The Unit 6: Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration, and the Human Cardiorespiratory System
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/66
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
Inputs of photosynthesis
light energy, carbon dioxide, water
2
New cards
Outputs of photosynthesis
glucose, oxygen
3
New cards
Balanced equation of photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2
4
New cards
Stroma
The fluid-filled internal space of the chloroplasts which encircle the grana and the thylakoids
5
New cards
Thylakoids
An internal system of interconnected membranes that carry out the light reactions of photosynthesis.
6
New cards
Outer Membrane
The outer membrane of the chloroplast envelope, like that of mitochondria, contains porins and is therefore freely permeable to small molecules
7
New cards
Inner Membrane
The inner part of the chloroplast membrane is impermeable to ions and metabolites.
8
New cards
Granum
A basic structural unit of the thylakoid membrane network of plant chloroplasts. It is composed of multiple flattened membranes forming a stacked arrangement of a cylindrical shape.
9
New cards
Lamella
colorless fluid that surrounds the grana (stacks of thylakoid) within the chloroplast.
10
New cards
Where do the two stages of photosynthesis occur?
The light reactions take place in the thylakoid membranes, and the Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma. The light reactions capture energy from sunlight, which they change to chemical energy that is stored in molecules of NADPH and ATP.
11
New cards
Light dependent reactions
Light-dependent reactions happen in the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplasts and occur in the presence of sunlight. The sunlight is converted to chemical energy during these reactions. The chlorophyll in the plants absorb sunlight and transfers to the photosystem which are responsible for photosynthesis.
12
New cards
Light Independent Reactions
The light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle) use stored chemical energy from the light-dependent reactions to “fix” CO2and create a product that can be converted into glucose. The ultimate goal of the light-independent reactions (or Calvin cycle) is to assemble a molecule of glucose.
13
New cards
how is the proton gradient established in light dependent reactions?
A proton gradient is created in light-dependent reactions by the movement of protons from the stroma to the thylakoid lumen through the thylakoid membrane, which is driven by the energy released from the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain.
14
New cards
What is the role of Rubisco in the Calvin cycle?
RuBisCO's primary function is photosynthesis and photorespiration. It catalyzes the first step in the C3 pathway or Calvin cycle, namely the carboxylation of RuBP. It leads to the production of two 3-PGA molecules.
15
New cards
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that contain chlorophyll and other pigments needed for photosynthesis. Chlorophyll absorbs light energy from the sun and converts it into chemical energy that can be used to produce sugars and other organic compounds.
16
New cards
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in chloroplasts that plays a key role in capturing light energy for photosynthesis.
17
New cards
Stomata
Stomata are small pores found on the surface of leaves that allow for gas exchange between the plant and its environment.
18
New cards
Guard Cells
Guard cells, which are specialized cells that surround the stomata, regulate the opening and closing of the stomata to control the rate of gas exchange and water loss.
19
New cards
Mesophyll Cells
Mesophyll cells are specialized cells in leaves that contain a large number of chloroplasts and are responsible for carrying out most of the photosynthesis in the plant.
20
New cards
Cuticle
The cuticle is a waxy layer that covers the outer surface of leaves and helps to reduce water loss by evaporation.
21
New cards
Xylem
Xylem is a specialized tissue that transports water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. Xylem is made up of elongated cells called tracheids and vessel elements that are interconnected to form a network of tubes.
22
New cards
Phloem
Phloem is another specialized tissue that transports sugars and other organic compounds from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Phloem is made up of cells called sieve tubes and companion cells that work together to move nutrients through the plant.
23
New cards
inputs of cellular respiration
glucose, oxygen
24
New cards
outputs of cellular respiration
carbon dioxide, energy, water
25
New cards
balanced equation for cellular respiration
C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6 O 2 --> 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + ATP
26
New cards
Where does Glycolysis occur?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. It is the first step in cellular respiration and involves breaking down glucose (a six-carbon sugar) into two molecules of pyruvate (a three-carbon compound).
27
New cards
Where does Citric Acid Cycle (kreb Cycle) Occur?
The citric acid cycle takes place in the mitochondria of the cell. Pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria, where it is converted into acetyl-CoA and enters the citric acid cycle. The cycle involves a series of reactions that oxidize acetyl-CoA and produce energy-rich molecules like NADH and FADH2.
28
New cards
Where does the Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron transport system) occur?
Oxidative phosphorylation occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. It involves the transfer of electrons from NADH and FADH2 to a series of protein complexes in the membrane, which generates a proton gradient across the membrane. This gradient is then used to power the production of ATP through the enzyme ATP synthase.
29
New cards
What are the parts of the mitochondria?
Outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, cristae, and matrix
30
New cards
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, where glucose is broken down into pyruvate, producing ATP and NADH in the process.
31
New cards
Krebs cycle
The Krebs cycle, also known as the citric acid cycle or tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, is a series of biochemical reactions that occur in the mitochondria of cells, where acetyl-CoA is oxidized to produce ATP and carbon dioxide.
32
New cards
Electron transport chain
The electron transport chain is a series of proteins and electron carriers located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria or the plasma membrane of bacteria, that transfer electrons from NADH and FADH2 to oxygen, generating a proton gradient that is used to produce ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
33
New cards
How is the proton gradient formed during the electron transport chain?
The proton gradient is created during the electron transport chain by the active transport of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane, from the matrix to the intermembrane space, using the energy released from the transfer of electrons through the electron carriers. This creates a higher concentration of protons in the intermembrane space than in the matrix, generating an electrochemical gradient that drives the synthesis of ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
34
New cards
Anerobic
a metabolic process that occurs without oxygen and typically produces less ATP than aerobic respiration.
35
New cards
aerobic
a metabolic process that requires oxygen to produce ATP
36
New cards
Alcoholic fermentation
Alcoholic fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration that occurs in some yeasts and bacteria, where pyruvate is converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide, producing a net of two molecules of ATP per glucose molecule.
37
New cards
Lactic acid fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation is a type of anaerobic respiration that occurs in some bacteria and in muscle cells during intense exercise when oxygen is limited, where pyruvate is converted into lactic acid, producing a net of two molecules of ATP per glucose molecule.
38
New cards
Final Products of Lactic acid fermentation and Alcoholic fermentation
The final product of alcoholic fermentation is ethanol and carbon dioxide, while the final product of lactic acid fermentation is lactic acid.
39
New cards
How does lactic acid fermentation relate with muscle fatigue in humans.
Lactic acid fermentation is a metabolic process that occurs in the muscles of humans when there is insufficient oxygen supply to meet the energy demands of the body during exercise. As a result, the body produces energy through the breakdown of glucose in the absence of oxygen, which produces lactic acid as a byproduct. When the concentration of lactic acid increases in the muscles, it leads to an accumulation of hydrogen ions, causing a drop in pH levels, which impairs muscle function and contributes to muscle fatigue. This buildup of lactic acid and hydrogen ions can lead to a burning sensation in the muscles and a decrease in the ability of the muscles to contract and generate force, ultimately leading to fatigue.
40
New cards
How does the energy output of the aerobic and anaerobic compare?
The aerobic phase of respiration, which occurs in the mitochondria of cells, is a much more efficient process for energy production than the anaerobic phase. During aerobic respiration, glucose is broken down completely to carbon dioxide and water, producing a large amount of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) energy in the process. The net yield of ATP from aerobic respiration is around 36-38 molecules per glucose molecule. In contrast, during the anaerobic phase of respiration, which occurs in the cytoplasm of cells, glucose is broken down incompletely to produce ATP energy in the absence of oxygen. This process produces lactic acid as a byproduct and only yields a net of 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule. Overall, the aerobic phase of respiration is a more efficient process for energy production and can sustain ATP production for longer periods of time compared to the anaerobic phase. However, the anaerobic phase can provide a quick burst of energy during short periods of intense physical activity when the body's demand for oxygen exceeds its supply.
41
New cards
how are cellular respiration and photosynthesis are related?
Cellular respiration and photosynthesis are two interrelated processes that occur in living organisms. Photosynthesis, which occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. During this process, light energy is converted into chemical energy and stored in the form of glucose molecules.
42
New cards
cardiovascular system: Transportation of nutrients and oxygen
The cardiovascular system transports nutrients, oxygen, and hormones throughout the body to nourish and support the various tissues and organs.
43
New cards
cardiovascular system: Removal of waste products
The system also carries away metabolic waste products, such as carbon dioxide, from the cells and transports them to the lungs for elimination.
44
New cards
cardiovascular system: Maintenance of body temperature
The system helps regulate body temperature by transporting heat generated by the cells away from the core and toward the skin, where it can be dissipated.
45
New cards
cardiovascular system: Protection against disease and injury
The cardiovascular system plays a role in the body's immune response by transporting white blood cells and antibodies to fight against infections and other foreign invaders.
46
New cards
cardiovascular system: Regulation of blood pressure
The system helps regulate blood pressure by adjusting the diameter of the blood vessels and controlling the force of heart contractions.
47
New cards
Heart structure: Right Atrium
The right atrium receives oxygen-poor blood from the body and pumps it to the right ventricle.
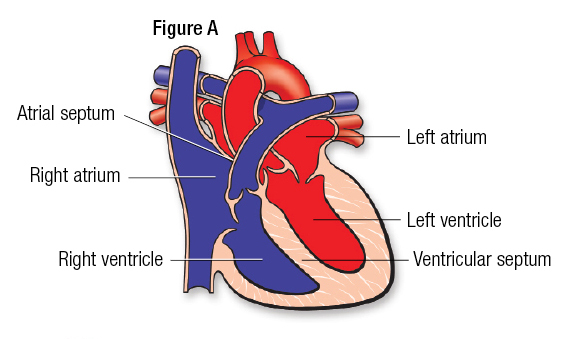
48
New cards
Heart Structure: Left Atrium
The left atrium receives oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and pumps it to the left ventricle.
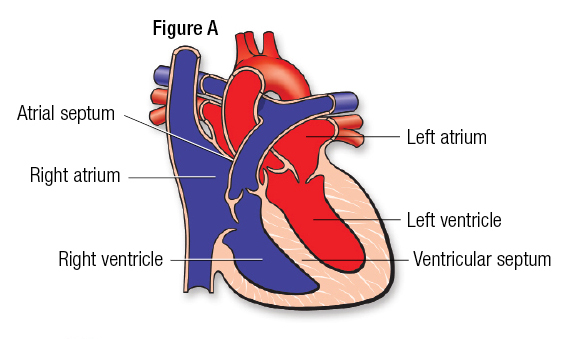
49
New cards
Heart Structure: Left Ventricle
The left ventricle pumps the blood to the aorta which will distribute the oxygenated blood to all parts of the body.
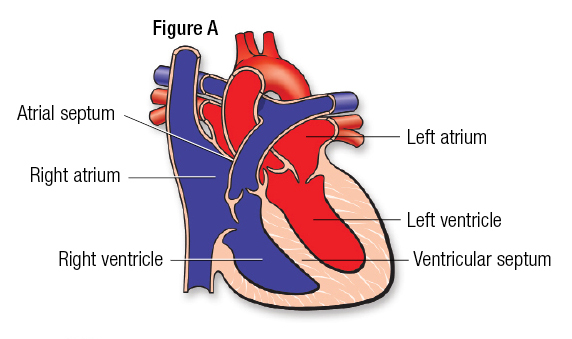
50
New cards
Heart Structure: Right Ventricle
The right ventricle pumps the blood under low pressure through the pulmonary valve into the pulmonary artery. From there the blood goes to the lungs where it gets fresh oxygen (C).
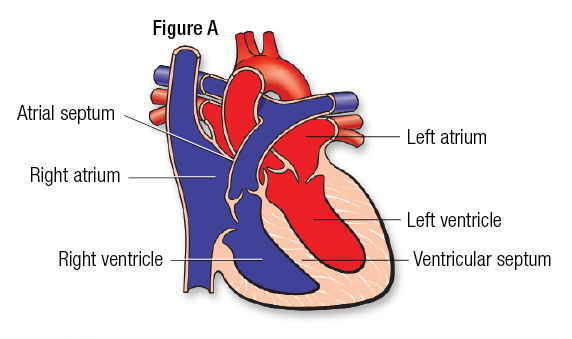
51
New cards
How does blood travel through the body?
Blood comes into the right atrium from the body, moves into the right ventricle and is pushed into the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. After picking up oxygen, the blood travels back to the heart through the pulmonary veins into the left atrium, to the left ventricle and out to the body's tissues through the aorta.
52
New cards
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body. Veins. Blood vessels that carry blood from the body back into the heart.
53
New cards
Veins
Veins have one-way valves instead of muscles, to stop blood from running back the wrong way. Generally, veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart, where it can be sent to the lungs. The exception is the network of pulmonary veins, which take oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
54
New cards
Capillaries
the smallest and most numerous of the blood vessels, form the connection between the vessels that carry blood away from the heart (arteries) and the vessels that return blood to the heart (veins). The primary function of capillaries is the exchange of materials between the blood and tissue cells.
55
New cards
Nose and nasal cavity
The nose and nasal cavity are responsible for filtering, warming, and moistening the air we breathe in.
56
New cards
Pharynx
The pharynx is a muscular tube that connects the nasal cavity and mouth to the larynx. It also serves as a pathway for food and liquid to pass through.
57
New cards
Larynx
The larynx, or voice box, contains the vocal cords and is responsible for producing sound. It also helps to protect the trachea and lungs by closing off during swallowing.
58
New cards
Trachea
The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube made of cartilage rings that connects the larynx to the bronchi. It serves as a passageway for air to move in and out of the lungs.
59
New cards
Bronchi
The bronchi are two branches of the trachea that lead to the left and right lungs. They further divide into smaller bronchioles that eventually lead to the alveoli.
60
New cards
Alveoli
The alveoli are small, grape-like structures within the lungs where gas exchange takes place. Oxygen from the air we breathe in diffuses into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide diffuses out and is exhaled.
61
New cards
How can oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange at the alveolus/capillary be described?
During gas exchange oxygen moves from the lungs to the bloodstream.At the same time carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the lungs. This happens in the lungs between the alveoli and a network of tiny blood vessels called capillaries, which are located in the walls of the alveoli.
62
New cards
What is the mechanism of breathing (inhaling and exhaling)
During inspiration, the diaphragm and external intercostal musclescontract, causing the rib cage to expand and move outward, and expanding the thoracic cavity and lung volume. This creates a lower pressure within the lung than that of the atmosphere, causing air to be drawn into the lungs.
63
New cards
how does gas pressure affect the flow of air during inhalation and exhalation?
Air flows because of pressure differences between the atmosphere and the gases inside the lungs. Air, like other gases, flows from a region with higher pressure to a region with lower pressure. Muscular breathing movements and recoil of elastic tissues create the changes in pressure that result in ventilation.
64
New cards
2-deoxyglucose
Stops glucose from being used in glycolysis thus not creating any pyruvate.
65
New cards
Arsenic
Stops pyruvate from being used in the Krebs cycle thus no NADH is made.
66
New cards
Cyanide
Attaches to the last last enzyme in the ETC, stops electrons from leaving the ETC
67
New cards
Oligomycin
Attaches to the ATP synthase, stops H+ from entering the ATP synthase thus no ATP is created.