Microscopic examination of urine
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What crystals are found in acidic urine?
Uric acid, calcium oxalate, cystine, bilirubin
What crystals are found in alkaline urine?
calcium carbonate, triple phosphate, ammonium biurate, calcium phosphate
What crystals are found in alkaline and acidic urine?
cholesterol, leucine, tyrosine, sulfa
What crystals are considered normal?
Uric acid, calcium carbonate, triple phosphate, calcium oxalate, ammonium biurate, calcium phosphate
What crystals are considered abnormal?
cystine, cholesterol, leucine, tyrosine, sulfa, bilirubin
What are the conditions for cast formation?
high urine acidity
high urine concentration
reduced urine flow
How are samples prepped for a microscopic urinalysis?
10-15 ml of well-mixed urine
centrifuge & decant
well-mixed drop of sediment
Is the oil lens used in microscopic urinalysis?
No, 40x is the max
What is done on 10x?
ID and quantification of casts and mucus. Look at 2-4 edges of coverslip and 10-15 fields in center
What is done on 40x?
Id and quantification of cells, microorganisms and crystals
What are polarizing lenses used for?
crystals
lipids
What is the matrix of a cast made out of?
Tamm horsfall protein
What are the only element in urine sediment that are unique to the kidney?
Casts
What is the progression of cast types?
Hyaline → cellular → granular→ waxy casts
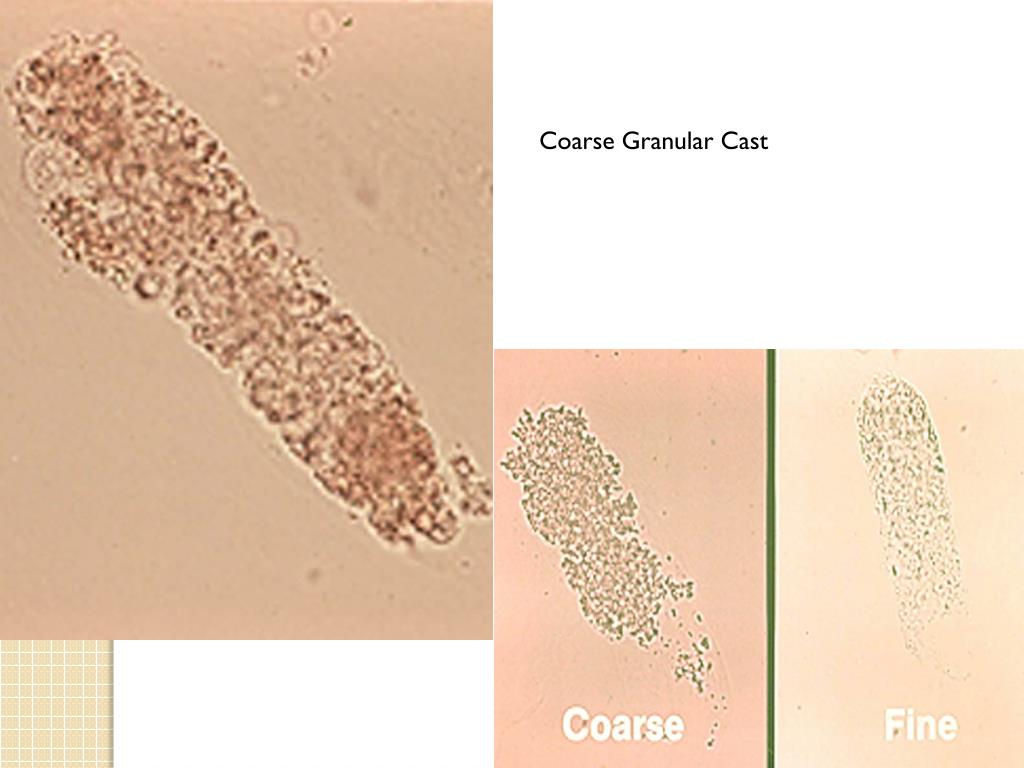
What are the two types of granular casts?
coarse
fine
What is the most common cast type?
hyaline/cylindroid
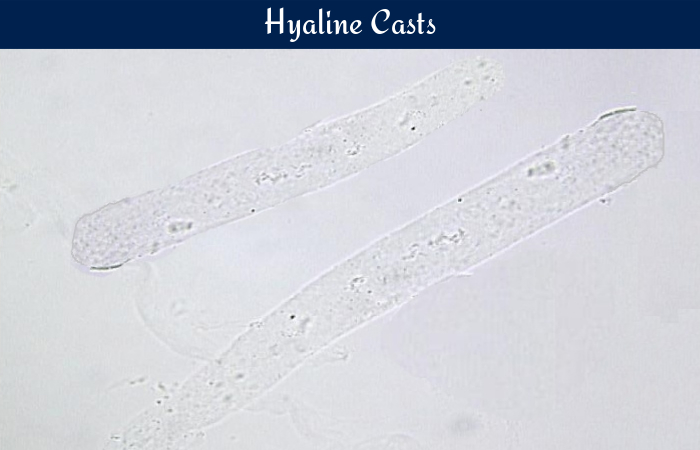
What are cellular casts?
TH protein + cellular element
any number is abnormal
associated with bleeding, infection, tubular damage
RBC casts
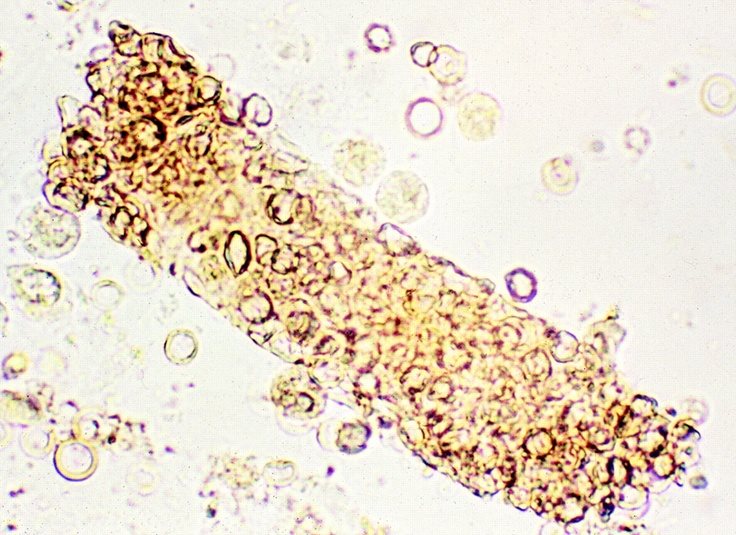
WBC cast
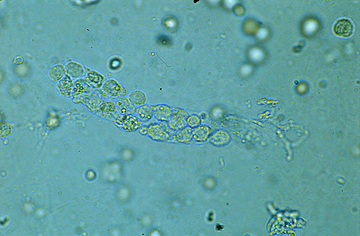
Granular cast
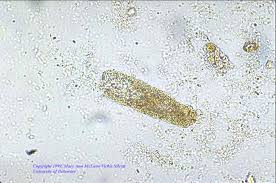
What are granular casts?
breakdown of cellular casts
any number is abnormal
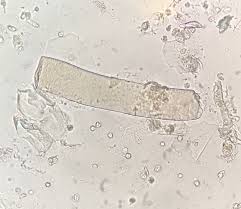
What are waxy casts?
aged granular casts
high refractive index
any number abnormal
Waxy casts
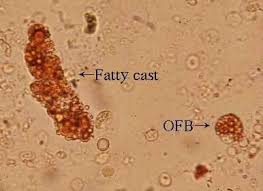
Oval fat bodies
Renal epithelial cells or macrophages that are filled with fat or lipid droplets
of cholesterol esters are present will form Maltese cross under polarizing light
Fatty casts
Red blood cells in urine are?
abnormal in any number
may be crenated or “ghost” cells
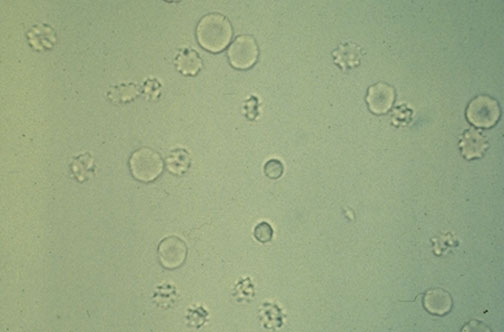
White blood cells in urine?
0-5/hpf is normal
associated with infection and inflammation
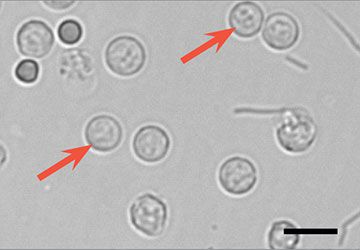
Glitter cells are?
WBCs in hypotonic solution, swollen so granules appear to glitter as they move
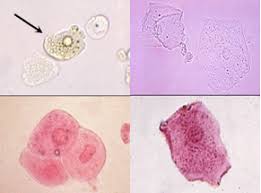
Squamous epithelial cells are?
normal
result of sloughing
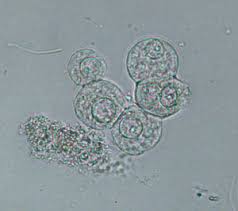
Transitional epithelial cells are?
few present is normal
from the bladder, renal pelvis and urethra
central nucleus
Renal epithelial cells are?
few present in normal
increased amounts associated with tubular necrosis, renal damage
most significant epithelial cell
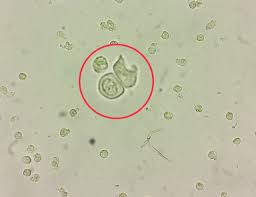
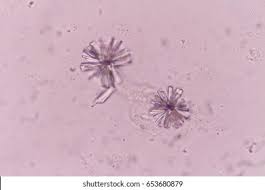
Uric acid crystals
acid urine
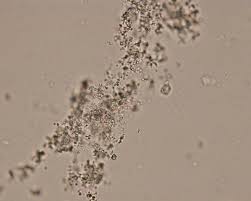
Amorphous urates
Only different between amorphous urates and phosphate is the ph
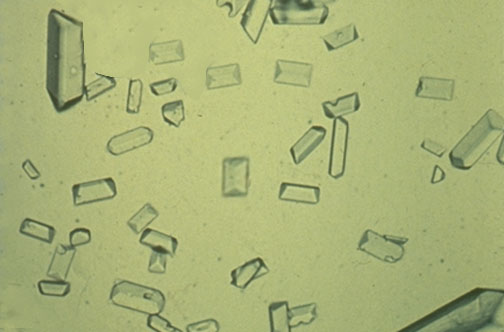
Calcium oxalate
Acid-neutral urine

hippuric acid
rare but insignificant, acid urine

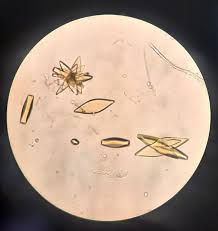
triple phosphate
alkaline urine
coffin lid
may be increased with stone formation
calcium carbonate
alkaline
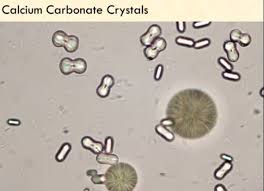
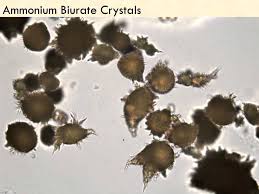
Ammonium biurate
alkaline
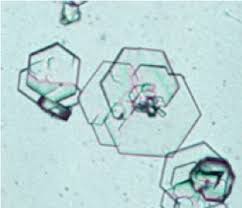
Cystine crystals
colorless
hexagonal
associated with metabolic defect
cholesterol
colorless
flat, notched rectangles
rarely seen
associated with tissue breakdown and renal disease

Leucine
yellow-brown spheres
rare
associated with severe liver disease
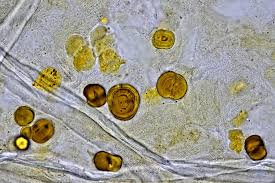
tyrosine
clumps of needles
associated with severe liver disease
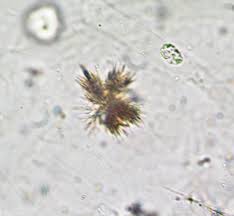
bilirubin
granules and clumped needles
yellow
associated with liver disease and bilirubinuria

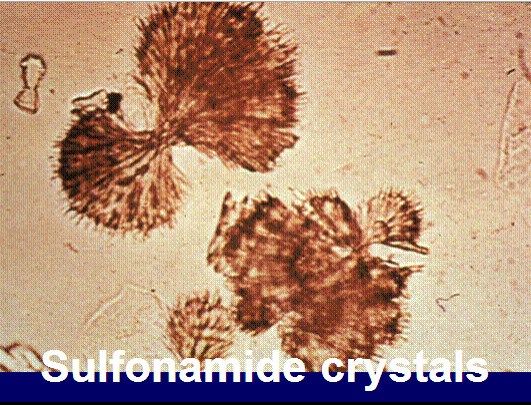
sulfa
sheaves of needles
associated with sulfa medications
can lead to tubular damage
What else can be found in urine?
bacteria
yeast
parasites
sperm
mucus
hemosiderin
When are bacteria usually reported?
when they are cocci
yeast in urine
often confused with RBCs
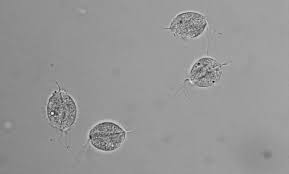
trichomonas
pin worm
sign of fecal contamination
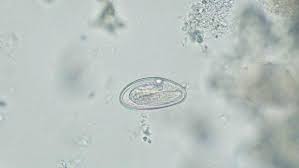
mucus
protein material
small amount normal
increased with poor collection and/or inflammation
easily confused with hyaline casts
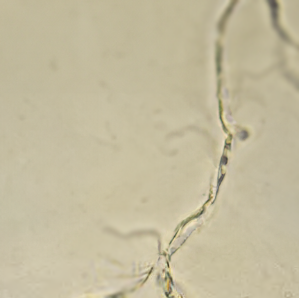
Hemosiderin
not normally found
yellow-brown granules
associated with rbc destruction
confirm with prussian blue
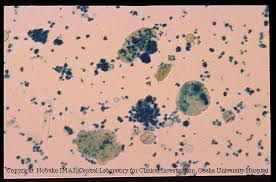
Starch
frequently found
must differentiate from significant findings
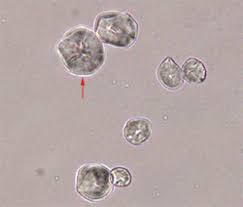
Oil/bubbles
will not form maltese cross
What are common artefacts in urine?
starch
oil/bubbles
glass fragments
hairs, pollen, talc, fiber
If the strip test is positive for protein what do we expect to see on the microscope?
may expect casts, wbcs, 3-4+ mucus
If the strip test is positive for blood what do we expect to see on the microscope?
RBCs
if not present:
lysis
misidentified as yeast
myoglobin
If RBCs seen on microscope but reagent strip test was negative?
consider possible vitamin C interference
yeast misidentified as RBCs
If the strip test is positive for nitrite what do we expect to see on the microscope?
bacteria
if bacteria present but nitrite is negative
non nitrate reducers
decreased incubation time
fully metabolized to nitrogen
If the strip test is positive for LE what do we expect to see on the microscope?
White blood cells
If the ph is acidic what crystal should we see?
Calcium oxalate
uric acid
other abnormal crystals
amorphous urates
If the ph is alkaline what crystals should we see?
triple phosphate
ammonium biurate
amorphous phosphates
What dye is used to stain triglycerides?
sudan III or oil red O
Calcium phosphate