C1.1 Enzymes and Metabolism
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are globular proteins, made up of amino acids. They are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without itself being consumed
Are enzymes reusable?
Yes, as long as the active site is not damaged
What is metabolism?
Metabolism is the interdependant and interacting chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, within cells
What are metabolic reactions catalysed with?
Enzymes that are specific to the reaction.
What are the two types of metabolic reactions?
Catabolic and Anabolic
What is a catabolic reaction?
Reactions that break down large molecules into smaller molecules, releasing energy. It is an exothermic reaction
What is an anabolic reaction?
Reactions that build up small molecules into larger ones, requiring energy. This is an endothermic reaction
Where does catabolism release its energy?
Catabolism releases energy in the form of ATP. For example, during respiration it converts glucose and oxygen into carbon dioxide, water and ATP
Where does anabolism get its energy?
Anabolism needs energy, which it receives from ATP that was released during catabolic reactions
For example, protein synthesis
What is the active site made up of?
The active site is composed of a few amino acids
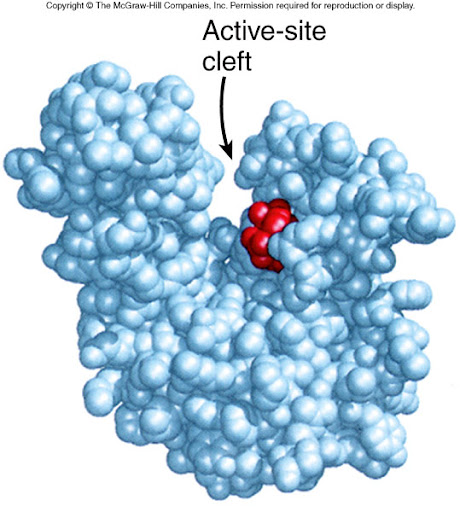
How is the globular shape of proteins created?
The polypeptide chain (a string of amino acids connected by peptide bonds) folds to create a globular shape, and held into place by the weak hydrogen bonds between r groups
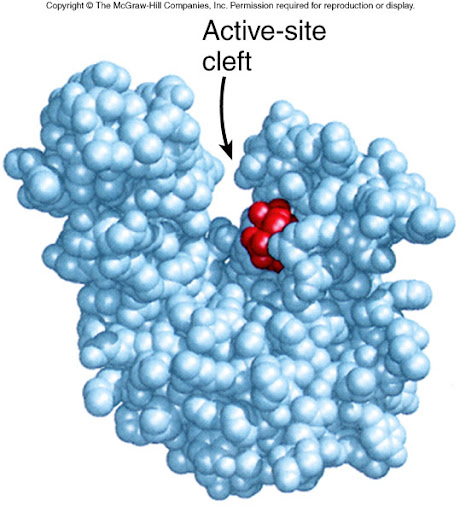
What happens if the shape of the globular protein is altered?
The enzyme can’t catalyse reactions
Why do most enzyme reactions occur in water?
Because the substrates are dissolved and move in random motion, colliding more often
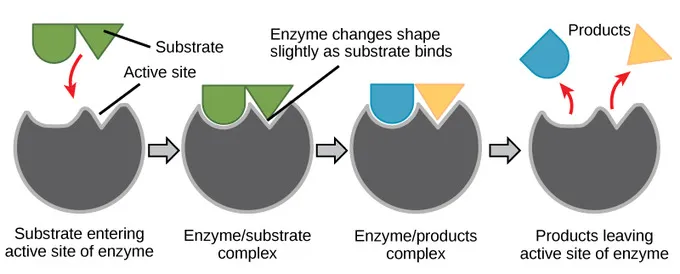
What is the coming together of a substrate and an active site called?
Collision
What is it called when the substrate and Enzyme are correctly aligned and fit?
Successful collision
What is induced-fit binding?
When the enzyme and the substrate slightly alter their shape to fit together. Changes to the shape make it easier for the substrate to break or make new bonds
What are factors affecting enzyme activity?
Temperature, pH, Concentration
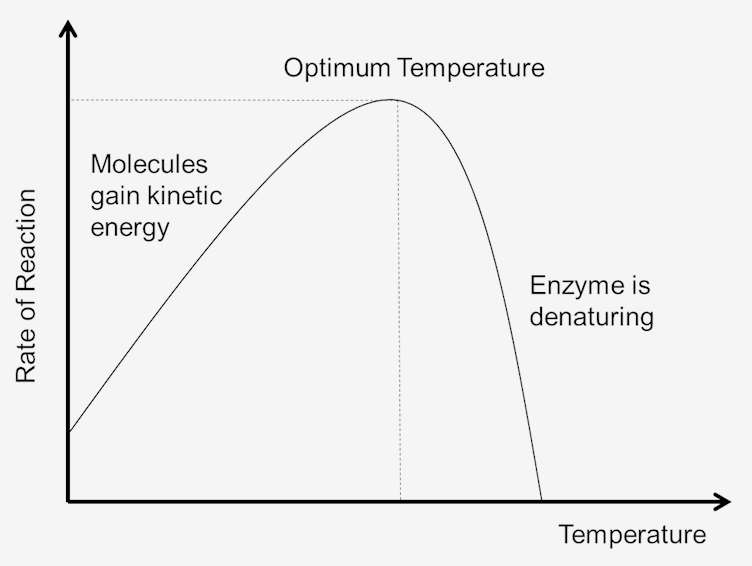
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
As the temperature increases, the molecules gain more kinetic energy, collide more, and enzyme activity increases
However, when the temperature is past the optimum temperature for enzymes, they vibrate too much, the active site changes shape, and the substrate can’t bind anymore, as the enzyme has denatured. This means that enzyme activity decreases
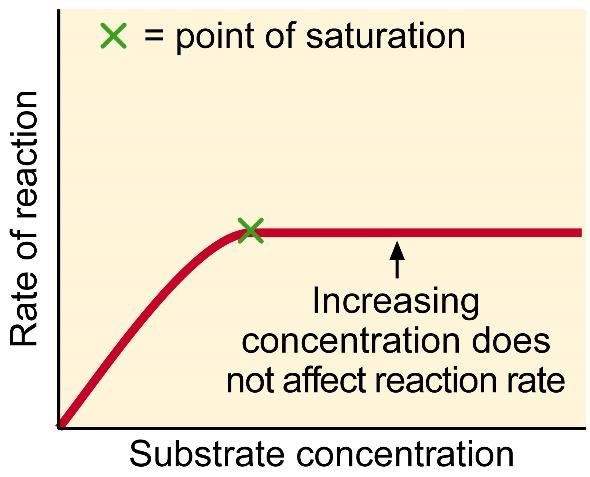
How does substrate concentration affect enzyme activity?
If there is more concentration of substrates, that means there is a greater collision frequency between substrates and enzymes, so enzyme activity increases
However, up to a certain point, the enzyme capacity is already to its maximum, so enzyme activity doesn’t increase any further. It plateaus.
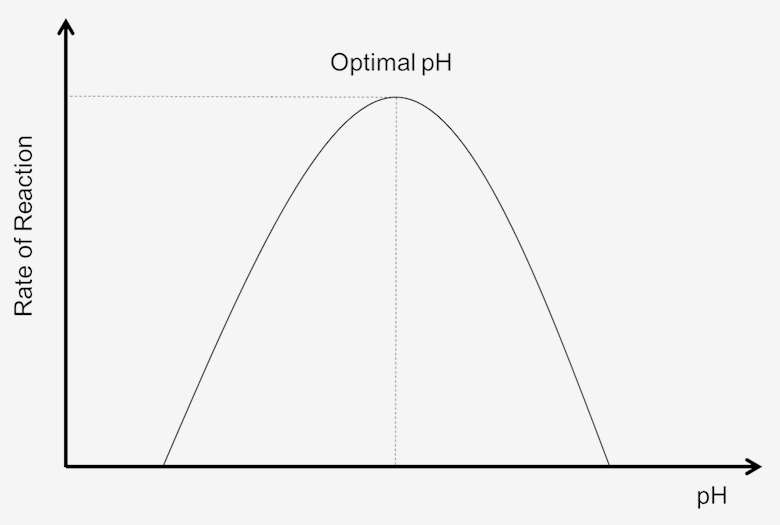
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
As the pH increases, so does the enzyme activity. However, when the pH is past its optimum point, enzymes denature
What is activation energy?
The initial input of energy that is required to trigger a chemical reaction - break bonds or make bonds
How do enzymes reduce the activation energy?
They find an alternative pathway for the reaction