[FC] TOPIC 5: Hazards Analysis Methods
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
HAZOP stands for?
HAZ — Hazard || OP — Operability
Hazard — any deviation in operation that can cause:
a release of toxic, flammable or explosive chemicals, or
any action that could result in injury to personnel
Operability — any deviation in operation within the design envelope that will cause:
a shutdown or
lead to a violation of environmental, health or safety regulations, or
negatively impact profitability
What is HAZOP?
A systematic process hazard analysis technique to IDENTIFY potential hazard & operating problems
Conducted by a multi-disciplinary team using qualitative technique based on "guidewords" to uncover deviations
Guidewords help to detect how deviations can lead to hazardous situations or operability problems
Purpose of HAZOP
Identify deviations from design/normal operations and uncover associated hazards and operability problems
Generate corrective actions to eliminate risks of these deviations that result in hazardous consequences or operability problems or reduce them to acceptable levels
When to conduct HAZOP and follow-ups?
Design Phase — When P&IDs reach ‘Approved for Design’ stage
Construction Site Inspections — Verify HAZOP recommendations are implemented
Pre-Commissioning — Conduct safety reviews plant procedures & safety audits
Operational Phase — Regular reviews (every 5 years) and after modifications to ensure continued safety
HAZOP study team
HAZOP study team should consist of:
Typically consists of 5-8 people with a range of relevant skills
Independent leader (not from the plant being studied)
Project engineer
Operations representative
Discipline engineers
Process
Instrument/ electrical
Mechanical/ maintenance
HAZOP minute recorder
One of the above
What information does HAZOP require?
HAZOP requires the following information:
P&IDs
Process flow diagrams
Heat and material balances
Layouts
Interlock logic diagrams
Equipment data sheets
Safety data sheets
Hazardous area layouts
What modes of operation does HAZOP consider?
Modes of operation to be considered during HAZOP study:
Normal operation
Reduced throughput operation
Routine start-up
Routine shut-down
Emergency shutdown
Commissioning
Special operating modes
Principle of HAZOP — flow
Preventive Actions | Mitigation Actions | |
↑ | ↑ | |
Identify Causes | ← PARAMETER → | Identify Consequences |
Principle of HAZOP — Guidewords, meanings and examples
GUIDEWORDS | MEANING | EXAMPLES / DEVIATION |
No (not, none) | None of the design intent is achieved | No flow when production is expected |
More (more of, higher) | Quantitative increase in a parameter | Higher temperature than desired |
Less (less of, lower) | Quantitative decrease in a parameter | Lower pressure than normal |
As well as (more than) | An additional activity occurs | Other valves closed at the same time (logic fault or human error) |
Part of | Only some of the design intention is achieved | Only part of the system is shut down |
Reverse | Opposite of the design intention occurs | Back-flow when the system shuts down |
Other than (other) | Complete substitution as another activity takes place | Liquids in the gas piping |
Early / late | The timing is different from the intention | - |
Before / after | The step (or part of it) is effected out of sequence | - |
Faster / slower | The step is done/not done with the right timing | - |
Where else | Applicable for flows, transfer, sources and destinations | - |
Principle of HAZOP — Examples of parameters
|
|
|
Principle of HAZOP — Examples of guidewords + parameter + eg. causes
Examples of Guidewords + Parameters + (eg. causes)
No Flow (eg. wrong flow path, blockage, incorrect blind plate, incorrectly fitted check valve, burst pipe, large leak, equipment failure, incorrect pressure differential, isolation in error)
More Flow (eg. increased pumping capacity, increased suction pressure, reduced delivery head, greater fluid density, exchanger tube leaks, cross connection of systems, control faults)
More Temperature (eg. ambient conditions, failed exchanger tubes, fire situation, cooling water failure, defective control, internal fires)
What is Bow-Tie Analysis?
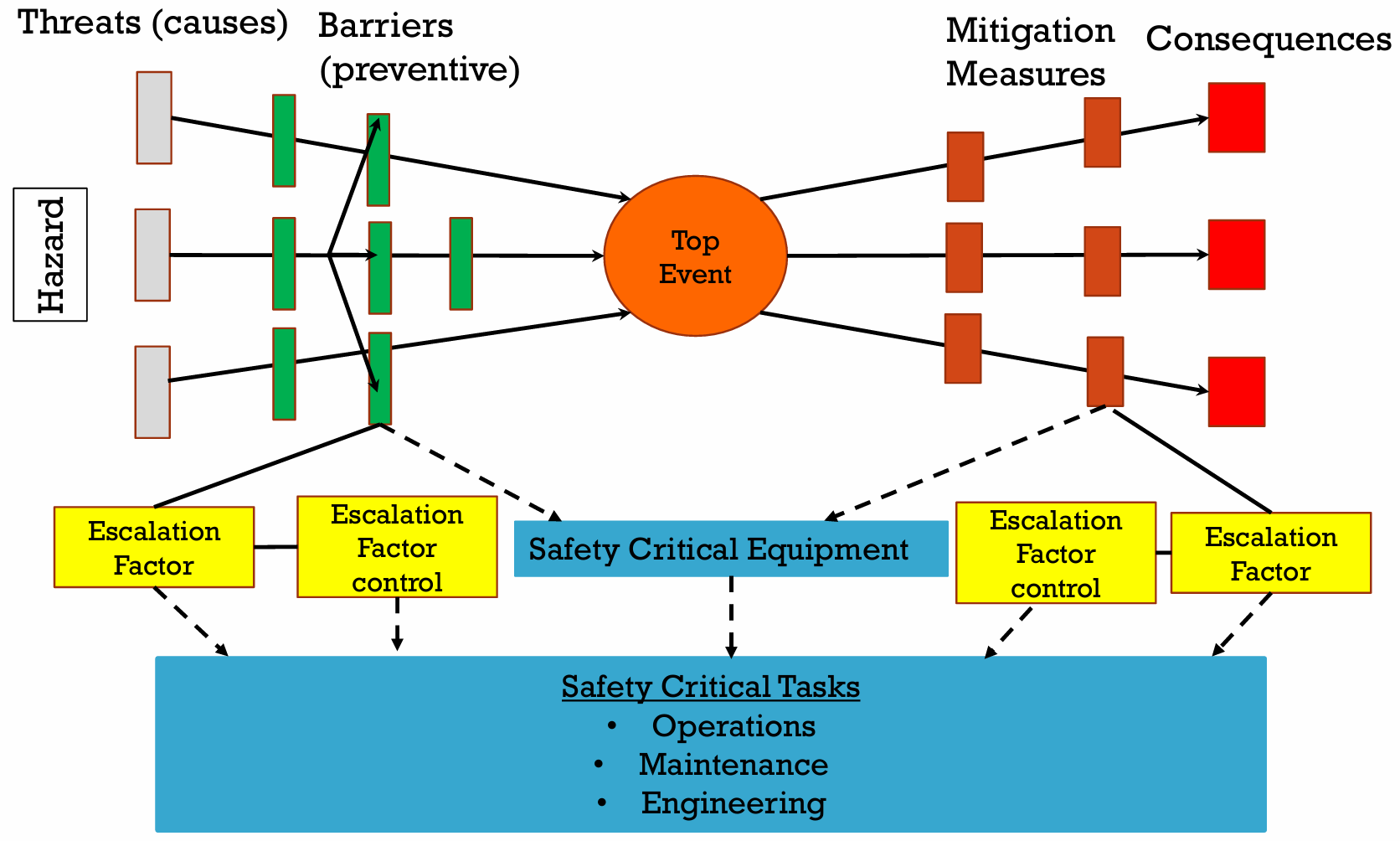
Links Hazards & Consequences to an ‘Event’ which enables development of Causes & Threats and Preventive & Recovery measures
Effective visualisation & better communication of hazards
What are the steps for Bow-Tie Analysis?
(1. Hazard)
2. Top Event
3. Consequence
4. Threat
5. Barriers
6. Recovery Measures
7. Escalation Factors & Controls
8. Critical Tasks
Bow-Tie Analysis — Hazard
1. Hazard — Anything, any source or any situation with the potential to cause:
Bodily injury, ill-health or death
Damage to equipment or properties
Delay to operations or work schedules
Bow-Tie Analysis — Top Event
2. Top Event — The incident that occurs as a result of a hazard being released
eg. Loss of containment
Electrical shock
Fall from height
Exposure to toxic material
Exposure to radioactive material
Effluent discharge into waterways
Emission of toxic gases
Bow-Tie Analysis — Consequence
3. Consequence — An event or chain of events that results from the hazard being released
eg. Serious injury
Death
Latent illness or disease which has long gestation period (Chronic illnesses)
Property damage (ie. own or public)
Environmental damage
Loss of reputation leading to loss in current & prospective business
Loss of revenue - paying for compensation, medical expenses, production loss or deferment
Bow-Tie Analysis — Threat
4. Threat — A possible cause that will release the hazard to become a top event
eg. Threat → Top Event
Corrosion/erosion of pipes → Loss of containment
Loose electrical wiring → Electrical shock/fire
Over-pressurisation of a vessel → Explosion
Incorrect valve positioning → Toxic gas release
Fatigue/lack of training → Incorrect operation of equipment
Extreme weather (eg. lightning) → Power surge/fire
Bow-Tie Analysis — Barriers
5. Barriers — Measures put in to prevent the release of a hazard or to prevent the occurrence of a top event once the hazard is released
eg. Guards or protective shields e.g. protective coatings, corrosion inhibitors, machine guards, fencing etc.
Pressure / safety relief valves
High temperature cut-off switches
Correct / valid / updated operating procedures
Safety interlocks in processes
Lowering speeds of equipment
Carry out maintenance when it is due
Reducing congestion in operating areas
Bow-Tie Analysis — Recovery Measures
6. Recovery Measures — All technical, operational, & organizational measures to reduce the impact of the Consequences due to the occurrence of the Top Event
eg. Gas, fire & smoke alarms
Emergency Shutdown systems
Firewater deluge systems
Fire and blast walls
Emergency Response plans, training & drills
Business Resumption Plans
Bow-Tie Analysis — Escalation Factors & Controls
7. Escalation Factors & Controls — Conditions that lead to increased risk due to loss of barriers or loss of recovery measures especially life saving or mitigating capabilities. Escalation Controls can then be identified for Escalation Factors.
eg. Abnormal operating condition (such as critical standby equipment is under maintenance during an emergency)
Plant operating outside the design envelope
Extreme environmental conditions - may not allow the activation of planned recovery measures
Incorrect operation of the plant due to unavailability of updated operating procedures
Human error due to lack of competence or ineffective training
Bow-Tie Analysis — Critical Tasks
8. Critical Tasks — Activities that need to be carried out to ensure the effectiveness and correct operation of Barriers and Recovery Measures