Open Stax - Chapter 4 (Anatomy & Physiology)
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
adipose tissue
specialized areolar tissue rich in stored fat.
apical
that part of a cell or tissue which, in general, faces an open space
areolar tissue
(also, loose connective tissue) a type of connective tissue proper that shows little specialization with cells dispersed in the matrix
basal lamina
thin extracellular layer that lies underneath epithelial cells and separates them from other tissues
basement membrane
in epithelial tissue, a thin layer of fibrous material that anchors the epithelial tissue to the underlying connective tissue; made up of the basal lamina and reticular lamina
collagen fiber
flexible fibrous proteins that give connective tissue tensile strength
connective tissue
These bind the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the protection, support, and integration.
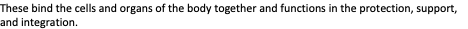
dense connective tissue
connective tissue proper that contains many fibers that provide both elasticity and protection
elastic cartilage
type of cartilage, with elastin as the major protein, characterized by rigid support as well as elasticity
elastic fiber
fibrous protein within connective tissue that contains a high percentage of the protein elastin that allows the fibers to stretch and return to original size
epithelial tissue

These are the sheets of cells that cover exterior surfaces of the body, line internal cavities and passageways, and form certain glands.
Fibroblasts
most abundant cell type in connective tissue, secretes protein fibers and matrix into the extracellular space
Fibrocartilage
tough form of cartilage, made of thick bundles of collagen fibers embedded in chondroitin sulfate ground substance
fluid connective tissue
specialized cells that circulate in a watery fluid containing salts, nutrients, and dissolved proteins
ground substance
fluid or semi-fluid portion of the matrix
hyaline cartilage
most common type of cartilage, smooth and made of short collagen fibers embedded in a chondroitin sulfate ground substance
loose connective tissue
(also, areolar tissue) type of connective tissue proper that shows little specialization with cells dispersed in the matrix
matrix
extracellular material which is produced by the cells embedded in it, containing ground substance and fibers
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
tissue that consists of a single layer of irregularly shaped and sized cells that give the appearance of multiple layers; found in ducts of certain glands and the upper respiratory tract
reticular fiber
fine fibrous protein, made of collagen subunits, which cross-link to form supporting "nets" within connective tissue
reticular lamina
matrix containing collagen and elastin secreted by connective tissue; a component of the basement membrane
simple columnar epithelium
tissue that consists of a single layer of column-like cells; promotes secretion and absorption in tissues and organs
simple cuboidal epithelium
tissue that consists of a single layer of cube-shaped cells; promotes secretion and absorption in ducts and tubules
simple squamous epithelium
tissue that consists of a single layer of flat scale-like cells; promotes diffusion and filtration across surface
stratified columnar epithelium
tissue that consists of two or more layers of column-like cells, contains glands and is found in some ducts
stratified cuboidal epithelium
tissue that consists of two or more layers of cube-shaped cells, found in some duct
stratified squamous epithelium
tissue that consists of multiple layers of cells with the most apical being flat scale-like cells; protects surfaces from abrasion
supportive connective tissue
type of connective tissue that provides strength to the body and protects soft tissue
tissue
group of cells that are similar in form and perform related functions
transitional epithelium
form of stratified epithelium found in the urinary tract, characterized by an apical layer of cells that change shape in response to the presence of urine
simple
when cells rest on basal lamina
stratified
when only basal lamina rest on lamina