D2.3 Water potential
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Solvation
Process of surrounding solute particles with solvent molecules
What happens in aqueous solutions (water is the solvent)?
Hydrogen bond formation betw solute + water molecules
Attractions betw both positively + negatively charged ions and polar water molecules
When water is used as a solvent, what are positive ions attracted to?
Partially negative oxygen in water
When water is used as a solvent, what are negative ions attracted to?
Partially positive hydrogen in water
Is water a good or bad solvent + why?
Good solvent (can dissolve solutes)
Bc it is polar
What happens when water dissolves ionic compounds?
Water forms shells around ions
Partially positive H attracted to negative ions
Partially negative O2 attracted to positive ions
→ prevents them from rejoining
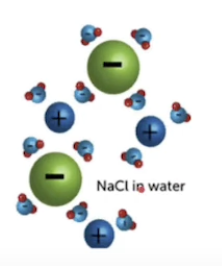
How does water dissolve polar molecules?
Water forms hydrogen bonds w solutes
Movement of water
From less concentrated to more concentrated solutions
Low solute conc → higher solute conc
Osmosis
Passive net movement of water across a partially permeable membrane from an area of low → high solute conc
until equal concs on either side (but not equal volume)
Thru chanell protein (aquaporins)
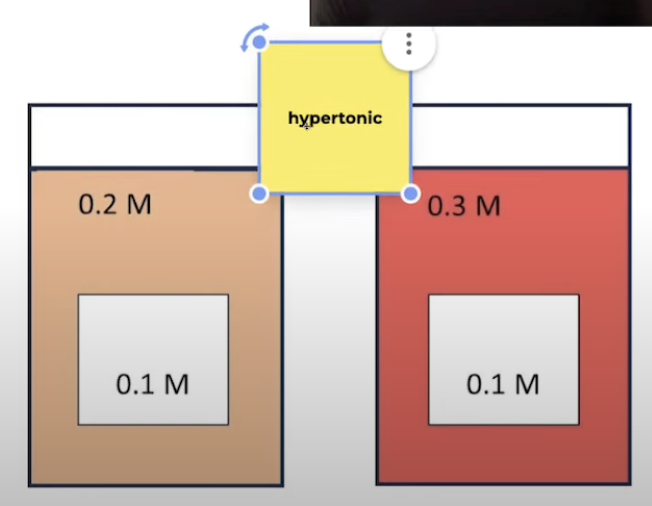
Hypertonic
Solution has higher solute conc than what it is being compared to
Water moves out of cells
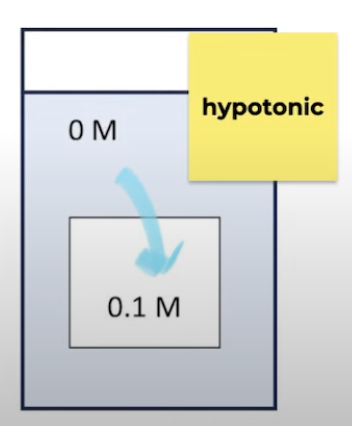
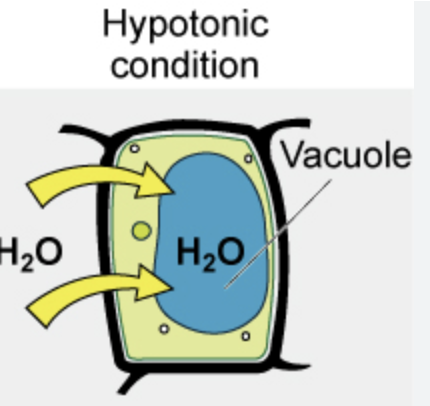
Hypotonic
Solution has lower solute conc than what it is being compared to
Water moves into cells
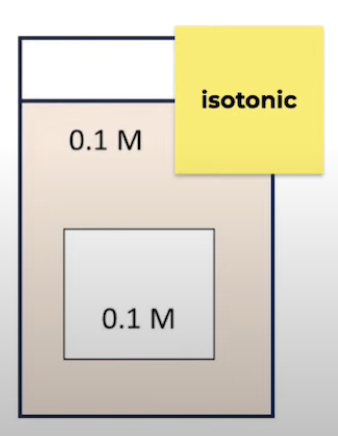
Isotonic
Solution has same solute conc to what it is being compared to
No net movement of water
Summary of
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
Isotonic
Hypotonic: Lower solute concentration.
Hypertonic: Higher solute concentration.
Isotonic: Equal solute concentration.
How does osmosis occur?
PPM = partially permeable membrane
PPM allows water to pass thru
But PPM less permeable to solutes
So when there is CG → osmosis occurs
How can cells control osmosis rates?
Change their solute conc
Eg contractile vacuoles
Change their membrane permeability to water
Osmosis of water thru aquaporins vs phospholipid bilayer
Quicker thru aquaporins
More aquaporins embedded in cell membrane → cell more permeable to water → faster osmosis
In isotonic environments, is there movement of water?
Yes
There is dynamic equilibrium
Osmolarity
Total solute conc in a cell (solvent)
Determines the direction of water movement by osmosis
Changes due to water movement in plant tissue bathed in hypotonic and those bathed in hypertonic solutions
APPLICATION OF SKILLS
Students should be able to:
Measure (%) changes in tissue length + mass,
Analyse data to deduce isotonic solute concentration.
Uuse standard deviation + standard error to help analyse data
If the mass of a plant increases, what type of solution was it placed in?
Hypotonic
If the mass of a plant decreases, what type of solution was it placed in?
Hypertonic
Bc water moves out of the cell
If the mass of a plant doesn’t change, what type of solution was it placed in?
Isotonic
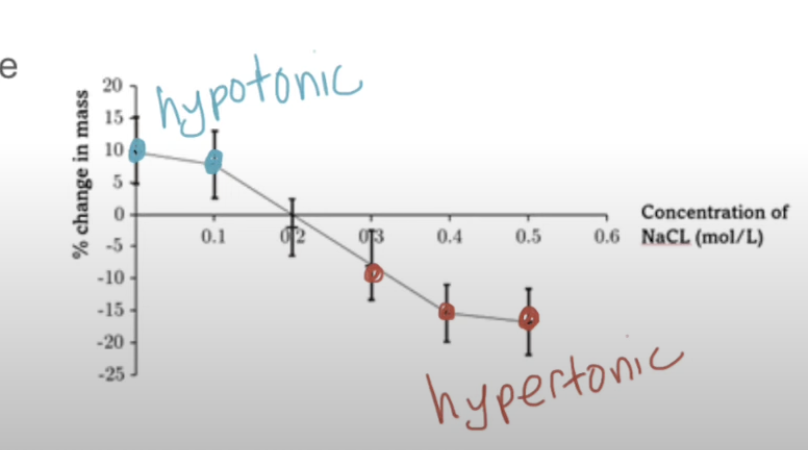
Find the osmolarity of the plant tissue (isotonic solute concentration- no net change in mass)
0.2
Solution + plant tissue have equal conc
Find where it crosses x axis (no net gain in mass)
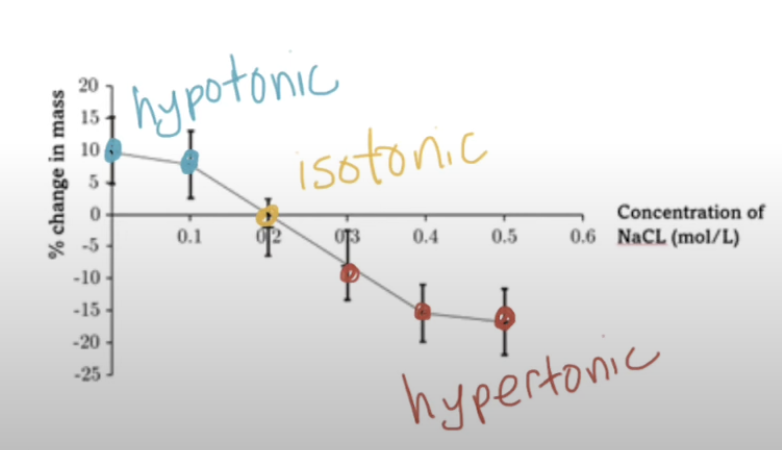
What can be determined if there are repeats for each concentration?
Standard deviation + standard error
This would allow the reliability of length and mass measurements to be compared
Standard deviation
Measures the spread of data around the mean
Shows how consistent the results are
Standard error
Estimates how reliable the mean is
Smaller error = the mean is more accurate
How is standard error shown graphically?
Error bars
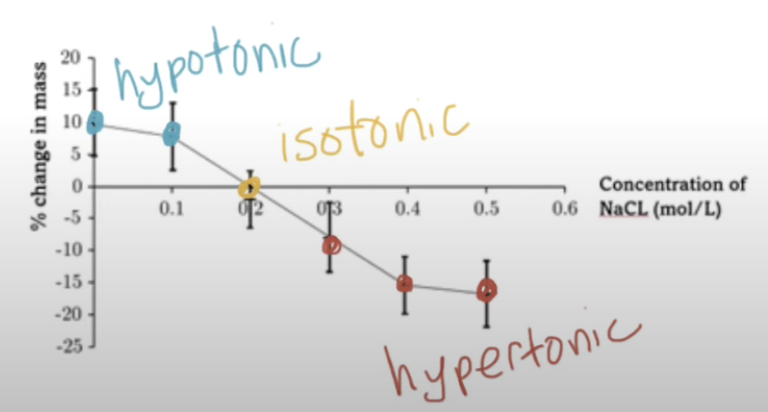
Control variables for osmosis experiment
Get plant tissue samples from sample plant
Same species
Same SA:V
Same time for osmosis to occur
Don’t include skin
Same temp of solution
What do the top + bottom of error bars show?
The range of values based on variation around the mean:
Top = mean + standard error (or deviation)
Bottom = mean - standard error (or deviation)
What does the full length of the error bar show?
The uncertainty / variability in the data
Do plant cells have a cell wall?
Yes
Do animal cells have a cell wall?
No
Function of cell wall
Prevents excess water entering, even if placed in a v hypotonic solution
Can handle lots of pressure
What happens if a animal cell (cell w/o a cell wall) is placed in a hypotonic solution?
Swells then bursts
Bc water enters
What happens if a animal cell (cell w/o a cell wall) is placed in a hypertonic solution?
Shrinks → then crenation
Bc water leaves
Why do freshwater eukaryotes need adaptations?
No cell wall
Placed in hypotonic environment → water enters → need to prevent from bursting
Adaptations of freshwater unicellular organisms (no cell wall)
Contractile vacuoles
Function of contractile vacuoles
Removes water
So prevents bursting
Needs energy
Why do multicellular organisms need to maintain isotonic tissue fluid?
To prevent harmful changes
Turgid
What happens if a plant cell (has cell wall) is placed in a hypotonic solution?
Develops turgor pressure
Becomes turgid
What happens if a plant cell (has cell wall) is placed in a hypertonic solution?
Plasmolysis
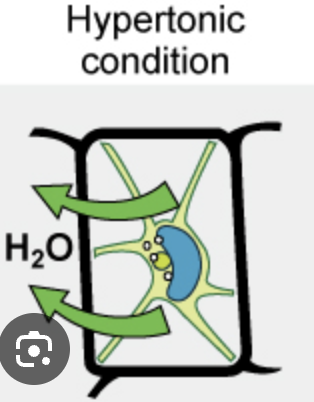
Plasmolysis
Plasma membrane pulls away from the cell wall
What are plant cell walls made of?
Cellulose
Why is it good if a plant cell is turgid?
Lots of pressure → helps keep the plant uprrught
What happens if a plant cell (has cell wall) is placed in an isotonic solution?
Becomes flaccid
Due to decreased pressure
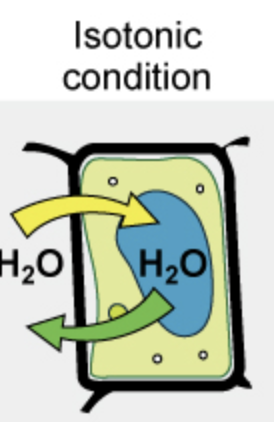
Net movement of water for cells in isotonic solutions
No net movement of water
What type of solution should animal cells (no cell wall) be kept/bathed in?
Isotonic
Why is saline used in medical procedures?
Bc it’s isotonic to human cells
Blood plasma needs to be isotonic to blood cells / other tissues
Medical applications of isotonic solutions
Intravenous fluids (IV) given as part of medical treatment
Bathing organs ready for transplantation
What is saline solution used for?
Rehydration