Biology Ultracentrifugation
1/6
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
Describe how a sample of chloroplasts could be isolated from leaves
Grind/blend cells/tissue/leaves and filter;
In cold, same water potential/concentration, pH-controlled solution;
Centrifuge/spin and remove nuclei/cell debris;
(Centrifuge/spin) at high(er) speed, chloroplasts settle out
A biologist separated cell components to investigate organelle activity. She prepared a suspension of the organelles in a solution that prevented damage to the organelles. Describe three properties of this solution and explain how each property prevented damage to the organelles.
(Ice) cold to prevent/reduce enzyme activity;
Buffered to prevent denaturing of enzyme/protein;
Same water potential/ Ψ to prevent lysis by osmosis/bursting (of organelle);
A biologist prepared a sample of organelles labelled C from liver. He used the following method.
1. Added to the liver tissues an ice-cold, buffered solution with the same water potential as the liver tissue.
2. Mixed the liver and solution in a blender.
3. Filtered the mixture from the blender.
4. Spun the filtered liquid in a centrifuge at a low speed. A pellet appeared in the bottom of the centrifuge tube.
5. Poured off the liquid above the pellet into a second centrifuge tube and spun this at a higher speed to obtain the sample of organelles labelled C
Explain why the biologist used a blender and then filtered the mixture (steps 2 and 3).
1. Break open cells / homogenise / produce homogenate;
2. Remove unbroken cells / larger debris;
Name the organelle that made up most of the first pellet after centrifuging at a low speed (step 4).
) Nucleus / nuclei;
The second centrifuge tube was spun at a higher speed to obtain the sample of organelles labelled C in the diagram (step 5). Suggest why
Mitochondria / organelle C less dense than nucleus / organelle in first pellet;
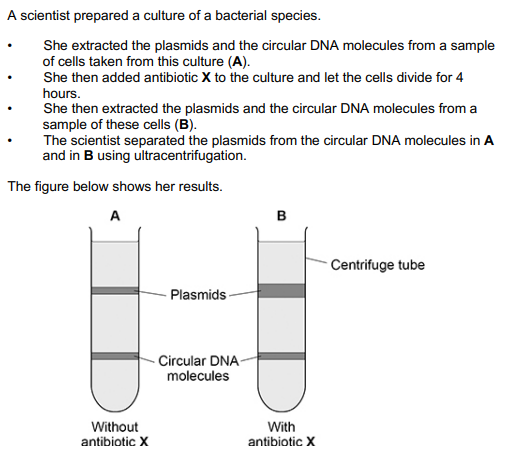
What can you conclude from the figure above about a structural difference between the plasmids and the circular DNA? Explain your answer.
1. Circular DNA is bigger/heavier/denser;
2. (Because band) moved further/is lower (in tube)/closer to bottom (of tube);