Tissue, Organs, and Organ Systems
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
function of circulatory system
transport blood around body
function of respiratory system
allow breathing
thorax
top part of body seperated from abdomen by diaphragm
bronchus
major air passages that diverge from trachea
bronchide
minor branches in which bronchus divides
lungs
gas exchange organ in mammals
trachea
airway leads from larynx to bronchi
alveoli
tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs
pleural membranes
thin layer of tissue that covers lungs and allows lungs to freely move inside ribcage
intercostal muscles
muscles that combine to fill space between ribs
ribcage
skeletal structure that forms thorax
diaphragm
muscular partition that contracts to increase volume of thorax and inflate lungs
How are alveoli adapted for diffusion?
have large surface area to volume ratio
have a thin membrane
How goes gas exhange work in the alveoli?
oxygen leaves alveoli and enter blood stream
carbon dioxide leave through alveoli and out
Oxygen moves from an area of high concentration to low concentration. This is called..
diffusion
formula for breathing rate
number of breaths/time to take the breaths
formula of heart rate
number of beats/time to take the beats
what type of circulatory system does a human have
double circulatory system where blood passes through heart twice during one system
left/right atrium
chamber of heart into which blood enters from pulmonary vein or vena cava
left/right ventricle
chamber in heart which pumps blood out of heart through pulmonary artery or aorta
valves
structure within heart or vein which prevents blood from flowing in wrong direction
aorta
artery that transports blood from heart to rest of body
pulmonary artery
blood vessel which transports blood out of heart to lungs
pulmonary vein
blood vessel which transports blood into heart from lungs
coronary arteries
arteries that branch off aorta and surround heart
vena cava
blood vessel which transports blood into heart from the rest of body (not lungs)
Name all the steps of blood flow through the heart.
Blood flows into the two atria from the vena cava and the pulmonary vein.
The atria contract, pushing blood into ventricles.
The ventricles contract, forcing blood into pulmonary artery and aorta.
Blood flows to organs through arteries, then arteries through veins.
What is the resting heart rate controlled by?
cells in right atrium wall that acts as a pacemaker
What do cells produce that spread to surrounding muscle cells causing them to contract?
small electric impulses
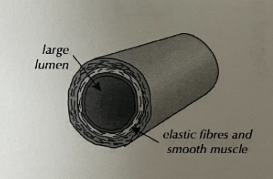
Function of arteries
carry blood away from heart
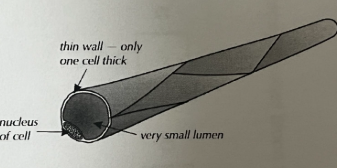
Function of capillaries
where blood passes substances back and forth from cells
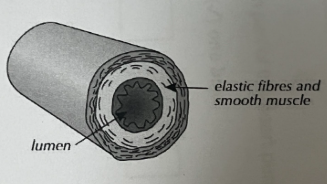
Function of veins
carry blood towards the heart
Adaptations of arteries
strong and elastic walls due to pressure
thick layers of muscle with elastic fibres to stretch
walls are thicker than lumen
Adaptations of capillaries
permeable walls
walls are one cell thick
narrow
Adaptations of veins
thinner walls as less pressure
bigger lumen to reduce resistance to blood flow
valves to direct blood in right direction
to assist blood in correct direction
The blood in the valves are at a…
low pressure
Arteries do not have valves because…
the pressure from the heart is strong enough to ensure the correct direction of blood flow
blood
type of tissue
function of white blood cells, its special features and why they’re important
to defend against microorganisms that cause disease
produces antibodies which releases antitoxins to fight microorganisms
engulfs unwelcome microorganisms through phagocytosis
function of platelets, its special features and why they’re important
to help the blood clot at the wound
can connect to eachother
stops microorganisms and without them, can lead to excessive bleeding
function of plasma, its special features and why they’re important
to carry all substances in blood
pale, straw-coloured
What substances can plasma carry?
red + white blood cells
platelets
carbon dioxide
urea