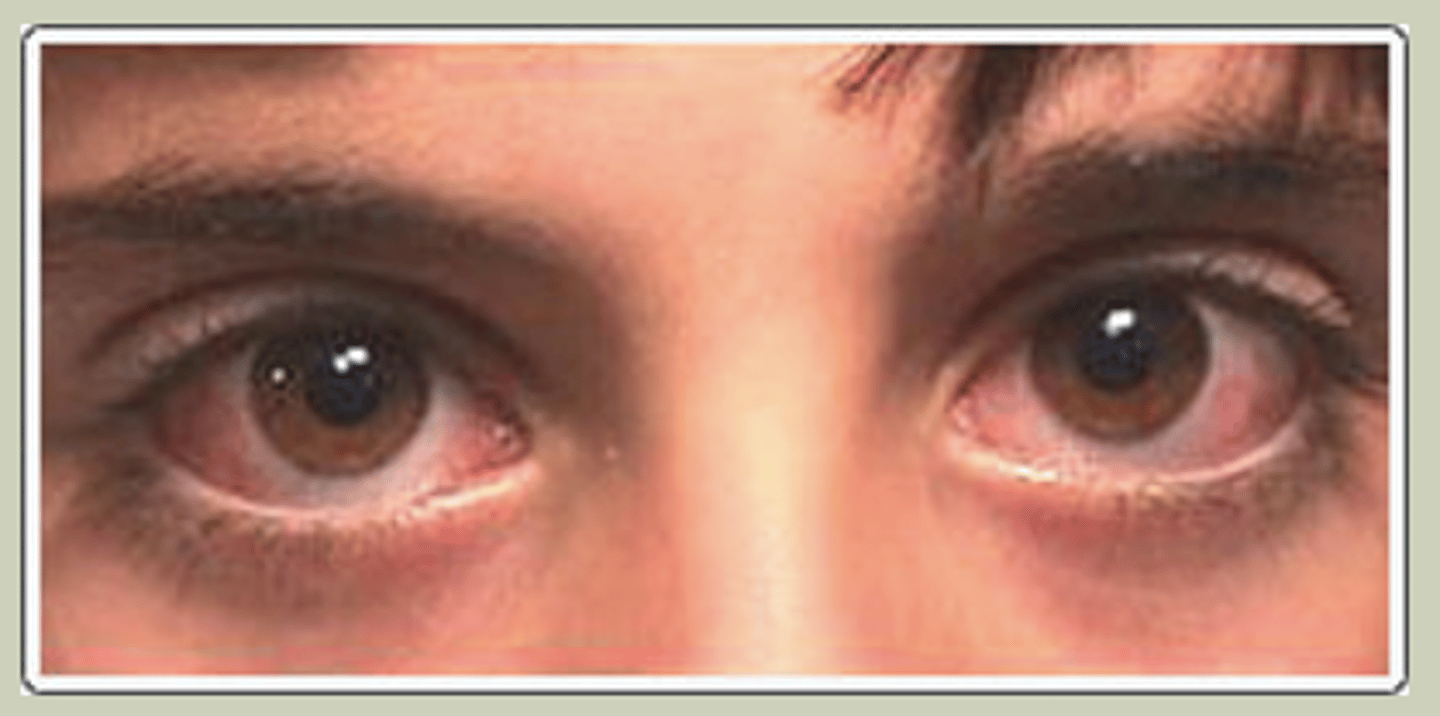
Allergic Conjunctivitis
-Bilateral presentation, IgE mediated by allergens
-SX: itching, tearing, redness
-Signs: bilateral red eyes with watery discharge, may have mild chemosis
-Worse in Spring/Summer
-TX Cold compress, mast cell stabilizer/Antihistamines; refer to ECP
Adenovirus Conjunctivitis
-Bilateral, asymmetric, conjunctivitis
-MC viral conjunctivitis presentation
-MC URI transmission
-SX: FBS, tearing, red eyes one eye worse than other
-Signs: Red eyes, watery discharge, NO lymphadenopathy
-Self-limiting condition
-TX: supportive therapy, patient education, refer to ECP
Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis
-Bilateral, symmetric presentation
-More common in adults
-SX: profuse watery discharge, periorbital pain
-Signs: Bilateral red eyes with serous discharge, pre-auricular adenopathy, pseudomembranes, or subepithelial infiltrates
-TX: Refer to ECP for pseudomembrane peeling, pt education about contagiousness
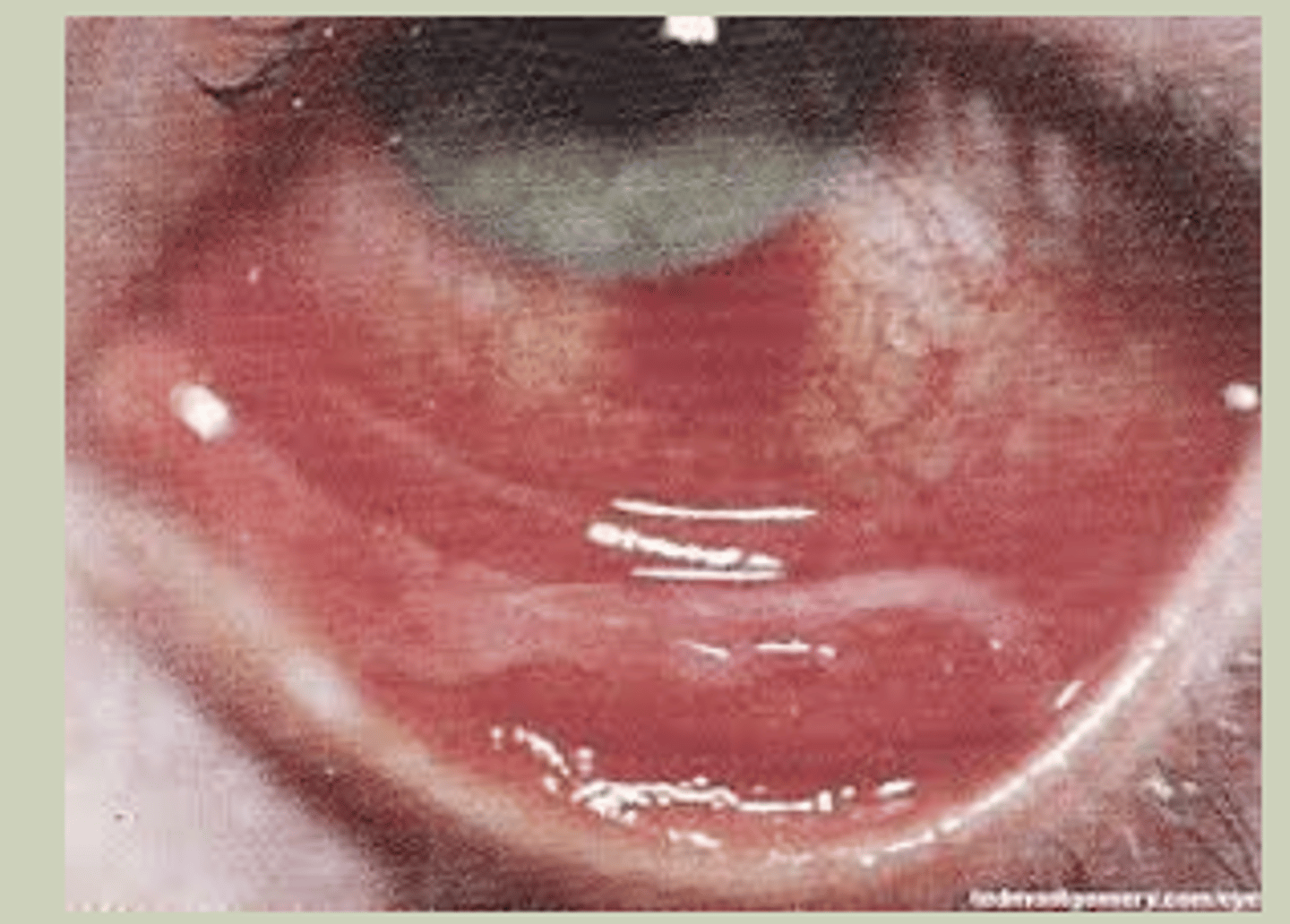
Anterior Uveitis
-Unilateral or Bilateral
-Non-granulomatous vs granulomatous
-SX: red eye, ocular pain, photophobia
-Signs: Cell and flare in anterior chamber; need slit lamp to see; may have hypopyon
-Can be sign of infectious/autoimmune process
-TX: Topical Steroid q1h, Cycloplegic BID, refer to ECP
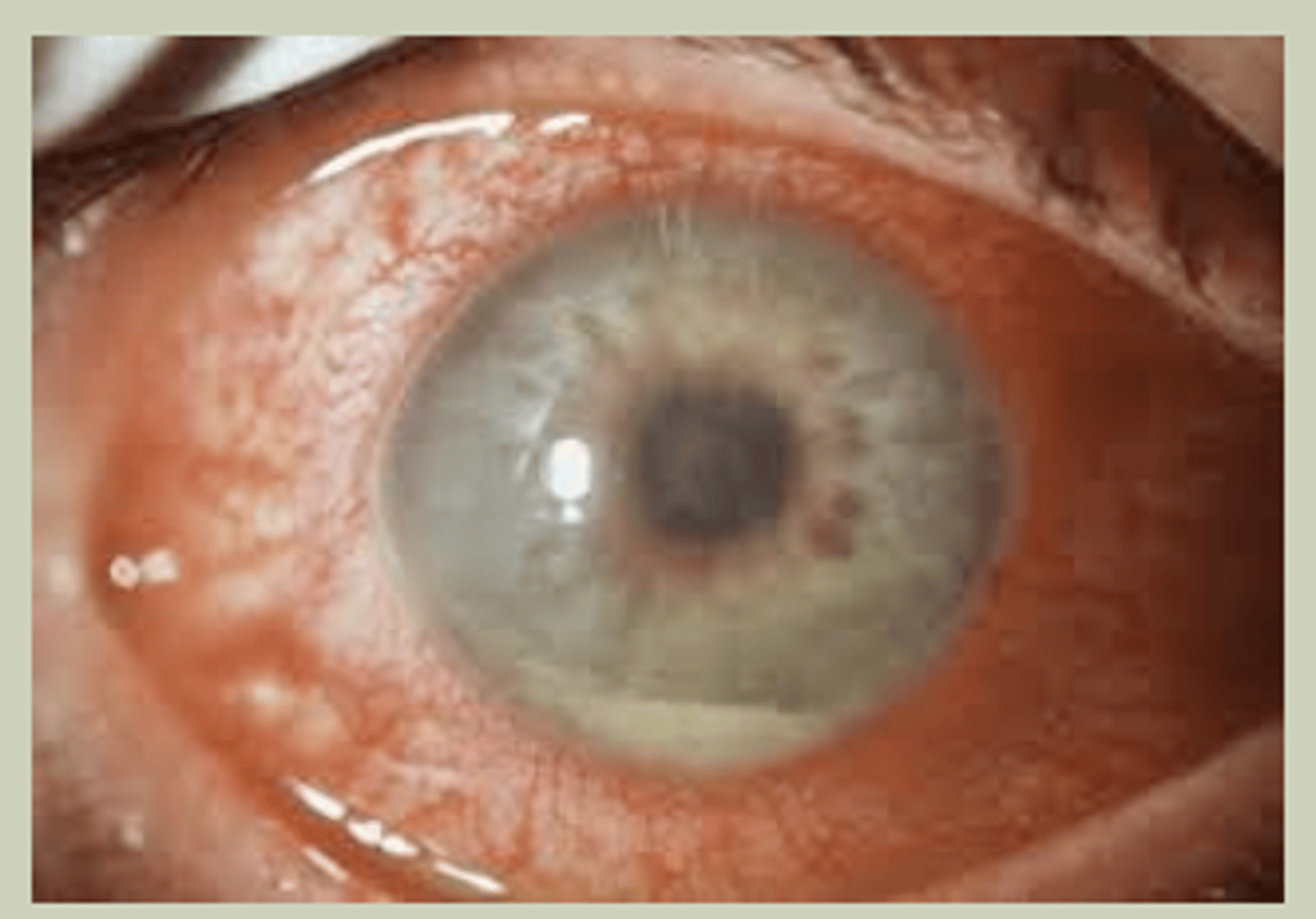
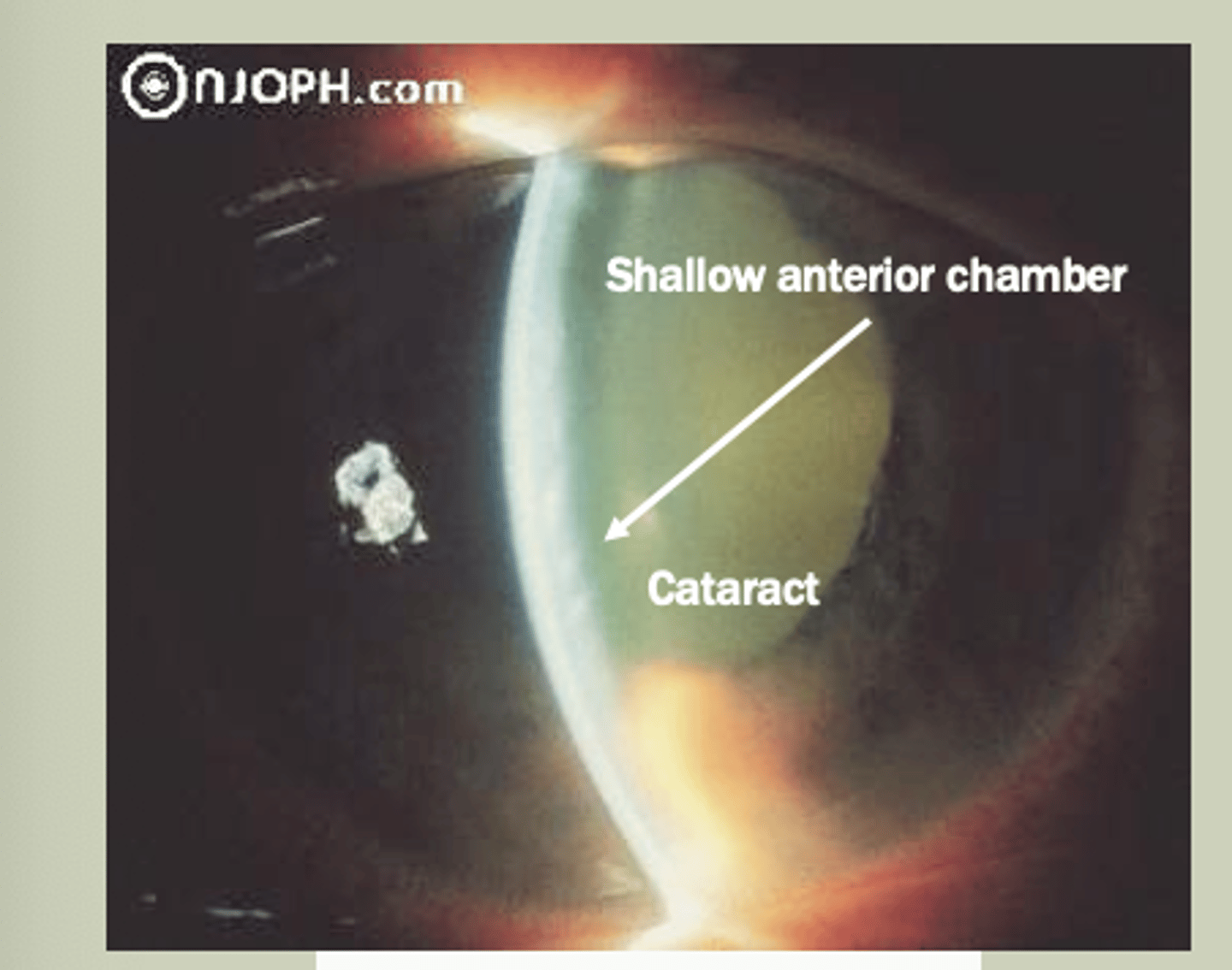
Acute Angle Closure
-Unilateral in older pts due to closure of drainage system
-SX: red eye with pain, blurred vision, may have headache/vomiting
-Signs: Pupil rxns is sluggish, hazy cornea, elevated IOP>30 mmHg
-TX: Refer to ECP STAT for Laser Peripheral Iridotomy (LPI)
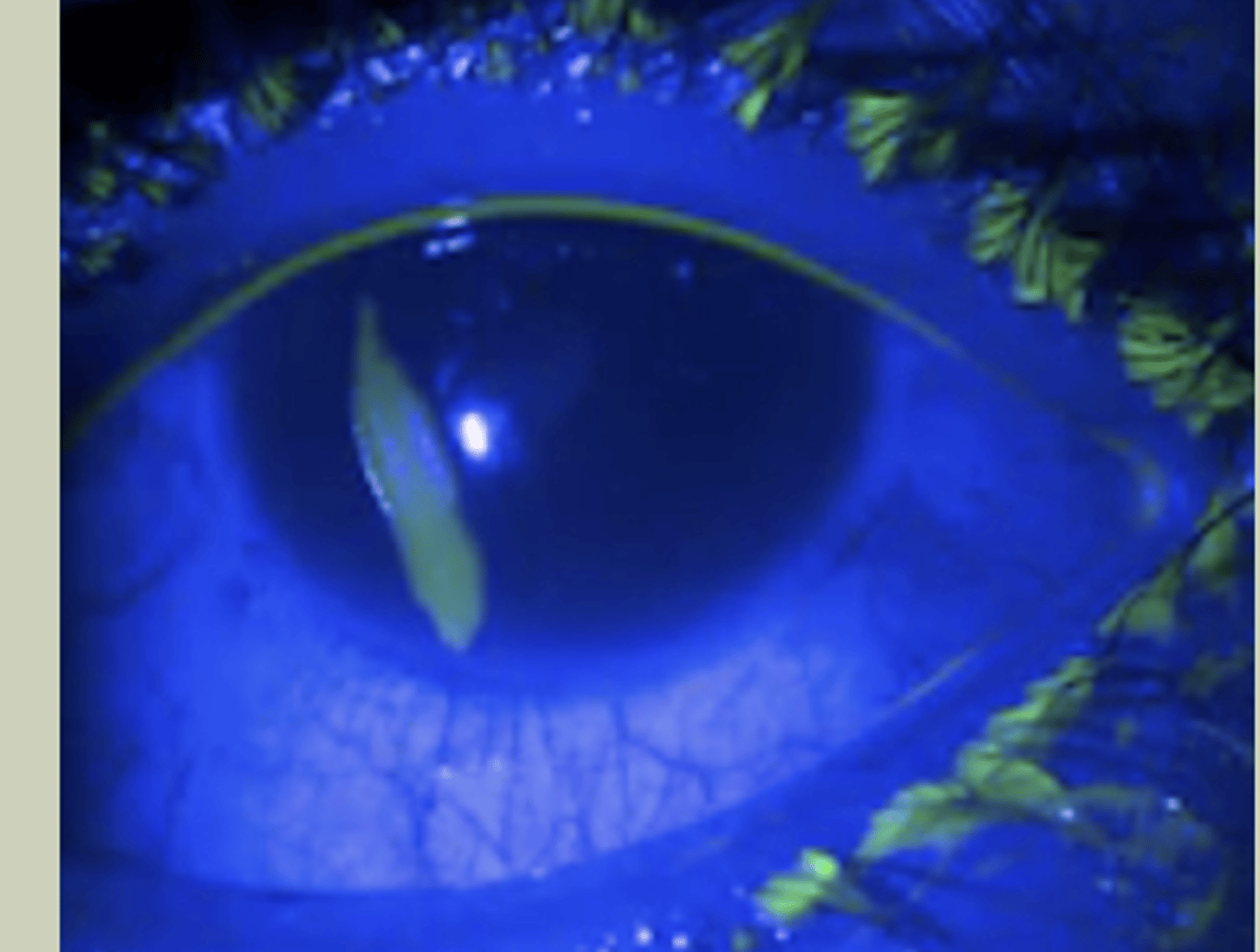
Corneal Abrasion
-Unilateral
-Hx of injury to eye
-SX: intense ocular pain, redness, photophobia, tearing that follows injury to eye
-Signs: redness, epithelial defect that stains FI
-TX: prophylactic topical abx BID, refer to ECP next day for monitoring
Traumatic Uveitis
-Unilateral
-Usually present after insult/injury to eye
-SX: red, dull/achy eye
-Signs: red eye with anterior chamber rxn- must be observed with slit lamp
-Etiology: Traumatic compromise of blood-aqueous barrier
-R/o orbital drop-off, EOM entrapment
-TX: Long-acting cycloplegics, topical steroids, refer to ECP
Myopia Nearsightedness
-Reduced vision at distance
-Good vision at near
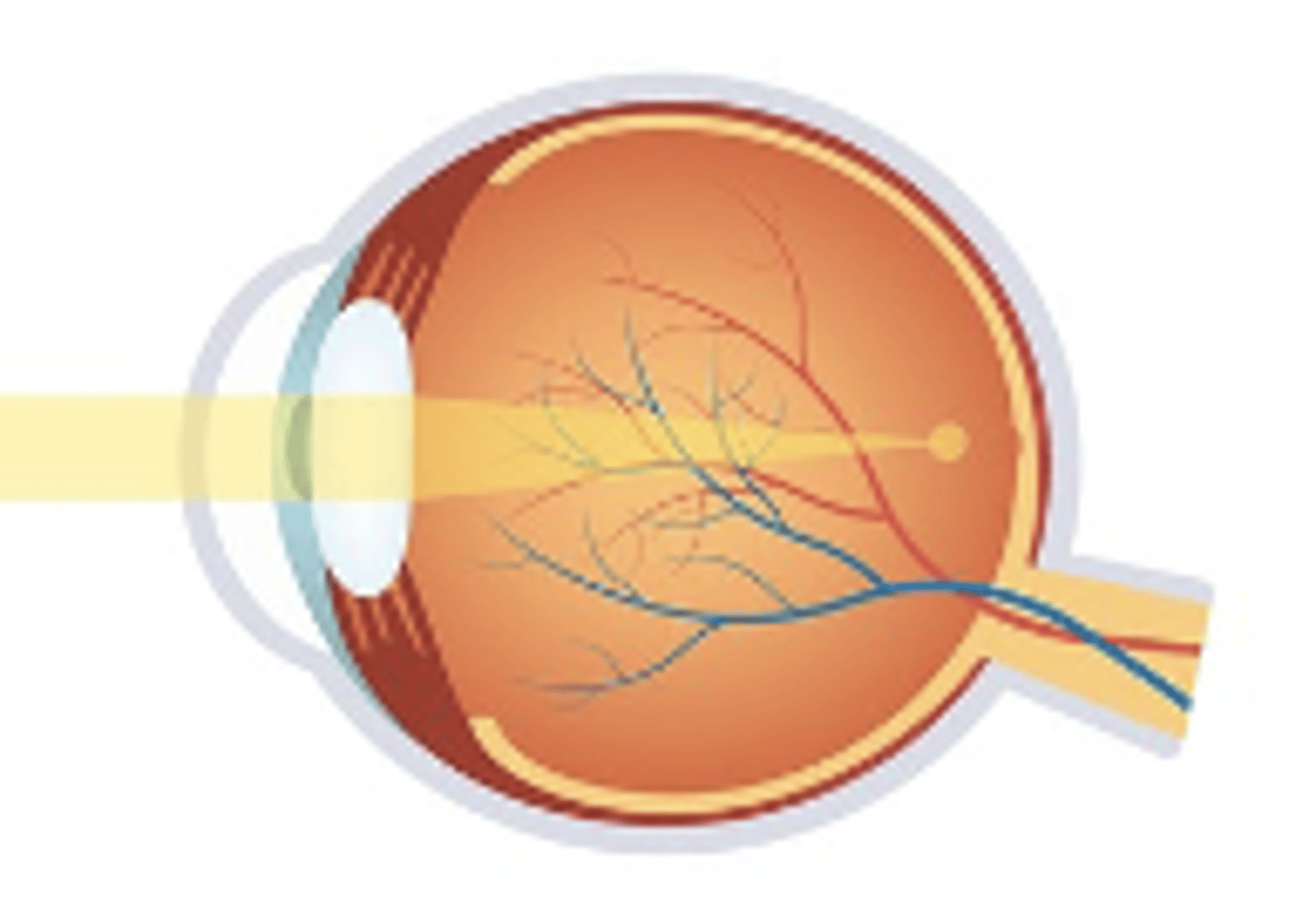
Hyperopia- Farsightedness
-Lower amount are asymptomatic
-Vision worse at near than distance
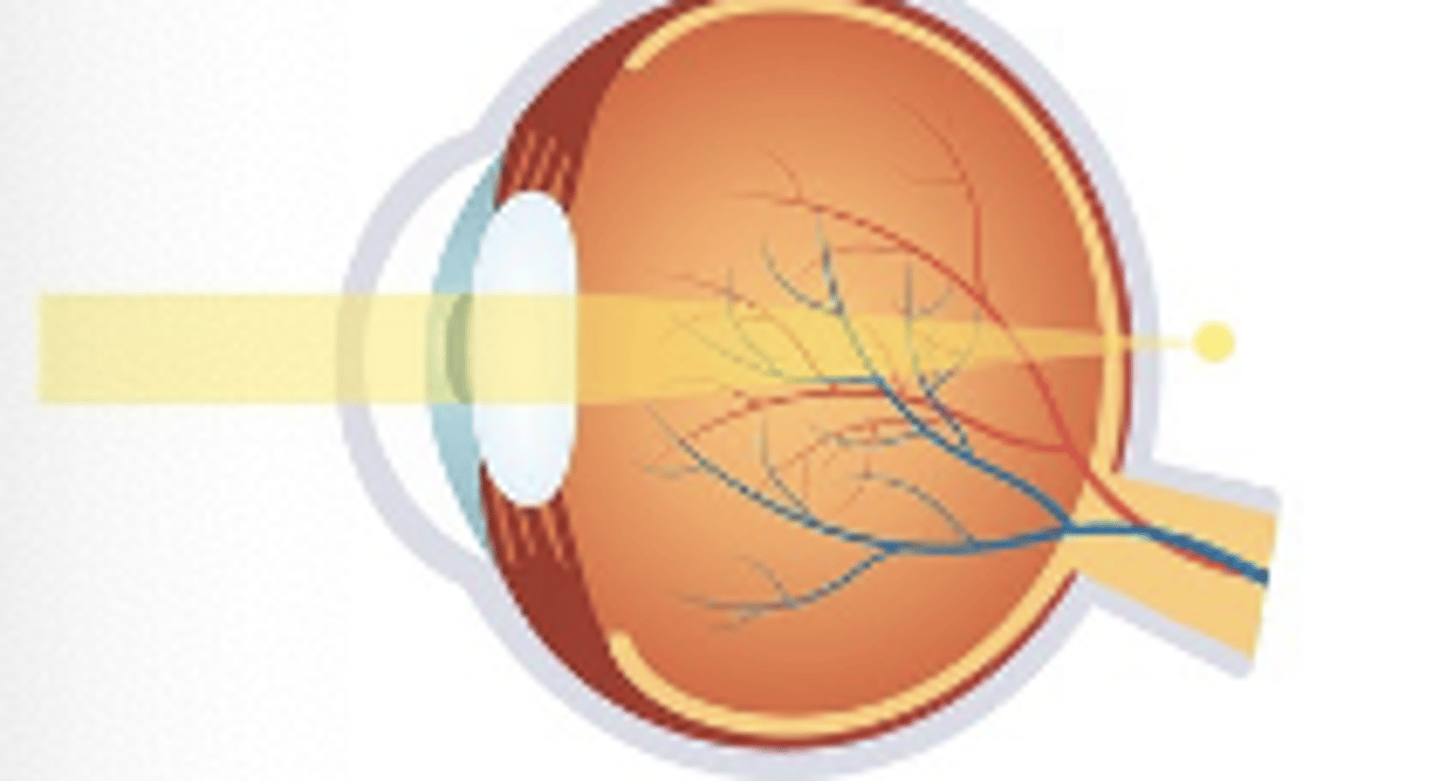
Astigmatism
-Eye shaped like a football not soccer ball
-Lower amounts are asymptomatic, vision worse at distance & near with higher amounts
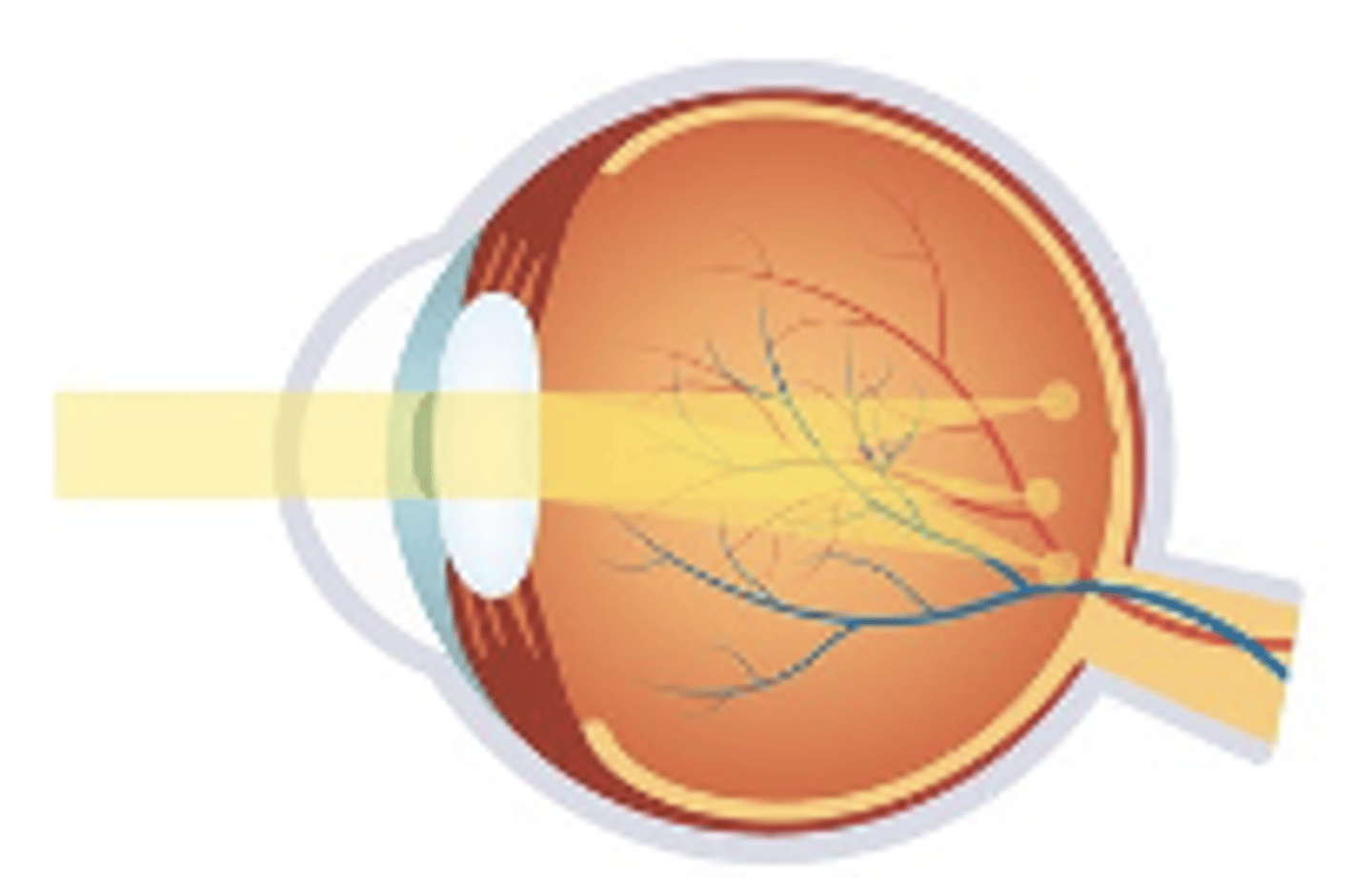
Corneal Scars
-Pt has predisposed condition to corneal scarring or previous infection
-Can be bilateral/unilateral based on etiology
-Glasses/Contact lenses will only correct up to point
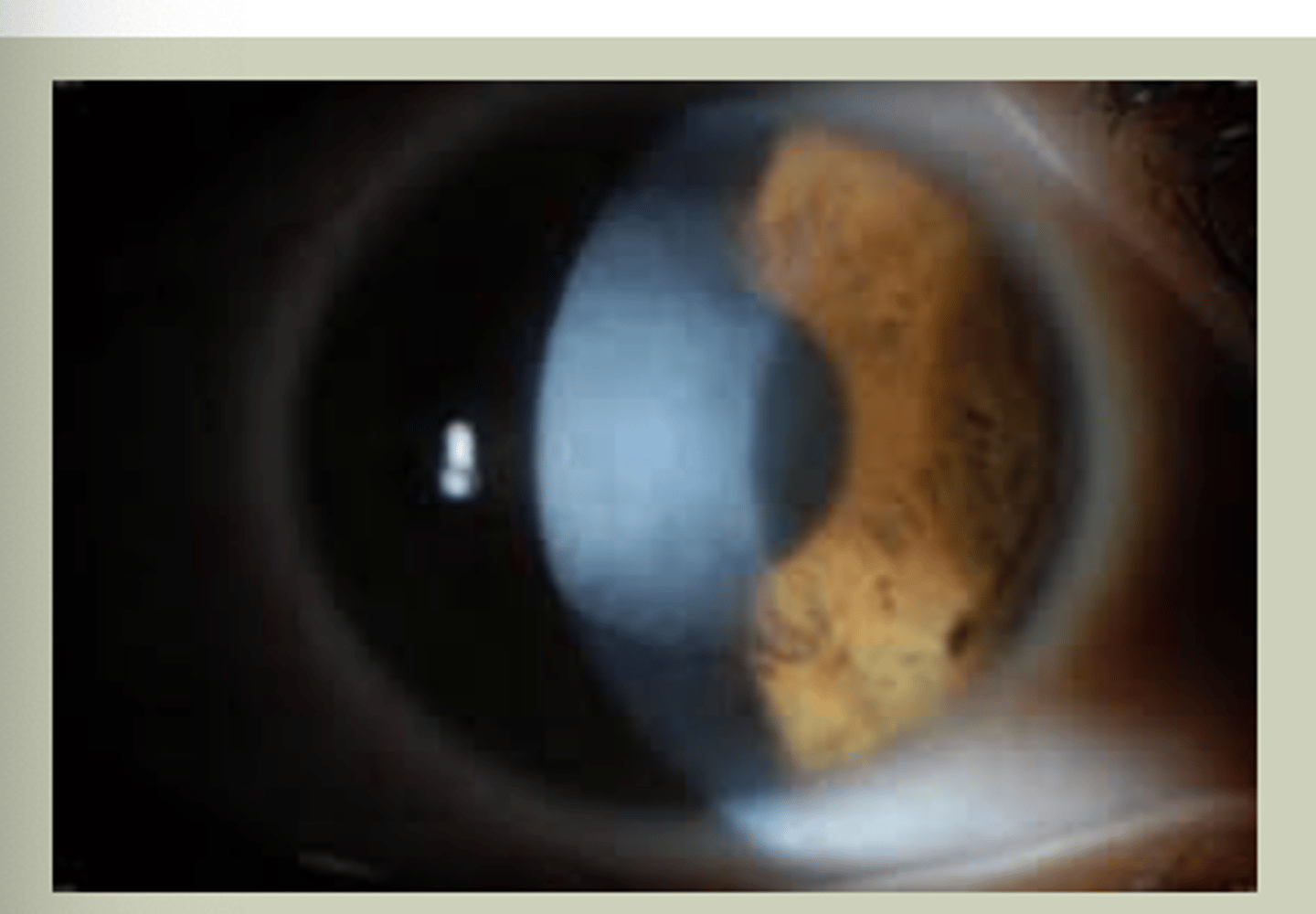
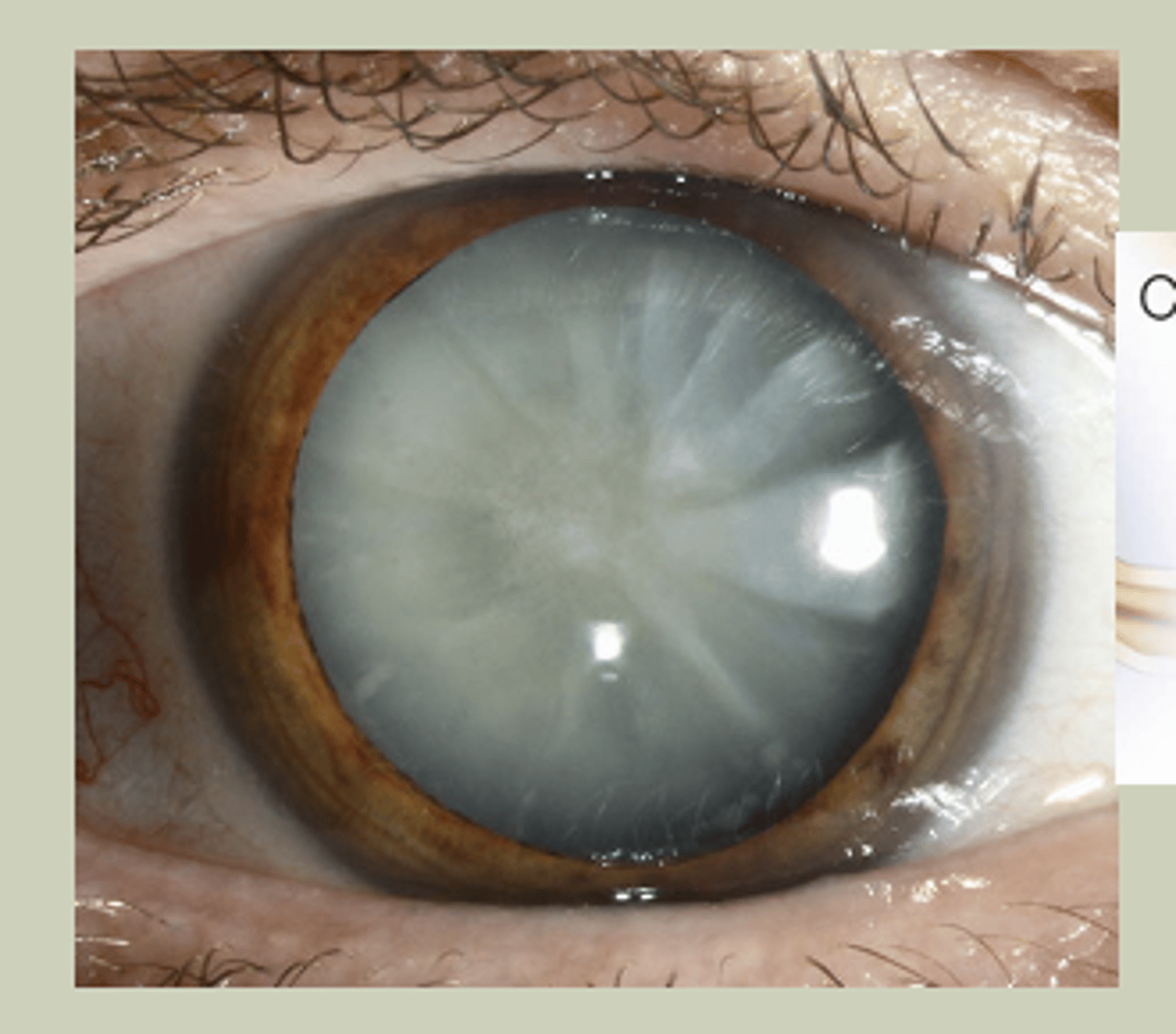
Cataracts
-Older pts, bilaterally
-Gradual onset
-Extraction may be indicated if affecting ADL's
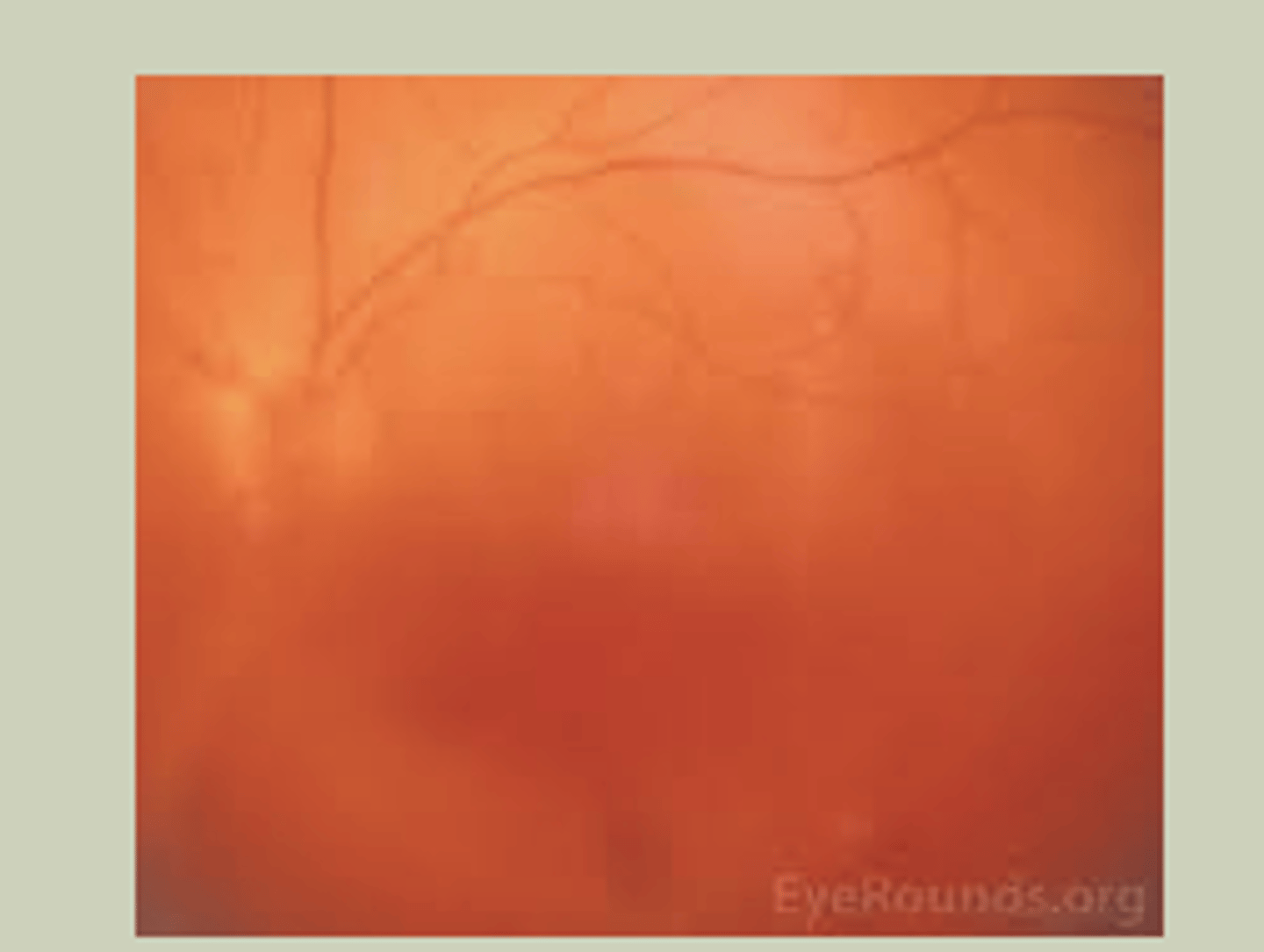
Vitreous Hemorrhage
-Sudden onset, painless blurred vision in one eye
-Poor control of DM
-Will not be able to evaluate fundus with DO
-TX: URGENT referral to ECP STAT referral to retinal specialist
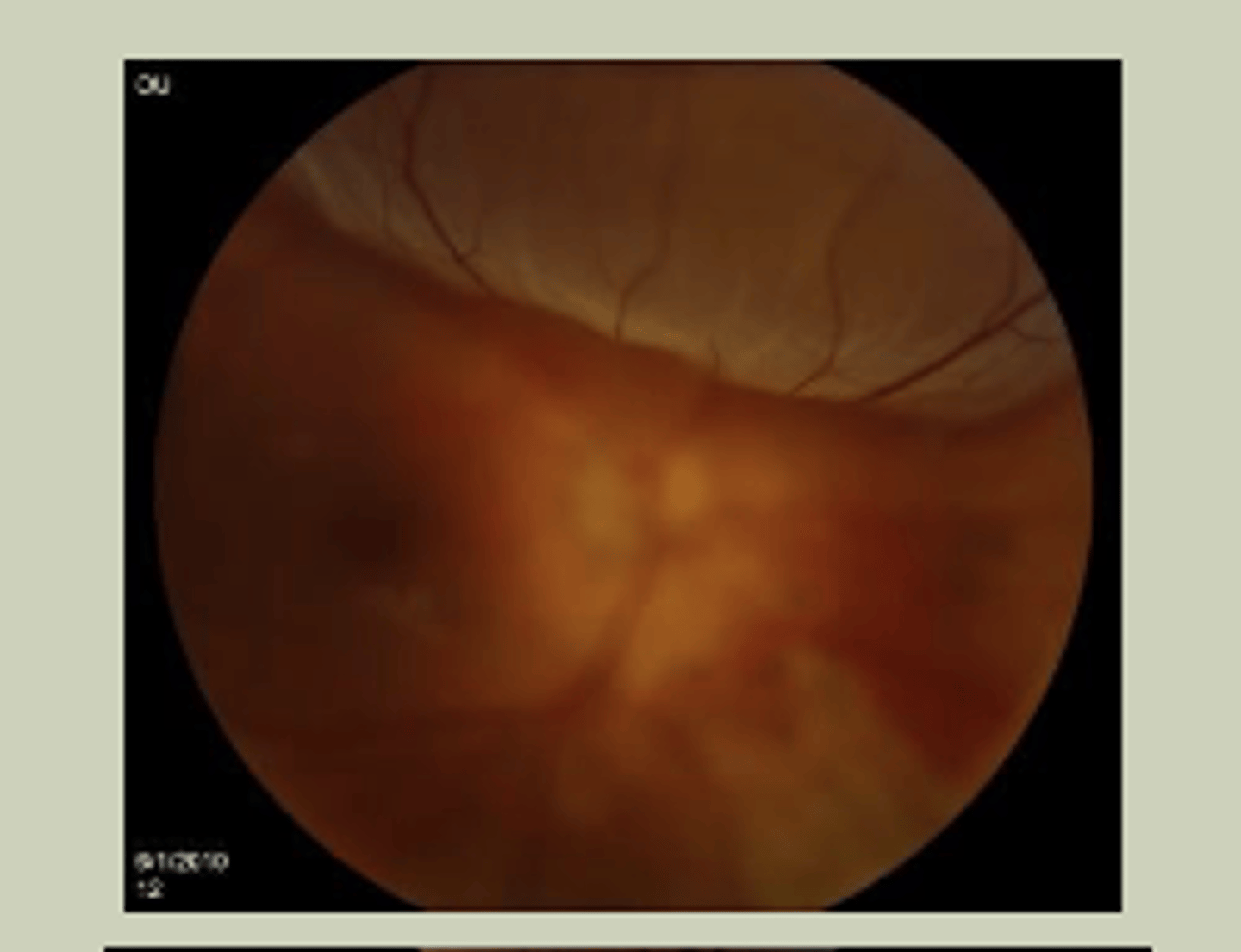
Retinal Detachment (RD)
-Sudden, painless loss of vision in one or more quadrants
-May report a veil in vision, flashes of light
-Associated with nearsightedness
-Macula-off visually worse than Macula-on
-TX: URGENT referral to ECP STAT referral to retinal specialist
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
-Sudden, painless blurred vision in one eye
-Associated with HTN
-See "Blood and thunder" on DO
-TX: URGENT referral to ECP STAT referral to retinal specialist
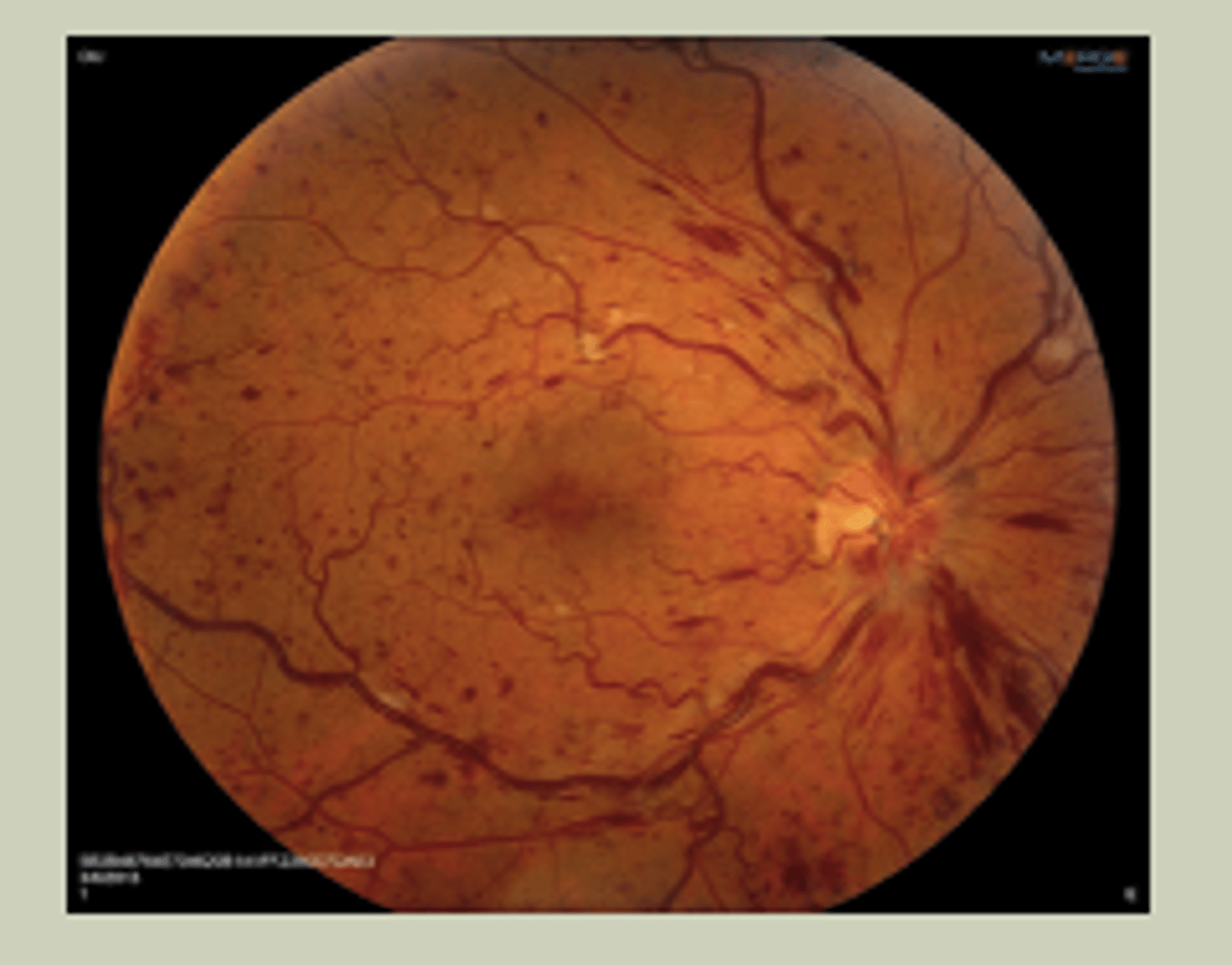
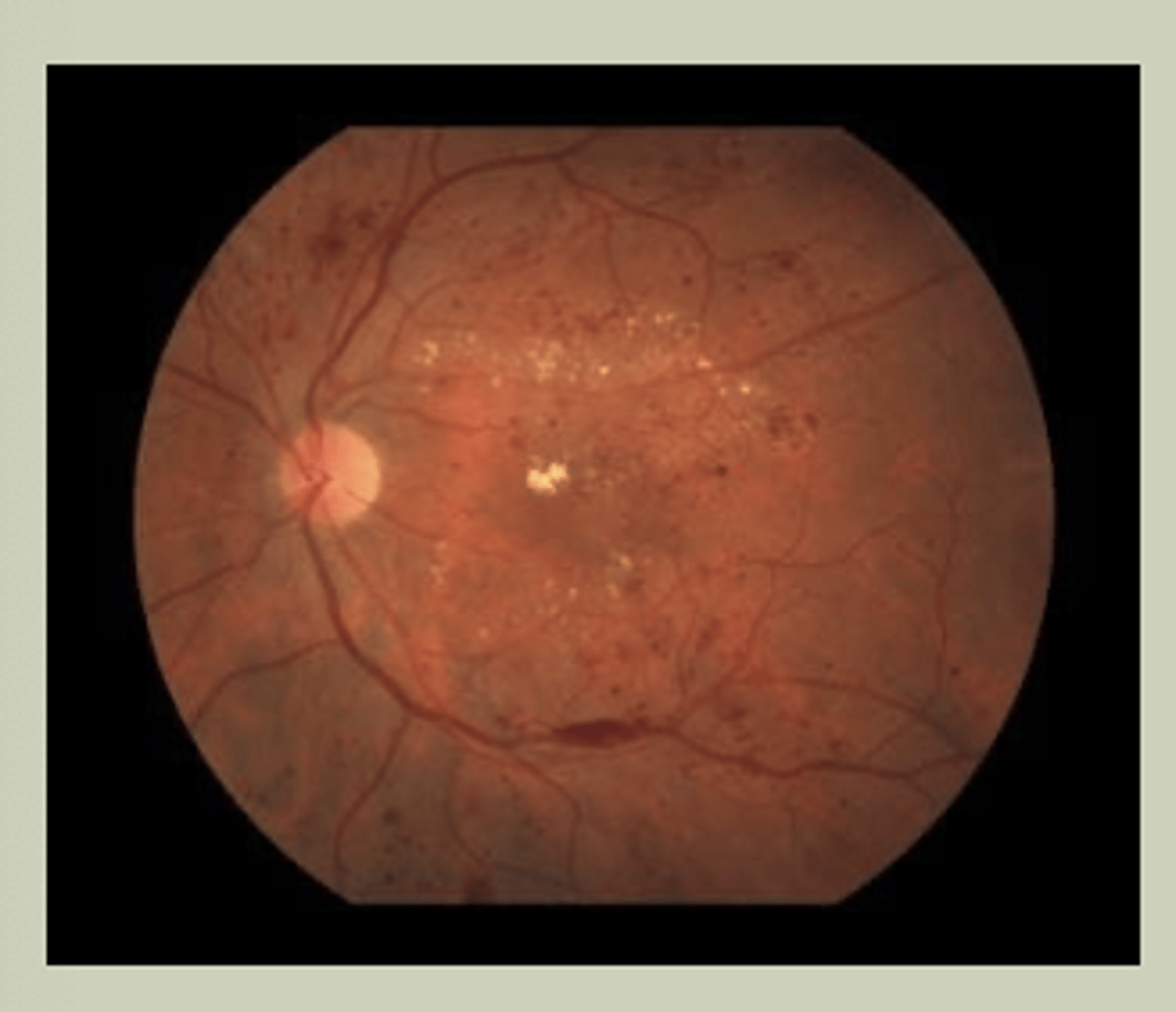
Diabetic Retinopathy
-Gradual change to vision bilaterally
-Hx of DM for many years
-May see blood, exudates, areas of ischemia with DO
-TX: URGENT referral to ECP
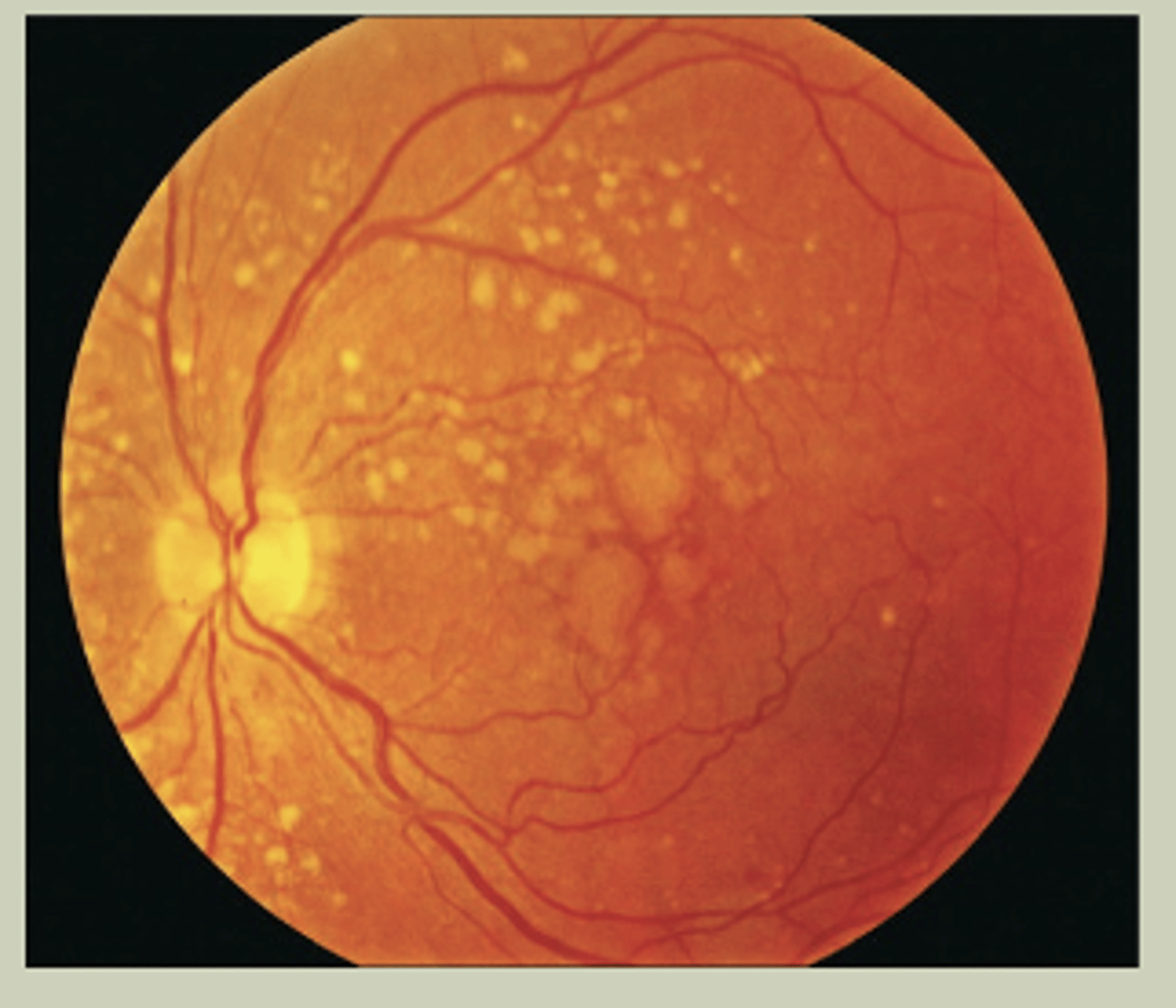
Age Related Macular Degeneration (ARMD)
-Gradual change to vision bilaterally
-Wavy vision or central missing spot in vision
-May see drusen in macular region with DO
-TX: URGENT referral to ECP
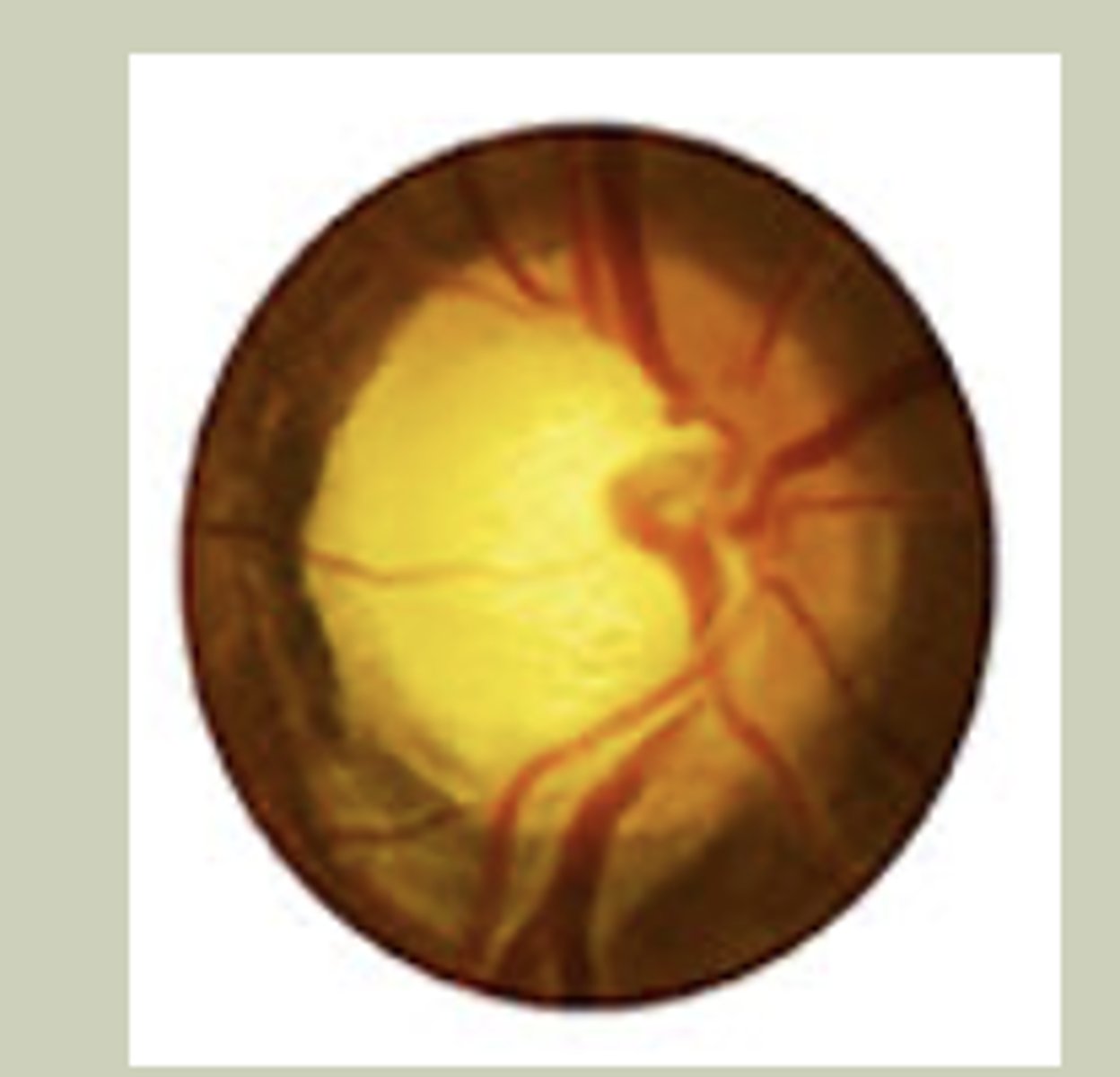
Glaucoma
-Gradual painless change to vision
-Unilateral or Bilateral
-Hx of being on glaucoma eye drops/surgies
-Will see large cup-to-disc ration on DO
-TX: Urgent referral to ECP
Optic Neuritis
-Sudden, painful change to vision unilaterally
-Younger patient, female>male
-Pain with H-motility testing
-May not see any abnormalities on DO of Optic Nerve
-TX: EMERGENT referral to ECP
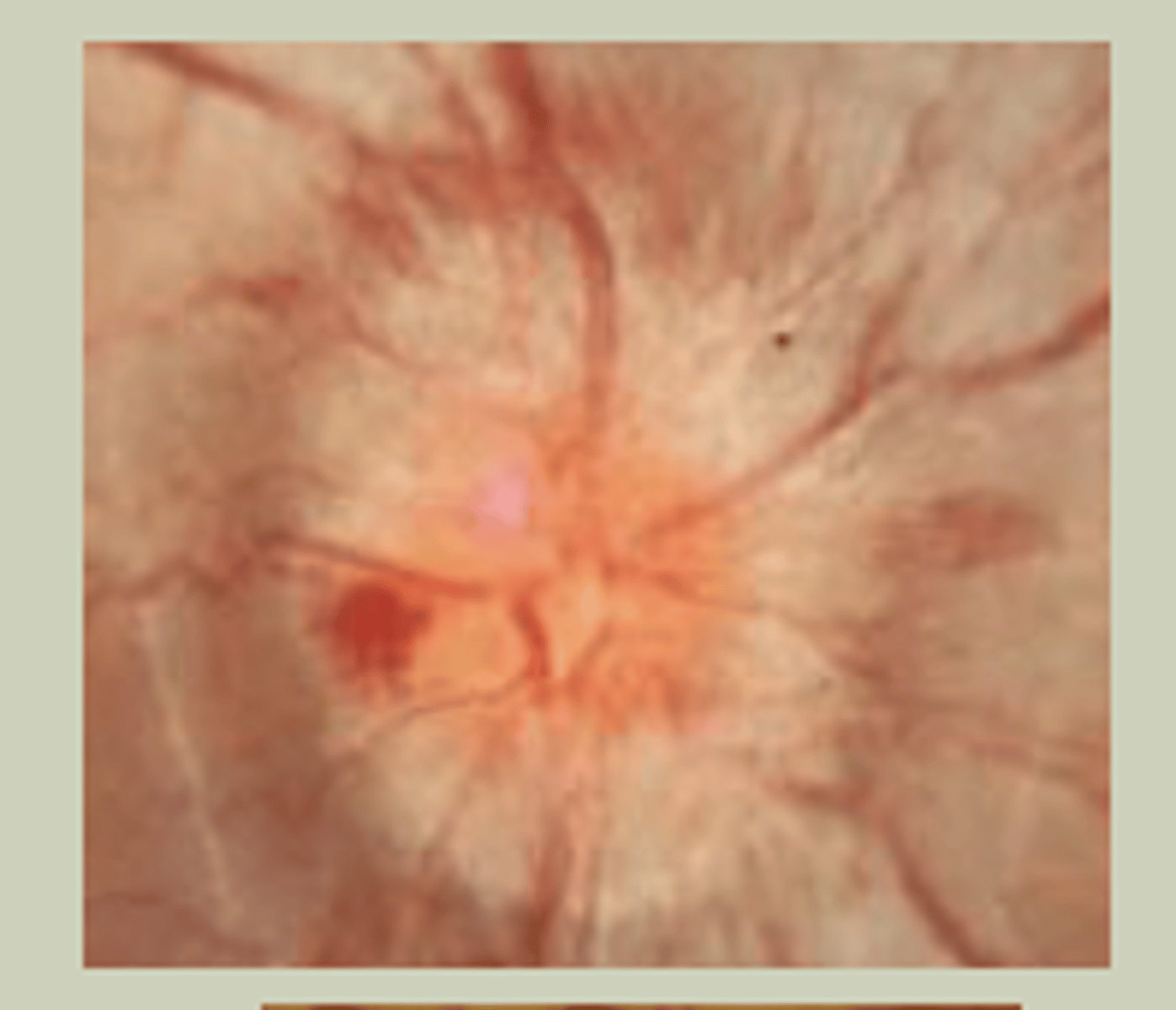
Arteritic Ischemic Optic Neuropathy
-Sudden, painful change to vision unilaterally
-Older pt>60 yo
-Jaw claudication, scalp tenderness, malaise
-Swollen optic nerve head
-TX: EMERGENT referral to ECP
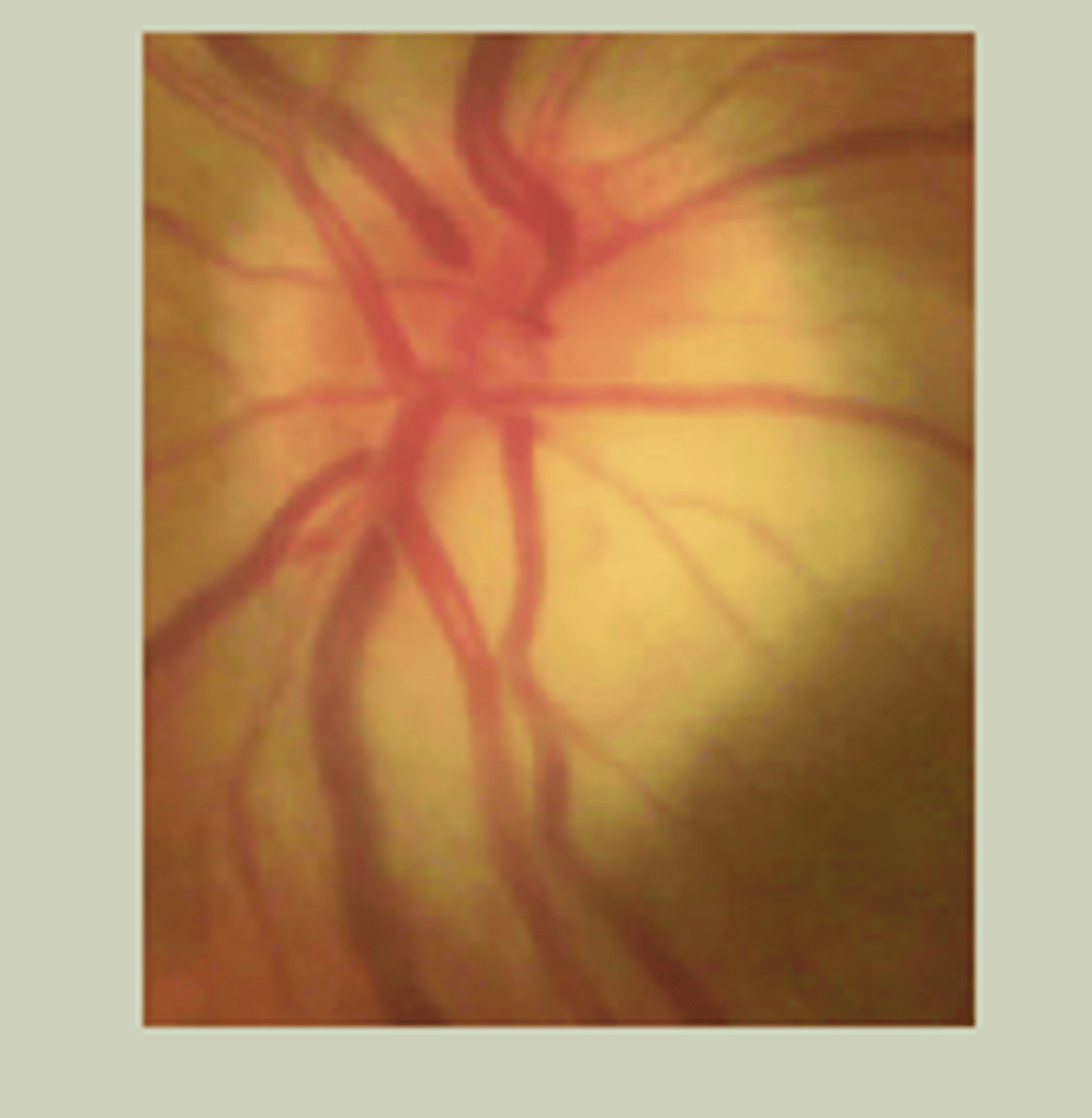
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion (CRAO)
-Sudden, painless LOV unilaterally
-Hx of HTN
-Associated with Giant cell arteritis
-Retinal Whitening with cherry red spot (macula)
-TX: EMERGENT referral to ECP/ED
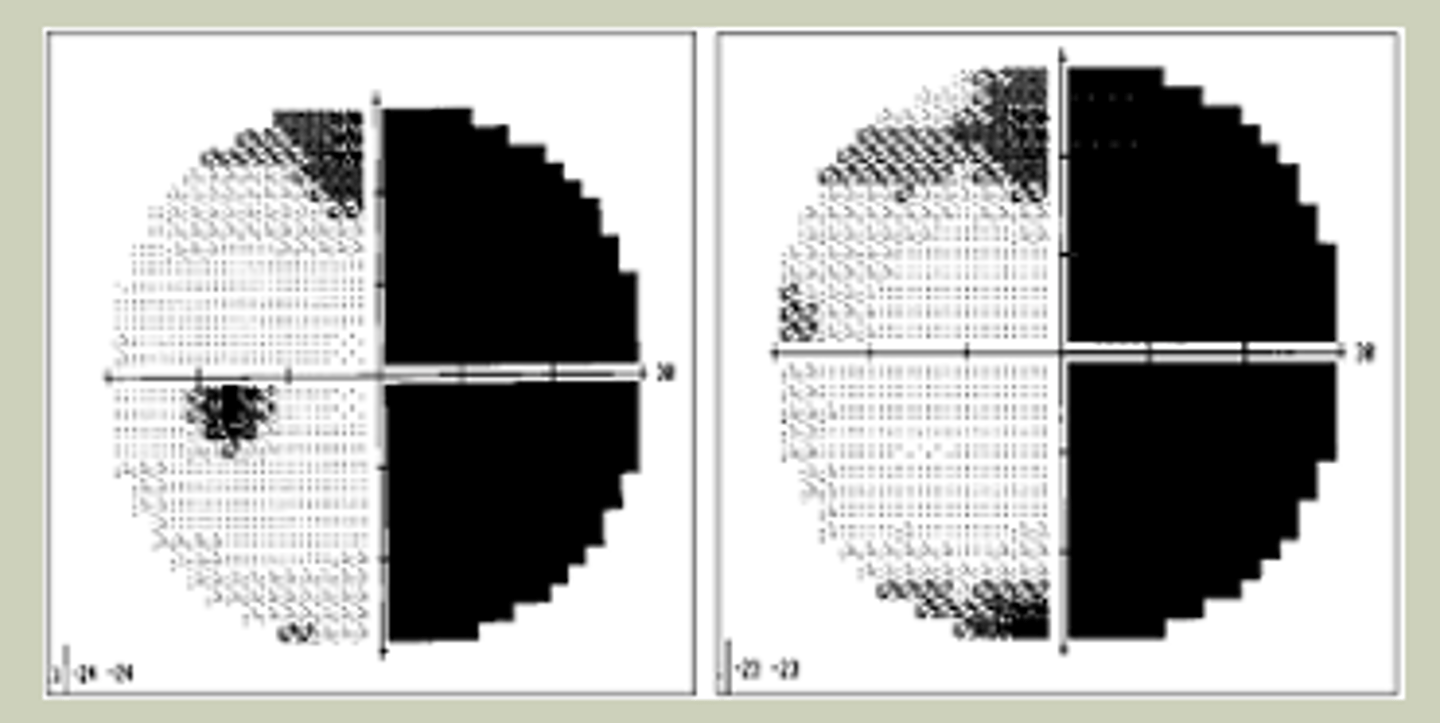
Visual Field Defects
-H/O CVA
-End-stage Glaucoma
-Chronic, longstanding vision loss, typically bilaterally
-Mya have mobility issues
-TX: Urgent referral to ECP
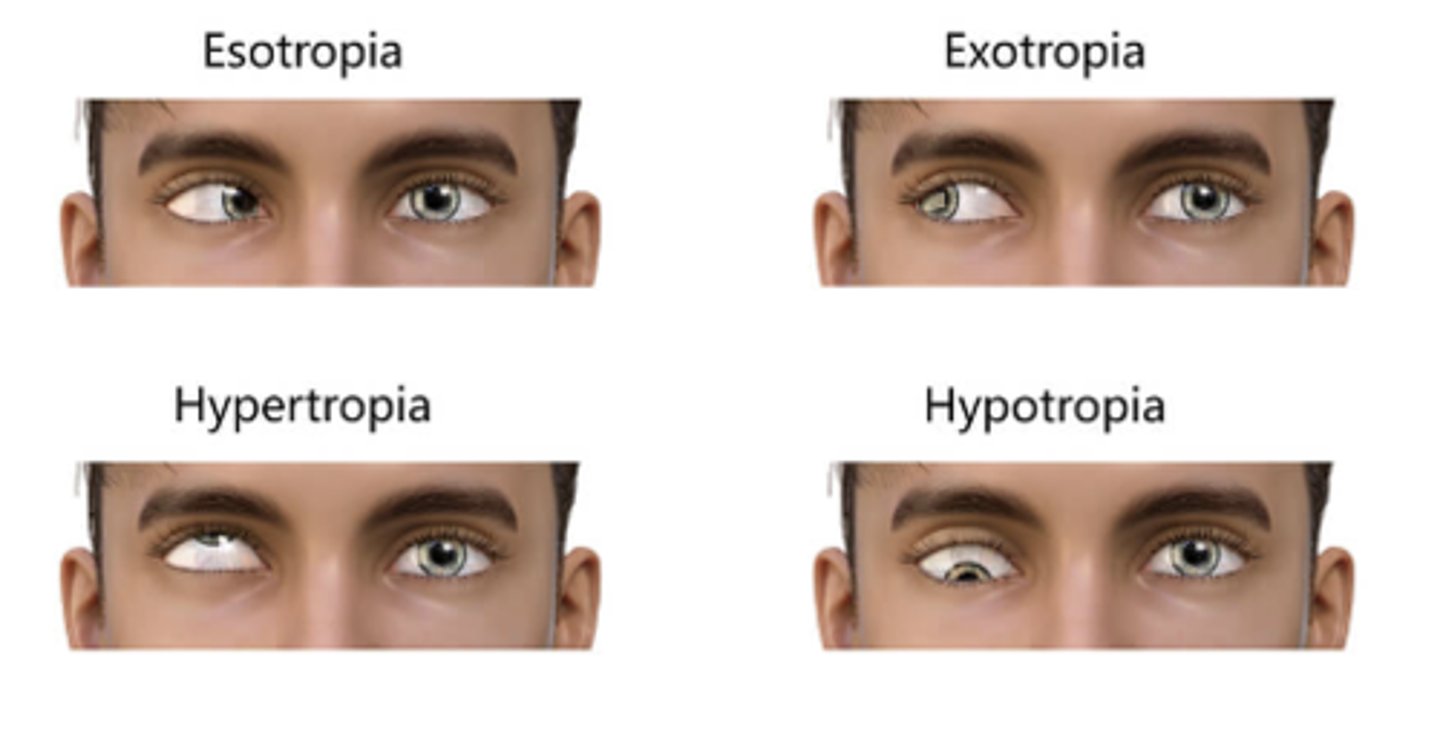
Strabismus
-Ocular misalignment where one eye is fixating
-Other eye is deviating
Strabismus in Children
-Starts as intermittent; may progress to constant
-Parent will report eye turn if questioned
-Child may close an eye (Diplopia)
-Emphasis on Hirschberg Test
-TX: Refer to EPC
Adult Onset Strabismus
-May be neurologic
-Diplopia
-Emphasis on H-motility test to isolate muscles
-TX: Urgent referral to ECP
Exophthlamos
-Eye bulging forward from orbit
-Thyroid eye disease: MC etiology
-Have pt tilt head back
Unilateral Exophthlamos
-Acute onset without thyroid disease
-TX: EMERGENT referral to ECP/ED if:
-Resistance to retropulsion
-Ipsilateral APD
-Restrcited EOM
-Eyelid swelling
-Fever
Bilateral Exophthlamos
-Acute onset with/without hx of thyroid disease
-Urgent if: Restricted EOM
-TX: EMERGENT referral if: APD (in either eye)
Papilledema
-Bilateral Optic Nerve head swelling secondary to increased intracranial pressure
-SX: chronic headaches that worsen with postural changes, pulsatile tinnitus, dimming vision, horizontal diplopia
-Signs: Difficulty with looking to right & left with H-motility test, bilateral swollen/elevated optic disc margins with DO
-Etiologies: Anything that occupies space within the cranium
-TX: EMERGENTLY to ECP/Ed