1.3 (cell membrane + transport)
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cell membranes and transport the higher the solute potential concentrations… (46) is last flashcard put into anki
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
cell membrane main component
phospholipids
whys it called a bilayer
has two layers
orientation of each phospholipid end + why
phosphate heads pointing outwards (towards water in cytoplasm) + fatty tails inwards (away from water)
when submerged in water phospholipids form
micelles
model name for phosphlipid bilayer + why
fluid- mosaic model
fluid = movement of molecules within a layer
mosaic = proteins studded through the phospholipid bilayer
cholestrol function
gives stability + regulates fluidity of membrane
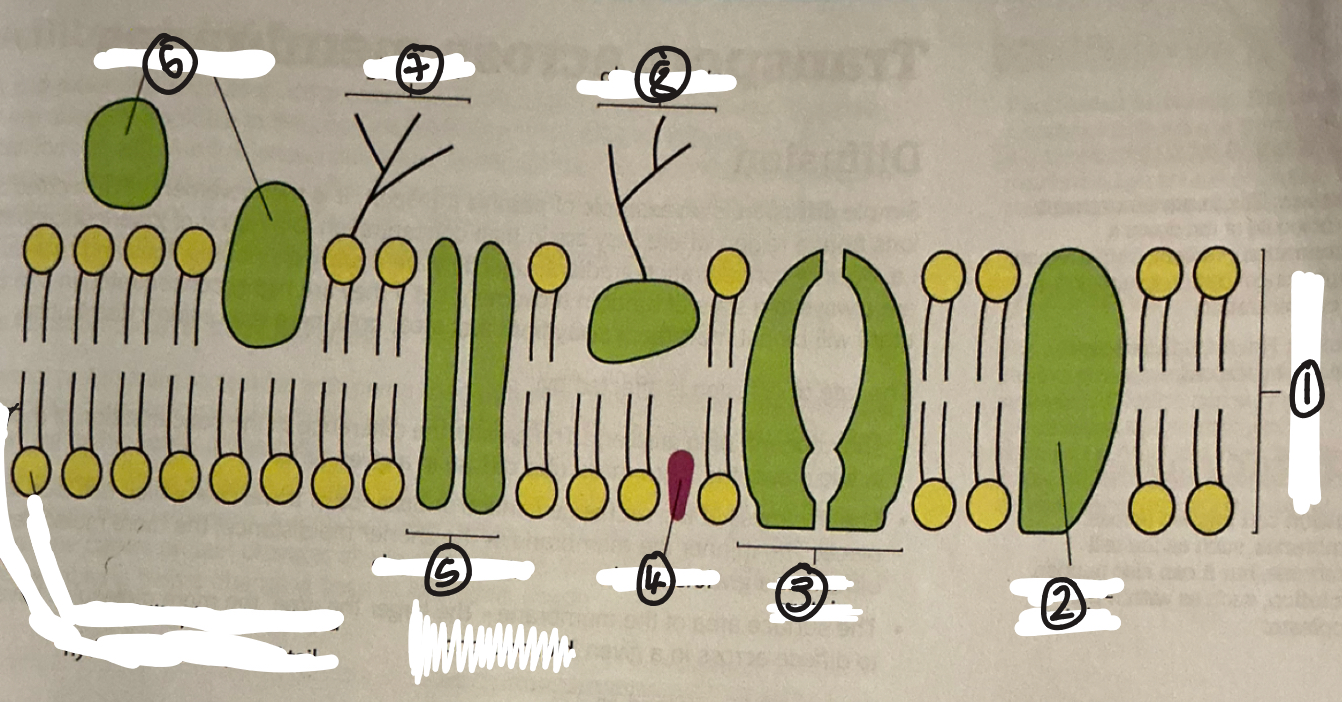
name 1
phospholipid bilayer
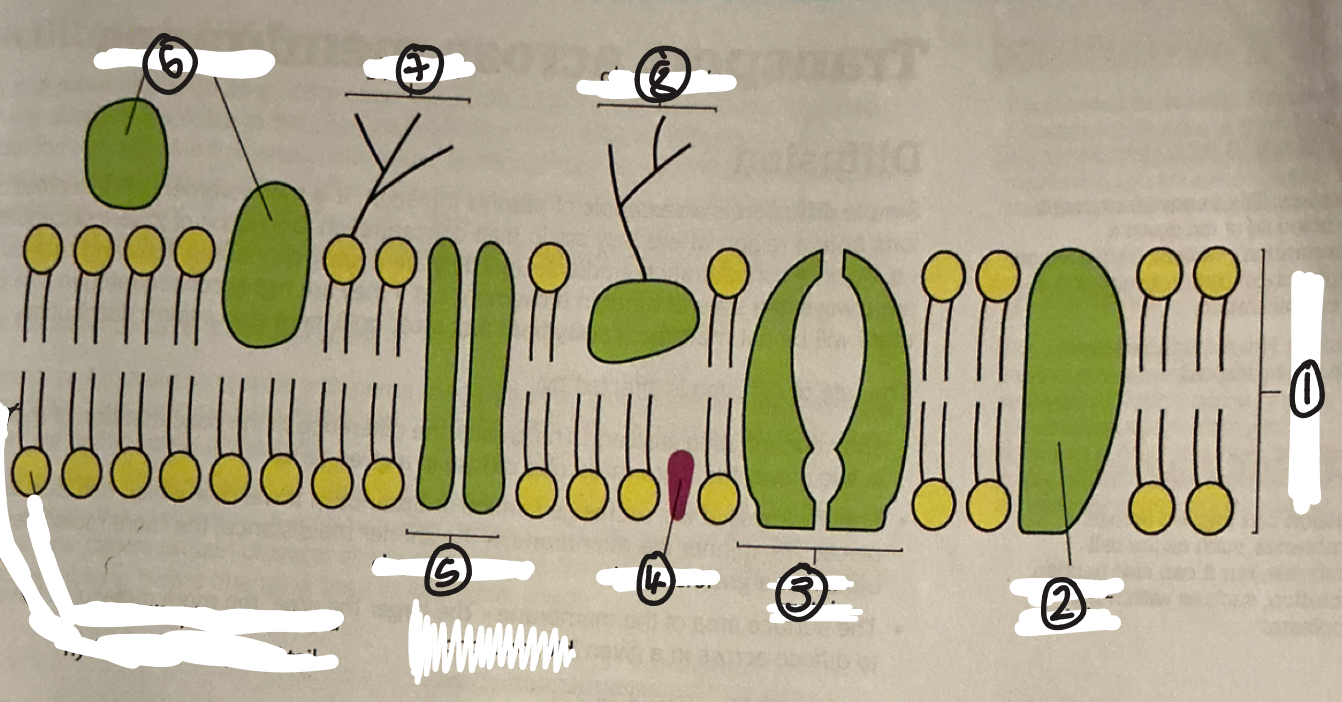
name 2
intrinsic protein
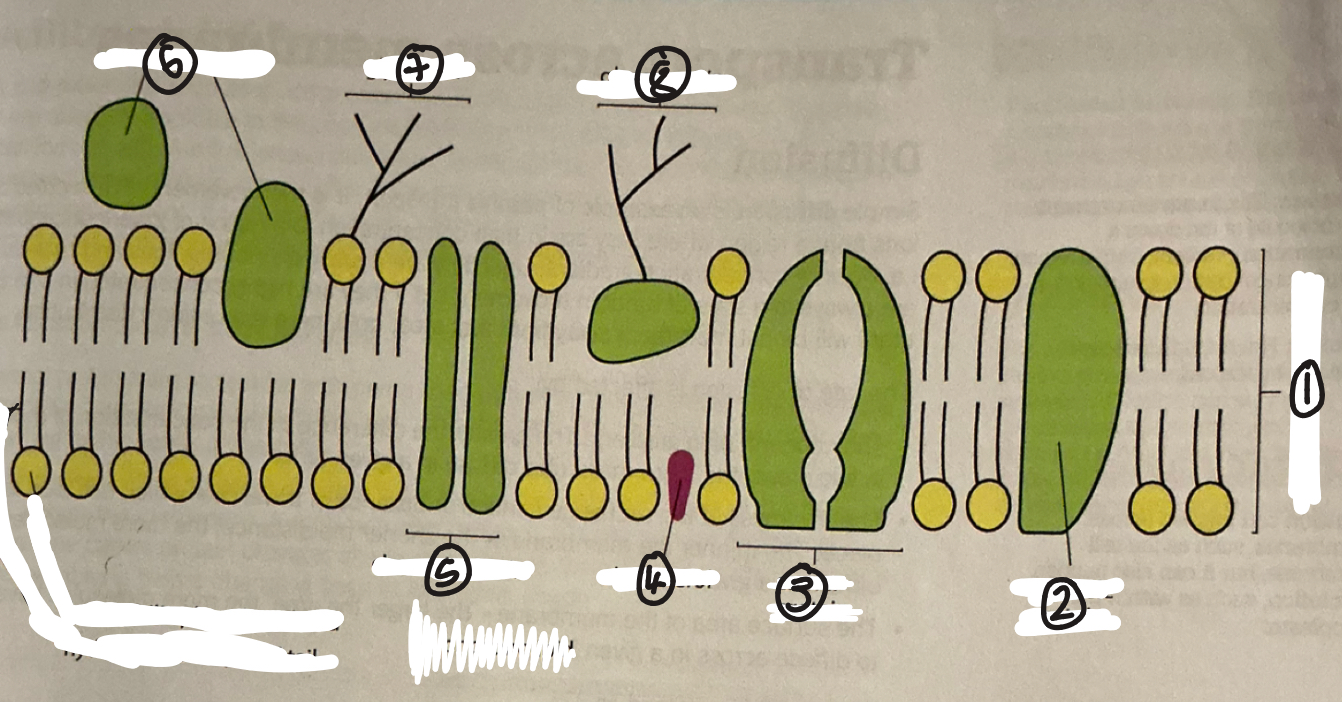
name 3
carrier protein
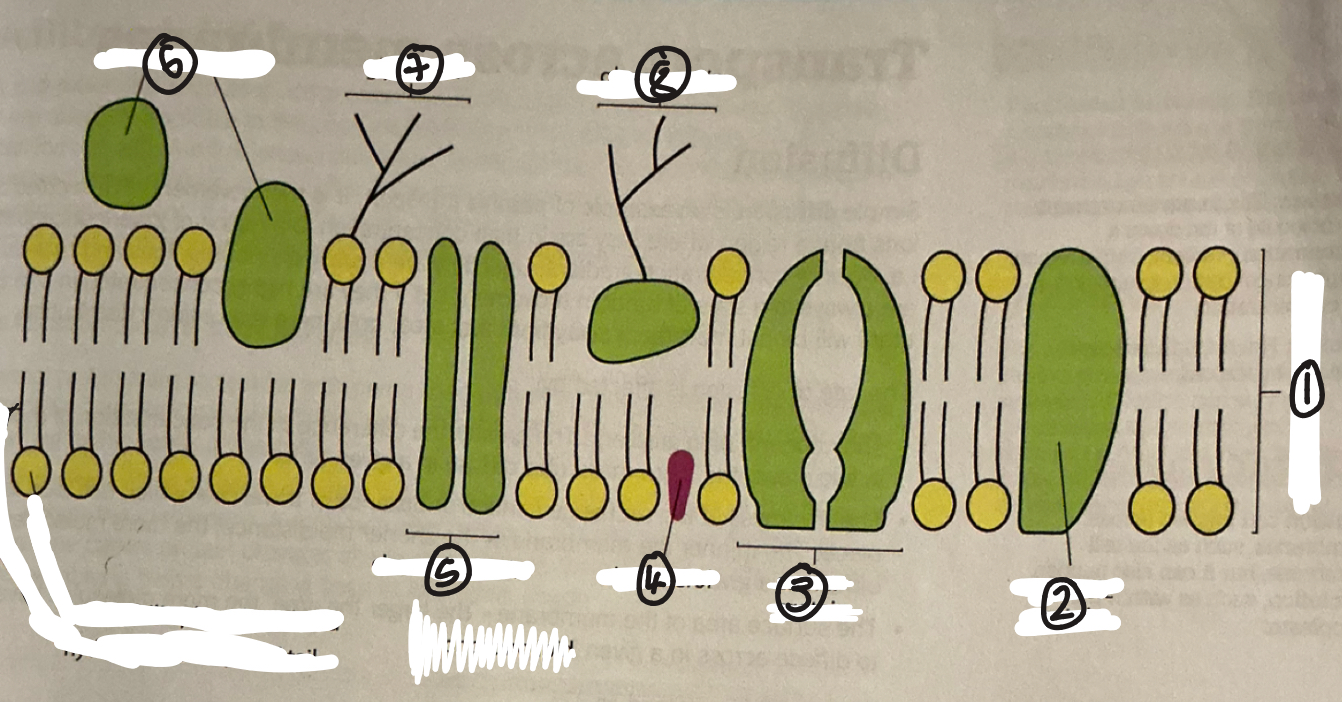
name 4
cholestrol
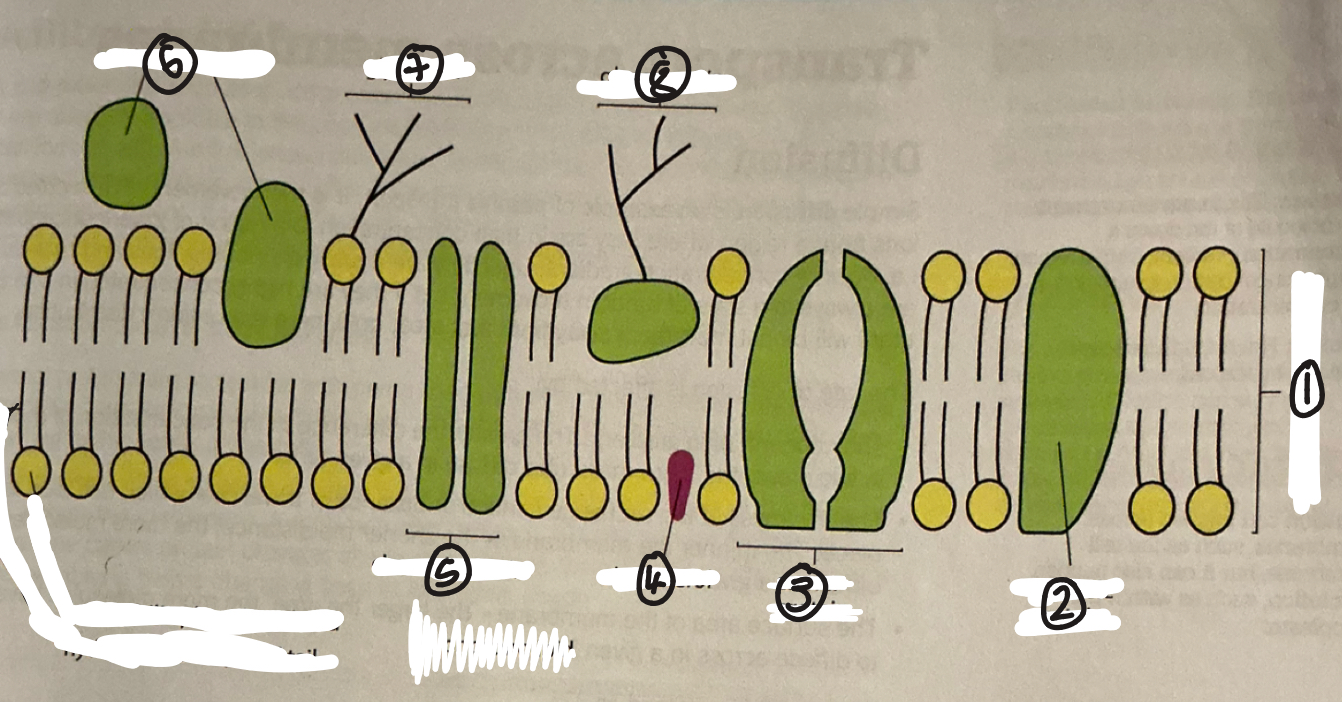
name 5
channel protein
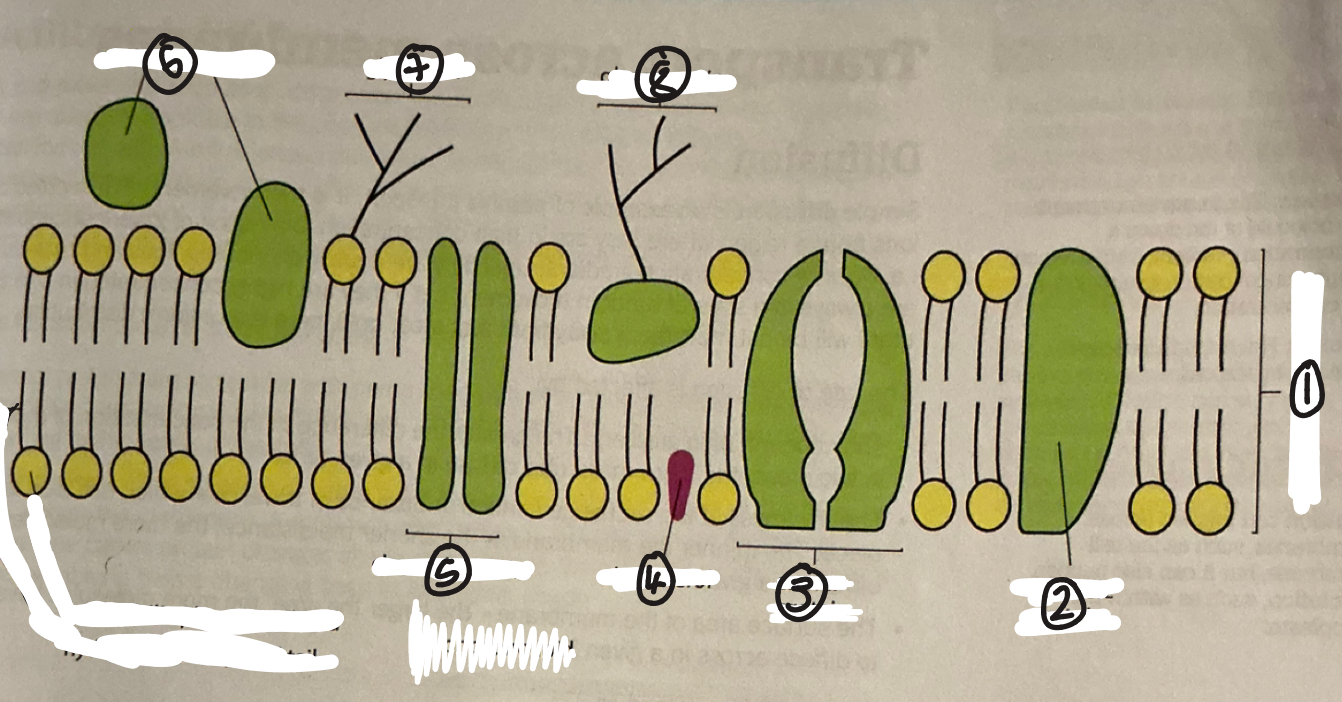
name 6
extrinsic proteins
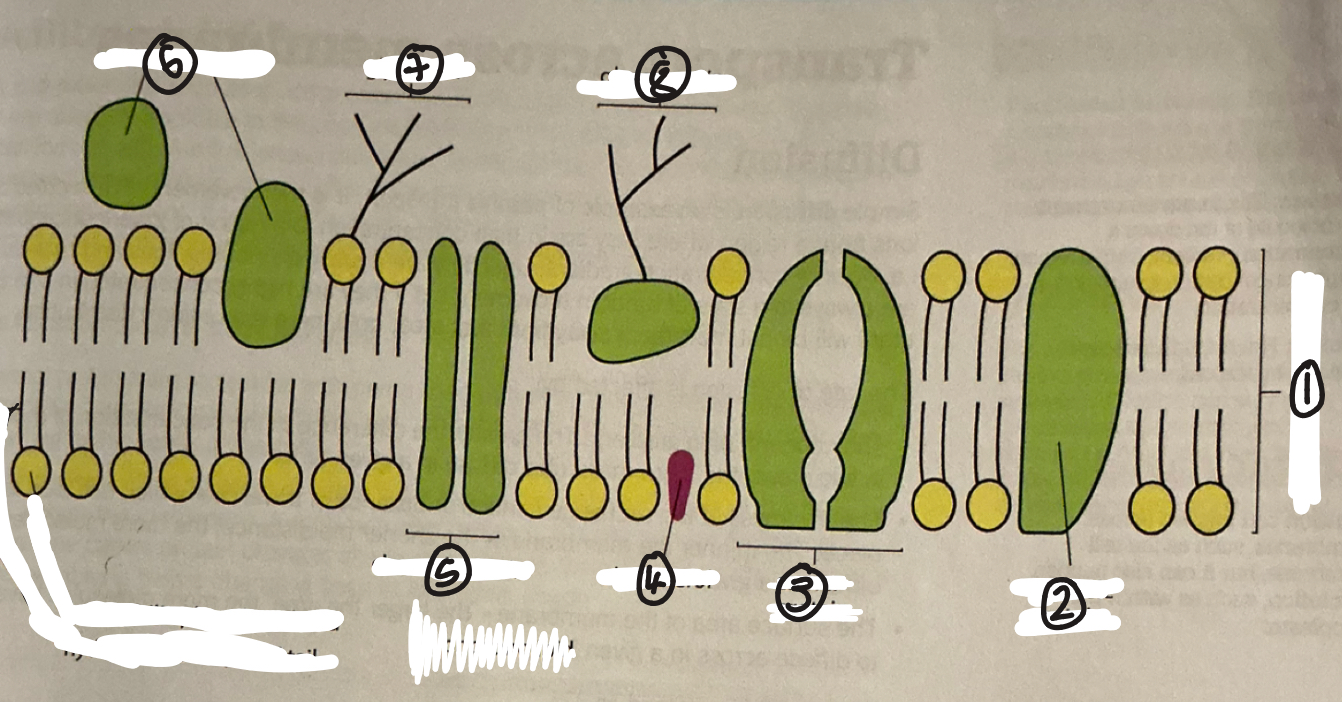
name 7
glycolipid
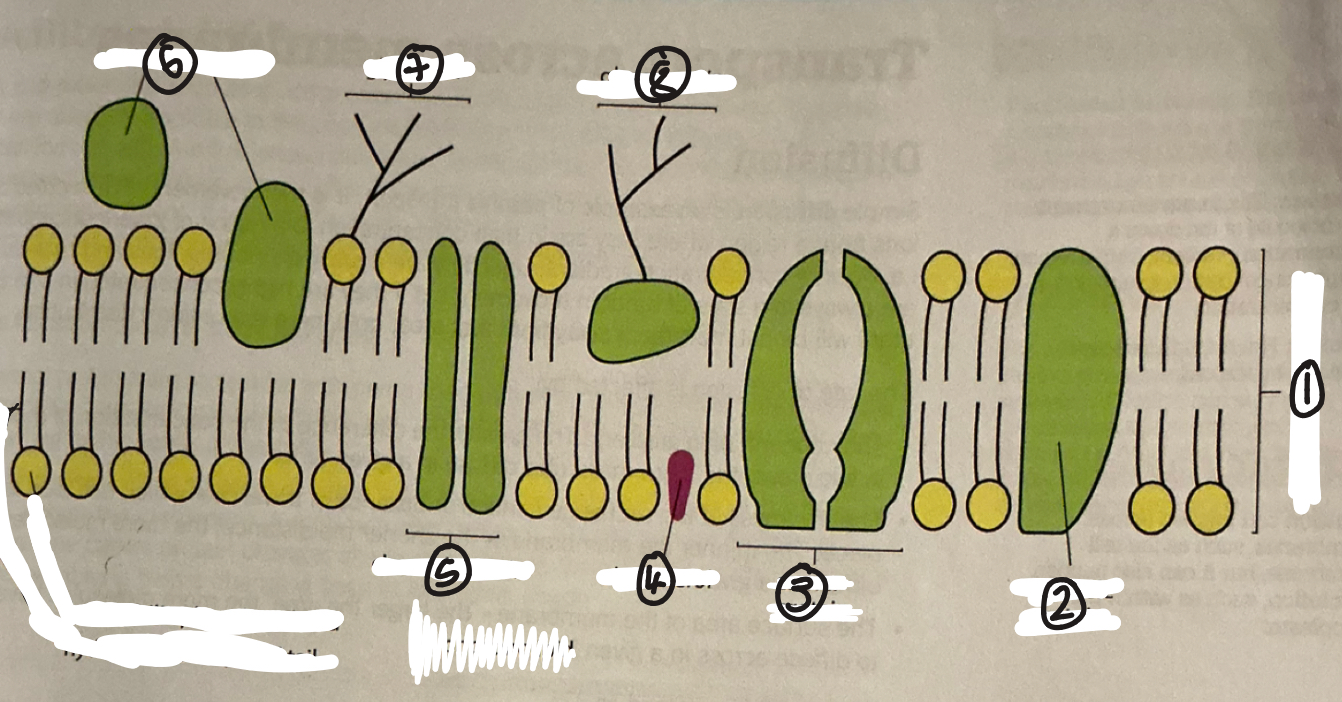
name 8
glycoprotein
cell membrane size
5-10nm
simple diffusion definition
passive net movement of molecules/ ions down a concentration gradient from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration
what type of molecules move through simple diffusion
very small non-polar molecules
facilitated diffusion definition
passive + down a concentration gradient- across a membrane by channel/ carrier proteins
what type of molecules/ ions move through facilitated diffusion
larger molecules + water soluble ions
factors affecting rate of facilitated diffusion
-temp
-difference in concentration of two sides
-frequency of carrier proteins available on plasma membrane
-type of carrier proteins (some are specific)
active transport definition
movement of molecules/ ions against a concentration gradient from a region of lower concentration to higher concentration using energy in the form of ATP and protein carrier molecules
how active transport in a carrier protein works
-molecule/ ion to be transported binds to carrier protein
-inside the cell ATP binds to carrier protein causing it to split into ADP + phosphate causing carrier protein to change shape + open to opposite side of membrane
-molecule/ion released on other side of membrane
-phosphate molecule released from protein + recombines with ADP to form ATP
-causes protein to revert to original shape, ready for process to be repeated
against a concentration gradient means
from lower to higher concentration
down a concentration gradient means
from higher to lower concentration
cells performing lots of active transport need lots of…
mitochondria
is cholesterol is plant cells or animal cells or both
animal cells
co-transport definition
a type of facilitated diffusion by which two substances are simultaneously transported across a membrane by a carrier protein
what molecules can pass through the phospholipid bilayer
-small molecules
-lipid soluble substances
-water soluble substances
things that affects rate of diffusion
-difference between concentration gradients
-thickness of exchange surface
-surface area of the membrane
-size of diffusing molecule
-temp
do fat soluble or water soluble molecules diffuse faster
fat soluble molecules
do polar or non-polar molecules diffuse faster
non-polar molecules
what are channel proteins
-molecules with polar group lined pores, water soluble ions can pass through
-channels open + close when needed
what are carrier proteins
-allow diffusion of larger, polar molecules
-molecule attaches to it’s binding site
-carrier protein changes shape + releases molecules on other side then returns to original shape
example of co-transport
sodium potassium pump
how sodium potassium pump works
Sodium (3)
Out
Potassium (2)
In
osmosis diffusion
the net passive diffusion of water molecules across a selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential
water potential (Ψ) definition
a measure of the free energy of water molecules and is the tendency for water to move
does water potential have a negative or positive scale
negative scale
pure water has a water potential of…
0
water potential is measured in
kilopascals (kpa)
more solute added to water does what to the water potential
lowers water potential (more negative)
water potential equation
Ψ = Ψs + Ψp
solute potential (Ψs)
a measure of the osmotic strength of a solution- reduction in water potential due to the presence of solute molecules
pressure potential (Ψp) definiton
the hydrostatic pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall- it is equal + opposite to the pressure exerted by the cell wall on the cell contents
pressure potential increases…
the tendcency of water to move out
the higher the solute potential concentrations…
the less likely the water is to move out
the polarity of protein molecules affects their…
position in the membrane
how is a glycocalyx formed
extracellular surfaces of the proteins are glycosylated
plasmolysis definition
the retraction of the cytoplasm and the cell membrane from the cell wall as a cell loses water by osmosis
endocytosis definition
the active process of the cell membrane engulfing material, bringing it into the cell in a vesicle
endocytosis definition
the active process of the cell membrane engulfing material, bringing into the cell in a vesicle
exocytosis definition
the active process of a vesicle fusing with the cell membrane, releasing the molecules it contains
phagocytosis definition
the active process of the cell membran engulfing large particles, bringing them into the cell in a vesicle
pinocytosis defintion
the active process of the cell membrane egulfing droplets of fliud, bringing them into the cell in a vesicle
exocytosis and endocytosis provides
a mechanism for bulk transport across a cell membrane
exocytosis and endocytosis change
the surface area of cells as they occur
transport across cell membranes is affected by
surface area
concentration gradient
temp
molecule size
lipid solubility
membrane thickness
active transport provides
a mechanism to increase the rate of transport across the membrane for certain molecules eg polar molecules
isotonic definition
cell has same water potential as surrounding solution
movement of water in isotonic solution
no net movement of water
hypertonic definition
water potential of the external solution is more negative (lower) than the solution inside the cell
movement of water in a hypertonic solution
water flows out of cell
how to remember what hypertonic is
hyper- lower- further away from zero (external solution)
hypotonic definition
water potential of external solution is less negative (higher) than the solution inside the cell
movement of water in a hypotonic solution
hypo- zero- closer to zero (external solution)
what happens to a plant cell in a hypotonic solution
turgid- cytoplasm pushed against cell wall
what happens to a plant cell in a isotonic solution
incipient plasymolsis- cystoplasm begining to pull away from cell wall
what happens to a plant cell in hypertonic solution
plasmolysed- cytoplasm completely pulled away from cell wall
what happens to animal cell in hypotonic solution
haemolysis- cell bursts
what happens to animal cell in isotonic solution
nothing- stays same
what happens to an animal cell in hypertonic solution
becomes crenated- cell shrinks + loses shape
turgid definition
a plant cell that holds as much water as possible- further entry of water is prevented as the cell wall cannot expand further
plasmolysis definition
the retraction of the cytoplasm and the cell membrane from the cell wall as a cell loses water by osmosis
incipient plasmolysis definition
cell membrane and cytoplasm are partially detatched from the cell wall due to insufficient water to make cell turgid
how does cyanide stop active transport
by blocking cellular respiration
two factors affecting permeability of the plasma membrane
-temp
-organic solvents
all membrane in cells are
selectively permeable
how does a glycoprotein act as a receptor
has a specific shape thats complementary to the communicaitng molecule
three roles of glycoproteins in membranes
-act as an antigen for cell recognition
-act as a receptor triggering a series of chemical reactions within the cell
-forms hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules to stabilize membrane structure
why can’t water molecules easily move through the phospholipid bilayer
water is polar and fatty acids are hydrophobic