NUCLEIC ACIDS
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Nucleic acids
molecules that store information for cellular growth and reproduction.
nucleotides
large molecules consisting of long chains of monomers called _____
pentose sugar
nitrogen containing base
phosphate
The nucleic acids DNA and RNA consists of monomers called nucleotides that consists of a:
DNA
mRNA
tRNA and rRNA
The nucleic acids have the following functions:
Storage of Genetic information (___)
Transmission of genetic information (___)
Protein synthesis (_____)
Adenine
Guanine
Purines are:
Cytosine
Uracil
Thymine
Pyrimidines are:
N - glycosidic bond
nucleoside has a nitrogen base linked by a _____ to C1’ of a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
phosphate ester
Nucleotide is a nucleoside that forms a _____ with the C5’ – OH group of a sugar (ribose or dexyribose).
Uridine
Cytidine
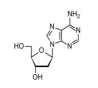
Adenosine
Guanosine
Deoxythymidine
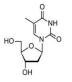
Deoxycytidine
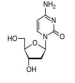
Deoxyadenosine
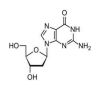
Deoxyguanosine
Adenosine 5’-monophosphate
Deoxyadenosine 5’-monophosphate
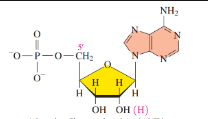
Guanosine 5’-monophosphate
Deoxyguanosine 5’-monophosphate
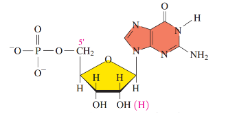
Cytidine 5’-monophosphate
Deoxycytidine 5’-monophosphate
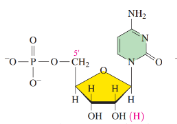
Uridine 5’-monophosphate
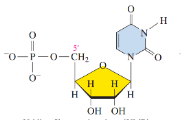
Deoxythymidine 5’-monophosphate
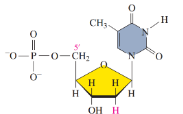
phosphodiester bonds
nucleotides are joined by _________
Initiation
Helicase unwinds the DNA to produce two strands: leading and lagging strand
Elongation
DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the leading strand (5' to 3'), Okazaki fragments pair with the lagging strand.
Ligation
DNA ligase seals the gaps between Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, forming a continuous DNA strand.
Termination
Replication stops when DNA molecule is copied, producing 2 identical double helices
Helicase
____ unwinds the DNA to produce two strands: leading and lagging strand
DNA polymerase
_____ adds nucleotides to the leading strand (5' to 3'), Okazaki fragments pair with the lagging strand.
lagging strand
Okazaki fragments pair with the _____
DNA ligase
______ seals the gaps between Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand, forming a continuous DNA strand.
Messenger RNA
TYPES OF RNA
carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes.
Transfer RNA
TYPES OF RNA
brings amino acids to the ribosome to make the protein.
Ribosomal RNA
TYPES OF RNA
makes up ⅔ of ribosomes where protein synthesis takes place
Ribosomal RNA
TYPES OF RNA
Function in the cell: Major component of the ribosome
Messenger RNA
TYPES OF RNA
Function in the cell: Carries information for protein synthesis from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes
Transfer RNA
TYPES OF RNA
Function in the cell: Brings amino acid to the ribosomes for protein synthesis
75
TYPES OF RNA: Ribosomal RNA
Percentage of Total RNA: _____
5 - 10
TYPES OF RNA: Messenger RNA
Percentage of Total RNA: _____
10 - 15
TYPES OF RNA: Transfer RNA
Percentage of Total RNA: ______
Chargaff’s Rule
In any double-stranded DNA, the amount of adenine (A) is always equal to the amount of thymine (T), and the amount of guanine (G) is always equal to the amount of cytosine (C). This reflects the complementary pairing of A with T and G with C.
ANTIPARALLEL
Two chains run _______, meaning the base pairs are in OPPOSITE DIRECTIONS
5’ to 3’
Leading strand runs from ___ to ____
3’ to 5’
Lagging strand runs from ___ to ___
DNA replication
genetic information is maintained each time a cell divides.
DNA replication
the DNA strands unwind
DNA replication
each parent strand bonds with new complementary bases.
DNA replication
two new DNA strands form that are exact copies of the original DNA.
tRNA
has a triplet called an anticodon that complements a codon on mRNA.
acceptor stem
tRNA bonds to a specific amino acid at the ______
AMINO ACIDS
tRNA reads the messages of nucleic acids and transform them into _____(then proteins)
transcription
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
mRNA is formed from a gene on a DNA strand
translation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
tRNA molecules bring amino acids to mRNA to build a protein
RNA polymerase
During transcription, _____ moves along the DNA template to synthesize the corresponding mRNA.
termination
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the mRNA is released at the _____ point
Transcription
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a section of DNA containing the gene unwinds.
Transcription
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
one strand of DNA bases is used as a template
Transcription
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
mRNA is synthesized using complementary base pairing with uracil (U) replacing thymine (T).
Transcription
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the newly formed mRNA moves out of the nucleus to ribosomes in the cytoplasm.
Genetic Code
_____ is a sequence of amino acids in a mRNA that determine the amino acid order for the protein.
AUG
start codon
UAG UGA UAA
stop codons
Initiation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a mRNA attaches to a ribosome.
Initiation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the start codon (AUG) binds to a tRNA with methionine.
Initiation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the second codon attaches to a tRNA with the next amino acid.
Initiation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a peptide bond forms between the adjacent amino acids at the first and second codons.
Translocation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the first tRNA detaches from the ribosome.
Translocation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the ribosome shifts to the adjacent codon on the mRNA
Translocation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a new tRNA/amino acid attaches to the open binding site
Translocation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a peptide bond forms and that tRNA detaches.
Translocation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the ribosome shifts down the mRNA to read next codon
Termination
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
all the amino acids are linked
Termination
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the ribosome reaches a "stop" codon: UGA, UAA, or UAG.
Termination
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
there is no tRNA with an anticodon for the "stop" codons.
Termination
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
the polypeptide detaches from the ribosome.
Activation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a tRNA attaches to its specific amino acid.
Initiation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a tRNA binds to the AUG codon of the mRNA on the ribosome.
Translocation
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
ribosomes move along mRNA adding amino acids to growing peptide chain.
Termination
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
a completed peptide chain.
Mutations
alter the nucleotide sequence in DNA.
Mutations
result from mutagens such as radiation and chemicals.
Mutations
produce one or more incorrect codons in mRNA.
Mutations
produce a protein containing one or more incorrect amino acids.
Mutations
produce defective proteins and enzymes.
Substitution
a base in DNA changes a codon in the mRNA.
Substitution
a different codon leads to the placement of an incorrect amino acid in the polypeptide.
Frame Shift Mutation
an extra base adds to or is deleted from the normal DNA sequence.
Frame Shift Mutation
all the codons in mRNA and amino acids are incorrect from the base change
Viruses
are small particles of DNA or RNA that require a host cell to replicate.
Viruses
cause a viral infection when the DNA or RNA enters a host cell.
Viruses
are synthesized in the host cell from the viral RNA produced by viral DNA.
Reverse Transcription
a retrovirus, which contains viral RNA, but no viral DNA, enters a cell.
retrovirus
contains viral RNA, but no viral DNA, enters a cell.
Reverse Transcription
the viral RNA uses reverse transcriptase to produce a viral DNA strand.
Reverse Transcription
the viral DNA strand forms a complementary DNA strand.
Reverse Transcription
the new DNA uses the nucleotides and enzymes in the host cell to synthesize new virus particles.
HIV-1 virus
____ is a retrovirus that infects T4 lymphocyte cells.
HIV-1 virus
decreases the T4 level and the immune system fails to destroy harmful organisms.
HIV-1 virus
causes pneumonia and skin cancer associated with AIDS
protease
Another type of AIDS treatment involves ____ inhibitors such as saquinavir, indinavir, and ritonavir
Protease inhibitors
______ modify the active site of the protease enzyme, which prevents the synthesis of viral proteins.