Unit 1 Xray Tube Construction v23.ppt
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Milliampere (mA) AND Time controls what
- Quantity (number of electrons boiled off)
- Density (Overall degree of darkness in an image.)
Higher mA the...
More electrons boiled off therefore more x-rays
Higher mA AFFECTS density how?
Higher ma AFFECTS density by making the radiograph darker
Time refers to the
Length of which we are allowing the electrons to travel from the tube to the other
The longer the Time, the more...
electrons traveling across therefore more x-rays
1. In an x-ray tube the mA heats the
Tungsten filament
2. The Tungsten filament starts to what
Become incandescent (glow)
3. It gets so hot to the point where the tungsten filament starts to... (Note: Think of the tungsten filament like a toaster where the metals inside the toaster glows (emit energy) to heat the bread)
Emit electrons or Boil off electrons
Boiling off the electrons is a process called...
Thermionic emission
4. The electrons are attracted to the...
Anode (+)
5. Since the attraction is not strong enough from the cathode to the anode what is required
Kvp (like a wingman to push the electrons to the anode)
What is the driving force behind the electrons
Kvp
6. When the electrons (cathode rays) hit the anode, it is converted into....
X-rays
***mAs treated as one unit:
Milliampere seconds
Kilovoltage (kV) controls
- Quality
- Penetrating Power
- Energy
- Density & Contrast
So higher kV is for... (hint: something to do with body) (Note: Higher kVp has more penetration)
for bigger/denser body parts like chest and abdomen
The more kV or x-ray penetration...
lower the contrast (more grays), the more X-rays pass through the body, potentially increasing density (darkness). (Note: which is why high kVp is for bigger/denser parts)
Kilovoltage (kV) PRIMARILY controls Contrast which is
Difference between black and white in an image.
The ideal/perfect kV provides
The right amount of absorption so it doesn't leave the patients body and the right amount of penetration
Kilovoltage (kV) SECONDARILY AFFECTS Density which is
Overall degree of darkness in an image.
1. Ceiling-Mounted (A) (Note: X-ray Room External Structure)
- Most common type
- Freely moves in all directions: transverse, longitudinal, up, and down.
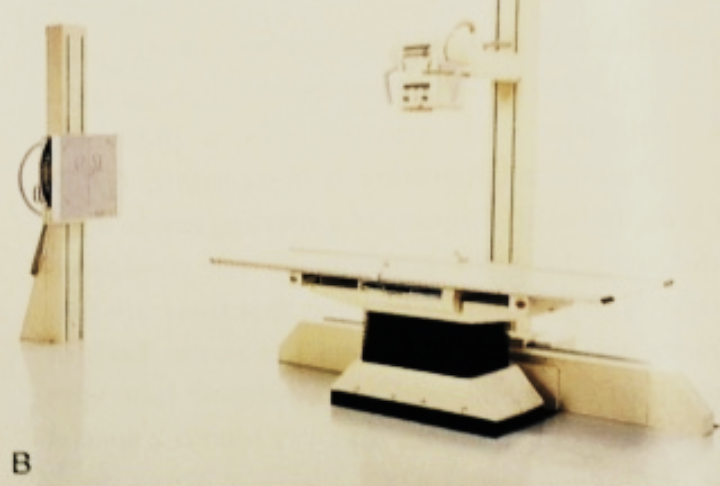

2. Floor-to-Ceiling (B) (Note: X-ray Room External Structure)
- Multi-directional movement
- Requires more effort to move compared to ceiling-mounted systems
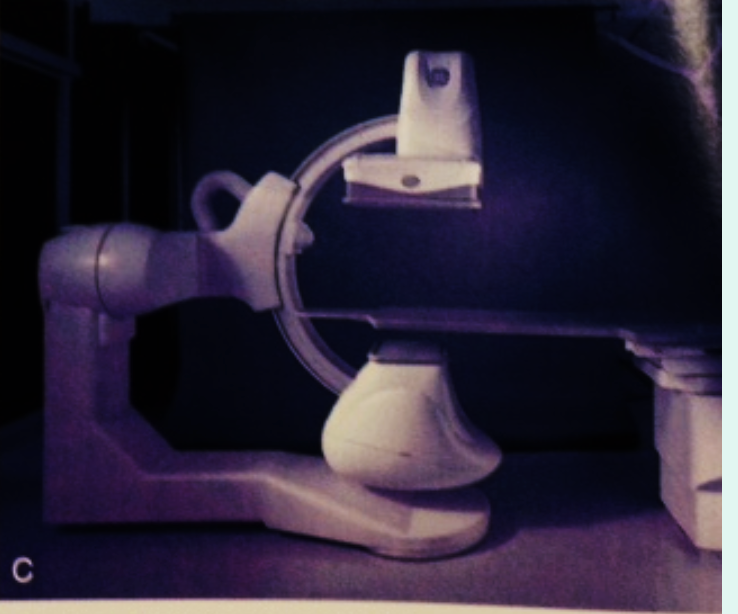

3. C-Arm (C) (Note: X-ray Room External Structure, its also C-shaped)
- Nearly limitless tube positioning
- Robotic and fluid motion
- Commonly used for Angiography (blood vessels)
What type (not form) of radiation is emitted in all directions from the tube?
Isotropic
Even though the x-rays are isotropic, the angle of anode....
Directs the X-rays
Where are the useful x-rays emitted through.
Emitted through the window
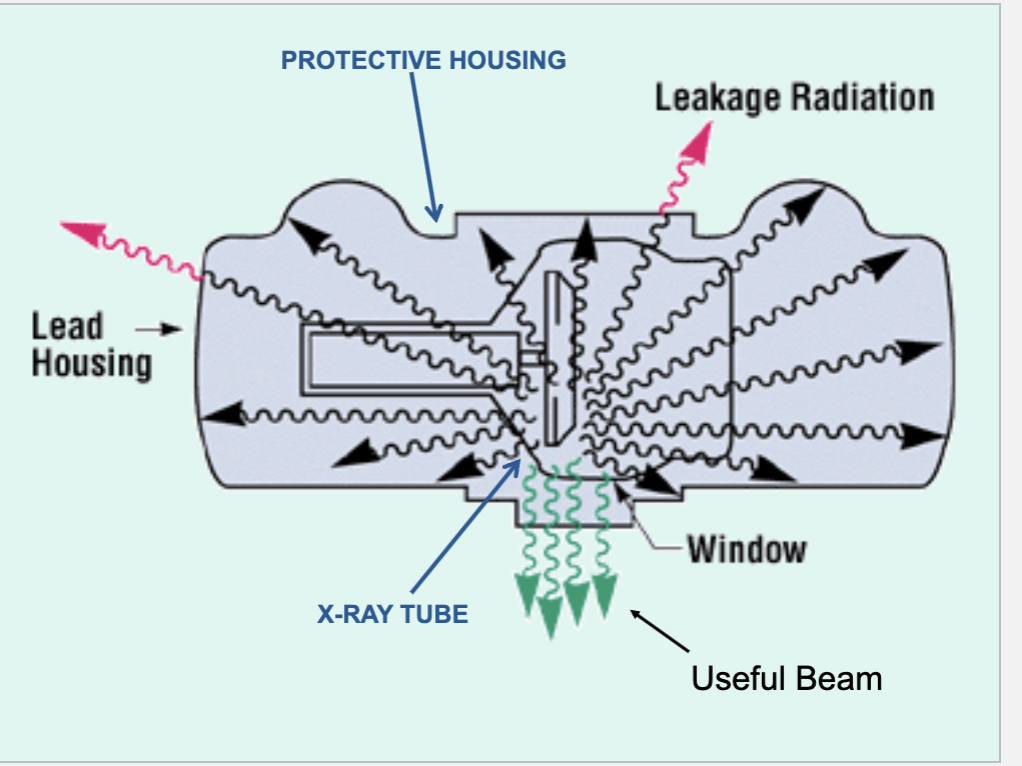
What is leakage radiation?
Anything that escapes the protective housing, causing non-diagnostic exposure to both patient and technologist
Leakage radiation occurs when
some X-rays are energetic enough to penetrate the lead shielding of the X-ray tube housing.
What is the maximum leakage radiation allowed from protective housing?
<100 mR/hr @ 1 meter (less than 100 mR/hr at a distance of 1 meter.)
What does the lead-lined housing in X-ray tubes reduce?
Reduces leakage radiation
Useful radiation (emits through the port) is known as...
Primary radiation
Any other types of radiation that leaves or escapes the lead housing is called
Secondary radiation
What does protective housing provide in terms of support to the X-ray tube?
Mechanical support

How does protective housing protect the X-ray tube?
Protects from damage caused by rough handling
What liquid is contained within the protective housing of an X-ray tube? (Note: Oil is located in the housing but outside the envelope)
Oil
What is the purpose of oil in the protective housing?
Insulates from shock and dissipates heat
What percent of electrons are converted to x-ray? What happens to the other 99%?
1%, Gets converted to heat
What material is known for withstanding large amounts of heat in x-ray tubes? (Note: The x-ray tube is INSIDE the housing, the outer layer of the tube is the envelope which is made out of …)
Pyrex
What are the benefits of using metal in x-ray tube envelopes?
More efficient, prevents tube arcing, longer tube life. (Note: Tube Arcing are electrons hit built-up metal (tungsten), causing a sudden electrical spark that can damage the X-ray tube.)
What is the main advantage of maintaining a vacuum (NO AIR) inside the X-ray tube?
Less collision of electrons with gas molecules → Less heat generated → Increased X-ray production → Longer tube life.
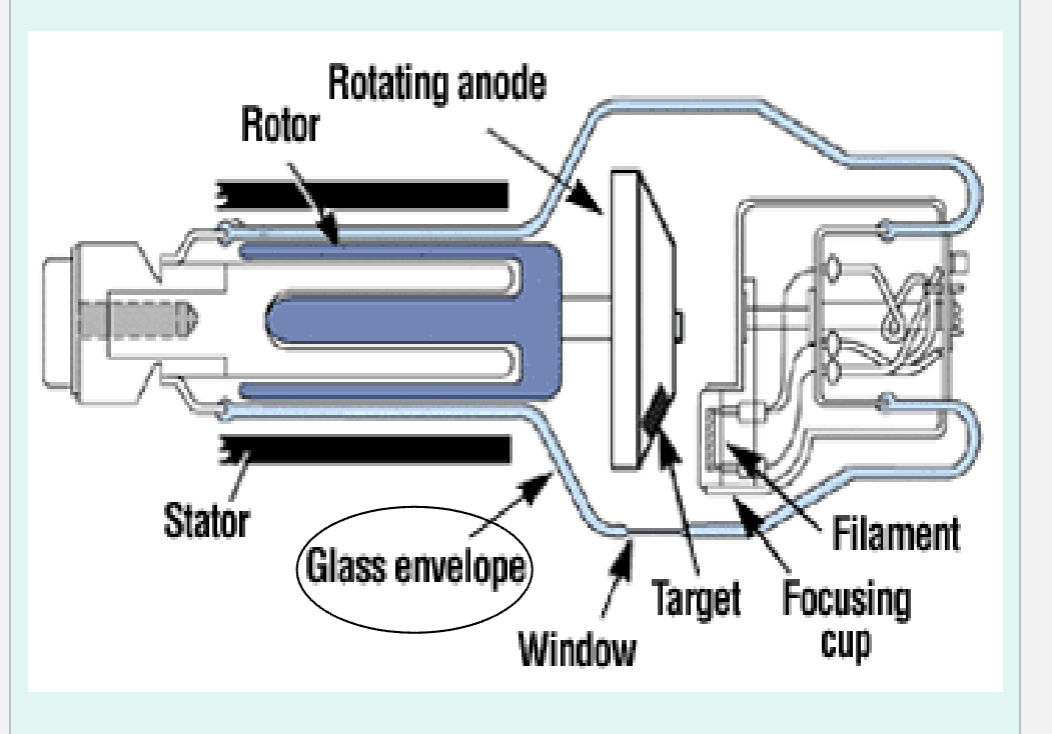
What is the cathode?
The negative electrode.
What is the function of the filament in a cathode?
It is heated to incandescence (glowing due to being heated) to produce thermionic emission.
How many coils of wire in the filament?
2 coils of wire
What material is commonly used for filaments due to its efficiency?
Tungsten.
What is the leading cause of tube failure in cathodes?
Vaporized tungsten.
What are the characteristics of the small filament in a Dual Focus Cathode?
It operates at 200 mA or less and provides better detail.
What are the characteristics of the large filament in a Dual Focus Cathode?
It operates at 300 mA or more and is used for larger body parts.
What can the large filament in a Dual Focus Cathode withstand?
It can withstand more heat.
Focusing Cup in a Dual Focus Cathode
Has a negative charge that confines the electron beam to a small area of the anode.
What is thermionic emission?
The process where electrons are 'boiled off' from a heated cathode.
What happens when low current (mA) is applied to the cathode in thermionic emission?
Low current decreases the amount of electrons boiled off.
What is a space charge?
A space charge is a cloud of electrons that forms around the cathode during thermionic emission.
What effect does the space charge have on subsequent electrons (the electrons that come after the initial ones)?
The space-charge effect prevents subsequent electrons from being boiled off due to electrostatic repulsion.
What law explains the repulsion between electrons in the space charge?
Coulomb's Law explains that same charges repel each other.
ANODE
• Is a Positive electrode
• Its Stationary or Rotating
Base of Anodes are made out of what metal?
Copper
What is the characteristic of a stationary anode
Does not require high tube current (mA) and power.
Where are Stationary Anode used in
Used in Dental and portable x-ray units
What places are rotating anodes found in?
Hospitals
What is the speed range of a rotating anode?
3,600 to 10,000 RPM
How does a rotating anode compare in terms of heat dissipation?
Better for heat dissipation
Rotating anode is a
X-ray tube that is capable of producing high-intensity X-ray beams in shorter time periods.
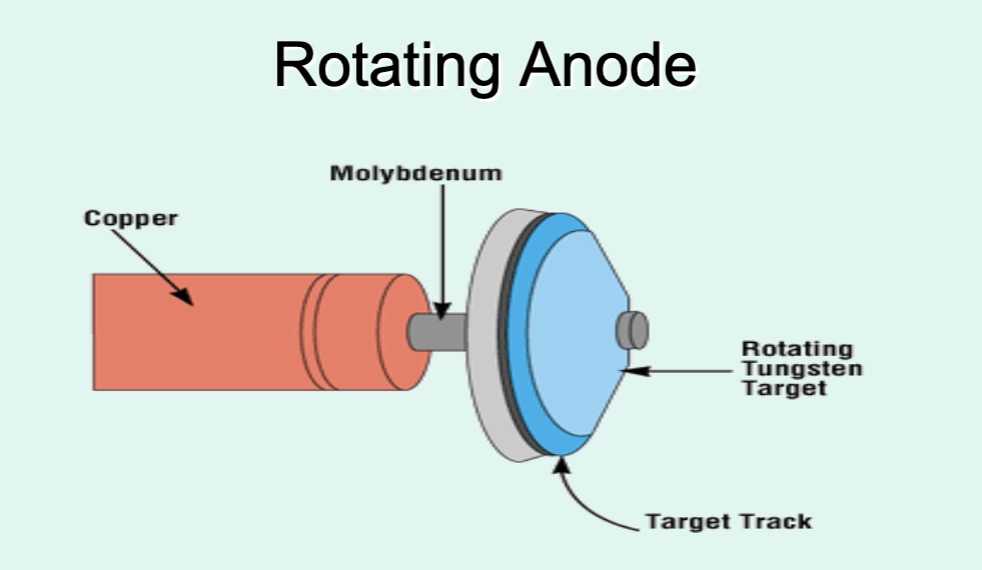
What does the target track allow for the electrons on a rotating anode?
It allows electrons to hit different areas.
How does the target track on a rotating anode affect its performance regarding heat tolerance?
Affects its performance by increasing the anode's heat tolerance and longevity.
What problem does the target track help prevent in rotating anodes?
It helps prevent pitting (divots).
What is pitting? (Quiz Question)
Divot created by the constant bombardment of the electrons that generally occurs with stationary nodes.
What are the heat loading capabilities of a rotating anode? (Note: how well the anode can handle and dissipate heat)
Increased heat loading capabilities
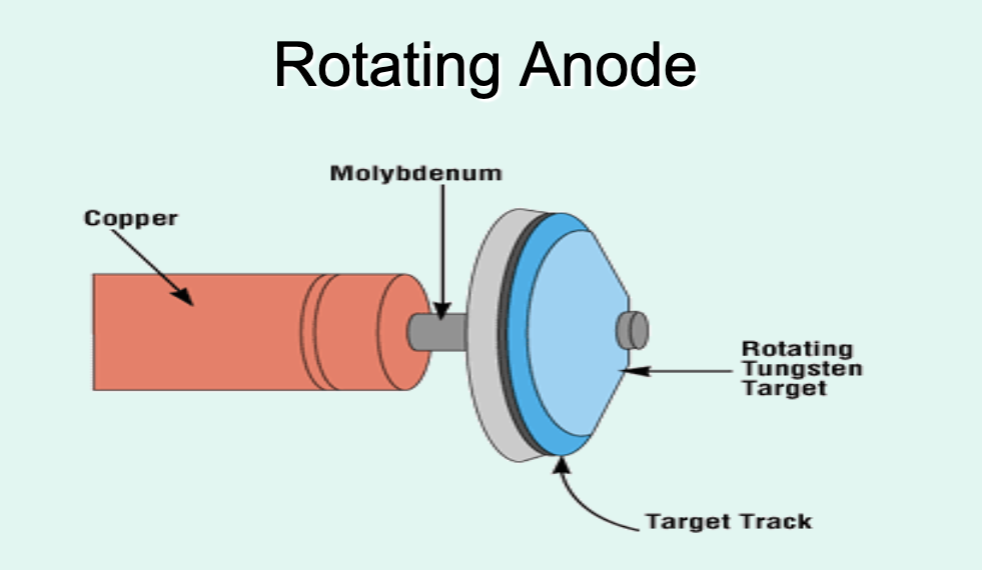
What is the target (track) area of a rotating anode?
Area of the disc where electrons strike and are converted to X-rays
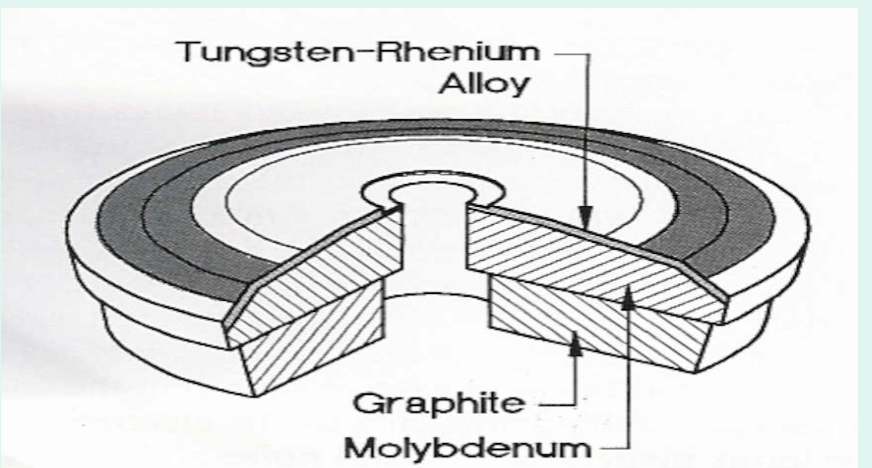
What is the composition (layers) of a rotating anode disc?
Disc made of 3 layers: Tungsten/rhenium, Molybdenum, Graphite
What is the atomic number of Tungsten? (Quiz question)
74
What is a benefit of Tungsten's high atomic number? (Quiz question)
Higher efficiency
What is the thermal conductivity of Tungsten? (Quiz question)
Better heat dissipation
What is the melting point of Tungsten in Celsius?(Quiz question)
3410°C
What is the melting point of Tungsten in Fahrenheit? (Quiz question)
6170°F
What does Tungsten's high melting point minimize? (Quiz question)
Minimizes occurrences of pitting (prevents surface damage, ensuring longer tube life)