Experiment 7: Esterification
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Organic Compounds
Primarily composed of carbon and hydrogen atoms along with heteroatoms such as oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and the halogens.
Functional Groups
Because of the vast number of organic compounds that exist in nature and that can be synthesized in the laboratory, they are placed in classes called _____ depending on the structural features present in the molecules.
Hydroxyl (OH) Group
Carboxyl (COOH) Group
Ester
Some example of organic compounds and their functional groups are alcohols which contain a _____, and carboxylic acids which contain a _____. When these two types of organic compounds react, they form an _____.
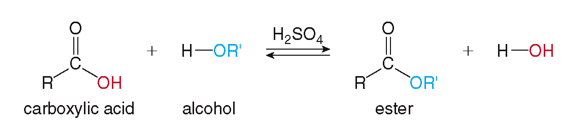
Esters
Structurally characterized by the presence of a carbonyl group with an alkoxy group attached to the carbonyl carbon.
Volatile substances that have lower boiling points than alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Both compounds occur naturally and are synthesized in the laboratory as scents of flowers and fruits.
Acid Catalyst
Fischer Esterification
In the laboratory, esters can be synthesized from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid in the presence of an _____ and heat through the process of _____.
Phenolphthalein
In this experiment, esters will be synthesized in test tubes from different alcohols and carboxylic acids and characterized with a simple, chemical test involving _____, a common acid-base indicator.
Synthesize esters from alcohols and carboxylic acids;
Describe the conditions required for the synthesis and hydrolysis of esters;
Observe the changes in the physical and chemical properties of alcohols, carboxylic acids, as they are combined into esters; and
Distinguish alcohols, carboxylic acids, and esters based on their physical, chemical, and structural properties
Objectives of the experiment.
Isoamyl Alcohol (Isopentyl Alcohol)
Ethanol
Methanol
Glacial Acetic Acid
Benzoic Acid
Salicylic Acid
Concentrated sulfuric acid
Sodium hydroxide
Phenolphthalein
9 reagents used.
Hot Water Bath
250 mL
Procedure 1.
Prepare a _____ by filling up a _____ beaker halfway with tap water and placing it on top of a stove. Set the stove to low setting once the water is hot.
Waft
Smell
10
10 or a Pinch
Carboxylic Acid
Procedure 2.
Before mixing the alcohol and the carboxylic acid, try to _____ and take note of their individual _____.
Add _____ drops of alcohol and _____ drops (if liquid) or a _____ (if solid) of _____ into a test tube.
Isoamyl Alcohol
Glacial Acetic Acid
Test tube A.
10 drops of _____
10 drops of _____.
Ethanol
Glacial Acetic Acid
Test tube B.
10 drops of _____.
10 drops of _____.
Methanol
Salicylic Acid
Test tube C.
Approximately 25 drops of _____, enough to dissolve acid.
Pea size of _____.
Ethanol
Salicylic Acid
Test tube D.
10 drops of _____.
Pea size of _____.
2
Concentrated Sulfuric Acid
Procedure 3.
Add _____ drops of _____ into the test tube with the alcohol and carboxylic acid.
10 minutes
Scent
Evaporating
Wafting
Procedure 4.
Place the test tube into the hot water bath for _____ or until a _____ is detected coming from the test tube. Avoid _____ the solution. You can start observing the scent by _____. Do not directly smell from the solution.
100 mL
Appearance
Procedure 5.
Transfer the test tube into a _____ beaker filled halfway with tap water to cool down. Observe any changes in the _____ of the contents of the test tube.
Waft
Procedure 6.
After cooling, carefully _____ the scent coming out of the test tube and describe the scent.
5
Sodium Hydroxide
2
Phenolphthalein Indicator
Procedure 1 in characterization.
Add _____ drops of _____ into test tube C followed by _____ drops of _____. Take note of any changes.
Hot Water Bath
10 minutes
Procedure 2 in characterization.
Place the test tube back into the _____ for _____ or until changes are observed. Take note of your observations.