PE 461 Midterm Fall 2022
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
Phosphocreatine breakdown is regulated by
Creatine kinase
Which of these is NOT part of an ATP molecule
An enzyme
5 carbon sugar
Adenine containing nitrogen
3 phosphate groups
An enzyme
Intracellular stores of ATP and PCr are sufficient to support maximum muscular effort for approximately
3-15 seconds
The two non-oxidative metabolic pathways are the
Phosphagen system and glycolysis
In order to lose 5 lbs of fat, how many more kcal must a person burn through exercise than they eat
17500
Which of these is NOT true?
Athletes should get 30-35% of their calories from protein
Gluconeogenesis is the production of glucose from amino acids
The American Heart Association recommends that people get 30% (or less) of their calories from fat
25 g of carbohydrate provides 100 kcal
Athletes should get 30-35% of their calories from protein
Which of these nutrients does NOT provide energy for our body
Vitamins
Fat
Protein
Carbohydrate
Vitamins
Which of the following statements is true regarding the relative roles of fat, carbohydrate, and protein as energy sources for cellular metabolism
Fat cannot provide all of the energy required for high-intensity muscular activity because the rate of energy release from fat is too low
Protein is the predominant fuel source during exercise
Much more energy is stored in the body in the form of carbohydrate the in the form of fat
Single glycogen reserves in the body are so large, only limited amounts of carbohydrate are needed in the daily diet
Fat cannot provide all of the energy required for high-intensity muscular activity because the rate of energy release from fat is too low
Which of these statements is NOT true?
As the exercise intensity increases, the body relies more on fats and less on carbohydrate for making ATP
A trained person uses more fat and less carbohydrate for a given submaximal exercise intensity
Intramuscular fat stores increase a little due to an exercise training program
At rest, about 47.5% of energy comes from fat, 47.5% from carbohydrate and 5% for protein (typically)
As the exercise intensity increases, the body relies more on fats and less on carbohydrate for making ATP
How much carbohydrate per day should a recreational athlete, who exercises 3-4 days per week at a moderate intensity for 45 minutes, eat?
3-6 grams/kg of body mass
In the human body, about what percent of energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP is used to produce muscle movement and other cellular processes?
30%
What is the main fuel used to make ATP during exercise
Carbohydrate
Which statement below is TRUE?
Protein can become carbohydrate
Fat can become protein
Carbohydrate can become protein
Fat can become carbohydrate
Protein can become carbohydrate
In order for glucose to be stored in the muscles or liver as a stored form of carbohydrate, it must be converted to which substance?
Glucose-1-phosphage
How is fat stored in the body?
As triglycerides
Which one of these statements is true?
Protein is primarily important for structural function in the human body
Carbohydrate is stored in large quantities in the human body
Eating a high protein/low carbohydrate diet is essential for appropriate adaptations to exercise
A high fat diet will enhance sports performance
Protein is primarily important for structural function in the human body
An energy system that uses all of its fuel from storage within the cytosol, does not use oxygen, and relies only a single enzyme describes which energy system?
Phosphagen system
Which one of these statements is NOT true?
Muscle glycogen can be used to maintain normal blood glucose levels
Excess carbohydrate intake will result in fat storage in the body
Fat is less readily converted to ATP than is carbohydrate
Liver glycogen can be used to maintain normal blood glucose levels
Muscle glycogen can be used to maintain normal blood glucose levels
The most important carbohydrate for ATP production in humans is
Glucose
The synthesis of molecules is called
Anabolism
The initial energy required to start a chemical reaction or chain of reactions
Activation energy
The addition of a phosphate group to a molecule
Phosphorylation
An enzyme found early in a metabolic pathway that determines the rate of the pathway
Rate limiting enzyme
The process of converting protein (or carbohydrate) into fatty acids
Lipogenesis
Term given to the study of processes that yield or consume energy in living organisms
Bioenergetics
Nerves that carry impulses towards the central nervous system.
Sensory nerves
An increase in electric potential across a cell membrane.
Hyperpolarization
A primary neurotransmitter that transmits impulses across the synaptic cleft, particularly in motor units between the nerve and the muscle cell.
Acetylcholine
A catecholamine released from the adrenal medulla that helps prepare the body for a fight-or-flight response. It's also a neurotransmitter secreted from most preganglionic nerves of the sympathetic nervous system.
Norepinephrine
The site at which a motor neuron communicates with a muscle fiber.
Neuromuscular junction
The cumulative effects of all the individual changes in a neurons membrane potential. Can also apply when multiple electrical stimuli are applied to a muscle at a sufficiently high frequency causing twitches to merge into higher forces.
Summation
The connective tissue sheath surrounding each muscle fasiculus.
Perimysium
Any muscle action that produces joint movement.
Dynamic contraction
The contractile element of skeletal muscle.
Myofibirls
Immature cells that can develop into mature cell types, such as myoblasts.
Satellite cells
An increase in size of existing individual muscle fibers.
Fiber hypertrophy
The "pumping up" of muscle that happens during a single exercise bout, resulting mainly from fluid accumulation in the interstitial and intracellular spaces of the muscle.
Transient hypertrophy
The loss of muscle mass associated with aging.
Sarcopenia
Loss of size, or mass, of body tissue.
Atrophy
Enzyme that controls the rate of protein synthesis within the myofibrils after resistance training.
mTOR
The initial energy required to start a chemical reaction or series of reactions.
Activation energy
The tearing down of body tissue, the destructive phase of metabolism.
Catabolism
The conversion of protein into glucose.
Gluconeogenesis
The process of turning a protein into a fatty acid.
Lipogenesis
An enzyme found early in a metabolic pathway that determines the rate of the pathway.
Rate limiting enzyme
The point during exercise of increasing intensity at which the end products of anaerobic glycolysis begins to accumulate above resting levels.
Lactate threshold
A series of chemical reactions that convert hydrogen ions from glycolysis and the Krebs cycle into water and produce energy for oxidative phosphorylation.
Electron transport chain
Cellular organelles that generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation.
Mitochondria
The compound that forms the common entry point into the Krebs cycle for the aerobic breakdown of carbohydrate and fat.
Acetyl coenzyme A
The process of breaking down stored fats to its basic units to be used for energy.
Lipolysis
The body's most concentrated energy source and the form in which most fats are stored.
Triglycerides
The first step in fatty acid activation in which fatty acids are broken down into separate two carbon units.
Beta-oxidation
Which Krebs cycle intermediate, made from pyruvate, is of key importance in preventing dangerous ketoacidosis?
Oxaloacetate
A sensory receptor in a muscle tendon that monitors tension.
Golgi tendon organ
The junction between two neurons.
Synapse
The basic functional unit of a myofibril.
Sarcomere
Highest tension developed by a muscle in response to stimulation increasing in frequency.
Tetanus
Muscle shortening
Concentric contraction
Extensions of the sarcolemma (plasma membrane) that pass literally through the muscle fiber, allowing nutrients to be transported and nerve impulses to be transmitted rapidly to individual myofibrils.
T-tubules
Reflex inhibition of a motor neuron in response to excessive tension in the muscle fibers it supplies, as monitored by the Golgi tendon organ.
Autogenic inhibition
The conversion of glycogen to glucose.
Glycogenolysis
Soreness or pain felt immediately after an exercise bout.
Acute muscle soreness
A method of estimating energy expenditure by measuring respiratory gases.
Indirect calorimetry
Muscle soreness that develops a day or two after a heavy bout of exercise and that is associated with actual injury within the muscle.
Delayed onset muscle soreness
Which type of nervous receptor is sensitive to pain?
Nocioceptors
Which of these statements about the nervous system is NOT correct?
The sodium-potassium pump moves 3 sodium atoms out, and 2 potassium into the cell per ATP used
Depolarization is when the inside of the cell becomes less negative relative to the outside
Norepinephrine is secreted by pre-ganglionic neurons in the brain
The neuromuscular junction is a synapse between a neuron and a muscle cell.
Norepinephrine is secreted by pre-ganglionic neurons in the brain
Which statement is NOT true?
Training can alter the order of activation of type 1 and type 2 motor units
Training can alter neural precision
Training can alter neural endurance
Training can alter neural speed
Training can alter the order of activation of type 1 and type 2 motor units
The basic structural element of the nervous system is the _______.
Neuron
At rest, which ion is in the highest concentration outside of an excitable cell?
Sodium
An action potential is generated when a stimulus ___________.
Opens sodium channels
Put the following events in action potential in the correct order.
1. Action of Na+/K+ ATPase
2. The difference in the charge across the cell membrane becomes more negative
3. Opening of the potassium gates
4. The difference in the charge across the cell membrane becomes less negative
5. Opening of sodium gates due to stimulus
5,4,3,2,1
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system causes which of the following?
Release of T3
Catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla
Saltatory conduction
Increased usage of protein for energy
Catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla
_______ is the name for the chemical released from the terminal end of a neuron that binds to a specific receptor on the next cell in the sequence.
Neurotransmitter
Which of the following is NOT true about the human brain?
Humans only use 10% of their brain capacity
20% of daily energy expenditure is for brain function
The brain is included in the CNS
There is minimal evidence showing people are left or right brain dominant
Humans only use 10% of their brain capacity
The _____ is a functional portion of the nervous system that controls involuntary body functions.
Autonomic nervous system
Which of the following best describes the relationship between sympathetic nervous system activity and sports performance?
There is no relationship between sympathetic nervous activity and sports performance
A negative linear relationship, indicating that less sympathetic function increases performance
A positive linear relationship, indicating that more sympathetic function increases performance
An inverted U, indicating that too much or too little can be detrimental to performance
An inverted U, indicating that too much or too little can be detrimental to performance
______ is the propagation of action potentials along myelinated axons from one node of Ranvier to the next node.
Saltatory conduction
What does the size principle state about motor neuron recrutiment?
Small motor units are activated first when muscle force is required
Which of these is NOT true?
An IPSP makes it easier for the cell to be activated
Transport proteins regulate sodium and potassium movement across the cell membrane
The action of the sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport, where something is moved against the concentration gradient
The imbalances in charges across the cell membrane results in the inside of the cell being -70mV compared to the outside
An IPSP makes it easier for the cell to be activated
Typically speaking, what is the threshold for a neuron to undergo an action potential?
-70mV
-95mV
-55mV
0mV
-55mV
Under which of these condition would you find the fastest rate of neural transmission?
Temperature of 39* C, pH 7.0, lots of myelin, larger axon diameter
What is the role of the Golgi tendon organ?
Monitor muscle tension
Which of these is NOT true about neurotransmitters?
Norepinephrine can cause different effects depending on whether it binds to an adrenergic or cholinergic receptor
Neurotransmitters can be measured with a blood test
After release from the vesicles, neurotransmitters can be degraded by enzymes
After release from the receptors, neurotransmitters can undergo reuptake in the releasing cell
Neurotransmitters can be measured from a blood test
Which of these statements is true?
Corpuscles sense things like touch and pressure
In response to strength training the EMG amplitude during maximal exercise is reduced
Activity of the parasympathetic nervous system will results in vasodilation of the coronary arteries
Serotonin causes feelings of sadness and dispair
Corpuscles sense things like touch and pressure
A depolarization of the post synaptic membrane caused by an excitatory stimulus.
Excitatory post-synaptic potential
A sensory receptor located in the muscle that senses how much the muscle is stretched.
Muscle spindle
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of skeletal muscles?
Intercalated discs
Multinucleated
Voluntary control
Striated
Intercalated discs
During what speed of movement will a person be able to lift the heaviest weight?
A slow movement
In the figure showing muscle proteins, which protein does the arrow point to?
Myosin
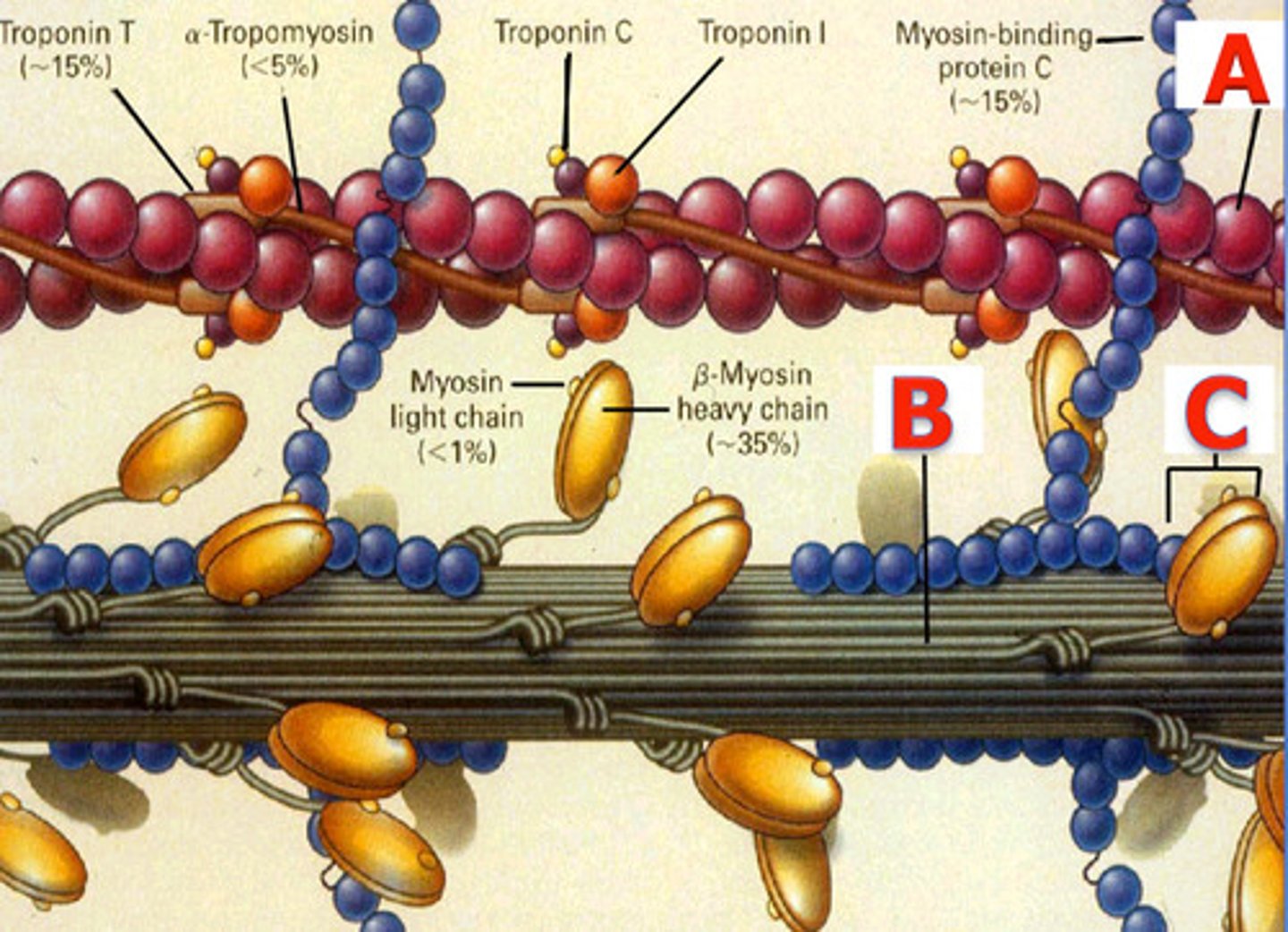
Calcium ions responsible for turning on muscle contractions are stored in the ______.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
During muscle contraction, which protein has the moving structures that pull on the others?
Myosin
Which of these is NOT true about skeletal muscles?
Muscle cells are also referred to as muscle fibers
Muscle cells require energy for both the action and relaxation phases of contraction
The individual muscle fibers within the skeletal muscle typically extend the entire length of the muscle
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates are referred to as a motor unit
The individual muscle fibers within the skeletal muscle typically extend the entire length of the muscle
Arrange the events leading to a muscle contraction in the correct order.
1. Release of calcium
2. Release of acetylcholine
3. Myosin binding to actin
4. Depolarization reaches the T-tubules
2,4,1,3
Which of the following is true?
Muscles carry out fine motor movements generally made up of motor units that contain only a few muscle fibers
A single motor neuron can innervate only one muscle fiber
The muscle-fiber composition of a a motor unit is generally mixed (type 1 and type 2 fibers)
A single muscle fiber may be innervated by multiple motor neurons
Muscles carry out fine motor movements generally made up of motor units that contain only a few muscle fibers.
Arrange the events of a muscle contraction in the right order.
1. Calcium binds to troponin, causing tropomyosin to move
2. Depolarization of the axon terminals
3. End plate potential in the muscle cell
4. The CNS sends a command in the form of a motor impulse
4,2,3,1
Which skeletal muscle fiber type has the lowest motor unit strength, the highest aerobic capacity, and the highest fatigue resistance?
Slow Oxidative
Which of these is NOT true about skeletal muscle fibers?
Myoglobin is the oxygen-transporting protein in muscles
FOG fibers are more fatigue resistant than type IIx
The reuptake of calcium from the sarcoplasm after contraction uses passive transport
Myoglobin gives slow-twitch muscles their dark red appearance
The reuptake of calcium from the sarcoplasm after contraction uses passive transport.
Which of these statements is NOT correct?
Cardiac muscle cells are striated
ATPase works with myosin to facilitate the power stroke of muscle contraction
Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber
Troponin covers actin binding sites on myosin
Troponin covers actin binding sites on myosin
The amount of force generated by a group of muscles depends on ________.
The type of motor units recruited, the number of motor units recruited, the frequency of stimulation of motor units
Which athletes would you expect to have the highest percentage of SO fibers in her body?
Paula Radcliffe, a world record holder in the marathon
Marion Jones, a world-class sprinter and jumper
Inge de Brujn, a world record holder for the 50m freestyle event in swimming
Gabriele Reinsch, a world record holder in discus
Paula Radcliffe, a world record holder in the marathon