Science Year 9 Semester 1 - Human Systems
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What is the nervous system?
The body system that senses the environment and controls our actions
What is the nervous system made up of?
Brain, Spinal Cord, Nerves, Sense Receptors
The nervous system also helps to…
Coordinate other body systems. It controls digestion, breathing and heart rate without you even needing to think about it!
What are the 2 main divisions of the nervous system?
The Central Nervous System and the Peripheral Nervous System
What does the central nervous system do?
Consists of brain and spinal cord. Makes sense of messages it receives from sensory organs and co-ordinates responses by the muscles and glands
What does the peripheral nervous system do?
Relays messages between sensory organs, the nervous system and the muscles and glands
What are neurons?
Neurons are specialised cells that transmit messages, in the form of electrical signals, within the nervous system
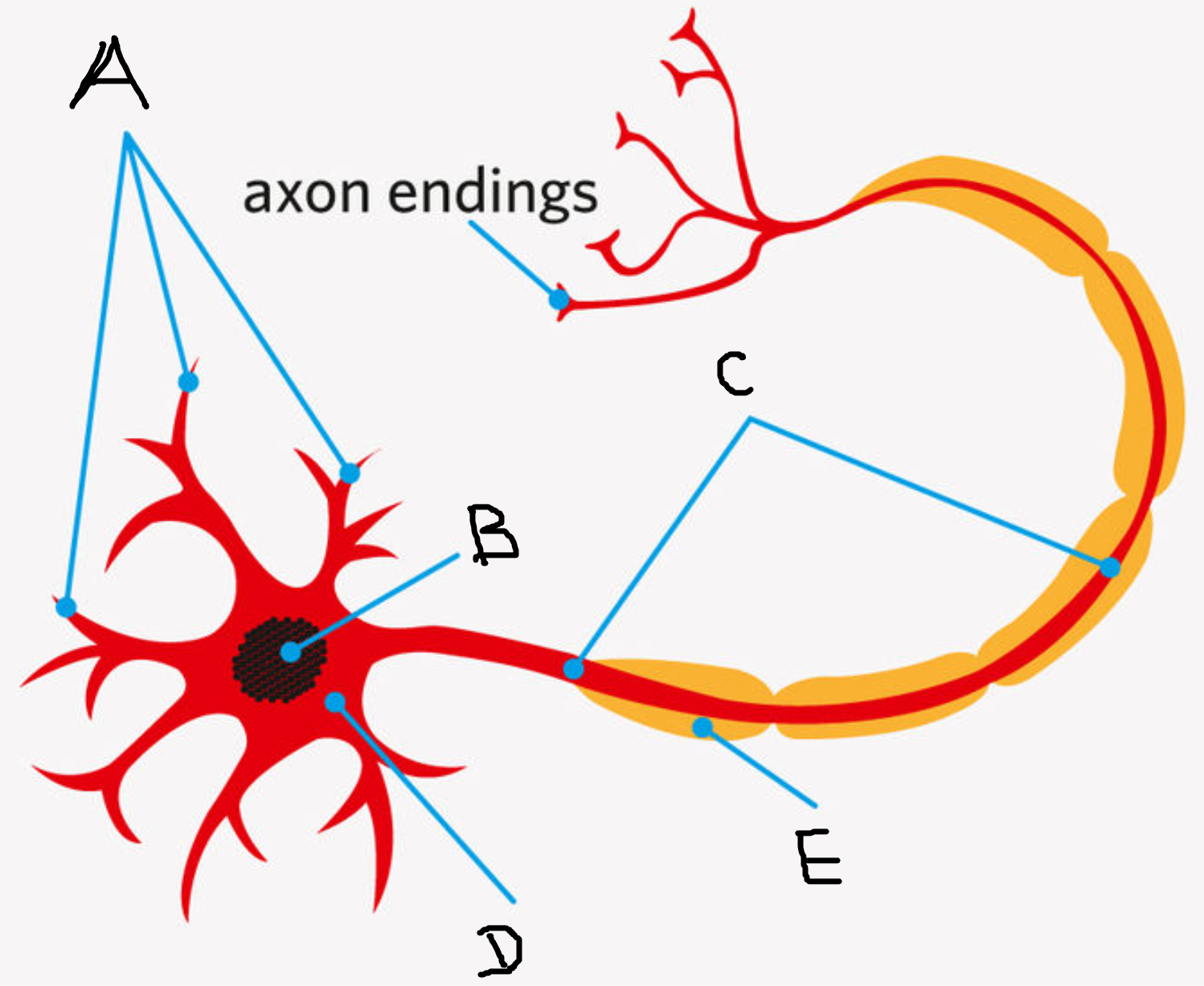
Complete the diagram.
A - Dendrites
B - Nucleus
C - Axon
D - Cell Body
E - Myelin Sheath
What are dendrites?
Branches that receive messages
What are axons?
A thread like structure that carries impulses to other neurons
What are cell bodies?
It is where the nucleus is located
What are axon terminals?
The spines at the end that send the message to the next neuron
What are myelin sheaths?
A fatty layer that insulates the axon and sometimes a dendrite
What is the autonomic nervous system?
It is an automatic division of the peripheral nervous system, meaning it operates without conscious control or awareness
What are the two parts of the autonomic nervous system?
Sympathetic Nervous System and Parasympathetic Nervous System
What does the sympathetic nervous system do?
Speeds the body up, gets ready for fight - flight - freeze.
(Tip: think sympathetic, speed, stress up)
What does the parasympathetic nervous system do?
Slows the body down and returns us to a state of homeostasis
(Tip: Parachutes us back to baseline)
What is the brain?
The organ in your head that processes information and controls your behaviour
What are the 5 main components of the brain?
Cerebrum, Cerebellum, Brain Stem, Pituitary, Hypothalamus
The cerebrum is broken down into 4 lobes, each with their own functions. Name them:
Frontal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe
Temporal Lobe
What is the function of the frontal lobe?
Planning, Organizing, Movement, Speech
What is the function of the parietal lobe?
Receiving and responding to sensory information
What is the function of the occipital lobe?
Receiving and responding to visual information
What is the function of the temporal lobe?
Hearing, Speech, Comprehension
What is a receptor?
Specialised cells that allow us to detect different types of stimuli
What is a chemoreceptor?
Are sensitive to chemicals such as odour molecules in the air.
They are located in the nose and tongue.
What is a mechanoreceptor?
Are sensitive to touch, pressure, sound and motion.
They are located in the skin, the inner ear and muscles.
What is a pain receptor?
Are sensitive to chemical changes in damaged cells.
They are located all around the body, but mostly in the skin.
What is a thermoreceptor?
Are sensitive to temperature changes.
They are located in the skin.
What is a photoreceptor?
Are sensitive to light.
They are located in the eyes.
What do sensory neurons do?
Transmit messages from sensory organs to the central nervous system
What do motor neurons do?
Transmit messages from the central nervous system to “effectors” such as muscles and glands to initiate a response
What do interneurons do?
Transmit messages from sensory neurons to motor neurons
Summarise the stimulus-response pathway.
A receptor detects the stimulus (e.g. thermoreceptor detects heat from a candle)
A sensory neuron transmits the signal to an interneuron in the central nervous system (CNS)
Interneurons transmit information within the CNS as part of the decision making process
A motor neuron transmits a signal from the CNS to an effector (a muscles or gland) which produces a response
A response is a change because of a stimulus. (e.g. muscles in the arm move away from the hot fire)
What are the 2 functions of the spinal cord?
Transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body
Carries out certain reflex actions
What is a spinal reflex?
An automatic & involuntary response to a sensory stimulus that involves the spinal cord
What are hormones?
Chemicals created by organs called glands. They are released into the bloodstream and circulate around the body.
How are hormones able to target specific organs if they're circulating through the whole body?
Each hormone molecule has a unique shape. The target cells have special receptors that match the hormone’s shape. When the hormone locks onto the receptor, it makes the cell behave a certain way.
What is homeostasis?
The body’s ability to maintain a stable state despite changes, such as temperature and levels of sugar, salt and water.
When you eat, your digestive system breaks down the carbohydrates in your food and releases glucose into the bloodstream.
What happens when blood glucose levels gets too high?
A special hormone called insulin is released from the pancreatic glands. It instructs the cells in the liver and muscles to absorb the glucose from the bloodstream and store it in the cells.
What’s worser to have - type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes?
Type 1 is worse to have. Type 1 diabetes means your pancreas doesn’t work completely and no insulin can be produced.
Type 2 diabetes means your pancreas is slowed down and doesn’t produce enough insulin or just ignores it.
What causes Type 1 diabetes?
Due to prolonged periods of time without proper treatment type 2 diabetes
Due to the immune system mistakenly attacking these cells
What causes Type 2 diabetes?
The main cause is due to your cells ignoring insulin, or you overwork your pancreatic system so much that it burns out