BISC 4165 - Microbio Lab Exam 1 (Week 1-6) Study Questions
1/59
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
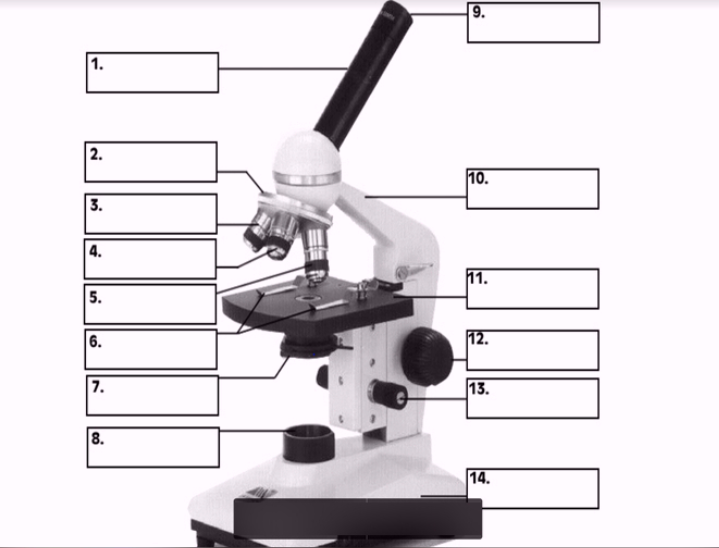
#1
body

#3, #4, #5
Objective lenses
#11
Stage
#10
arm
#7 (two items)
Condenser
Diaphragm
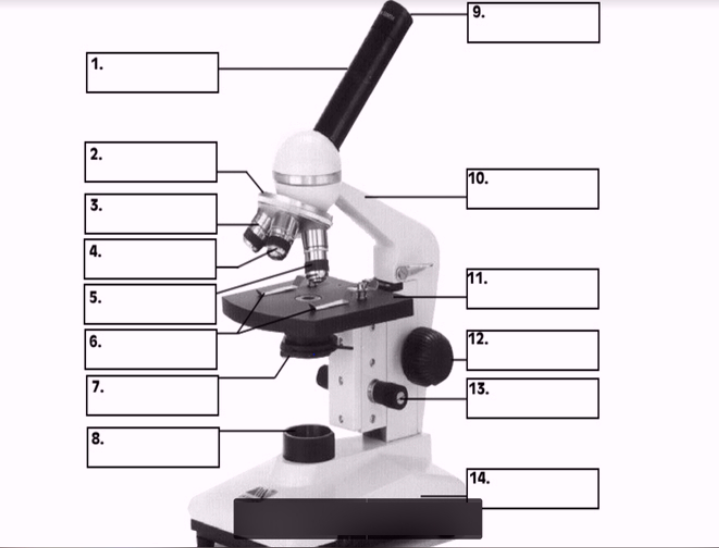
#8
Illuminator
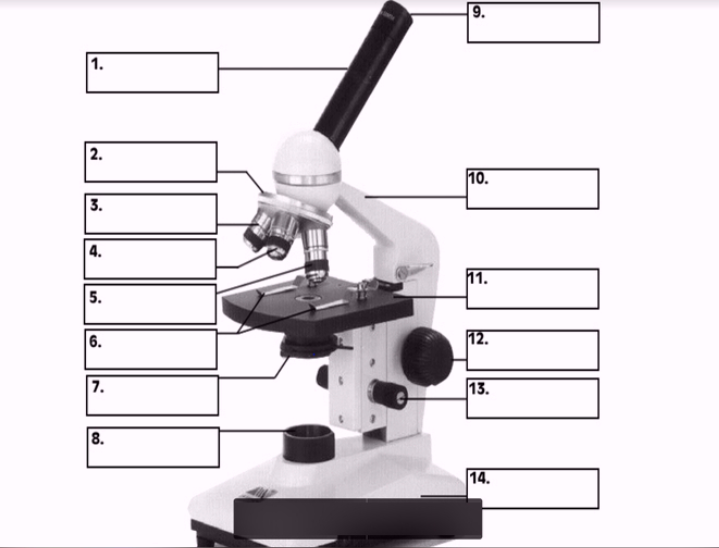
#12
Coarse focus
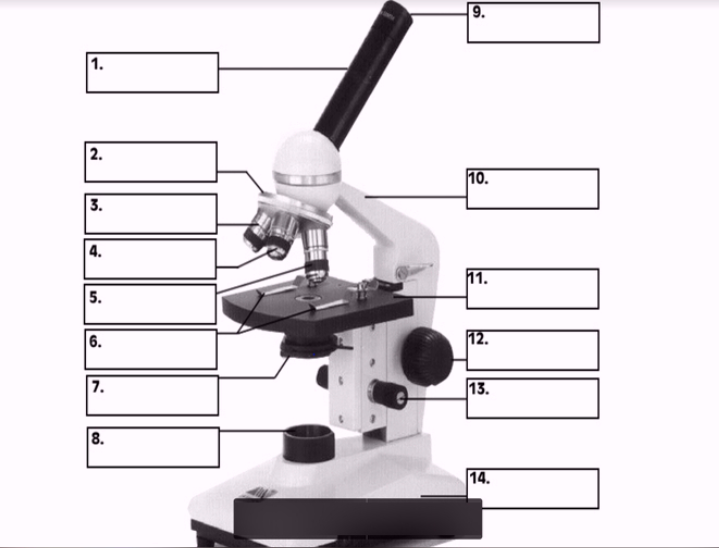
#13
Fine focus
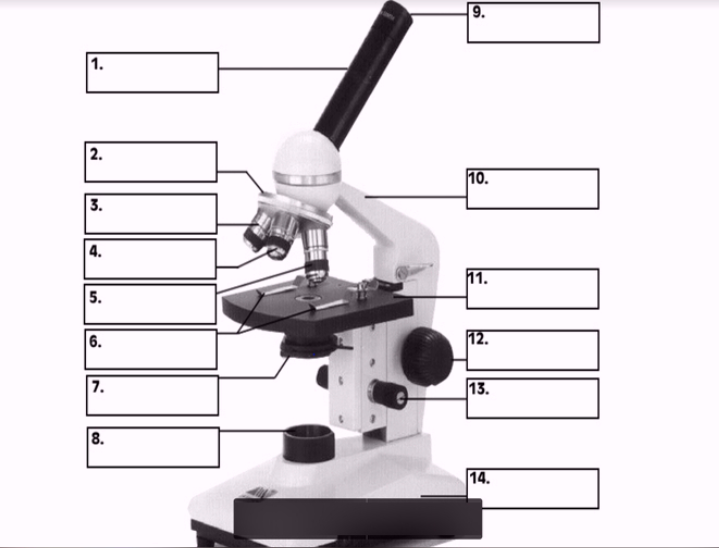
#14
base
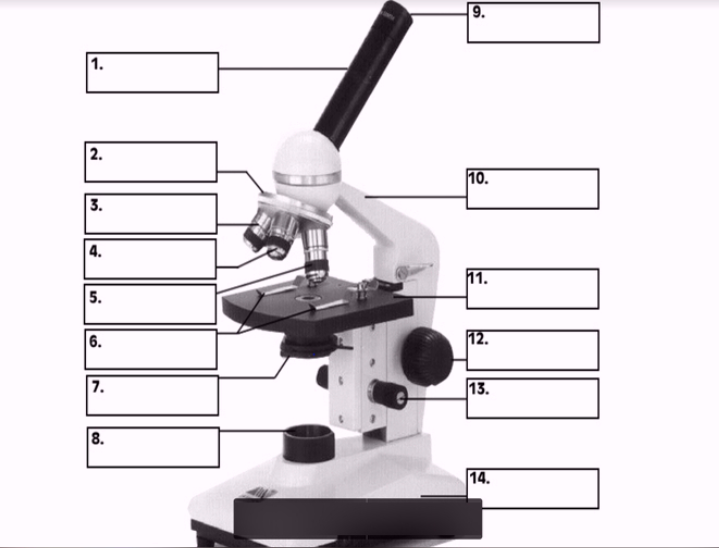
#9
Ocular lens
ocular lens (10x) x objective lens (4x, 10x, 40x, 100x) = total magnification
How to calculate total magnification
when magnification is increased, the amount of light must be _____ .
increased
“focused-in” levels of all the objectives are in approximately the same plane
parfocal
In the streak plate technique, why is it important to sterilize the inoculating loop before pulling from the previous streak to streak a new area of the agar plate?
reduces # of bacteria transferred into next quadrant » dilution effect » thins out bacterial population
if not sterilized, too many bacteria will be transferred
keeps loop stile without contaminants
what is the purpose of the streak plate technique?
isolate individual bacterial colonies from a mixed sample
list the steps of plate to plate transfer
divide agar into 3 sections
sterilize loop
load loop from culture plate onto sterile agar
streak first section of agar
sterilize loop
streak sample from previous section, turn 90 degrees, streak second section of agar
sterilize loop
streak sample from previous section, turn 90 degrees, streak third section agar
an individual colony on agar plate is essentially a pure culture. explain.
streaking dilutes the inoculum to the point only one bacterial cell is deposited every few millimeters on the surface of the agar
a colony grows, which is the descendant of the one bacterial cell
so there is only one bacterium in the individual colony
why are petri dishes containing agar media generally incubated in an inverted position?
airborne particles may have settled on the lid condensation
prevents condensation from dripping onto agar during incubation, which can contaminate
list 4 reagents of the gram stain and what color gram positive and negative cells would be after each step
Crystal violet - purple (+), purple (-)
Iodine - purple (+), purple (-)
Alcohol - purple (+), clear (-)
Safranin - purple (+), pink/red (-)
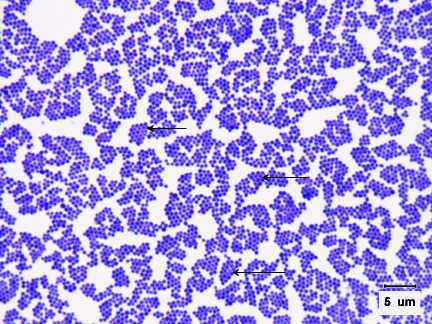
what is the gram stain, morphology, and arrangement
gram positive, staphylococcus
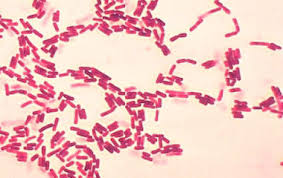
what is the gram stain, morphology, and arrangement
gram negative, streptobacilli
what color are gram negative bacteria?
pink/red
what color are gram positive bacteria?
purple
what shape is a cocci?
circular
what shape is a bacilli?
rods
what shape is a spirochete?
spiral
what shape is a vibrio?
curved rod
what arrangement is a strepto-
strip
what arrangement is a staphylo-
cluster
list several factors that affect the outcome of the gram-staining procedure
improper heat fixing - if heated too much, cell wall can rupture making positive look negative
cell density - thick smears may not decolorize properly
concentration and freshness of gram staining reagents
length and thoroughness of washing crystal violet
concentration and amount of decolorizer, duration of decolorizer step
age of bacterial culture - gram only viable for cultures 24 hrs old
for the best results, gram stain procedure should be performed on cells from the younger, outer edge of a colony. True or false? Why?
True
what is meant by a pure culture?
all cells present in the culture originated from a single cell type
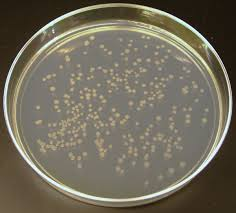
pure or mixed culture?
pure culture
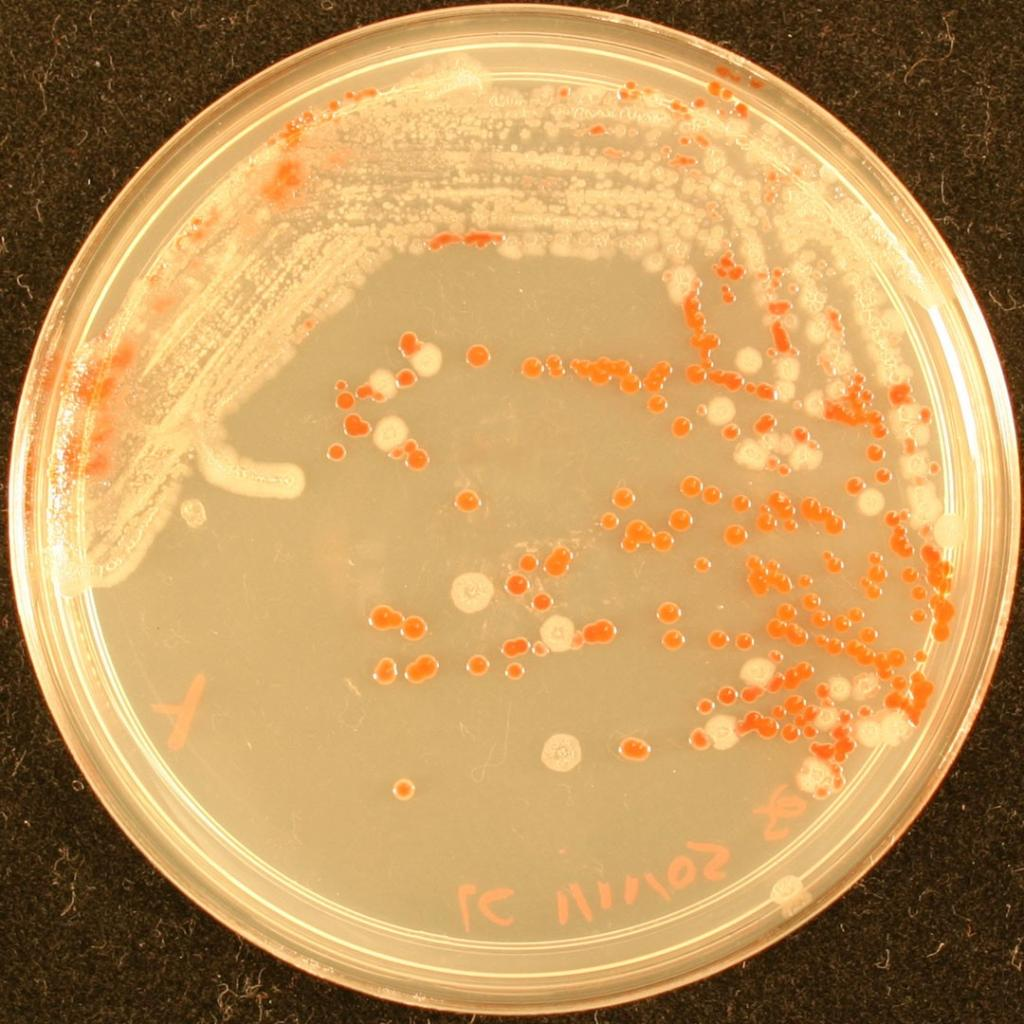
pure or mixed culture?
mixed culture
why is obtaining a pure culture an essential laboratory procedure?
allows colony characteristics that can help identify bacteria
allows for biochemical, microscopic, serological, and susceptibility tests to be performed without being impacted by contamination of other species
Eosin methylene blue agar (EMB)
selects for gram negative bacteria
differentiates between e. coli and other enteric bacilli
phenylethyl alcohol agar (PEA)
selects for gram positive bacteria
MacConkey agar
selects for gram-negative bacteria
differentiates between lactose fermenters and non-lactose fermenters
Mannitol salt agar (MSA)
selects for staphylococci
differentiates between staphylococcus aureus and other staphylococcus species
how accurate is a lab analysis of 24-hr, unrefrigerated, non-midstream urine culture?
inaccurate
sample should be refrigerated after 30 mins » overgrowth (false +)
non-midstream means genitalia were not cleansed » contamination
if you serially dilute a sample with 3 1:10 dilutions, what is the dilution of the last tube?
1:1000
if you add 1 mL to 99 mL of water, what is the dilution of the sample?
1:100
10 mL of urine were collected from patient (tube #1). 1 mL was taken from the original sample and added to 9 mL of sterile broth (tube #2). 3 more 1:10 serial dilutions were made (tube #3, 4, 5). 0.1 mL of each culture was plated onto TSA and incubated. Plate 4 contained 60 colonies. How many bacteria per mL were present in the original sample?
# of bacteria in original sample/mL of original sample = # of colonies x 1/Vsample x 1/dilution
Vsample = 1 mL
Dilution = 10-4
(60 CFU/0.1 mL) x (1/10-4) = 6.0 × 105 CFU/mL
What is the correct range for accurate counting?
30-300 colonies
what are the functions of a capsule? what color is the capsule after staining for a capsule?
capsule - protects cell against phagocytosis, helps cell adhere to surfaces in biofilm protection, protection from dehydration and nutrient loss
capsule will appear as a white halo, negative acid stain colorizes the cell and background, not the capsule itself
what is the function of flagella?
motility
what is the function of endospores?
survivability in adverse conditions (poor nutrient availability, low humidity, and high temp, can remain dormant for a long time)
resistant to UV, desiccation, freezing, and disinfectants
why can’t mycobacterium tuberculosis be gram stained? what stain would you use?
cell wall is waxy » stains poorly
must use acid fast stain
what 2 bacteria genera form endospores (sporulate)?
bacillus and clostridium
what lab diagnostic test could you use to examine dermatophytes? What about candida albicans?
dermatophytes - KOH prep method
candida albicans - gram stained swabs
what enzyme do dermatophytes produce in order to infect keratinized tissue?
keratinase
what is the function of the KOH in KOH prep?
KOH is strong alkali that dissolves keratin in skin, nails and hair, but does not dissolve the fungi, making it easier to visualize hyphae
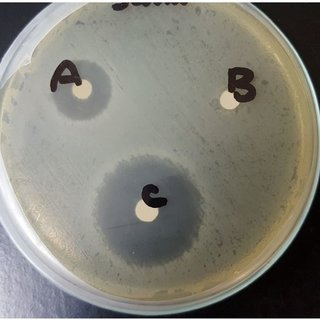
which bacterium is most resistant to antibiotics?
B
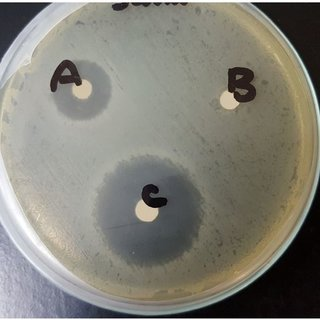
which bacterium is most susceptible to antibiotics?
C
if a bacterium is resistant to an antibiotic, will it have a large or small zone of inhibition?
small
if a bacterium is susceptible to an antibiotic, would it have a large or small zone of inhibition?
large
when given a set of broth dilution tubes how do you determine the MIC?
antibiotic dilutions are added to tubes containing the same amount of bacteria
the lowest concentration of antibiotic that inhibits growth is the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
when looking at spore tests, how do you determine if a spore test is positive (ex. the autoclave did not achieve sterility)?
spore strips contain endospores, which are run through the autoclave and then incubated in a growth medium
medium turns cloudy and yellow » confirms positive spore test
why are bacterial spores used in sterilizer monitoring rather than other microbial forms?
spores are the most resistant microbial form to sterilization methods, hence they mark a standard for sufficient sterilization
what are the recommended conditions for achieving sterility by autoclaving?
121 Celsius at 15 psi for 20 minutes