Principles of Chemistry Exam 1 - University of Iowa
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
Scientific Law
A statement that describes what scientists expect to happen every time under a particular set of conditions
Scientific Theory
A well-tested explanation for a wide range of observations or experimental results.
Types of Matter
Solid, liquid, gas
Characteristics of Solid
Definite shape, definite volume, not compressible, high density
Characteristics of Liquid
Indefinite shape and definite volume
Characteristics of Gas
Indefinite shape and indefinite volume
Pure Substances
A sample of matter, either a single element or a single compound, that has definite chemical and physical properties
Elements
A molecule composed of one kind of atom; cannot be broken into simpler units by chemical reactions.
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Homogeneous mixture
A mixture that is uniform in composition; components are evenly distributed and not easily distinguished
Homogeneous Mixture Example
Salt water
Heterogeneous Mixture
A mixture that is not uniform in composition; components are not evenly distributed throughout the mixture
Heterogeneous Mixture Example
Oil and water
Atoms
Building blocks of matter
Molecules
Groups of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
Sig Figs
All the digits that can be known precisely in a measurement, plus a last estimated digit
Uncertainty in Measurement
A digit that must be estimated is called uncertain. A measurement always has some degree of uncertainty.
Accuracy in Measurement
A description of how close a measurement is to the true value of the quantity measured.
Precision of Measurement
The exactness of a measurement
Metric units of length
Kilometer (km)
Meter (m)
Decimeter (dm)
Centimeter (cm)
Millimeter (mm)
Micrometer (um)
Nanometer (nm)
Metric units of volume
Liter (L)
Milliliter (mL)
Metric units of mass
Grams and kilograms
Metric units of temperature
Kelvin (K)
Conservation of Mass
The principle stating that matter is not created or destroyed during a chemical reaction
Law of Composition
A given compound always has the same composition, regardless of where it comes from
Law of Multiple Proportions
If two or more different compounds are composed of the same two elements, then the ratio of the masses of the second element combined with a certain mass of the first element is always a ratio of small whole numbers
Dalton's Atomic Theory
1) elements are composed of atoms. 2) atoms of same element are identical, but differ from other elements. 3) elements can mix together 4) atoms only change when mixed with other elements
Atomic Number
Number of protons
Mass Number
The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in an atomic nucleus
The number on the bottom
How to calculate Protons
The number in the top
How to calculate neutrons
Mass number - atomic number
How to calculate electrons
Atomic number
Structure of atoms
Protons, neutrons, electrons
Symbol
The letter or letters that represent an element
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons
Examples of Isotopes
Carbon-12, Carbon-13, Carbon-14
Average atomic mass formula
(Percent to decimal)(mass) + (percent to decimal)(mass)
Isotopic abundance formula
(mass)(x) + (mass)(1-y), then solve for x and y by substituting
Periodic Table Trends: Moving L to R
Atomic radius decreases, ionization energy increases, electronegativity increases.
Period Table Trends: Moving Top to Bottom
Atomic radius increases, ionization energy decreases, electronegativity increases
Information given from Chemical Formula
Symbols of the reactants and products, show the physical state of a substance, and if the formula is balanced
Empricial formula
A formula giving the proportions of the elements present in a compound but not the actual numbers or arrangement of atoms.
Molecular Formula
A chemical formula that shows the number and kinds of atoms in a molecule, but not the arrangement of the atoms.
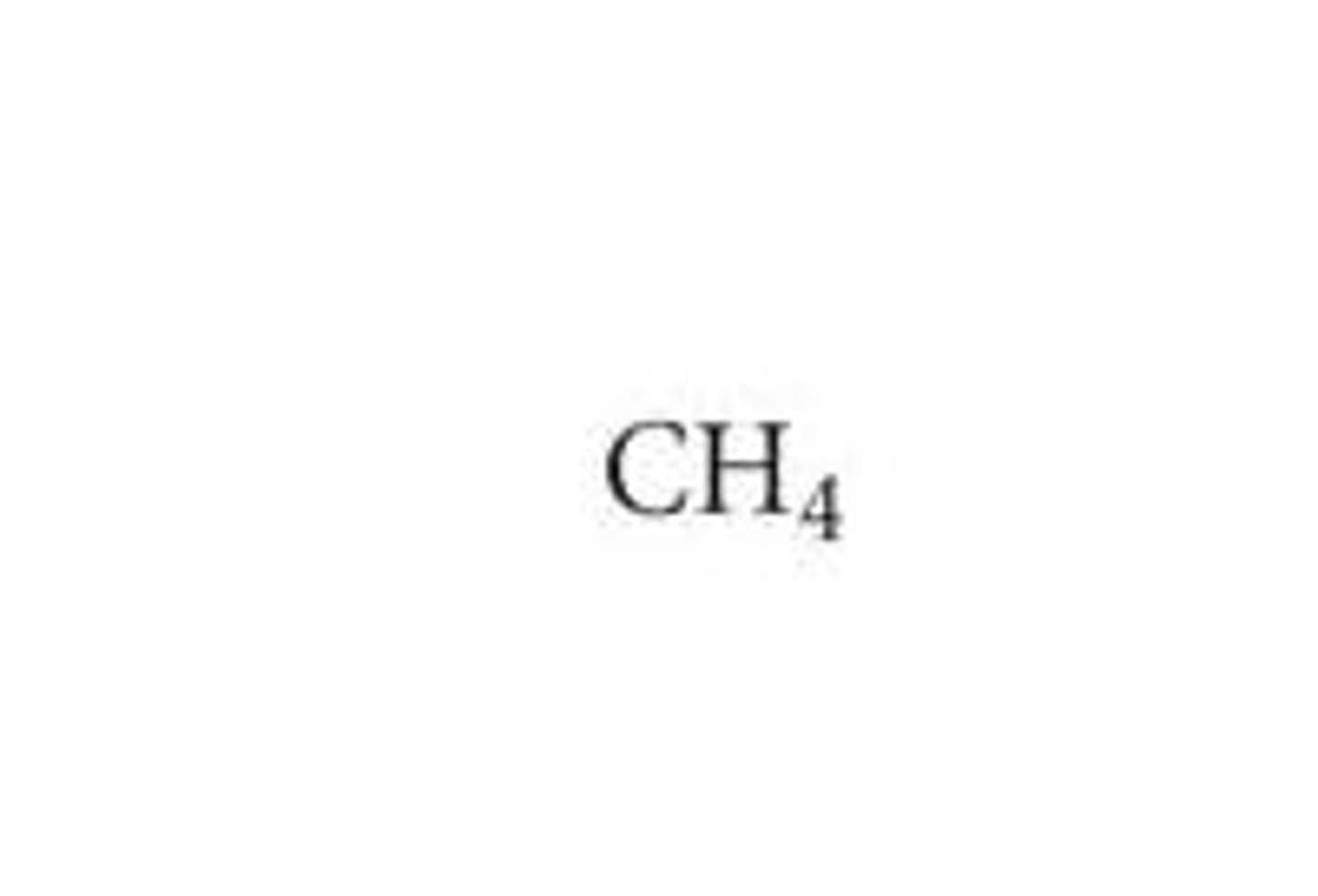
Molecular formula (picture) : Ch4
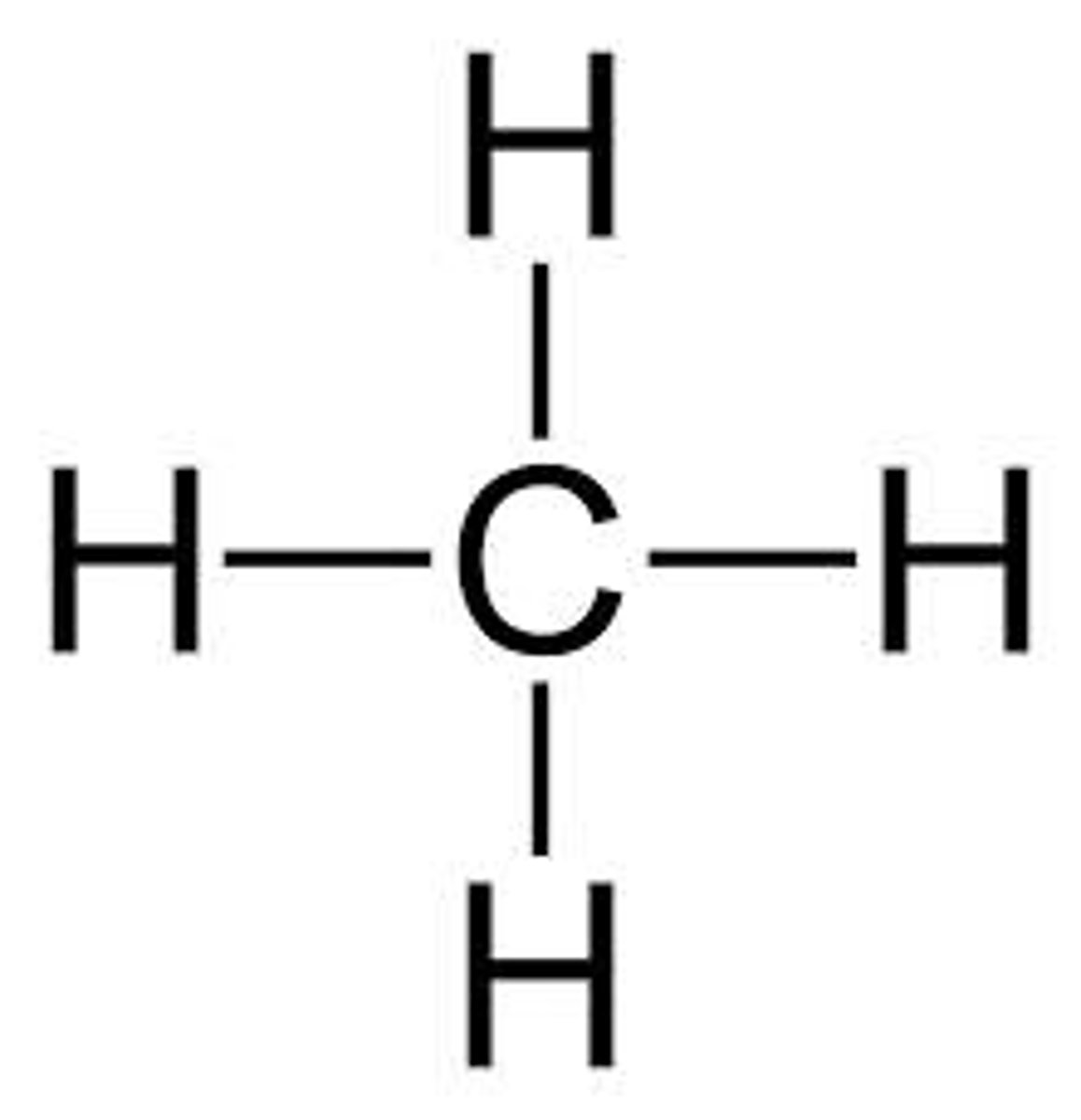
Structural formula (picture): Ch4
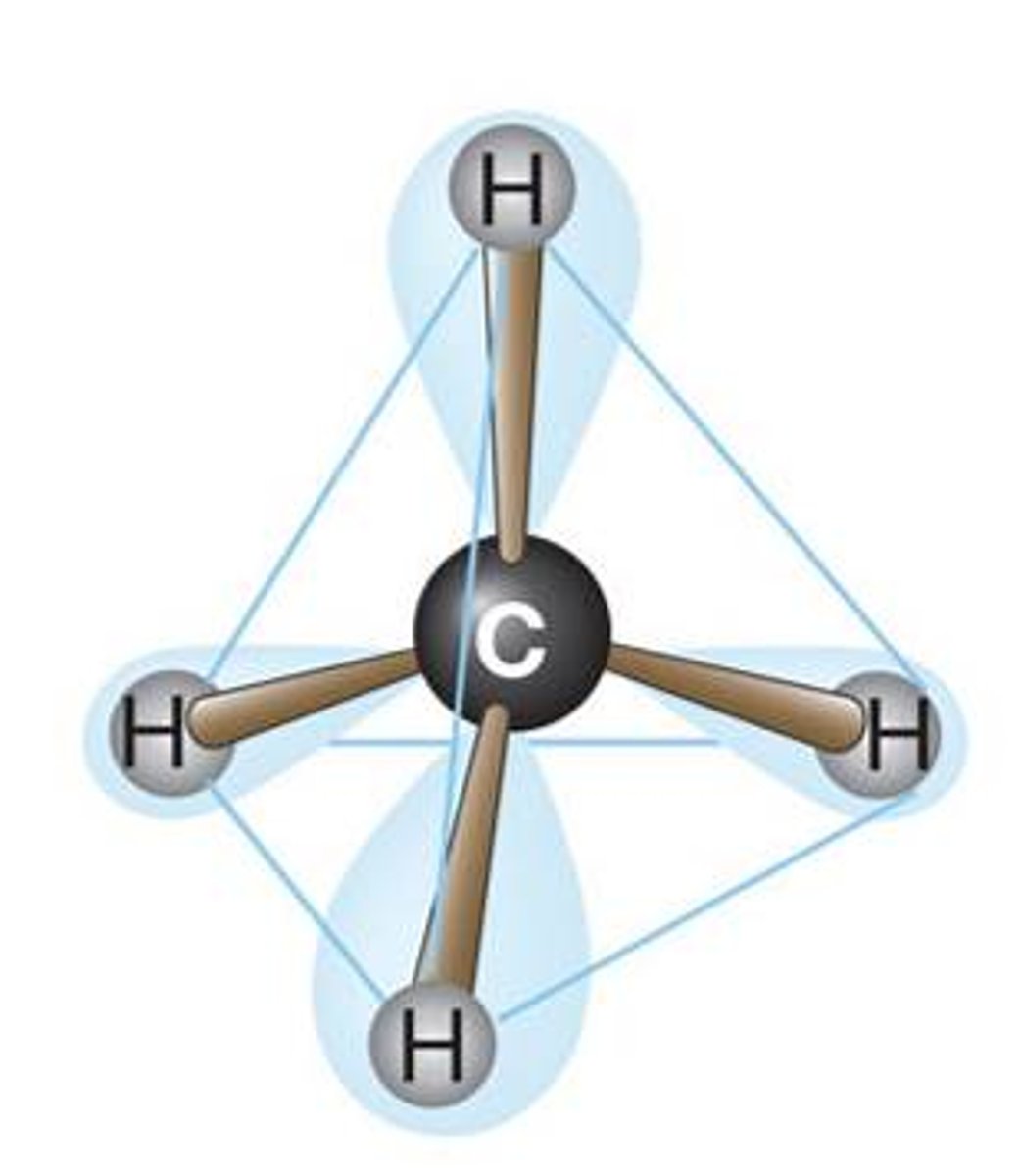
Ball and Stick Model: Ch4
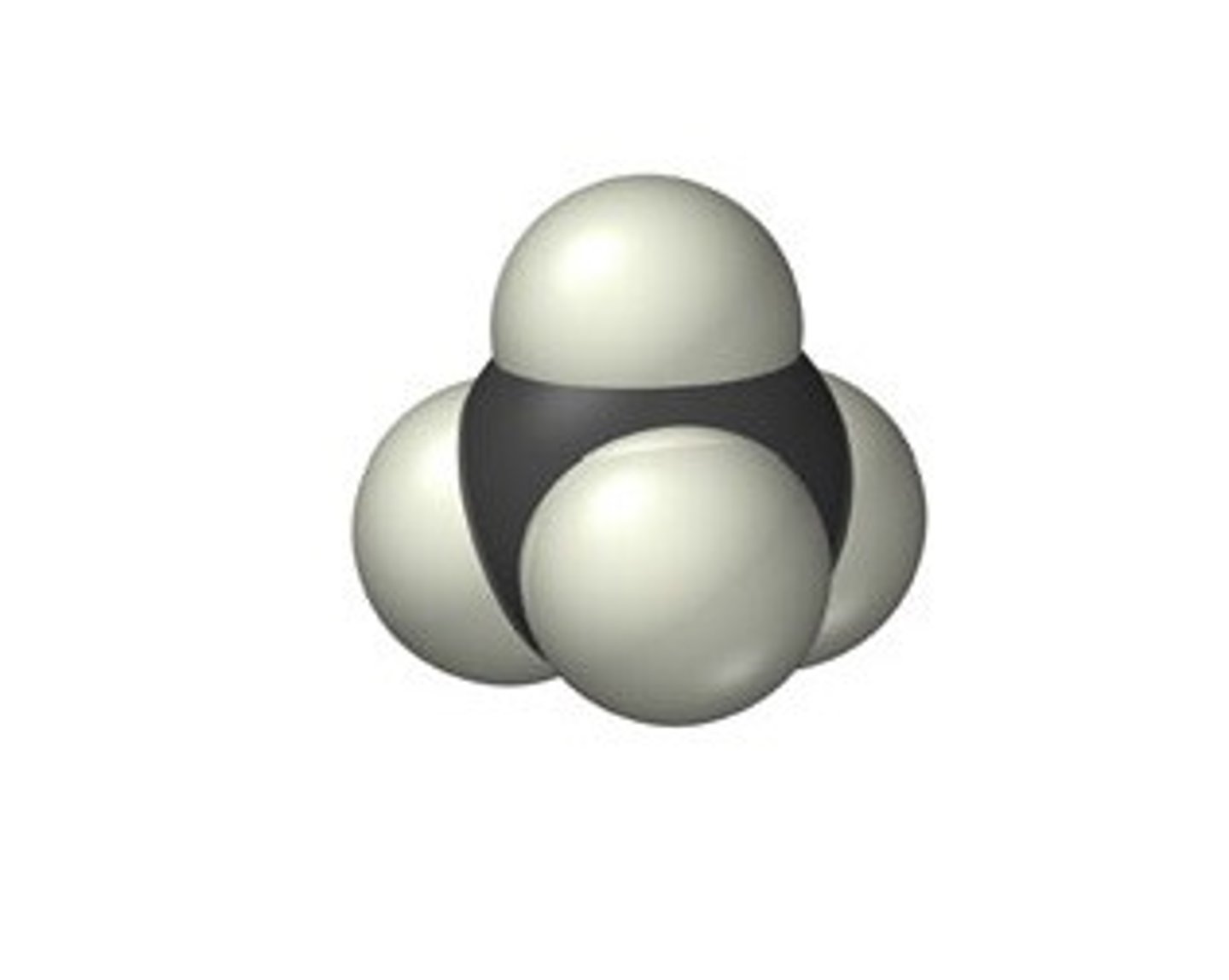
Space-filling model: Ch4
Ions
Positively and negatively charged atoms
How are ions formed?
When atoms lose or gain electrons
How do you determine the charges of ions?
By the groups
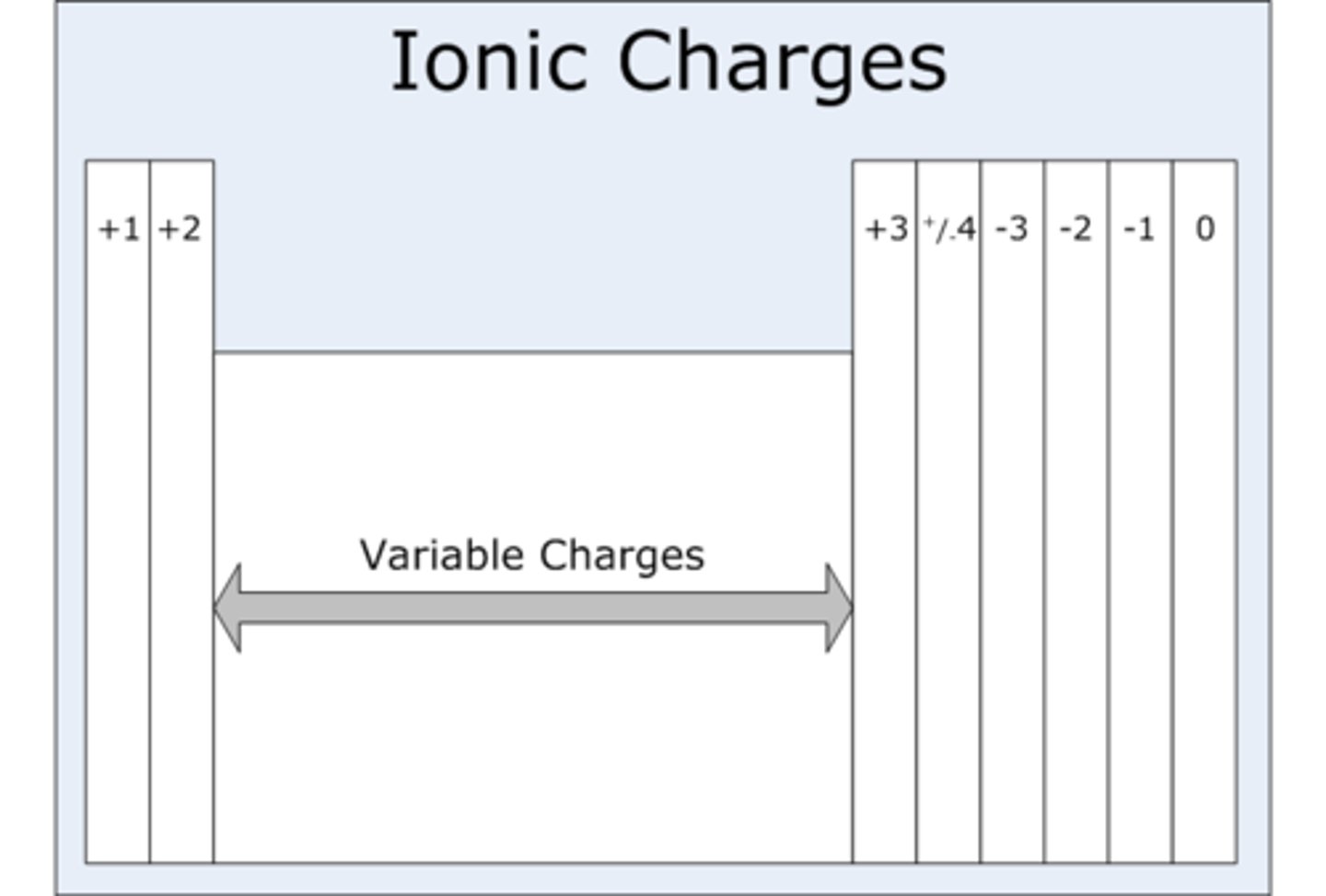
Ionic compound
A compound that consists of positive and negative ions
Examples of Ionic compounds
NaCl, MgO
Covalent compound
An element or chemical compound in which atoms are held together by covalent bonds
Examples of Covalent compounds
SO4, ClO3
Binary Acid
An acid composed of only two elements, one of which is hydrogen
Oxyacids
Acids that contain hydrogen, oxygen, and a third element usually a nonmetal.
How to write Binary acid
hydro + element+ ic acid
How to write Ionic Compounds (1 oxidation state)
Metal + Nonmetal + ide
How to write Ionic Compounds (2+ Ions)
Metal name(oxidation state as Roman numeral in parenthesis) + nonmetal name + ide
How to write Molecular Compounds (nonmetal + nonmetal)
(Prefix + 1st element) + (prefix + 2nd element name with ide)
Polyatomic Ions
Ions that are made of more than one atom
How to write Binary Aqueous Acids
hydro + element name with ic + acid
How to write Oxoacids
element name + suffix + acid
-ate to
-ic
-ite to
-ous
1+ Charged Cations
H+ Hydrogen Ion
Li+ Lithium Ion
Na+ Sodium Ion
K+ Potassium Ion
Ca+ Calcium
Ag+ Silver Ion
NH4+ Ammonia Ion
Cu+ Copper(I)
2+ Charged Cations
Mg++ Magnesium Ion
Ca++ Calcium Ion
Sr++ Strontium Ion
Ba++ Barium Ion
Zn++ Zinc Ion
Cd++ Cadmium Ion
Co++ Cobalt(II)
Cu++ Copper(II)
Fe++ Iron(II)
Mn++ Manganese(II)
Hg++ Mercury(II)
Ni++ Nickel(II)
Pb++ Lead(II)
Sn++ Tin(II)
3+ Charged Cations
Al+++ aluminum Ion
Cr+++ Chromium(III)
Fe+++ Iron(III)
1- Charged Anions
H- hydride Ion
F- Fluoride Ion
Cl- Chloride Ion
Br- Bromide Ion
I- Iodide Ion
CN- Cyanide Ion
OH- Hydroxide Ion
C2H3O2- Acetate Ion
ClO3- Chlorate Ion
ClO4- Perchlorate Ion
NO3- Nitrate Ion
MnO4- Permanganate Ion
3- Charged Anion
N--- Nitride Ion
PO4--- Phosphate Ion
2- Charged Anion
O-- Oxide Ion
O2-- Peroxide Ion
S-- Sulfide Ion
CO3-- Carbonate Ion
CrO4-- Chromate Ion
Cr2O7-- Dichromate Ion
SO4-- Sulfate Ion
How are balanced chemical equations symbolic representations?
They are symbolic representations of chemical and physical changes
Reactants
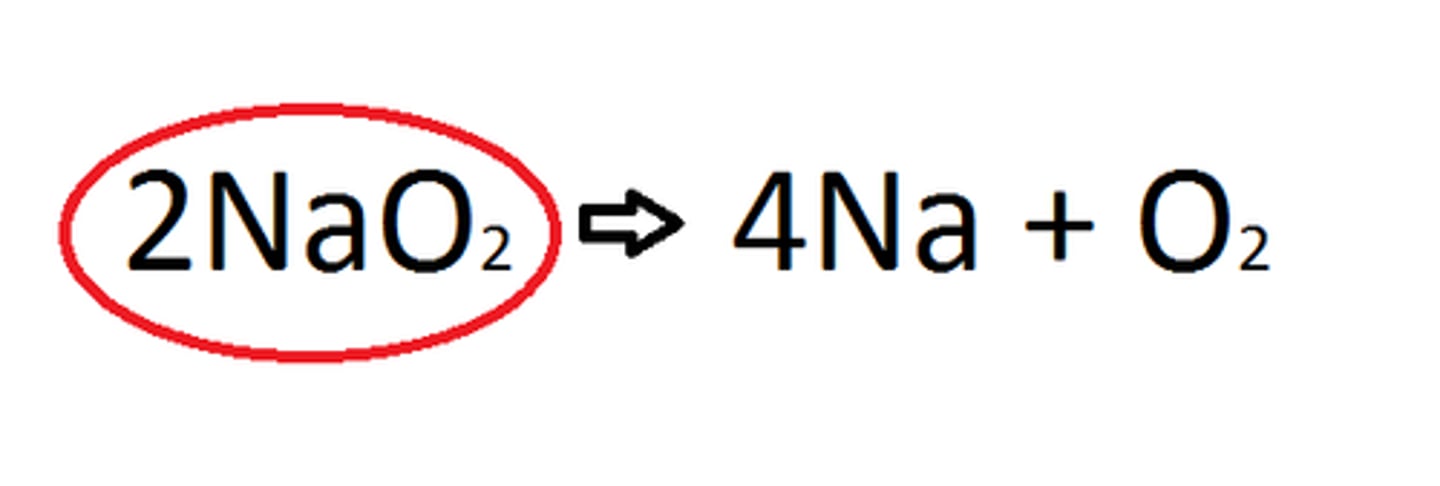
Products
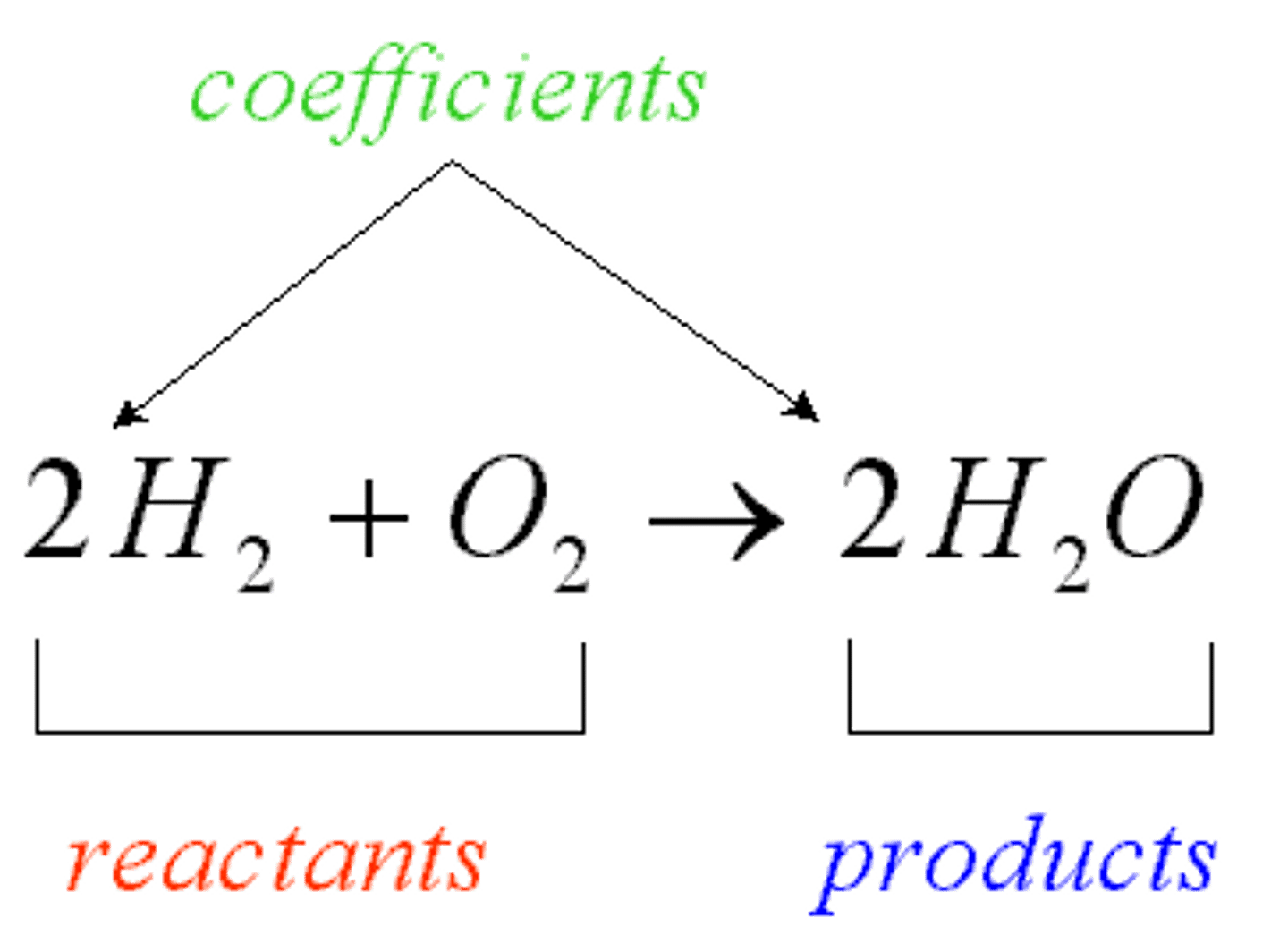
Decompostion Reactions
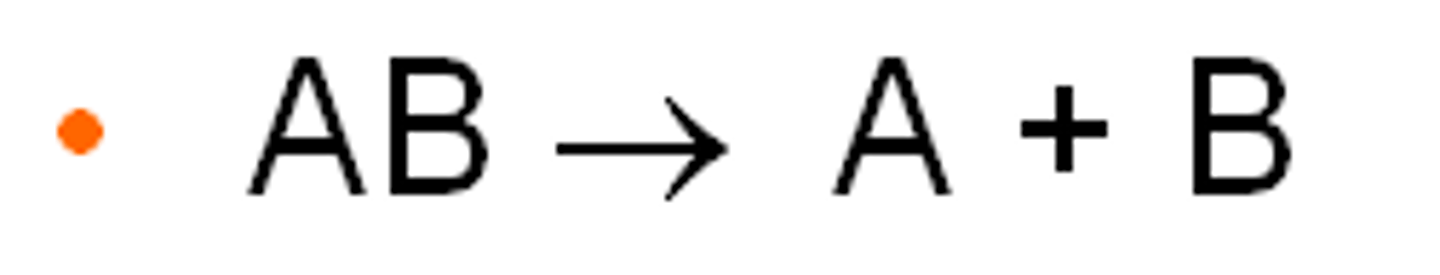
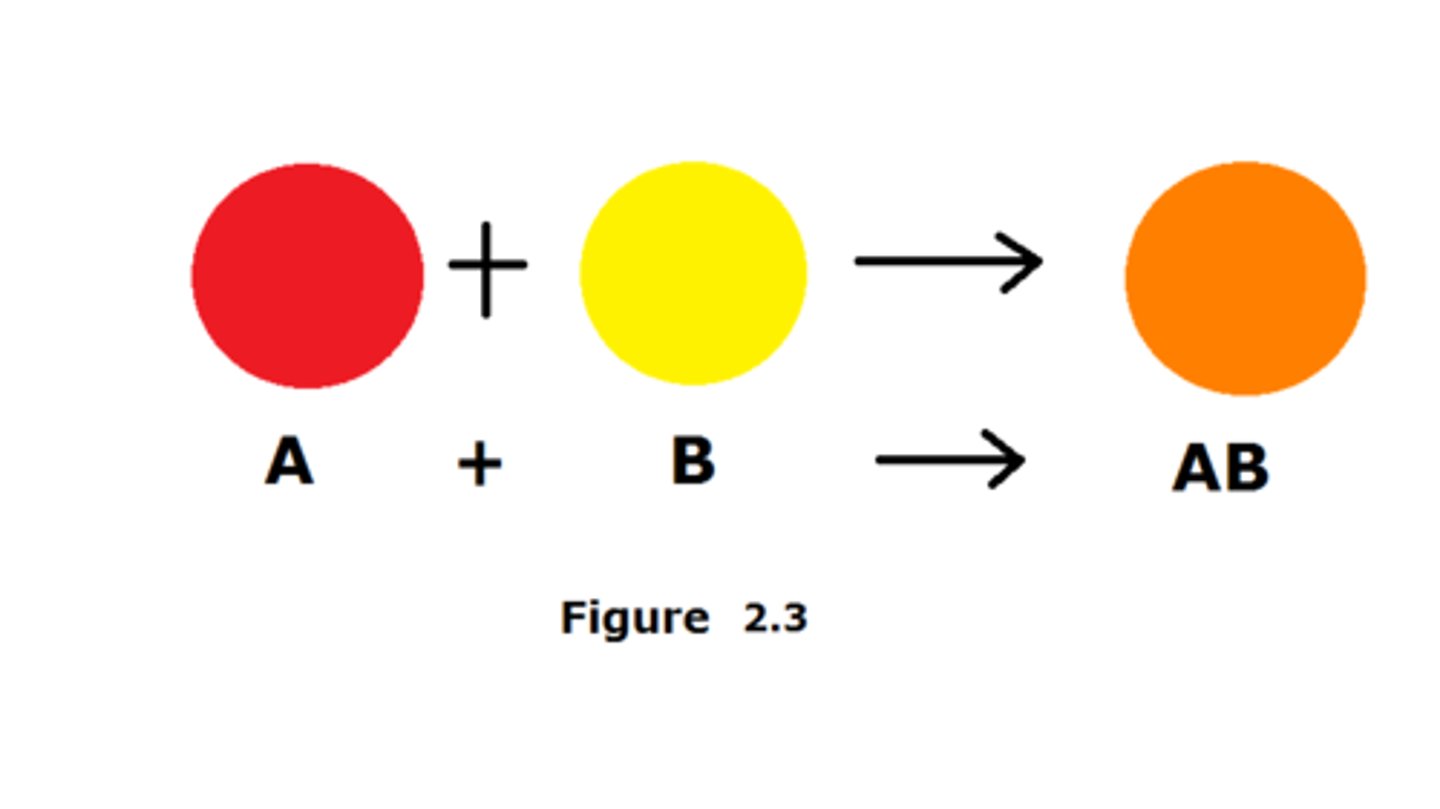
Combination Reactions
Two or more substances react to form one product
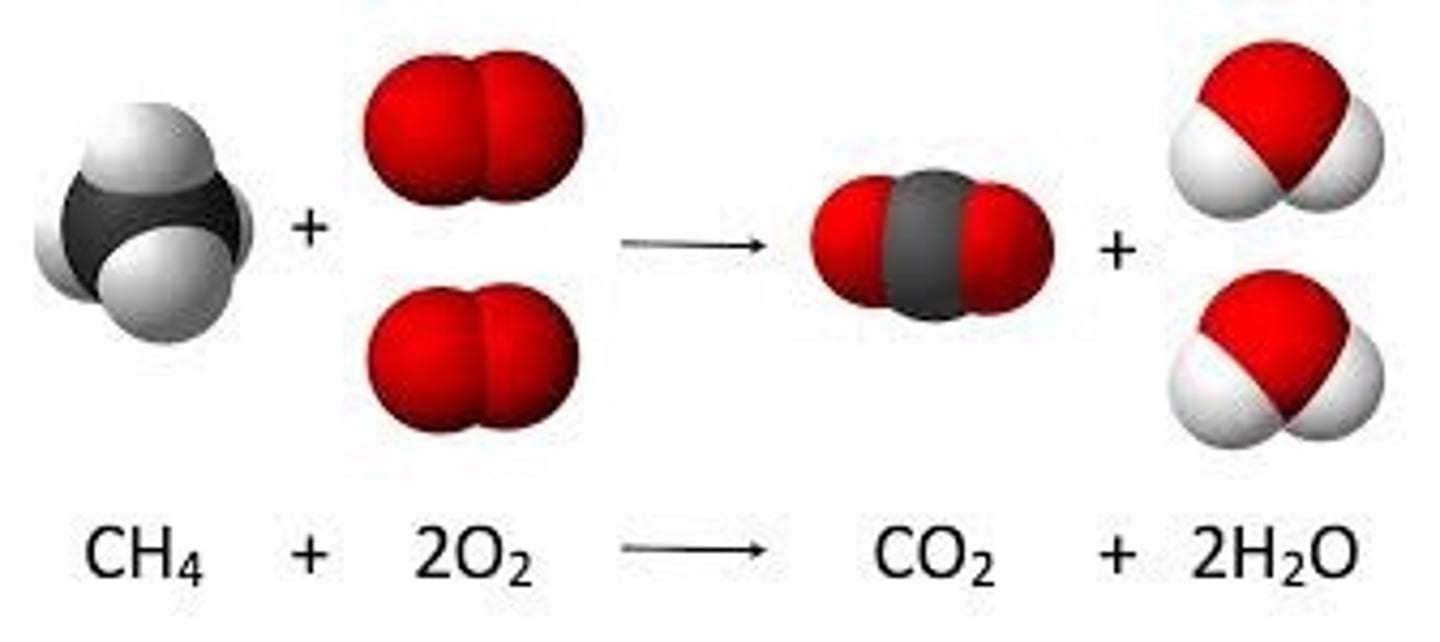
Combustion Reaction Examples
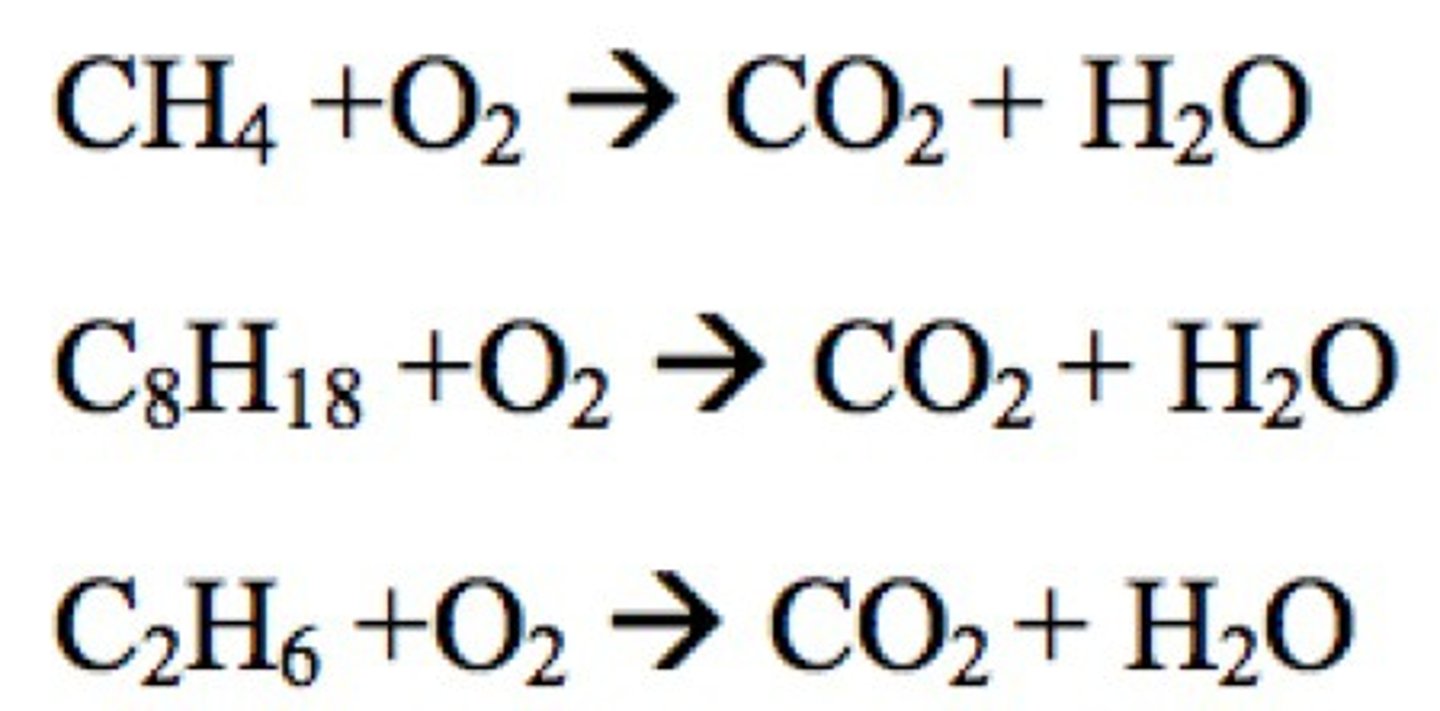
Combustion Reaction
A chemical reaction that occurs when a substance reacts with oxygen, releasing energy in the form of heat and light
Calculate molecular weight
Use dimensional analysis (g/mol)
Formula/Molecular weight
Sum of the atomic mass of the atoms in the chemical formula of a substance
Percent Compostion
The percent by mass of each element in a compound
Percent Composition formula
% composition = (# of atoms of an element)(atomic weight of element) / (formula weight of substance)
Molar Mass
The mass of one mole of a substance in grams
Avogadro's number
number of representative particles in a mole
6.022 * 10^23
Molar Mass Example
K2O
2 mols K x 39g=78g
1 mol O x 16g=16g
ADD THOSE TOGETHER
MM=94g/mol
Interconverting Grams to Moles
Use Molar Mass
Interconverting Moles to Formula Units
Use Avogadro's Number
Empricial Formula
A formula giving the proportions of the elements present in a compound but not the actual numbers or arrangement of atoms.
Use Empricial Formula to find Molecular Formula
1. Calculate the empirical formula mass.
2. Divide the gram molecular mass by the empirical formula mass.
3. Multiply each of the subscripts within the empirical formula by the number calculated in Step 2.
Use Molecular Formula to find Empricial Formula
1. Get the mass of each element by assuming a certain overall mass for the sample (100 g is a good mass to assume when working with percentages
2. Convert the mass of each element to moles
3. Find the ratio of the moles of each element
4. Find the ratio of the moles of each element.
5. Use the mole ratio to write the empirical formula, Multiplying the mole ratios by two to get whole number
Mole Ratio
A conversion factor that relates the amounts in moles of any two substances involved in a chemical reaction
Mass to Mass Conversions
Mass A --> Moles A --> Moles B --> Mass B
Limiting Reactant
The substance that controls the quantity of product that can form in a chemical reaction
Why can 1 limiting reactant limit the yield of the product?
Because once it's all used up the reaction can't continue to form the product.
Calculate excess reactant
1. Write the chemical equation
2. Calculate the moles of product from the first reactant.
3. Calculate the moles of product from the second reactant.
4. Identify the limiting reactant and the excess reactant.
5. Calculate the mass of excess reactant used up.
6. Calculate the mass of unused excess reactant.
7. Calculate the mass of limiting reactant needed to react with the unused excess reactant.
Theorectical yield
The maximum amount of product that can be produced from a given amount of reactant
Actual Yield
The measured amount of a product obtained from a reaction
Percent Yield
The ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield expressed as a percent
actual yield/theoretical yield x 100
Electrolytes
Substances that release ions in water
Nonelectrolytes
Substances that form no ions in water and cannot conduct electricity