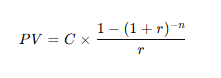Chapter 25
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is a warrant?
A call option issued by a company giving the holder the right (not obligation) to buy shares directly from the company at a fixed price for a certain time.
How do warrants differ from exchange-traded options?
Warrants usually have longer maturities and cause new shares to be issued (dilution) when exercised.
What happens when a warrant is exercised?
The holder pays the exercise price, the company issues new shares, and existing shareholders are diluted. The company receives new equity capital.
What factors affect warrant value?
↑ Stock price → value ↑; ↑ Exercise price → value ↓; ↑ Interest rate → value ↑; ↑ Stock volatility → value ↑; ↑ Time to expiration → value ↑; ↑ Dividends → value ↓
Why are warrants worth slightly less than similar call options?
Because of dilution — new shares are created when exercised.
Formula to adjust for dilution in warrant value
Warrant value = Call price × ( n / (n + nₓ) ), where n = existing shares, nₓ = number of warrants.
What is the gain from exercising a call option?
Share price – exercise price.
What is the gain from exercising a warrant?
(n / (n + nₓ)) × (Firm value per share net of debt – exercise price).
What is a convertible bond?
A bond that can be exchanged for a fixed number of shares any time before maturity.
What are the three components of convertible bond value?
1️⃣ Straight bond value (SBV) 2️⃣ Conversion value 3️⃣ Option value
Formula for Straight Bond Value (zero-coupon case)
SBV = Par value / (1 + r)^t
Formula for Straight Bond Value (coupon bond case)
SBV = Σ [Coupon / (1 + r)^t] + [Par value / (1 + r)^T]
Example – Litespeed convertible bond: given par = 1000, r = 10%, t = 10. What is SBV?
SBV = 1000 / (1.1)^10 = 385.54
How to calculate conversion value?
Conversion value = Conversion ratio × Current stock price. Example: 25 × 12 = 300
How to calculate option value of a convertible bond?
Option value = Market price – Straight bond value. Example: 400 – 385.54 = 14.46
Why might firms issue warrants or convertibles?
To reduce agency costs and delay large interest payments until the firm is more profitable.
What does “agency cost reduction” mean here?
Aligning interests of shareholders and bondholders by linking debt repayment to stock performance.
What is a callable convertible bond?
A convertible bond that the firm can call back (redeem) before maturity, forcing bondholders to either convert or take cash.
What are bondholder options when a convertible bond is called?
1️⃣ Convert to shares, or 2️⃣ Take the cash call price.
When is conversion preferred to surrender?
When conversion value > call price.
What is the firm’s optimal call policy?
Call the bond when its value is equal to or greater than the call price (forces conversion).
What is the conversion ratio?
The number of shares each bondholder receives when converting one bond into stock.
Formula for conversion ratio?
Conversion Ratio = Number of shares received per bond (given or stated in the bond indenture).
What is the conversion price?
The effective price paid per share when the bond is converted.
Formula for conversion price?
Conversion Price = Par Value ÷ Conversion Ratio.
What is the conversion premium?
The percentage by which the conversion price exceeds the current stock price.
Formula for conversion premium?
Conversion Premium = (Conversion Price – Current Stock Price) ÷ Current Stock Price.
What is the conversion value?
The market value of the stock that would be received if the bond were converted immediately.
Formula for conversion value?
Conversion Value = Current Stock Price × Conversion Ratio.
How does the conversion value change with the stock price?
It rises or falls in direct proportion to changes in the stock price.
What is the minimum value of a convertible callable bond?
Max ( SBV, Current Conversion Value)
What is the formula for an annuity?