Unit 4 Communication and Coordination (Nervous System)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
3 basic functions of the nervous system
a. Detects changes (stimuli) in the internal or external environment
b. Evaluates the information detected
c. Can respond by initiating changes in muscles or glands
central nervous system vs peripheral nervous system
CNS – Central nervous system
Brain & Spinal Cord
Controls & Coordinates all communication within the body.
PNS – Peripheral nervous system
All neurons extending beyond the brain and spinal cord
A communications network extending to all parts of the body.
neuroglia
GLIA or GLIAL CELLS - do not usually conduct information but support the function of
neurons structurally & metabolically
Schwann cells
Cells that produce myelin - they are located within the myelin sheath ( axon).
difference between gray matter and white matter
White matter: Made up of myelinated axons and responsible for learning/cognition
Gray matter: made up of neutrophils, glial cells, neuronal cell bodies, capillaries, synapses,
and a few myelinated axon. Responsible for sensory perception, muscle control, self-control,
decision-making, memory, and data processing
nerves
Excitable cells that conduct chemical-electrical messages, making all nervous system functions possible. *“Wiring” for the nervous system’s information circuits.
sensory, interneurons, motor
List and describe the 3 classes of neurons based on their function.
unipolar, bipolar, multipolar
List and draw the 3 classes of neurons based on their structure.
2 main functions of neurons
a. conduction route for transmission of info from CNS to all other areas of body
b. communication within the CNS to integrate information
resting membrane potential across the cell membrane
membrane potential maintained when the neuron is not conducting electrical signals; usually around -70millivolts
What causes an action potential
membrane potential of an active neuron = nerve impulse transmission; caused by a stimulus on the resting neuron membrane.
Resting state
more K+ on the inside of the cell and Na+ outside of the neuron (-70mV inside).
depolarization
Na+ rushes inside the neuron changing the internal membrane charge to positive
Repolarization
period of time where resting membrane potential is restored allowing K+ to flow to outside of the neuron space.
The Na+/K+ pump swaps the Na+ and K+ so that it returns to resting neuron state.
What restores the ion (Na+, K+) distribution after an action potential?
saltatory conduction
The action potential in a myelinated neuron “leaps” from node to node.
Myelinated fibers conduct impulses faster than unmyelinated because ______ ________
is faster than point-to-point
action potential reaches axon terminal
The next neuron is directly excited through a chemical synapse, or it is excited by a chemical
synapse (using neurotransmitters).
acetylcholine
Junctions with motor effectors (muscles, glands); many parts of brain; Excitatory or inhibitory; involved in memory.
dopamine
Brain; autonomic system; Mostly inhibitory; involved in emotions/moods; regulating motor control.
serotonin
Several regions of CNS; Mostly inhibitory; involved in moods/emotions, sleep.
endorphins
Several regions of CNS; retina; intestinal tract; Mostly inhibitory; act like opiates to block pain.
GABA
Brain; Inhibitory; most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain
frontal lobe
which lobe contains personality and decision making
parietal lobe
which lobe contains the sensory cortex and motor cortex
occipital lobe
which lobe contains the visual cortex?
temporal lobe
which lobe contains the auditory cortex; memory, emotion, language and hearing
cerebrum
which part of the brain controls sense perception, voluntary muscle contraction and
mental activities (thinking, reasoning, learning,
memory, intelligence, and sense of responsibility)
hypothalamus
which brain structure regulates and coordinates autonomic and involuntary activities (temp, hunger, thirst, etc.)
medulla oblongata
which brain structure is the vital control centers for homeostatic functions (breathing, circulation, digestion, vomiting, sneezing, swallowing, coughing, and hiccupping).
corpus callosum
Allows for communication between left and right brain hemispheres
cerebellum
controls posture, maintains balance, and coordination of motor
activity
meninges
The layers that cover and protect the spinal cord and brain—they also supply important blood vessels and nutrients to CNS.
3 layers of the meninges
Dura mater – outer layer of meninges made of strong white fibrous tissue; also serves as the
inner periosteum of the cranial bones
Arachnoid membrane – delicate, cobweb-like layer between the dura mater and pia mater
Pia mater – transparent layer that adheres to the outer surface of the brain and spinal cord;
contains blood vessels
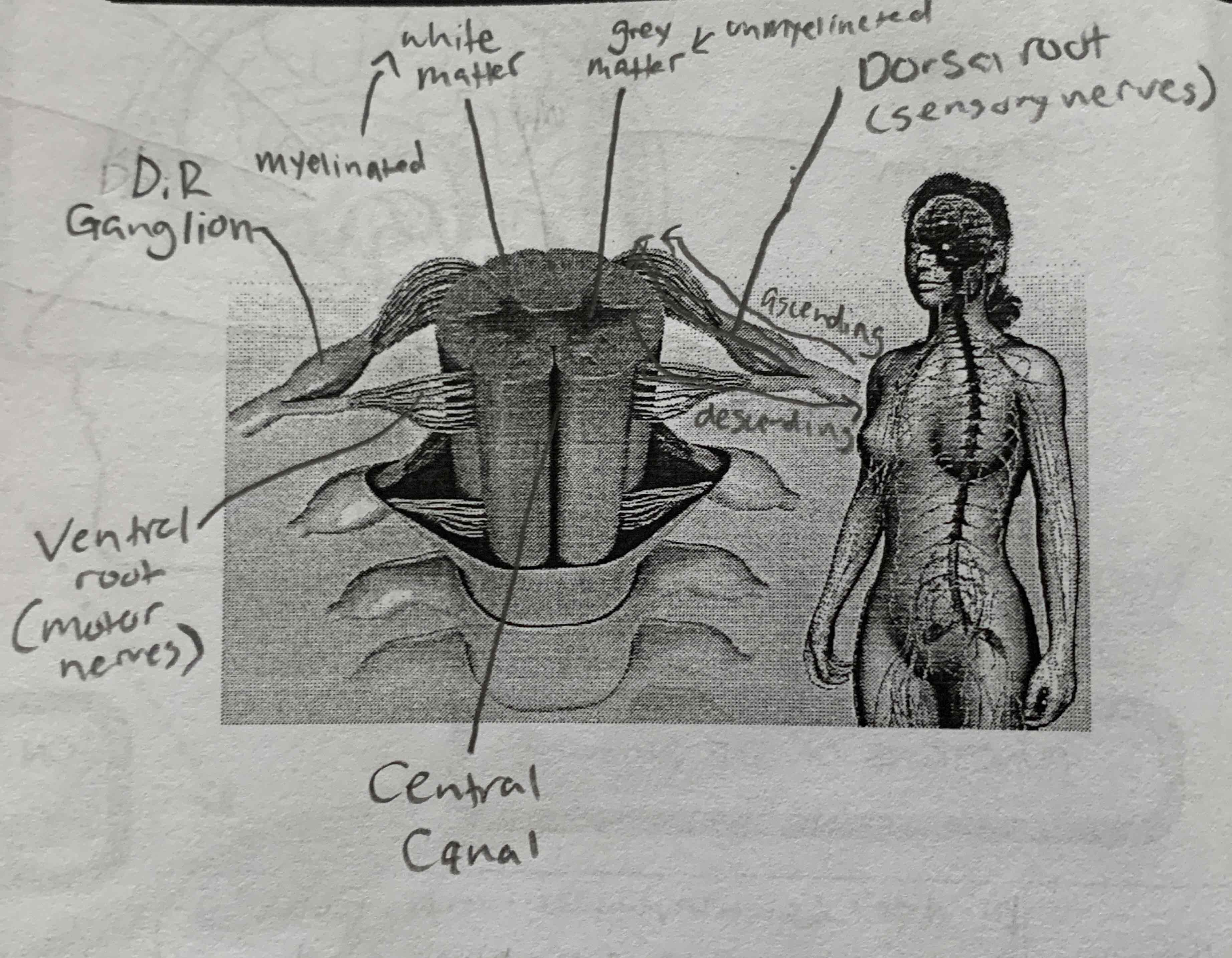
Afferent/sensory
fibers carry nerve impulses to the CNS can be divided into somatic or viscera
efferent/motor
fibers carry nerve impulses away from CNS can be divided into autonomic or somatic
sympathetic
known as “fight or flight”; response and prepares the body for increased activity using noradrenaline.
parasympathetic
known as the “rest and digest” response and generally maintains the body during relatively quiet conditions using ACH.
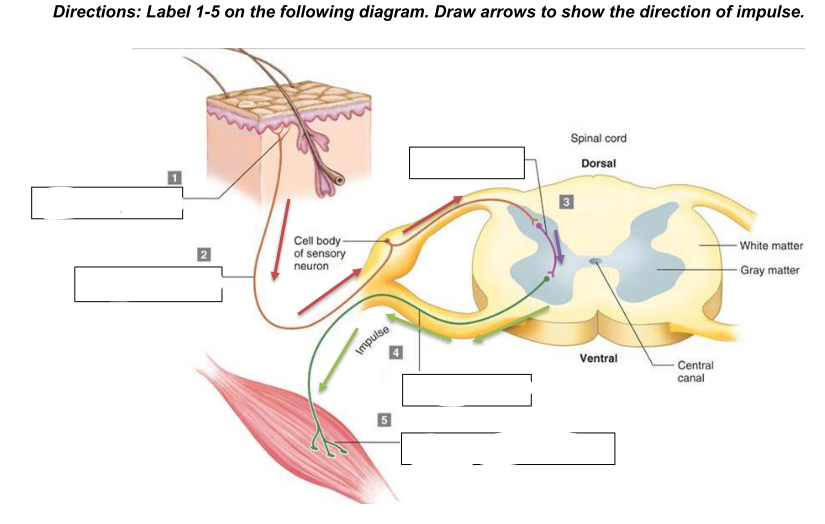
components of a reflex arc
a. Stimulus (change internal or external)
b. Receptor - detects a stimulus, such as heat, pressure, or pain; responds to the external or internal stimulus and converts it into an electrical impulse.
c. Afferent pathway (sensory neuron) - transmits the electrical impulse from the receptor to the spinal cord or brain. It carries the signal toward the central nervous system (CNS).
d. Central Nervous System (integration center) - located in the spinal cord or brain. Here, the sensory neuron synapses with an interneuron, which processes the information and then relays it to the appropriate motor neuron. The
integration center decides how the body should respond to the stimulus.
e. Efferent pathway (motor neuron) - carries the response signal from the CNS to the effector. This neuron sends the command to initiate a movement or action, such as muscle
contraction.
f. Effector - the muscle or gland that carries out the response to the stimulus. It could be a muscle contracting (e.g., pulling your hand away from a hot object) or a gland secreting a substance
g. Response (resulting reaction to stimulus)
Receptor
What is 1?
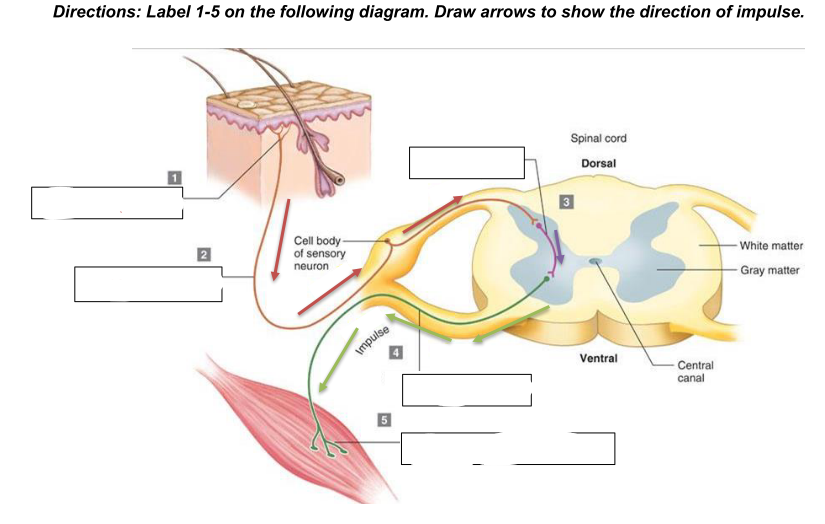
sensory neuron/afferent pathway
What is 2
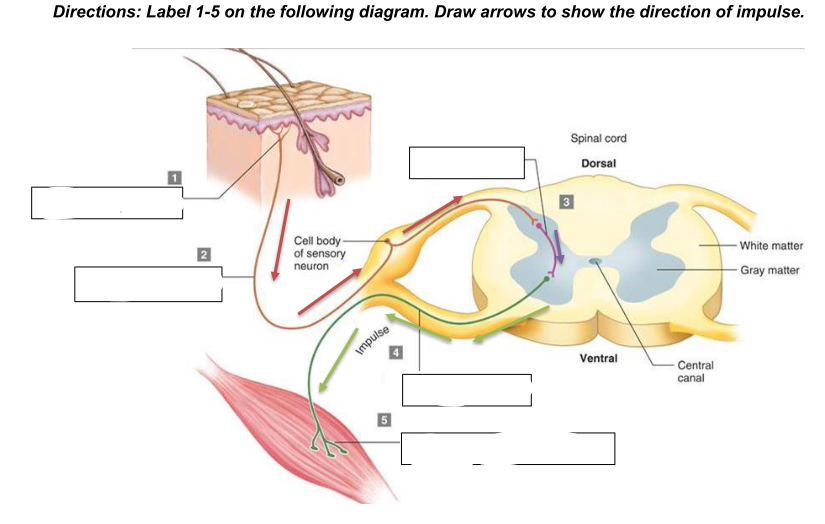
interneuron
what is 3
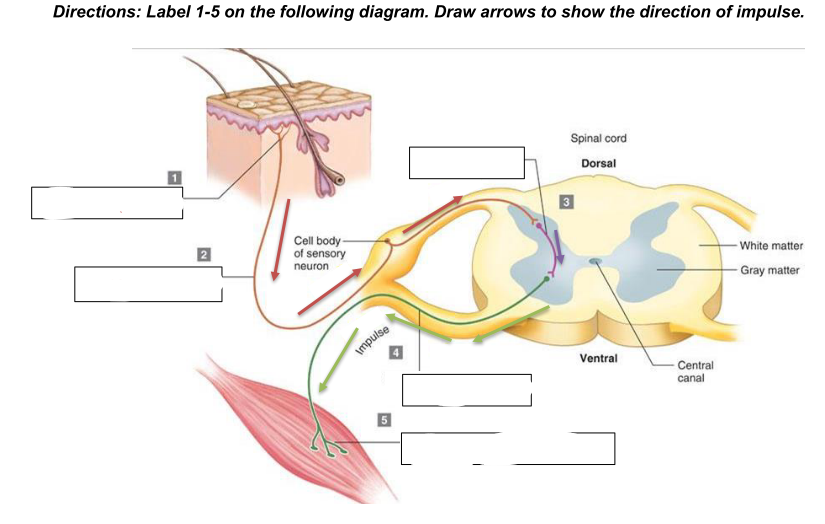
motor neuron/efferent pathway
what is 4
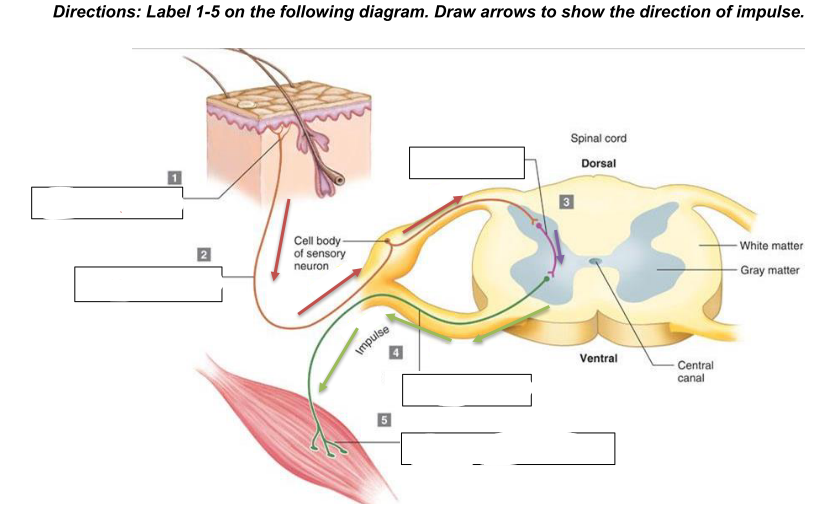
effector (skeletal muscle)
what is 5
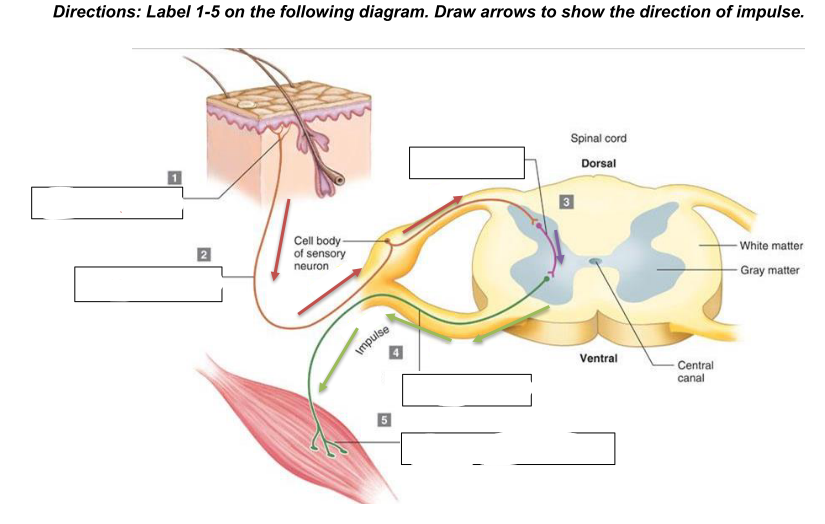
generalized reflex arc
what does the diagram show
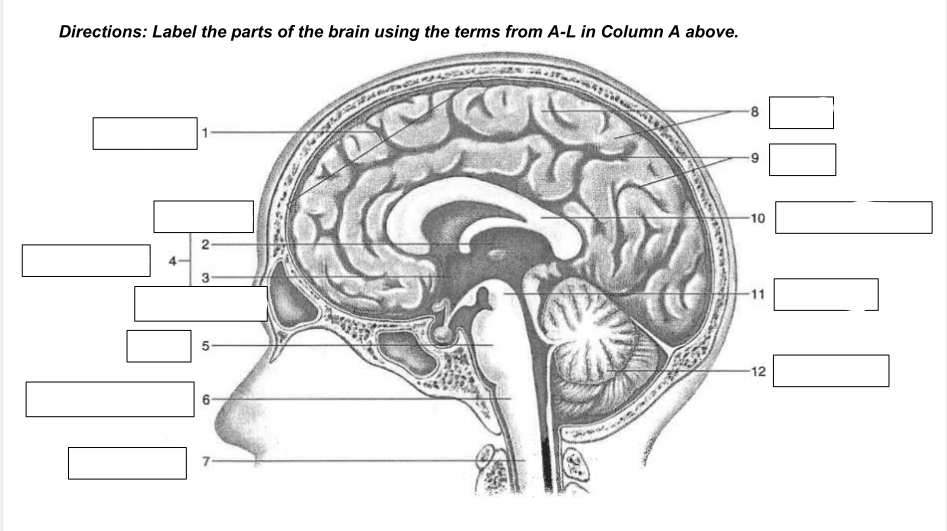
cerebrum
1
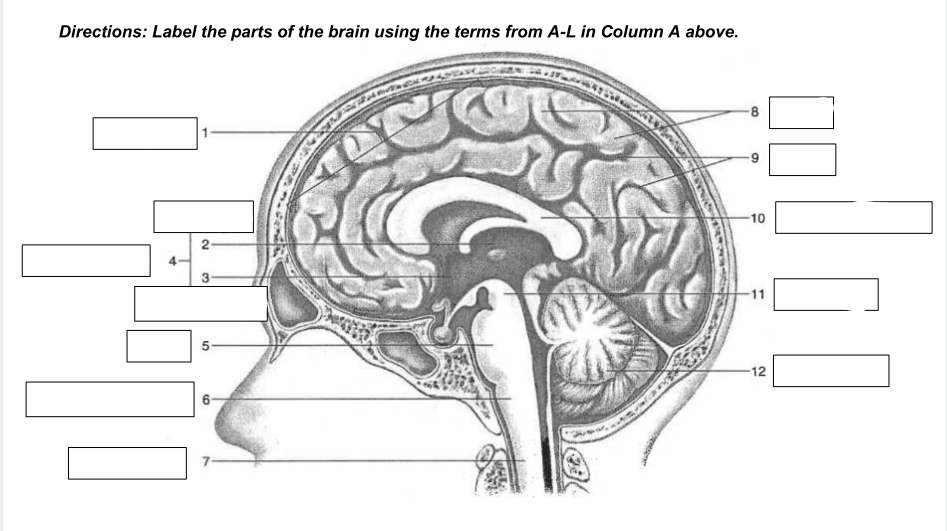
thalamus
2
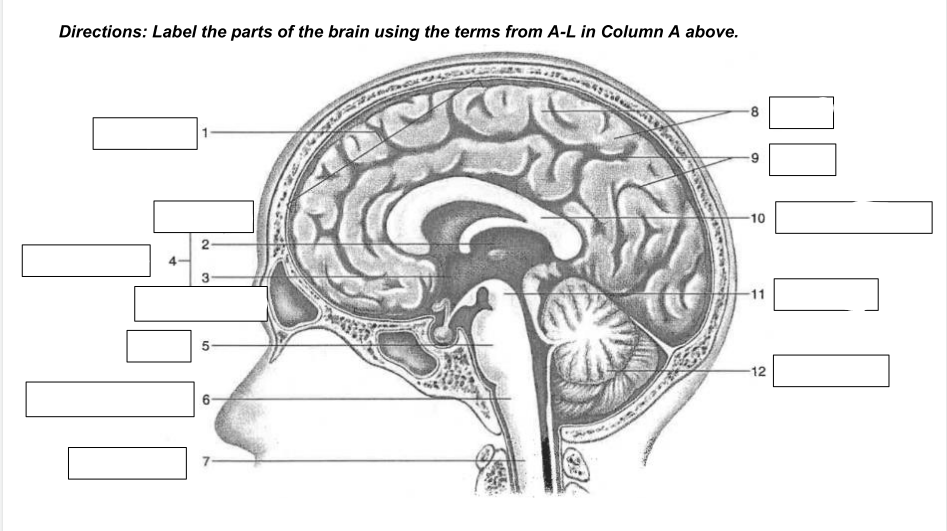
hypothalamus
3
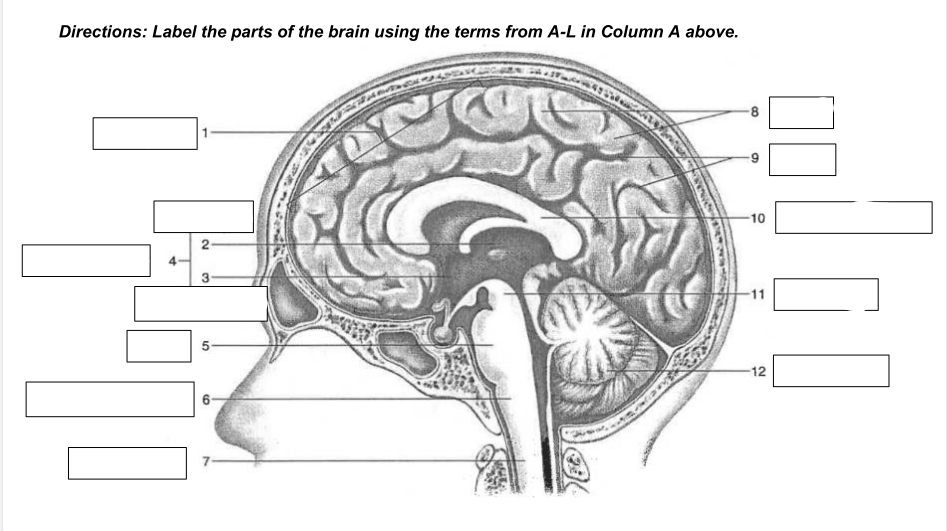
diencephalon
4
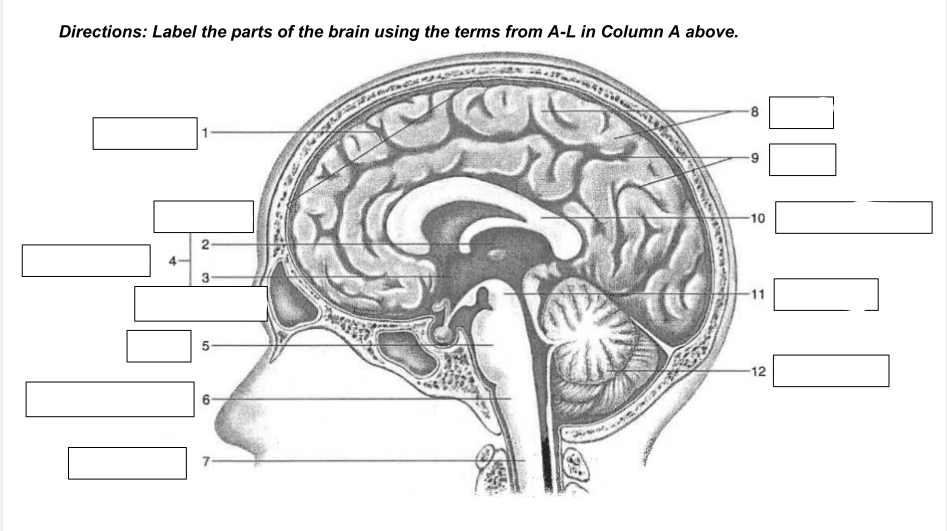
Pons
5
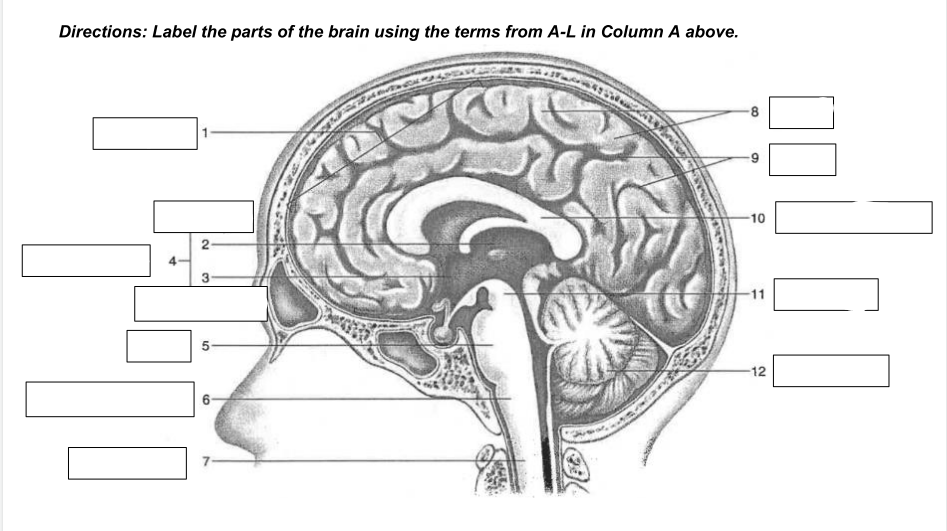
medulla oblongata
6
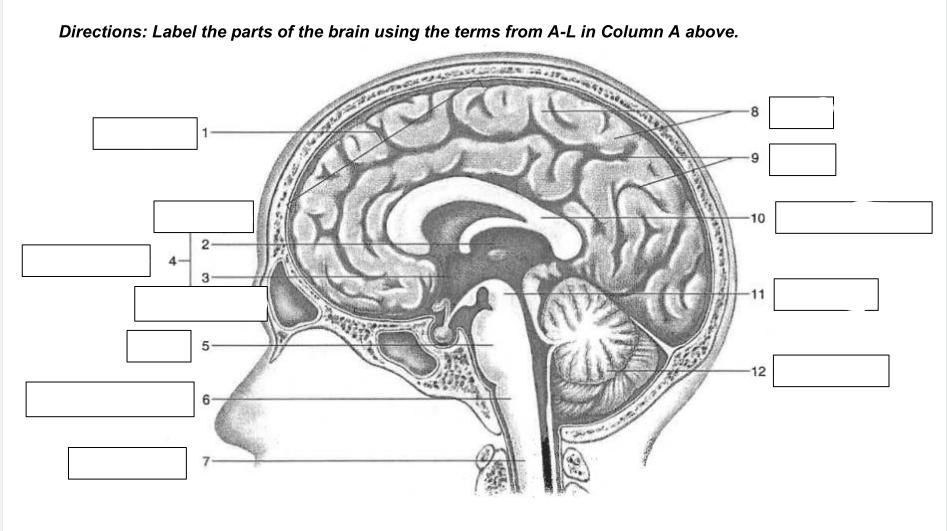
spinal cord
7
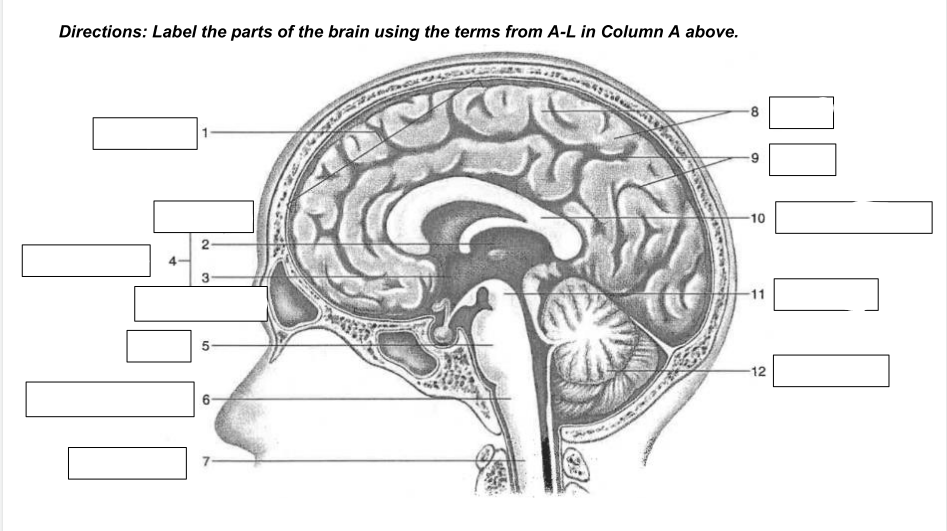
gyri
8
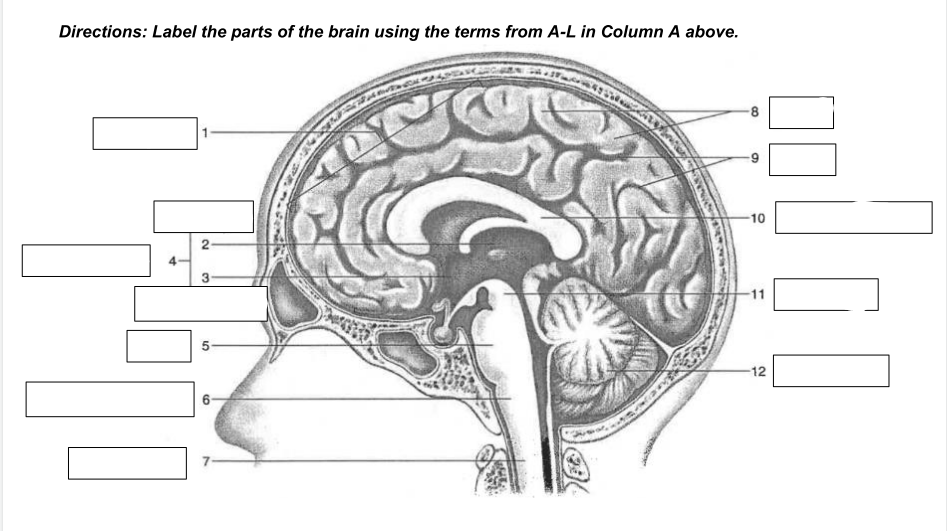
sulci
9
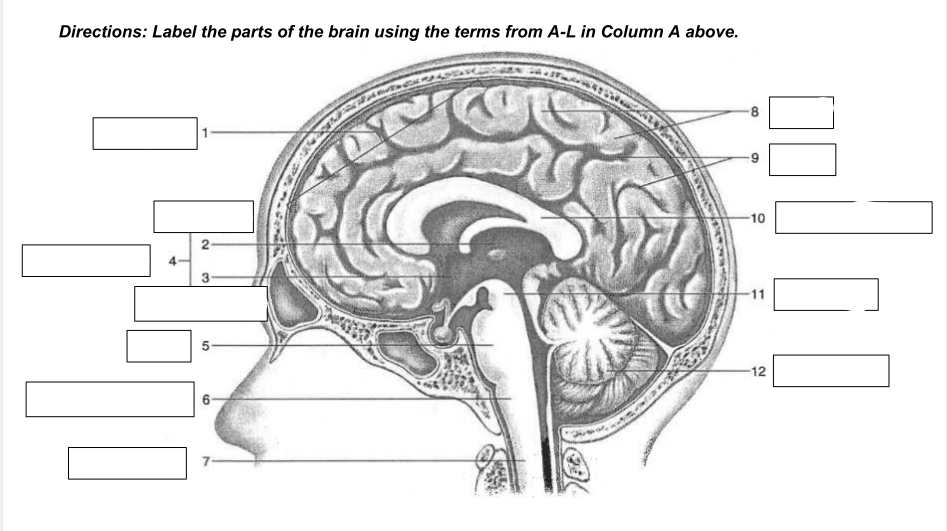
corpus callosum
10
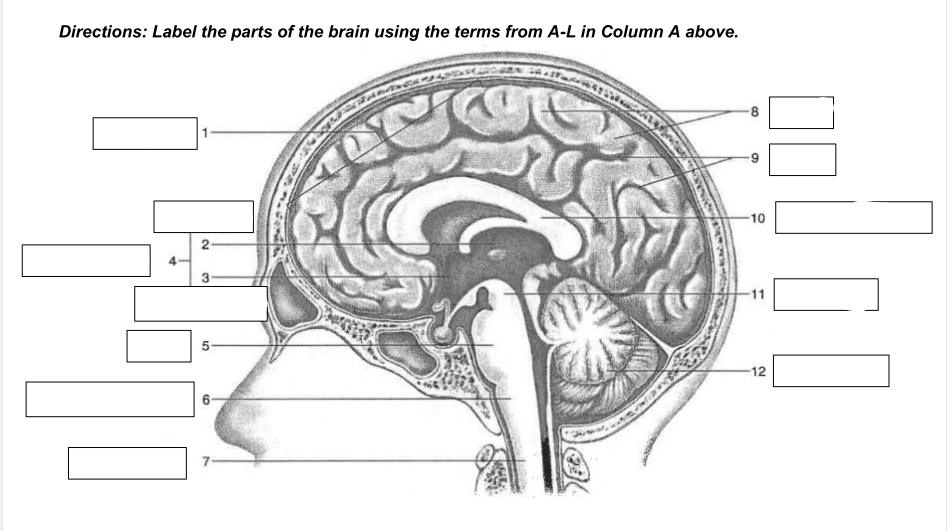
midbrain
11
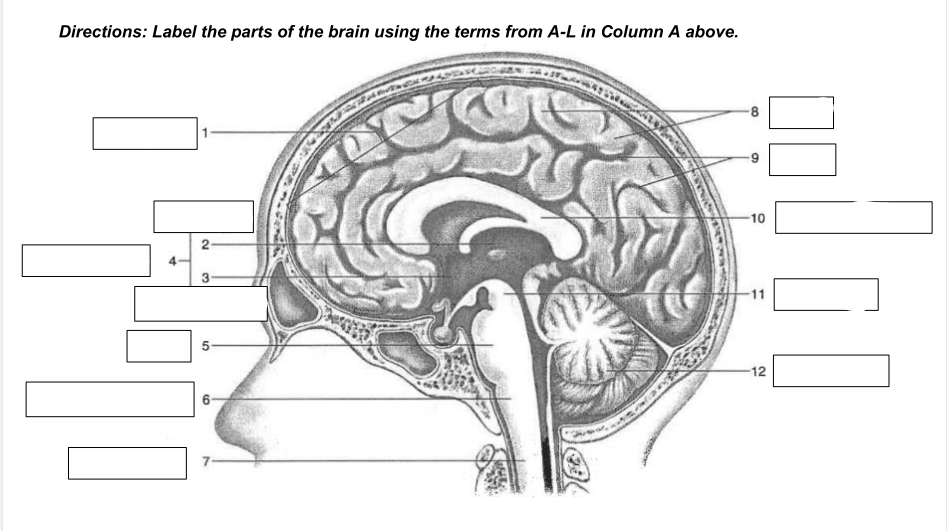
cerebellum
12
stimulus, involuntary, rapid, same way each time
what are the 4 properties of all reflexes?
somatic (afferent in PNS)
carries info from skin, skeletal muscles, & joints (external)
visceral (afferent/sensory in PNS)
carries information from visceral organs (internal)
autonomic (efferent/motor in PNS)
automatically controls smooth & cardiac muscles and glands
somatic (afferent/sensory in PNS)
consciously controls skeletal muscles
synaptic transmission
what is in the picture
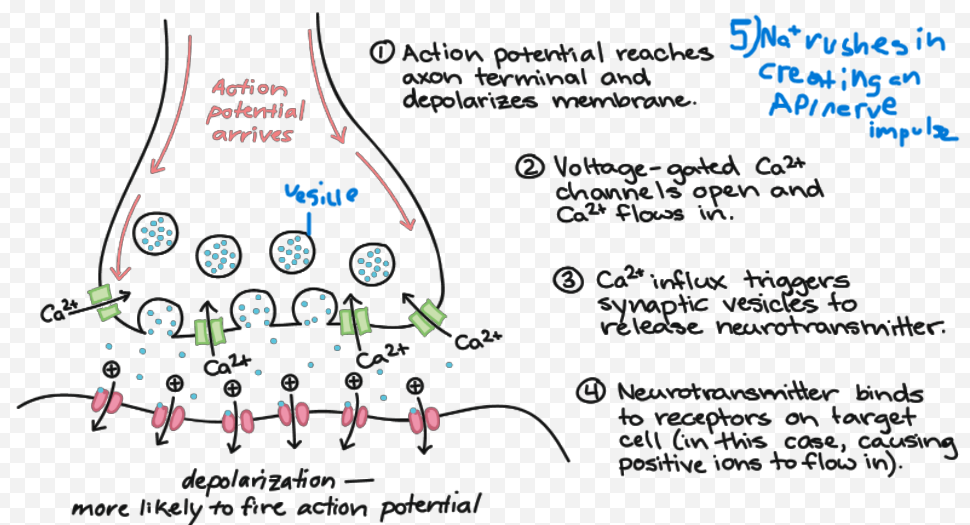
cerebral cortex
Thin layer of gray matter on surface of cerebrum
hypothalamus
Maintains homeostasis by regulating visceral activities
thalamus
Receives all sensory impulses except for smell, sends them to cerebral cortex
pons
Rounded bulge on underside of brainstem; regulates breathing
brainstem
Most primitive functions in brain; Includes the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
gyri
Wrinkles and bumps on the surface of cerebrum
sulci
Shallow grooves on surface of cerebrum
medulla oblongata
Regulates cardiac, vasomotor and respiratory activities
cerebrum
Determines personality and intelligence
midbrain
Part of brainstem between diencephalon and pons
hippocampus
Processes memories
transverse fissure
Separates the occipital lobe & cerebellum
cerebrospinal fluid
Maintains ion balance in CNS
spinal cord
A portion of the CNS; a slender column of nervous tissue
ventricles
Produces cerebrospinal fluid
meninges
Protective membrane between bone and soft nervous tissue
limbic system
Controls emotions and feelings
temporal lobe
Stores memory of visual scenes, music, and complex patterns; understands speech
frontal lobe
Responsible for thinking, planning, and problem solving
Pituitary gland
Sits in a bony cavity attached by a thin stalk to the hypothalamus at the base of the brain; produces and stores several hormones.
spinal cord
examine this picture. what is it a diagram of?
sequence of events of a nerve impulse
sodium channels open and sodium ions diffuse inward
the membrane becomes depolarized
potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse outward
the membrane becomes repolarized