biology: cell structure and function, cell movement
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
peripheral proteins
bound to the surface of the membrane
psuedopodia
packages particles into food vacuole, which fuses to lysosome to be digested, cell surrounds particles with this
high temp cholestrol
reduces movement
mosiac
to be comprised of many macromolecules
membrane carbohydrates
interact with the surface molecules of other cells, facilitating cell-cell recognition
glycoproteins
proteins that have carbohydrates covalently bonded to them
plants contransport
uses sugar and amino acids
phagocytosis
cell engulfs particles to be digested by lysosomes (cell eating)
pintocytosis
cell takes in dissolved molecules in a protein coated vesicle, to mediate
receptor mediated endocytosis
specific uptake of molecules via solute binding to receptors on plasma membrane. allows cell to take up large quantities of a specific substance
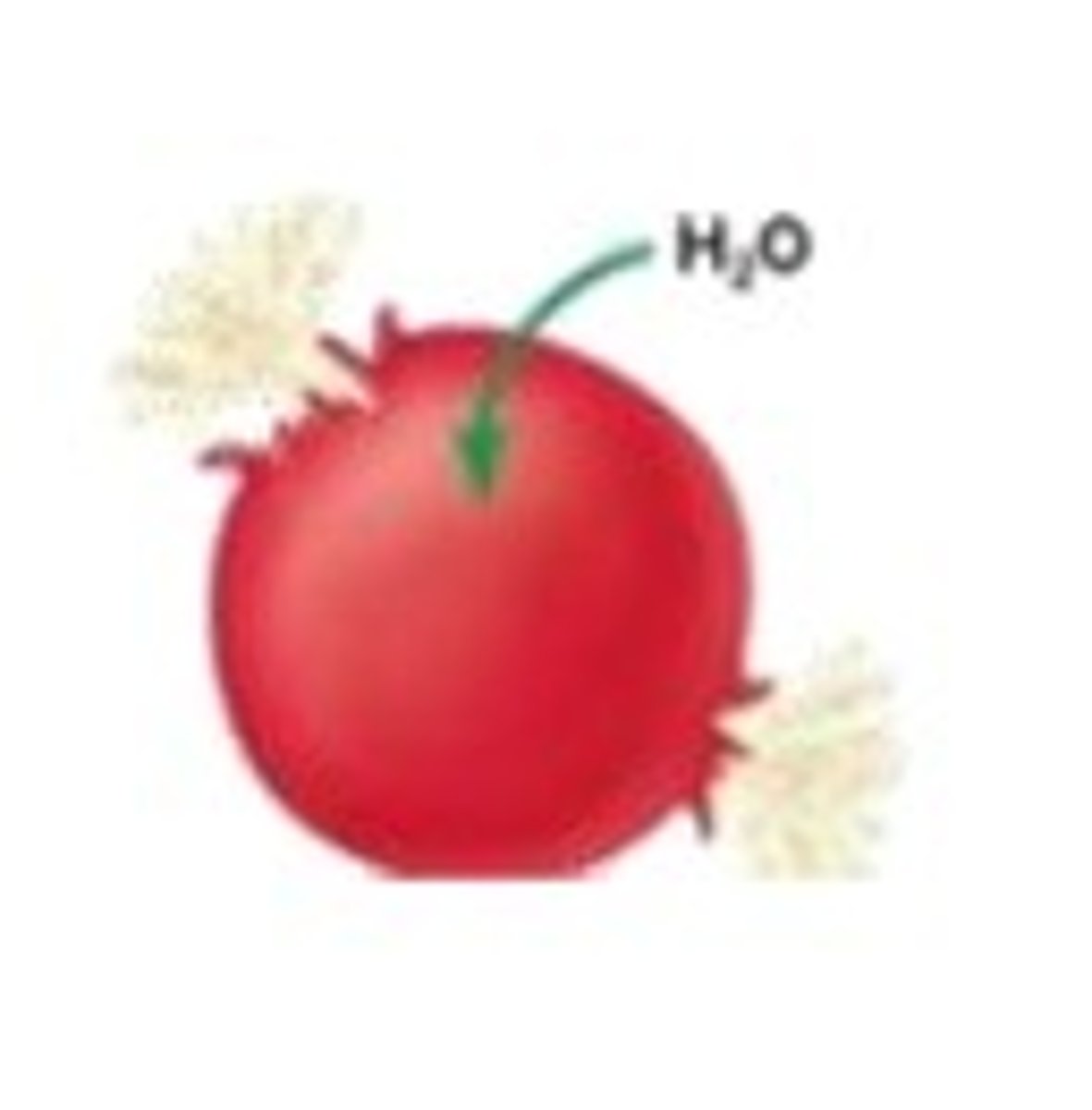
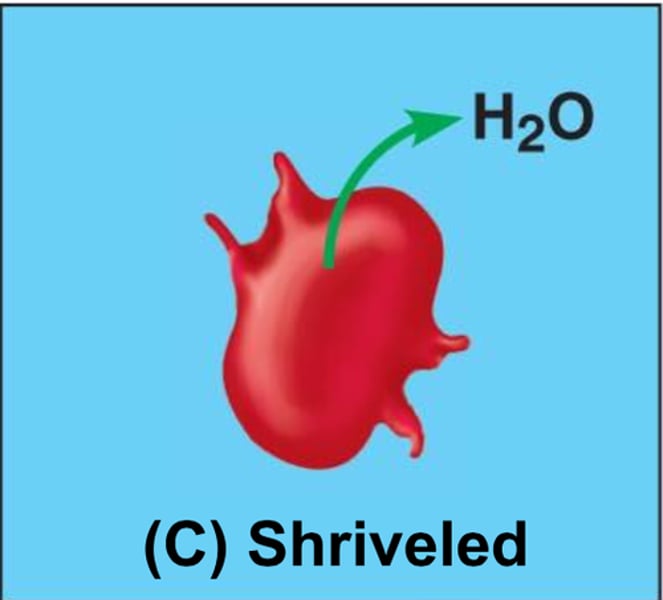
tonicity
ability of an extracellular solution to cause a cell to gain or loose water
hypertonic
having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
cholesterol
helps maintain fluidity of a cell
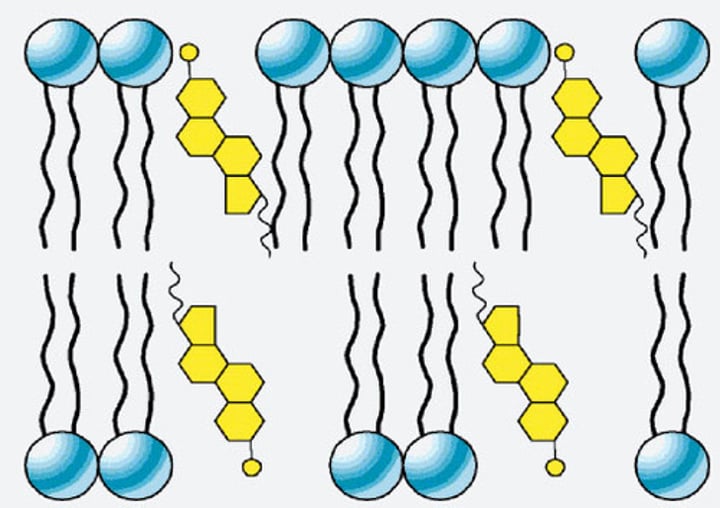
low temp cholestrol
increases movement, reduces tight packing of phospholipids
membrane proteins
integral proteins and peripheral proteins
integral proteins
embedded in the hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
glycolipids
carbohydrates covalently bonded to lipids
selective permeability
condition or quality of allowing some, but not all, materials to cross a barrier or membrane
Easy passage across the membrane
small, non polar, hydrophobic molecules
-ex: hydrocarbons, CO2, O2, N2
difficult passage across the membrane
hydrophilic, polar molecules, large molecules, ions
passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
concentration gradient
A region along which the density of a chemical substance increases or decreases.
diffusion
substances move from high to low concentration, down concentration gradient
active transport
the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy/ATP
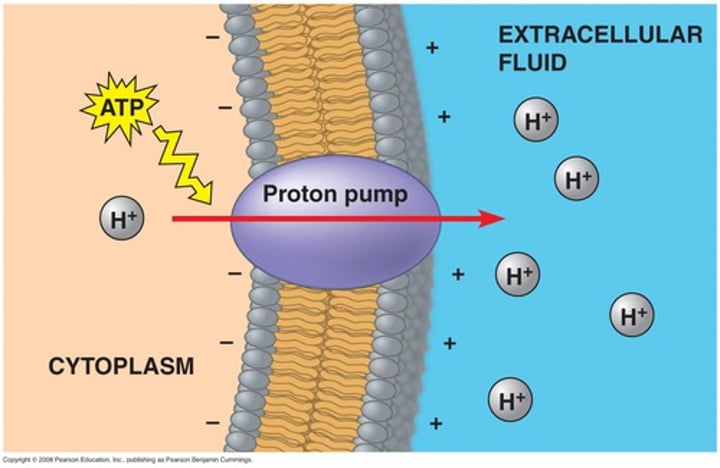
proton pump
active transport protein that transport hydrogen ions out of a cell against their concentration gradient, generating a membrane potential in the process, mostly H+ cells
contransport
uses energy stored in electrochemical gradients (generated by pumps) to move substances against concentration gradient
favorable movement
downhill diffusion
unfavorable movement
uphill diffusion
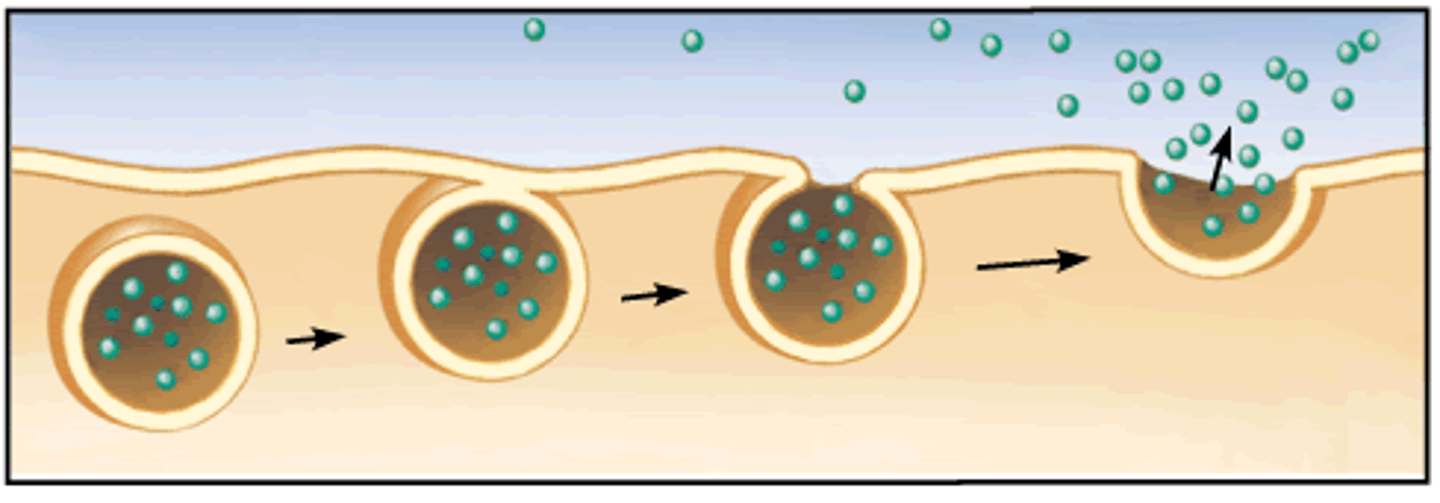
exocytosis
secretion of materials via vesicles, which cam fuse to membrane via a bilayer, released to extracellular fluid
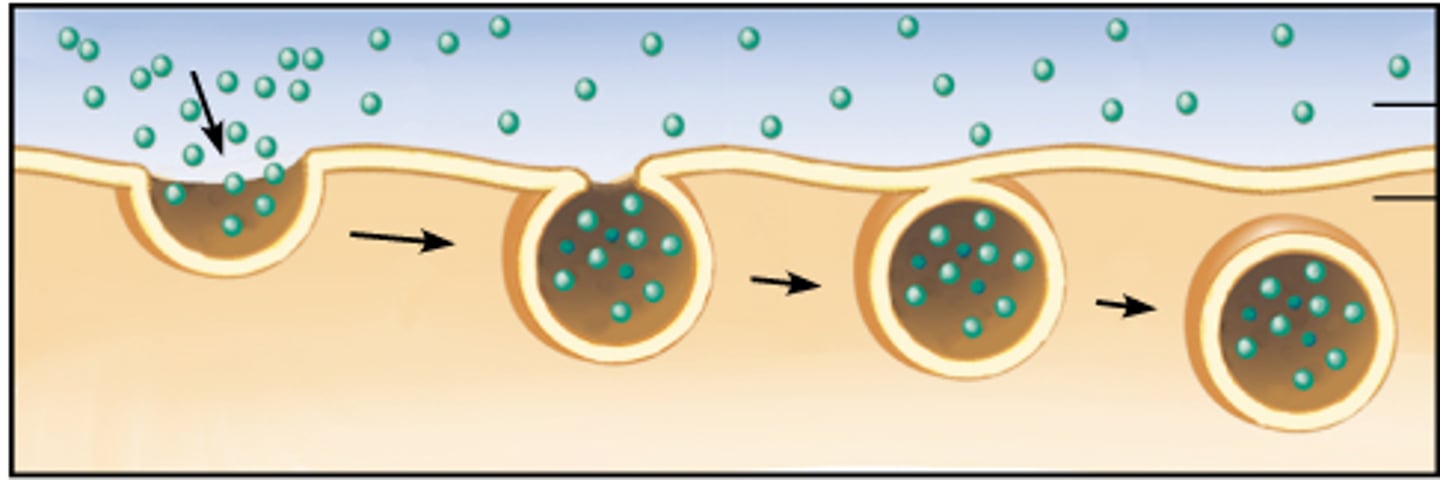
endocytosis
uptake of molecules from vesicles fused from plasma membrane
osmosis
diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
osmoregulation
regulation of solute concentrations and water balance by a cell or organism
isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
hyptonic
having a lower concentration of solute than another solution